The prevalence of food allergies in infants, according to WHO, is about 10%. This is a fairly large percentage and recently there has been a tendency towards its growth. It’s not uncommon to encounter a mother in the pediatrician’s office complaining of food allergy symptoms in her baby. To effectively treat food allergies in infants, the doctor must try not only to prescribe medications, but also to explain the rules for caring for the baby and explain the intricacies of diet therapy.
In the development of allergies, hereditary predisposition is of great importance. Therefore, if mom or dad have allergic reactions, then the baby’s risk of developing food intolerance becomes higher.
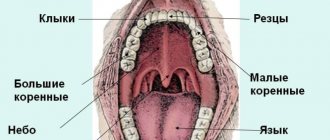
Symptoms of food allergies in infants
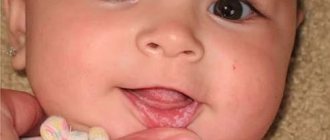
1. Manifestations of food allergies are varied. The most common manifestation is a rash. Immediately after an allergen enters the body, an acute allergic reaction—urticaria—may develop. Bright red swollen spots of different sizes and shapes appear on the baby’s skin. A bubble with transparent contents may appear in the center of the spot. Its size can vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters. This rash usually goes away within 1-3 days. But it’s still worth showing the baby to the doctor. Since sometimes a child needs medication, and in case of an extensive rash, or its unfortunate location, even emergency help. You need to remember which product caused this reaction and not give it again.
2. Other types of rash are not as severe. Therefore, it is not always possible to determine a clear connection between its occurrence and the product. Such rashes are usually not bright, small-pointed. They are prone to undulating flow. The rash usually becomes brighter in the evening and fades in the morning. The skin becomes dry, flaky, and sometimes cracks. Most often, such a rash is located on the cheeks, buttocks, outer surfaces of the thighs and forearms. This type of rash requires special attention from specialists - examination and specific treatment.
3 The second most common manifestations are gastrointestinal symptoms. These include: swelling of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, swelling of the esophagus, single or repeated vomiting. Most often, such symptoms appear acutely, immediately after consuming the allergen. In addition, the baby may experience abdominal pain. He can groan, be capricious, and kick his legs. Food allergies can manifest as loose stools. This can be either diarrhea or constipation. Less obvious signs of a food allergy in a baby may include frequent heavy regurgitation, low weight gain, poor appetite, and weakness. Manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract may occur with or without a rash.
4 Much less often in infancy, manifestations from the respiratory system are possible; if food gets into the mucous membranes, swelling of the upper respiratory tract may occur. This condition is acute and life-threatening. It requires immediate medical attention. With prolonged contact with the allergen, allergic rhinitis or asthma may develop. More often, such reactions appear not after ingestion of food, but after inhalation of its particles. The most common cause of respiratory allergies is inhalation of fumes from cooking or frying fish.
In addition, there are severe acute allergic reactions such as angioedema or anaphylactic shock. Such reactions occur immediately after contact with the allergen and develop very quickly. They are extremely rare and require emergency medical attention.
Causes
The causative agent of streptoderma, the photo of which you will find below, is group A streptococcus. However, it is worth noting that infection can only develop in a situation where certain factors are present:
- skin damage,
- lack of following basic hygiene rules,
- weak immune system,
- disruption of the endocrine system,
- dermatological diseases,
- depressive mood
- vitamin deficiency,
- constant washing of the skin, which leads to damage to the protective layer,
- strong influence of different temperature ranges,
- poisoning,
- circulatory disorders.
Causes of food allergies in newborns
Food allergies in babies who have just been born are very rare. The baby receives only mother's milk. This is food that nature created for your baby and nothing can be better than it. Therefore, the peak age of food allergies in breastfed infants can be considered around 4–5 months, when the baby begins to receive complementary foods - products added to breast milk: vegetables, fruits, cereals, meat, dairy products and others. The situation is somewhat different with bottle-fed babies. The formula itself can cause food intolerances. Therefore, when choosing a mixture, it is better to consult a specialist.
How to choose products that are right for your child
A dermatologist may recommend not one, but several drugs to choose from. They have a similar mechanism of action, but their prices may differ significantly. It depends on the active and auxiliary substances, manufacturer, and release form. When choosing a cream for a child’s atopic skin, you need to take into account possible individual intolerance to individual components.
You need to purchase drugs from well-known manufacturers with a good reputation: Russian, European, American. It is equally important to contact large pharmacy chains that work directly with manufacturers and control the quality of drugs on sale - this will protect you from purchasing counterfeit drugs. Consider the age of the child: choose creams and gels with a pleasant smell so that the child enjoys going to the shower.v
When choosing drugs for oral administration, it is preferable to buy syrups, powders, drops, rather than tablets and capsules that are difficult for a child to swallow.
What is the most common allergen in infants?
1. The first place is occupied by intolerance to cow's milk protein. It should be noted that most modern formulas for feeding infants are based on cow's milk proteins. This is the reason why the baby is allergic to the formula. In addition, a breastfed baby can also have a reaction to cow's milk protein if the mother has an excess of dairy products in her diet. We are not talking about a specific component of milk or formula. Cow's milk contains many different proteins: albumins, globulins, casein. Some of them cause an allergic reaction more often, others less often. Casein makes up about 80% of all milk proteins. Its composition in cow's milk is identical to that of goat's. This explains the cross-reaction in babies to cow's and goat's milk. Therefore, if you are intolerant to cow's milk, it is not recommended to replace it with goat's milk, or mixtures based on goat's milk, in the child's diet. Some proteins are destroyed by heat treatment. This is due to the lower reactogenicity (ability to cause reactions) of boiled milk. There is a protein similar in composition to the protein of beef or veal meat. If the baby is intolerant to this type of protein, there will be a cross-reaction to milk and meat products.
2. The next most common cause of allergies in an infant is a chicken egg. The egg also contains a protein called ovalbumin that is an allergen. Therefore, it is recommended to start introducing eggs into the diet with the yolk and in small portions. Watch your baby's reaction to this product carefully. When feeding eggs and protein for the first time, you should also carefully monitor the reaction. Don't forget that eggs are found in some pasta and baked goods.
3. Gluten is a common cause of food intolerance. This is a protein found in some grains. In order to prevent an undesirable reaction, it is recommended to start complementary feeding with gluten-free cereals. These include: buckwheat, corn, rice. Cereals rich in gluten, such as semolina, millet, and oatmeal, should be introduced closer to the age of one. In the first year, a reaction to gluten is less common than intolerance to cow's milk protein or egg white.
4. In addition, brightly colored fruits and vegetables can cause food reactions. Such as carrots, beets, pumpkin, peach. It is better to postpone their introduction into the diet and give preference to green and white vegetables - such as zucchini, cauliflower and broccoli. It’s best to start introducing your baby to fruits with green apples and pears. It is also better not to rush with exotic fruits such as mango or kiwi.
Do not forget that an allergic reaction is possible to any product. When giving a treat to a baby for the first time, a mother should remember the risk of intolerance. Try not to rush, especially with the introduction of the very first complementary foods. Give unfamiliar foods to the child in small portions in the morning so that it is possible to control the reaction to them throughout the day.
Therapy
Streptoderma has occurred ? Even in cases where the initial examination was carried out by a pediatrician, only a dermatologist can select therapy. Doctors in this field have an understanding of drugs with a narrow scope of action.
The first step is to limit the child’s diet. The course of treatment also involves avoiding water procedures, which can cause the spread of the disease. Healthy areas of the skin should be washed with a solution of chamomile, and damaged areas should not be touched at all.
The sick person needs to choose the right wardrobe, from which items of clothing made from synthetics and wool must be removed.
Doctors advise popping blisters that form on the skin with a disinfected needle, after which the abscess should be drained twice a day. Healthy areas of the skin are washed with a boron solution.
If crusts appear on the skin, they should be treated with antibacterial gels or ointments.
In more complex situations, many other medications may be prescribed:
- antibiotics for streptoderma of the tetracycline or chloramphenicol series,
- means that prevent the occurrence of an allergic reaction,
- means aimed at improving the body's immune system,
- vitamin preparations,
- antipyretic.
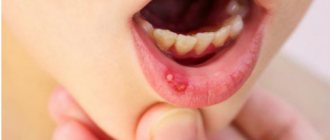
The set of medications must be discussed with the doctor. With the right treatment, the symptoms disappear within a week, but after the severe form is eliminated, scars may remain. This is what streptoderma looks like .
what does streptoderma look like?
How to recognize a food allergy and not confuse it with other diseases?
Most often, in order to diagnose a food allergy, a doctor only needs an examination and a detailed interview with the mother. Mom can point out that she herself has a food allergy or point the doctor to a specific food. Sometimes it is difficult to make such a diagnosis right away. Then the doctor may order an examination. First, a general blood test. And then, if necessary, specific allergy tests: examination for immunoglobulins, and at a later age, provocative tests. It is these tests that were chosen as the most informative in the latest clinical recommendations. In addition, your baby may need to consult an allergist, dermatologist or gastroenterologist, depending on the symptoms that are bothering him. And also, additional examination from the gastrointestinal tract.
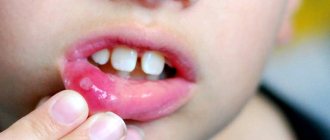
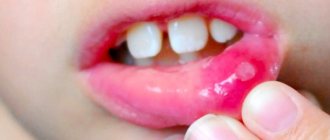
What to do if your child has a swollen upper lip
If parents know that the condition in question was caused by a blow or insect bite, or an allergy to an external irritant, then you should not consult a doctor. You can apply a cold compress to the area and give the baby one of the usual antihistamines - after 20–30 minutes the swelling will become much less.
But in the case of a tumor of unknown origin or the presence of other changes in the child’s health (weakness, complaints of pain and burning, increased general body temperature), you must immediately contact a pediatrician. The doctor will conduct an initial examination and find out the true cause of this condition. Only after this will he give a referral for examination by a dentist, if required.
In turn, the dentist will visually assess the condition of the oral cavity, make a diagnosis and make medication prescriptions. They can be very different:
- antibacterial drugs;
- antiviral agents;
- antiseptic solutions for irrigating the oral cavity and rinsing it;
- antifungal drugs.
If a child has a swollen upper lip, the doctor will tell you what to do in this situation. Self-medication in this case can cause deterioration of the condition and rapid spread of the inflammatory process. If the cause of the swelling is a purulent focus, then the lack of qualified assistance can lead to serious consequences: damage to the soft tissues and periosteum of the jaw, and general blood poisoning.
Treatment and prevention of allergies
According to the latest WHO recommendations, the basis for the prevention of food allergies in children is breastfeeding. Children who receive exclusively breast milk in the first months of life are much less likely to suffer from food allergies. At the same time, mothers of healthy children who are breastfed do not require special diets. Their diet should be complete and varied, including proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. As well as microelements and vitamins. Mothers of children who are at risk for food intolerance are advised not to limit their diet too much. It is necessary to completely exclude those foods to which the mother herself has a reaction and keep a food diary.
If artificial feeding is necessary, children prone to allergies choose special hypoallergenic formulas. To treat existing manifestations, the mixture should be selected by a specialist. According to the latest clinical recommendations, if you are intolerant to cow's milk protein, choose mixtures with fully hydrolyzed protein or amino acid composition. In this case, it is not correct to prescribe hypoallergenic mixtures and mixtures based on goat’s milk protein. Soy-based mixtures themselves can cause an allergic reaction.
Another important step for the prevention and treatment of food allergies is the correct introduction of complementary foods. Complementary foods should be introduced in a timely manner - no earlier than 4 months and no later than 6. To begin with, hypoallergenic foods are selected - white and green vegetables, gluten-free cereals. On one day, the baby is given only one complementary food product, in small quantities, and the possible reaction is observed. At the beginning, a new product should be introduced no more than once a week. Mothers of babies who are predisposed to allergies or already have allergic manifestations are recommended to keep a food diary. There, the mother writes down all the foods she fed the child during the day and possible reactions to them.
The doctor, if necessary, can prescribe medications to the baby. They can be either for oral administration or for skin treatment. Children with chronic allergic rashes require special skin care. It is necessary to use special children's detergents with a neutral pH. And after washing, use special care products - emollients. It is better to consult a doctor about which emollient to choose. If there are manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract or respiratory system, the child needs specific treatment, which can only be prescribed by a doctor during an in-person examination.
Online consultation with a pediatrician
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
Skin care
To relieve itching and prevent infection of the affected skin, you need to properly care for your skin:
- It’s better not to take a shower, but to take a cool bath for about 10 minutes; use medicated bathing products with a soft base that cleanse but do not dry the skin;
- moisturizing and softening – the skin should not be dry to prevent flaking and cracking; regularly apply a moisturizer recommended by a dermatologist;
- Do not let your child scratch the affected areas to avoid infection - apply anti-itching products to the atopic areas.
Cream or gel relieves discomfort during an exacerbation and allows you to sleep, eat, and play peacefully. Apply the drug to cleansed skin, treat atopic lesions and the areas around them. Do not exceed the recommended dosage and frequency of use.
How long do food allergies last in infants?
Children with food allergies have an increased risk of other allergic reactions or illnesses in the future. There is also a chance that intolerance to the product will remain with the baby for life. However, up to 50% of allergic reactions in babies go away by the age of one year. And up to 90% by 5 years. Most of the patients I have worked with at 3 years old go to kindergarten without any manifestations of the disease.
It is possible to protect your child from food allergies by paying close attention to his diet and the mother’s diet during breastfeeding. And if allergies cannot be avoided, contact a specialist and be healthy.
Symptoms
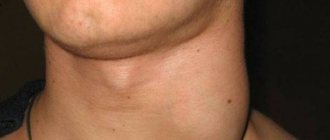
With atopic dermatitis in children, skin tightness, redness appears, the skin flakes, feels rougher to the touch, and thickening may appear. Microscopic bubbles form, around which moisture is released. The child is worried and scratches the affected areas. When an infection occurs, local inflammation develops and the wounds heal poorly. With significant spread in young children, general intoxication of the body manifests itself: the temperature rises, the peripheral lymph nodes enlarge. Due to severe itching, sleep and appetite are disrupted, and the child often cries. Dermatitis most often affects the face, neck, armpits, scalp, groin, areas under the earlobes, popliteal fossae, and elbows.
Preventive measures and prognosis
Due to the high risk of infection, sick children should keep their distance for some time and not contact other people. Quarantine is provided for up to 10 days. For the entire period of therapy, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene.
To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to disinfect the child’s personal belongings. Sick children should have a proper diet rich in nutrients. To improve the quality of the immune system, certain measures should be taken.
streptoderma treatment
As a rule, streptoderma ICD 10 in children is cured without any problems. Exacerbation of the disease and re-infection are observed mainly in children from disadvantaged families or in children with weak immunity. With timely treatment, symptoms disappear within one week. If you do not attach any importance to this, the disease can develop into a more severe form. In the worst case, the disease can lead to blood poisoning. For streptoderma, treatment with ointments and antibacterial agents is mandatory.
Types of disease
- Streptococcal impetigo. The most common standard form of the disease. A characteristic rash forms on the face, arms and legs. This form is also the most limited, since the pathogen does not move beyond the upper layer of the skin, which has certain protective mechanisms. The appearance of the integument does not change, only individual blisters with liquid appear on the reddened areas. Initially, the patient will experience itching, after which the blisters become darker, which helps the blister to crust over. The duration of this process reaches one week. However, it is worth remembering that if the rash resolves, bacteria are further transferred to healthy areas of the integument, which has its negative consequences for the sick person.
- Bullous impetigo. The rashes are located on the arms and legs and had a fairly impressive diameter. Once the blisters open, these areas of skin develop ulcers that can spread quickly.
- Streptococcal diaper rash. Most of the patients are young children and overweight people. The location of the rash is under the mammary glands, in the axillary folds, intergluteal or inguinal-femoral folds. If you are overweight, the abdominal area is affected.
- Ringworm common. Appears in the form of bright pink rashes. The place of appearance is the face. The rash may become smaller due to exposure to direct sunlight. Those areas of the skin that are affected will not take on a tan like before.
- Streptococcal infection is characterized by the formation of blisters in the corners of the mouth. After the blisters disappear, a crack appears in their place, which in a matter of minutes becomes covered with a yellow crust. It also happens that children tear off the crust, but it forms again.
- Streptococcal ecthyma is the most complex form of the disease. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of characteristic lesions and scars on the arms and legs. In case of development of ecthyma, as a rule, there is a deterioration in health.
Causes of complications and re-infection
The reason for re-infection may be incorrect therapy when, for example, if you have primary criteria for improvement, you decide to stop therapy. The most important thing is to remember that you need to unquestioningly follow the advice and instructions of your doctor.
streptoderma complications
Therapy and drugs
Throughout the spread of the disease, basic hygiene rules should be observed: in the first days, it is forbidden to take baths and wet impetigo, and it is forbidden to comb the affected areas.
Therapy for this disease is aimed at destroying the pathogen and strengthening the protective functions of the immune system. As a complex treatment, antibacterial drugs of the category of cephalosporins, macrolides and penicillins are prescribed. If you have bullous streptoderma, you should stop taking medications. As an immunocorrective treatment, the drugs “Likopida”, “Amiksin” and their analogues are effective. Treatment with drugs for . Restoration of microflora in the intestines occurs with the help of probiotics and prebiotics. Appropriate antihistamines will help get rid of scabies.
Means that increase the body’s resistance to infections in the form of solutions - “Eleutherococcus”, “Echinacea”, “Leuzea”, etc.
Sets of vitamin nutrients should also be taken in accordance with the instructions.
Local treatment includes antiseptic drugs that prevent the spread of putrefactive bacteria. Such medications include various alcohols, brilliant green, as well as their analogues - “Fukartsin”, “Chlorhexidine”, “Miramistin”, “Rivanol” or the cauterizing agent “Resorcinol”.
The use of a huge number of zinc-based pastes, preparations and ointments for streptoderma in children with intense scabies.