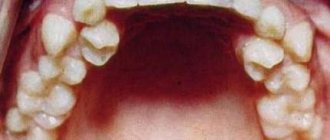
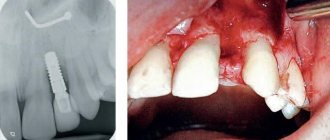
Polyodontia (hyperodontia, hyperdentia) is the appearance of supernumerary teeth. Normally, an adult has 28-32 teeth (including wisdom teeth); with polyodontia, an indefinite number of extra teeth appear. About 2% of the world's population suffers from the pathology.
There are no methods to prevent the development of polyodontia, but it is possible to reduce the number of complications caused by the disease. Therefore, it is necessary to be attentive to your health and undergo a preventive examination with a dentist twice a year. If you suspect that an extra tooth has appeared in your mouth, you should immediately consult a doctor. Particular responsibility lies with parents, since children are not able to independently monitor the health of their teeth.
Concept and signs of supernumerary teeth
Hyperdentia (hyperdentia from hyper and lat. dens, dentis tooth) is an anomaly in the number of teeth.
Up to a certain age, children should ideally have twenty milk teeth, which are gradually replaced by permanent ones, and there are 32 of them. With hyperdontia, these numbers shift by one or more positions in a larger direction, since in this case there are one or several more tooth buds than normal.
Supernumerary teeth, as a rule, erupt after the main teeth, but there are exceptions when the supernumerary has erupted and taken the place where a normal tooth should be. As a result, teeth shift and bite changes. Only in rare cases does hyperdontia make itself felt during the period of milk eruption. Most often, this anomaly occurs among men, which accounts for about 65% of the total number of such cases.
In 15% of cases of this anomalous phenomenon, more than two supernumerary teeth erupt on the gum or palate. The most common phenomenon among hyperdontic anomalies is the eruption of supernumerary teeth in the area of the lateral incisors on the upper jaw, and less often on the lower jaw. Such teeth may differ from normal ones in shape, structure, color, which indicates their abnormal origin.
Diagnostics
Identifying erupted supernumerary teeth is not difficult. Often, patients themselves, already at the initial examination, complain that they have a tooth that should not be there.
The situation is more complicated with hyperdontia with impaired eruption . In such cases, the main diagnostic method is x-ray (panoramic radiography). It allows you to clearly visualize all dental elements, both normal and supernumerary, as well as their location. The disadvantage of the technique is that the X-ray image is flat and cannot be used to characterize the exact relative position of all teeth and their root systems. Therefore, patients often undergo additional computed tomography .
Hyperdontia in an adult
In adults, hyperdontia is much more common than in children. Additional teeth are mainly located in the palate or on the gums, which is unnatural and contrary to the norm. The eruption of an “extra” tooth can cause the following symptoms:
- Impaired diction. The person begins to burr and vaguely pronounce some sounds and sound combinations.
- A feeling of discomfort caused by the abnormal position of supernumerary teeth. Such teeth provoke curvature of the dentition.
- Malocclusion. This problem entails a number of dental diseases, such as pathological tooth wear, impaired diction and others.
- Damage to the oral mucosa with subsequent inflammation;
- Impaired chewing function, which leads to gastrointestinal problems.
This type of anomaly often causes nervous breakdowns and mental disorders. Due to the displacement of the dentition, healthy teeth lose their strength and begin to loosen under the pressure of the growing supernumerary rudiment. The jawbone swells, which leads to pain. Constant aching pain leads to irritability, apathy and deterioration in general well-being.
Why does retention occur?
Most often, wisdom teeth cannot fully erupt. This is due to the peculiarities of their location. In the process of evolution, eights have lost their meaning. Some people don't have them at all. In others, they often “sit” under the gum and contribute to the displacement of neighboring units, which causes the bite to change.
Retention is caused by:
- heredity;
- premature removal of baby teeth, which leaves little room for constant sweat;
- excessively thick gum walls (very rare);
- malocclusion, severe crowding.
Hyperdontia in children
Sometimes the eruption of extra abnormal teeth in children is almost asymptomatic. The only sign of polyodontia is the number of teeth erupted, which exceeds a certain norm for a particular age. Most often, this anomaly is accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms, which should cause concern among parents and become a reason to consult a dentist.
Signs of polyodontia in children:
- a rapid increase in temperature, which is difficult to bring down and lasts from one to several days;
- a strong aching or throbbing pain is felt at the site where the irregular tooth erupts;
- there is a feeling of discomfort when talking, eating, drinking;
- a slight swelling of the cheek and even the wing of the nose is noticeable on the side where the extra element erupts;
- due to excessive salivation as a reaction to an irritating factor, a wet cough and difficulty breathing may occur;
- gastrointestinal disorder as another reaction of the body to the inflammatory process and high temperature.
The symptoms of the eruption of supernumerary teeth in children are similar to those observed when the first milk teeth appear, only in this case the situation is a little complicated by the fact that the germination of an extra tooth is not something normal and inherent in nature. This makes it more difficult for the child to tolerate this phenomenon than the eruption of healthy baby teeth.
What does the cost of treatment depend on?
The cost of treatment is determined by various factors, including the complexity of the anomaly and the method of its correction. If the patient does not show signs of deformation of the jaw arch, then simple removal will be required:
- extraction of one supernumerary element costs around 1,500 rubles,
- with its dystopia and retention, complex removal is required, and the cost of the procedure will vary from 3,500 to 15 thousand rubles.
The need for orthodontic correction significantly increases the cost of treatment. Here the price will depend on the specific technique, type of corrective structure, its materials and additional procedures.
Causes of jaw abnormalities
To date, doctors have not reached a unanimous opinion about the causes of such an anomaly as hyperdontia. There are different hypotheses about this:
- Atavism. Historians have proven that primitive people, due to the way of life they led, naturally had 36 tooth primordia. The results of studies of the remains of those times indicate that people had six incisors on the upper and lower jaws. Therefore, polyodontia is a kind of genetic anomaly that makes itself felt after thousands of years;
- Many doctors are inclined to the theory that one embryo splits into several in the womb, when, in fact, they begin to form. This theory also states that an anomaly can develop throughout pregnancy if it was quite severe, the woman suffered serious illnesses or led an unhealthy lifestyle (bad habits, drugs, alcohol and others);
To date, research continues to establish the true cause of hyperdontia. Based on these data, modern doctors are more inclined to the second version than to the first.
Types of hyperdontia
Depending on the location of the supernumerary teeth, several types of polyodontia are distinguished:
- Conical or awl-shaped tooth . In this case, excess rudiments erupt between the upper central and lateral incisors. The name of the anomaly comes from the peculiar shape of the supernumerary tooth, which looks like an awl. This form of hyperdontia is dangerous because the sharp end of the tooth often injures the mucous membrane, which is why an inflammatory process develops when an infection gets there.
- Additional molars . Such teeth grow between the main molars, displacing the dentition from the correct position.
- Extra fangs . This type of anomaly is typical for the upper jaw.
- Supernumerary premolars . These additional teeth are located on the lower jaw. Each type of anomaly looks different depending on where and how the extra teeth are located. These differences can be clearly seen in the photo.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of polyodontia is carried out exclusively by a specialized doctor - an orthodontist, who conducts a preliminary examination of the oral cavity and dentition, refers the patient to x-rays (orthopantomography) and analysis of anthropometric casts of teeth made of plaster. Such models are made for a more detailed study of a specific anomalous phenomenon, on the basis of which a diagnosis is then made and treatment is prescribed.
Table of normal human teeth. Deviation from the norm - polyodontia
When examining plaster models made on the basis of dental casts, the doctor measures the size of the teeth, and then analyzes the data obtained based on a special table by Wetzel and Ustimenko. The length of each row of teeth must be measured. This indicator may fluctuate depending on such characteristic individual characteristics of a person as crowding of teeth or the presence of large gaps between them. In the first case, the length will be less than normal, and in the second, a little longer. To diagnose asymmetry, the distance from the midline of the palate (or hyoid frenulum) to the far point of the dentition in one direction or the other is determined.
What to do?
The presence of supernumerary teeth is an abnormal phenomenon, so the issue of eliminating this problem must be resolved. How, this is another question, to give an unambiguous answer to which is impossible. As a rule, there can be several ways to solve a problem. The choice of treatment method depends on where the extra tooth is located, what shape it is, and what stage of eruption it is at.
Facilitating teething in baby
Drug treatment allows you to relieve unpleasant and painful symptoms during the eruption of excess buds. This option is the only one for children with baby teeth if the tooth is only at the eruption stage. When it finally germinates, it will be necessary to use more radical methods. The dentist prescribes medications that will help relieve pain, reduce fever and stop the inflammatory process in the soft tissues of the gums.
Simple tooth extraction
Surgery. This method is the fastest and most effective, since removing an extra tooth easily solves the problem and relieves a person from unpleasant sensations and discomfort. This treatment method is used when there is too little space in the dentition for an extra tooth or there is no space at all. Most often, supernumerary teeth are removed when there is crowding of the teeth. To free up some space in the dentition, the wisdom teeth are removed first, and if this was not enough, the premolars are also removed.
Braces and other orthodontic treatment methods
Orthodontic treatment is a method that involves correcting the bite, straightening the teeth, etc. The result is achieved by installing braces or other orthodontic structures that allow you to straighten crooked teeth and return them to their place, where they should be. The duration of wearing braces depends on many factors:
- the age of the patient (children have their own specifics);
- complexity of the situation;
- locations of supernumerary teeth and others.
At the first and second stages of the disease, the doctor may decide to install special expansion plates or aligners. Can also apply the separation method.
Consequences of poor quality treatment
If the treatment is not well-carried out, impacted teeth will continue to interfere with the normal development of the bite and dentition, which causes a violation of chewing ability, leading to a number of problems with the gastrointestinal tract, and impaired diction, which negatively affects pronunciation and pronunciation. Also, after unsuccessful treatment, healthy teeth that are located next to the additional one may begin to deteriorate.
Preventive measures
The essence of preventing dental anomalies is to eliminate the possible causes of their appearance even at the stage of formation of rudiments, that is, all responsibility for possible dental anomalies depends entirely on the child’s mother.
To prevent this unpleasant phenomenon, you need to eat right, food should be balanced and healthy. It is important to give up bad habits and follow your doctor’s recommendations. When the baby is small, you need to make sure that he does not suck his finger or pacifier for more than a year and regularly take him for examinations to the dentist for timely detection and elimination of dental problems. Moscow metro station Zvezdnaya, Danube Avenue, 23
How impacted units are removed
The operation to remove an impacted tooth is always difficult. It can only be performed successfully by an experienced and highly qualified dental surgeon. Unerupted wisdom teeth are especially difficult to pull out.
On average, surgery takes about one and a half to two hours. It includes the main steps:
Introduction of anesthesia. This may be local anesthesia, sedation or general anesthesia - it all depends on the location and depth of the unit. The doctor also takes into account the individual wishes of the patient and his state of health.- Excision of the gum and gaining access to the bone tissue in the area of the impacted tooth. A laser or scalpel is used. The first option is more preferable, as it makes the operation less invasive and eliminates the risk of bleeding.
- Preparation of exposed bone to gain access to a submerged tooth. Boron is used here.
- Removing the impacted unit with forceps - an elevator. If the tooth contains several roots and is large, it is first sawed and then removed in pieces.
- Performing plastic surgery of hard and soft tissues, suturing (if necessary).
- Treating the surgical wound with antiseptics and anti-inflammatory solutions.
After the extraction of an impacted tooth, the patient spends some time in the maxillofacial surgery hospital. He is prescribed daily wound treatment and various physical procedures. These measures can reduce the likelihood of developing postoperative complications.