Seal
Swelling of the gums, of varying severity, is a common problem. It can either be accompanied by unpleasant or painful sensations or occur without pain. But even in cases where the swelling does not cause discomfort, the process should not be left to chance. In the vast majority of cases, the tumor indicates inflammation occurring in the tissues of the gum or tooth.
Kabanova Natalya Aleksandrovna – dentist-therapist at the Dentoclass clinic.
Causes of the pathological condition
There are many reasons that lead to a swelling of the cheek from a tooth. Among them are:
- Toothache. A tooth hurts due to caries or pulpitis. Swelling may also occur after the element is removed. With proper treatment, the symptom goes away on its own within 2-3 days.
- Inflammation of the salivary glands and ducts. The cheek swells due to improper oral care or infection with viral and infectious pathogens.
- Sinusitis is inflammation of the sinuses. Swelling spreads to other areas of the face - eyes and cheeks.
- Damage to the lymphatic system. This factor is the most common cause of cheek swelling without tooth pain.
- Neuritis of the facial nerves. Pathology develops due to hypothermia of the body. Additionally, the problem is accompanied by impaired facial expressions and pain when talking and eating.
- Mumps is a viral disease that leads to damage to the salivary glands. One of the symptoms of mumps is swelling of the submandibular lymph nodes and cheeks. Swelling can manifest itself both unilaterally and bilaterally.
- Infectious mononucleosis. In terms of symptoms, the disease is similar to a sore throat and occurs in an acute form.
- Diphtheria. Occurs due to damage to the body by the Loeffler bacterium. Diphtheria is accompanied by the appearance of white plaque on the tonsils and fever. Antibiotic therapy does not give a positive result in treatment.
- Traumatic injuries to the soft tissues of the cheek. The healing period after injuries takes 2 to 3 weeks.
- Allergic reactions. There are situations when the cheek is swollen due to individual intolerance to food or oral hygiene products. You can get rid of the problem only by eliminating the provoking factor.
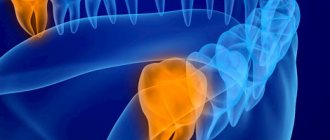
Why does wisdom tooth hurt?
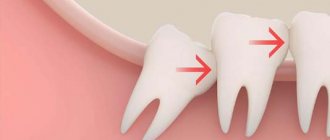
Wisdom teeth almost always grow crooked. Problems with teething are dictated by the following anatomical features:
- “Eights” appear later than all other teeth. As a rule, the jaw bones are fully formed, the dentition is stable, and the “newbie” simply does not have enough space;
- The third molars do not have milk “predecessors”, and the rudiments of wisdom teeth developed for too long and not in very favorable conditions. Because of this, they erupt chaotically, damaging the adjacent tooth or causing inflammation of the gums.
When talking about the causes of pain associated with one or more molars, it is worth distinguishing between some concepts. Toothache can occur against the background of abnormal eruption, due to deformations of soft tissues of neighboring teeth. This clinical picture is typical only for “eights”; other teeth are cut much more smoothly.
Causes
However, the cause of toothache may also lie in fairly classic causes associated with common dental pathologies: caries, periodontal disease or periodontitis. If you systematize all the reasons that cause tooth pain, you will get the following list:
- The wisdom tooth rests too much on the tissues of the oral cavity, squeezing and injuring them;
- The tooth is rotated around its axis. The greater the angle of rotation, the more tense the dental nerve is, which provokes pain;
- Carious cavities have formed on the surface of the wisdom teeth; if they reach the dental tissues, the pain will intensify;
- Tartar deposits have formed, which rub the gums and cause inflammation;
- Due to the fact that the rapid growth of the “eight” and crooked eruption damaged the root system of the neighboring molar, it is this neighboring tooth that hurts;
- If the wisdom tooth, due to its incorrect position, begins to pinch the jaw nerve, pain occurs in the lower jaw. In this case, neuritis manifests itself in this way;
- A follicular cyst has formed at the neck of the tooth. It often occurs against the background of permanent damage to the gum tissue and the tooth itself.
It is worth noting the fact that a follicular cyst near wisdom teeth is often accompanied by all sorts of complications. For example, an abscess may occur that can even deform the jaw in a neglected state. The periodontal tissues may also become inflamed and pericoronitis may develop.
Inflammatory processes of the tissue covering the wisdom tooth
Inflammation of the hood is a common phenomenon. If a wisdom tooth erupts through several crown cusps at once, phenomena may occur when the chewing surface of the crown is partially covered by tissue. The part of the gum and mucous membrane that overhangs the molar and is called the hood. He is constantly susceptible to injury and prone to inflammation.
Under the surface of the hood, particularly favorable conditions arise for the accumulation of various biological “garbage” and the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Often even the slightest damage causes irritation. The gums around the “eight” may not hurt much, so they don’t always turn to people with such a problem.
However, if the inflammatory process is severe, the tissues not only swell, but are also irritated. The patient complains of painful swallowing, sometimes it is difficult even to simply open his mouth. There may be pus and severe hyperemia on the gum near the wisdom tooth. Only a doctor can save you from such an obsessive and severe dental inflammation by excision of the hood.
Lack of space during teething
If there is not enough space for the wisdom tooth in the dentition, neighboring tissues are injured during eruption. The pain is total. It hurts not only the place where the molar erupts, but also the neighboring teeth. Swelling, hyperemia, and severe pain that are permanent may also be observed. It is difficult for the patient to open his mouth, especially if the “eights” grow in the direction opposite to the jaw. Such teeth must be removed. This is due to the fact that a crooked tooth can damage the entire dentition, up to its noticeable curvature.
Caries
If a wisdom tooth is affected by caries, the first symptom indicating the disease will be pathological increased sensitivity of the teeth. They will react painfully to any irritants - sour, spicy, salty foods, sweets, cold irritants.
Situations often occur when the curvature of a wisdom tooth injures the neighboring tooth, which causes caries in it. The most dangerous situation is when the “eight” damages the root of the neighboring “seven”. Caries develops just below the gum, and the doctor is not always able to visually identify the carious lesion. At the same time, a severely advanced form of “root” caries is difficult to treat and the tooth can almost never be saved.
Pulpitis
In acute pulpitis that affects the wisdom tooth, patients complain of acute pain that occurs in attacks. The disease and its main manifestations are characterized by a spontaneous nature. Unpleasant sensations can occur spontaneously and last up to 15 - 30 minutes. At night the pain intensifies.
In the chronic form of wisdom tooth pulpitis, the pain is not so pronounced. Unpleasant, aching sensations occur against the background of exposure to cold or heat. If the irritant is removed, the pain continues for some time.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is characterized by aching pain that constantly worries the patient. At the same time, the diseased tooth will react to any irritant with acute pulsating, shooting pain. Slight mobility of the affected tooth is also noted, and swelling and soreness of the gums are often observed.
It is interesting that with chronic periodontitis the pain is almost not disturbing. Very minor unpleasant sensations can only appear when the “figure eight” is tapped on the patient’s tissues.
Tumor due to improper treatment
Why else can pathology be observed? Separately, it should be noted the swelling of the cheek, which arose as a result of illiterate therapy. If the cheek is swollen after a complex tooth extraction, then this is a variant of the norm. The symptom disappears on its own after a few days. Typically, such swelling is small in size and does not cause pain to the patient. The situation does not require repeated surgery.
The opposite situation arises if we are talking about an infectious process that has begun after medical care has been provided. Complications are more often observed after the removal of wisdom teeth or a retained element. Such operations cannot be performed without significant damage to soft tissue. Complications arise due to doctor errors or when the patient fails to comply with the dentist’s recommendations during the recovery period.
The impacted tooth is located in the deep tissues of the gums due to incomplete eruption or incorrect location
The gums also swell due to improper sanitation of the diseased tooth. In this case, repeated assistance from a specialist is required, followed by taking medications and local treatment of the affected area. After complex removal of an element, swelling can be observed for up to 2 weeks.
Swelling also often develops due to allergic reactions to painkillers used by the dentist during treatment. In this case, additional symptoms are observed (heavy breathing with whistling, shortness of breath), but the tooth does not hurt. A person requires urgent hospitalization to cleanse the body of the allergen.
What to do if your cheek is swollen after tooth extraction?
Often after a tooth extraction procedure, many people experience swelling that may persist for some time.
Its appearance is natural, since tooth extraction is essentially a surgical operation, after which the wound remaining in the oral cavity remains open. It recovers fairly quickly, but damaged gum tissue will remain swollen for some time. The size of the tumor may depend on several factors, such as the complexity of the removal procedure, the individual characteristics of the person, and the professionalism of the dentist.
Symptoms that require urgent help
You should not postpone a visit to the doctor if your cheek is swollen from a tooth. The condition can be fatal.
The list of dangerous signs includes:
Headache after tooth extraction
- Unbearable toothaches that appear constantly. The condition indicates that an infection has attached to the surgical field. Severe pain is acceptable only after operations involving cutting out part of the bone tissue. Pain sensations decrease after 1-2 days, otherwise urgently contact the dentist.
- Temperature rises to 38 degrees and weakness.
- Pain when opening the mouth, swallowing and eating food.
- A compaction revealed by palpation of the problem area.
- Absence of a blood clot in the socket. A clot does not form due to intensive mouth rinsing on the first day after surgery or other illiterate actions of the patient that provoked a violation of soft tissue regeneration. The condition threatens the occurrence of acute symptoms and infection of the maxillofacial tissue.
Also, immediate consultation with a doctor is required in cases where the tumor is rapidly growing in size.
Due to the lack of blood clot formation, infectious complications develop after a tooth has been removed (pulled out).
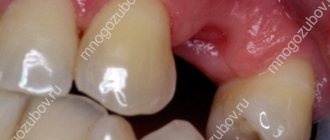
Possible causes of gum swelling
Depending on the location of the tumor, its nature, the presence or absence of pain, we can talk about the following causes of the disease:
- Caries or pulpitis. Negligence towards oral health leads to inflammation spreading from the tooth tissue to the gums. Most often, both caries and pulpitis are accompanied by constant pain (sharp, aching, throbbing), but sometimes the process is painless. So, for example, if a neurovascular bundle was removed during a previous intervention, there may be no pain. In this case, tooth decay continues and over time, inflammation affects the gums.
- Gingivitis or periodontitis. Improper oral hygiene leads to an increase in the number of pathogenic microorganisms. Gingivitis is an inflammation caused by bacteria and occurs without disruption of the periodontal bonds, and often without pain. However, if you do not pay attention to the problem, the disease progresses to the stage of periodontitis, which is characterized by destruction of the alveolar part of the bone tissue. Both gingivitis and periodontitis are accompanied by redness and swelling of the gums.
If the gums are swollen at the root neck of the tooth, and the shape of the swelling is elongated (along the border of the gums), we can most likely say that the cause is gingivitis or periodontitis. In this case, pain is mild, and at the initial stage of inflammation is completely absent. Bleeding gums can be considered an additional symptom of these diseases, but it does not always occur.
- Abscess (flux). If swelling of the gums affects a large area, is localized at a distance of 10-15 mm from the neck of the tooth and is accompanied by throbbing pain that intensifies with pressure, the cause is almost certainly purulent inflammation. If you do not consult a doctor, the abscess gives rise to various complications, including phlegmon - acute purulent inflammation, which in advanced cases can be fatal.
In addition to the above reasons, swelling can be caused by gum injury, wisdom tooth eruption, or surgery. It is important to understand that slight swelling of the gums, which persists for 1-2 days after tooth extraction or other dental surgery, is normal. However, if the swelling does not go away within this time or becomes more extensive, you should see a dentist.
As for wisdom teeth, it is better to immediately consult a doctor without waiting for swelling to appear. This is due to the fact that very often the “eights” have certain defects that interfere with their eruption and cause inflammation of the gum tissue. The decision on the advisability of preserving a wisdom tooth is made after an X-ray examination, which makes it possible to identify certain pathologies in its development. If swelling has already appeared, but the tooth can be saved, most often a hood resection is performed, that is, the upper part of the gum that covers the crown is removed.
Swelling of the gums when wisdom teeth erupt is a common problem.
First aid measures
What can you do at home to reduce the intensity of the symptoms? If the gums are swollen, but the condition is not accompanied by a general deterioration in the condition: a rise in temperature and signs of intoxication, then first aid measures can be carried out.
How to remove a tumor? First aid includes the use of various herbal remedies to rinse the mouth. For this purpose, chamomile, St. John's wort, and oak root are used. Herbs will relieve inflammation and stop the proliferation of pathogenic flora in the mouth. The procedure is performed every 2 hours for 1-2 minutes.
Instead of herbal decoctions, antiseptic drugs are used - Stomatodin, Chlorophyllipt. The drugs are diluted with warm water and rinsed with them every 3-4 hours.
Chlorophyllipt is used in dentistry for exacerbation of infectious diseases
What should not be done if the gum area is swollen? If a tumor occurs, they refuse to heat the problem area. This leads to a worsening of the situation and further spread of the pathological process.
If your tooth hurts badly and your cheek is swollen, take anti-inflammatory drugs - Nise, Nurofen, etc. Analgesics – Solpadeine and Ketanol – can help relieve swelling well. The latter remedy has many side effects, but can cope with any type of pain. If a child’s cheek is swollen, then preference is given to anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of syrup.
Treatment of pathology
What to do if there is a problem? After providing emergency assistance, the patient should consult a doctor. The specialist performs the necessary manipulations and then gives the patient recommendations regarding caring for the damaged area at home. These include mouth rinsing, physiotherapeutic procedures and local treatment of the soft tissues of the mouth. Providing emergency assistance for a cheek tumor is prohibited for children; women during pregnancy; adults who suffer from immunodeficiency; persons prone to allergic reactions.
General antibacterial drugs
Ideally, a suitable medication is prescribed after taking a swab from the mouth and identifying the causative agent of the problem. But if the situation is urgent, then to quickly eliminate the flux, the patient is prescribed new generation antibiotics. The action of the tablets is aimed at destroying and slowing down the spread of bacteria. For pathology use: Biseptol, Ampiox, Amoxiclav, Lincomycin.
Ointments
In addition to antibiotic therapy, topical medications are used. The use of products is permissible only with the permission of the dentist, since self-prescription of ointments rarely leads to recovery.
To reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process, Levomekol containing metaluracil and chloramphenicol is prescribed. Levomekol is rubbed into damaged membranes of the oral cavity 3-4 times a day. After treatment, you should not eat or drink water for 1 hour.
List of ointments that are used if a child’s cheek is swollen
To quickly get rid of the symptoms of swelling, you can use antimicrobial ointments in combination, for example, Streptomycin and Ichthyol. The drugs are mixed in equal proportions and applied to the damaged gum. Another popular drug of combined action is Metrogyl Denta.
Means for rinsing procedures
How to rinse the problem area? To quickly get rid of the remaining pus after surgery, and to prevent the development of swelling of the cheeks, use folk and household rinses. Several recipes are suitable for this purpose:
- Soda solution: 1 tsp. the main ingredient is dissolved in 100 warm water. Mouth baths are done at least 4 times a day.
- Miramistin. The drug is sold ready-made and does not require prior dilution. To treat foci of infection, take 20 ml of liquid into the mouth and rinse the mouth for 1 minute. After this, the liquid is spat out.
- Propolis solution. The drug is purchased at the pharmacy and diluted with boiled water in a ratio of 1:10. The product is used after meals.
- A mixture of St. John's wort, oak bark and sage: take 1 tsp. each ingredient and pour 500 ml of boiling water. The product is infused in a tightly closed container for 6 minutes. After filtering, the solution is used 3 times a day to relieve gum inflammation.
- A blend of green tea and sage. The dry collection is brewed with 500 ml of boiling water with the addition of 1 tsp. salt. The solution is recommended to be used warm. Before each procedure, it is advisable to prepare a fresh product.
- A mixture of chamomile, birch buds and calendula: the components are mixed in equal proportions and diluted with 1 liter of water. The mixture is boiled for 10 minutes, and then left to cool completely.
It is important to refuse the procedure in the first 24 hours after the intervention so as not to wash out the clot.
Prevention
The main procedure for preventing cheek swelling is timely treatment of caries and other dental problems.
Simple recommendations will also help maintain oral health:
- Regular dental care. Dentists advise using more than just a brush and paste. To effectively clean your mouth from plaque, you can use dental floss, floss and irrigators. You should also not forget about cleaning your tongue, since most of the bacterial flora is concentrated there.
- Pay attention to the condition of your gums. If these structures are loose and bleeding, they turn to a specialist - a periodontist.
- Visit your dentist at least once every 6 months for a diagnostic examination and professional teeth cleaning.
- Change your eating habits. Carbonated drinks, sweets and alcohol have a detrimental effect on the condition of teeth and enamel. To maintain dental health, it is better to consume fermented milk products, fresh vegetables and fruits.
Swelling of the cheek should not be ignored; in addition to aesthetic problems, the condition can threaten human health. More often, the problem develops against the background of developing caries and improperly performed dental work. If the inflammation is not accompanied by bleeding, fever and other dangerous signs, then emergency measures are taken at home, and then see a dentist. Preventive methods regarding cheek swelling are simple and accessible to every person. Their implementation will minimize the frequency of visits to the dentist.