Quick transition Treatment of epiglottitis
Epiglottitis is an acute inflammatory disease of the epiglottis and adjacent structures that can lead to life-threatening airway obstruction.
In the case of the infectious nature of the disease, inflammation occurs as a result of bacteremia and/or direct invasion of the microorganism into the mucous membrane of the epiglottis.
As a result of swelling and accumulation of inflammatory cells between the epithelial layer and the cartilage of the epiglottis, the latter increases in size. The swelling progresses rapidly and covers the entire vestibule of the larynx (the area of the larynx below the vocal folds is usually not affected), the airways narrow down to complete obstruction, leading to cardiac arrest and death.
For what reasons can swelling of the larynx occur in a child?
One of the reasons why laryngeal edema in a child can be called a fairly common problem is the structure of the larynx. In young children, the larynx has a funnel shape, although it is much narrower than in adults. The inflammatory process of the mucous membrane and swelling lead to a narrowing of the already narrow larynx, resulting in breathing problems. In addition, the mucous membrane in children contains many blood vessels and has a looser structure, which contributes to a more rapid development of inflammatory processes. Due to the narrowness of the lumen of the larynx, in the absence of medical assistance, the child may suffocate.
Depending on many factors, laryngeal edema develops in a child, the causes of which vary instantly, acutely or gradually. The most dangerous are the fulminant and acute forms, since the child’s body does not have time to adapt to the insufficient supply of oxygen. The speed of development of the process depends directly on the reasons that caused it:
- fulminant edema develops when a foreign body enters the body or when an allergy enters the body;
- acute edema develops with acute laryngitis, with complications of diseases such as measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria, influenza;
- gradual swelling develops with neck injuries and for other reasons.
The most common are swelling of the throat with laryngitis in a child and allergic swelling of the throat in a child.
It is imperative to find out the reason why laryngeal edema developed in a child, since the effectiveness of treatment depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis. It is not recommended to use information on the topic “a child’s throat is swollen: what to do” taken from the Internet, since the choice of treatment method requires knowledge of the exact diagnosis. Making an appointment with a specialist is the best way to solve the problem. Specialists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) use certified safe medications and effective technologies, which is one of the conditions for the complete recovery of young patients.
Prevalence
The incidence of epiglottitis decreased sharply after the introduction of the Hib vaccine into the routine childhood immunization program. Before the vaccine was available, the incidence was approximately 5 per 100,000 children under 5 years of age. Among immunized children, the incidence of epiglottitis ranges from 0.6 to 0.8 cases per 100,000. The average age of children with epiglottitis has increased from 3 to 6–12 years.
The incidence of epiglottitis in adults has been largely stable over the past few decades, ranging from 0.6 to 1.9 cases per 100,000 people annually.
Symptoms of throat swelling in a child.
The following symptoms indicate that laryngeal edema has developed in a child:
- breathing becomes intermittent, shallow, difficult;
- the voice becomes hoarse;
- neck muscles tense;
- the child complains of a lump in the throat;
- pain in the neck is felt;
- there is a feeling of lack of air.
The manifestation of psychoneurological symptoms is also possible:
- irritation and anxiety;
- dizziness;
- convulsions;
- slurred speech.
Swelling of the throat in a child due to allergies is characterized by swelling of the face and enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes. Without help, loss of consciousness may occur.
The answer to the question of how to treat swelling of the throat in a child can only be given by a qualified specialist. Self-prescribing medications to a child can lead to a sharp deterioration in the baby’s condition. Since the symptoms of laryngeal edema in children develop quickly, in particular, laryngitis causes acute laryngeal edema in a child, all actions should be aimed at ensuring access of air to the lungs. In the absence of timely medical care, complications may occur, in particular:
- acute laryngeal stenosis with shortness of breath and facial hyperemia;
- increased sweating, disruption of the body's systems and organs.
It is better to consult with a qualified doctor about how to treat a swollen throat in a child, since only a doctor, after an examination, will prescribe procedures and medications that can relieve swelling of the throat in children, the symptoms of which depend on the cause of the disease.
When to get urgent help for a swollen throat in a child
If you suspect swelling of the child's throat, you should immediately call a doctor if the following symptoms are present:
- the cough became “barking”;
- it is difficult for the baby to speak;
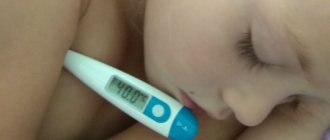
- the temperature rose sharply;
- the skin of the lips turned blue;
- shortness of breath appeared;
- loss of consciousness.
The presence of shortness of breath is a good reason to call an ambulance, since oxygen deprivation can cause irreparable harm to the child’s health. Such symptoms indicate a sharp deterioration in health. If left untreated, suffocation may occur.
The pediatric department of JSC "Medicine" (academician Roitberg's clinic) in Moscow offers home-call services for a pediatrician. To urgently call a pediatrician at home, just call +7 (495) 229-00-03.
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is located in the center of Moscow at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10, a five-minute walk from the Mayakovskaya metro station.
Types of tracheitis
There are several classifications of this disease:
- according to duration, tracheitis is divided into acute and chronic, the latter most often occurs with periods of exacerbation and remission;
- according to its etiology (reason), it can be infectious or non-infectious;
- Based on the nature of changes in the mucous membrane, they distinguish between catarrhal (when the surface layer of the mucous membrane becomes inflamed), hyperplastic (when the mucous membrane becomes inflamed and thickens) and atrophic tracheitis (when the mucous membrane becomes thinner and loses a significant number of cells capable of performing its functions).
The approach to its treatment depends on the type of disease.
Diagnosis of throat swelling in a child
Diagnosis of laryngeal edema in a child is made on the basis of examination of a small patient, collection of anamnesis and complaints, as well as examination data, if necessary. During the consultation, the doctor clarifies the presence of pathologies that could cause swelling of the throat and examines the child using indirect laryngoscopy.
If difficulties arise with stopping the diagnosis, the pediatrician refers to an otolaryngologist who conducts a comprehensive examination. To diagnose laryngeal edema in children, specialists from the pediatric department of JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) can use the following types of examination:
- endoscopy;
- Ultrasound;
- microlaryngoscopy or videomicrolaryngoscopy;
- radiography of the OGK;
- X-ray of the larynx;
- bronchoscopy, etc.
No preliminary preparation for the examination is required.
Specialists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) in Moscow use modern diagnostic technologies and the latest diagnostic equipment, which makes it possible to obtain accurate examination data.
Who to contact
If laryngeal edema develops in a child, treatment is prescribed by the pediatrician based on the results of the examination. In difficult cases, based on the results of the examination, the pediatrician may refer you to an otolaryngologist (ENT), an infectious disease immunologist, or an allergist.
The pediatric department of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) offers the services of qualified experienced specialists working in various fields of medicine.
You can make an appointment with a pediatrician on the website page. Our clinic is located in the center of Moscow at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10, a five-minute walk from the Mayakovskaya metro station.
Treatment of throat swelling in a child
If laryngeal edema occurs, treatment must begin immediately. The choice of treatment and medications depends on the diagnosis. Parents are strongly discouraged from giving their children medications on their own, as this may result in worsening the condition and causing side effects.
The main goal of using therapeutic measures is to eliminate the underlying pathology that provoked the swelling. For viral or bacterial etiology of laryngeal edema, the doctor will prescribe antiviral, antibacterial or antifungal drugs. If laryngeal swelling in a child is caused by an allergy, the doctor will prescribe medications that will relieve swelling and stop the effects of allergens.
To restore the mucous membrane and normalize the condition of a small patient, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures.
Infection is the main cause of tracheitis
In most cases, tracheitis is infectious in nature. The cause of inflammation of the mucous membrane is viruses and bacteria; associations of different pathogens are possible, that is, the presence of both a viral and bacterial infection at the same time. During the ARVI season, tracheitis in a child occurs as a result of infection with influenza viruses and other types of viruses, the number of which is very large. Subsequently, the addition of a secondary bacterial infection (streptococcal, staphylococcal, etc.) is often noted.
First aid: how to relieve swelling of a child’s throat before the doctor arrives
If swelling of the larynx occurs in a child, first aid is to provide access to air into the lungs. The child should be seated and under no circumstances allowed to lie down, since the horizontal position increases blood flow to the larynx. If swelling of a child's throat occurs, first aid should be provided immediately to avoid suffocation. It is necessary to provide an influx of fresh cool air, which will make breathing easier. It is also recommended to give a warm drink, for example, warm milk with soda, which will partially relieve inflammation and reduce swelling. Humidifying the air will help relieve spasms. You can humidify the air using a special device or placing a container of water in the room. Before consulting a doctor, children should not be given throat medications.
Predisposing factors
The development of tracheitis is promoted by:
- general hypothermia;
- decreased immunity;
- lack of vitamins;
- rickets in a child;
- impaired nasal breathing (with chronic runny nose, severe curvature of the nasal septum, adenoids);
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- long-term use of inhalers with glucocorticosteroids (hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs), which is sometimes necessary in the treatment of bronchial asthma;
- living in an area with unfavorable environmental conditions;
- presence of a smoker in the family.
All this does not cause clinically significant inflammation of the tracheal wall, but disrupts its barrier function and facilitates the penetration of pathogens.
How to make an appointment with a doctor
To receive highly qualified medical care, you must make an appointment with a pediatrician who will conduct an examination and comprehensive medical examination of the child. If necessary, the pediatrician will consult with or refer other specialists.
To make an appointment with a specialist in the pediatric department of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg), use one of the following methods:
- a quick entry form on the main page of the center’s website;
- by telephone 24/7;
- using a mobile application.
The clinic of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is located in the center of Moscow at 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10, a five-minute walk from the Mayakovskaya metro station, as well as not far from the Belorusskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya and Novoslobodskaya metro stations .