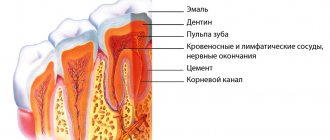
Chronic pulpitis is a form of pulpitis, inflammation of the pulp. Pulp is the soft tissue of the tooth, which is responsible for the blood supply to its hard tissues and consists of nerve endings, blood vessels and connective tissue. As a rule, chronic forms of pulpitis occur when acute forms are suppressed, but sometimes they can be a primary process without an acute stage.
Chronic pulpitis is an inflammatory process of the nerves and blood vessels of the tooth, which gradually causes severe changes in structure and function. If the disease is present, a person reacts sharply to cold and hot foods and experiences pain while chewing solid food. Pathology can be accurately determined using x-rays and electroodontodiagnosis. The development of the chronic form occurs in the absence of proper treatment of acute pulpitis.
Fact: the disease is much more often detected in the chronic form rather than in the acute form. People aged 20-50 years are at risk.
Filling made of light-curing material for classes I and V - 2,000 rubles.
Filling made of light-curing material in classes II, III, IV - 3,000 rubles.
Placing a temporary filling - 400 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (frontal group) - 6,500 rubles.
Resection of the root apex (chewing group) - RUB 9,000.
Mechanical and medicinal treatment of canals for periodontitis (1 canal) - 1,100 rubles.
Closing perforations (MTA) - RUB 6,500.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- The cost of a dental consultation is 1,000
- The cost of an orthodontist consultation is 2,000
Make an appointment
Causes of pulpitis
Photos of chronic pulpitis are presented in this article. This disease can occur for various reasons.
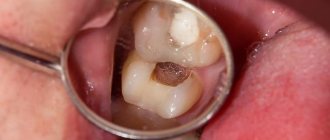
The pathology can become chronic if acute pulpitis is not treated for 12 weeks. The disease appears due to toxins and bacteria. They penetrate into the pulp through channels and through the blood. Complications of deep caries, increased abrasion of enamel, mechanical injuries and opening of the pulp can contribute to the development of pathology.
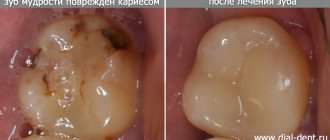
Advanced caries
Ignoring the symptoms of caries and the lack of professional treatment can lead to the further development of this disease with penetration into the deep layers of dental tissue, including the pulp. Once in it, pathogenic microorganisms will cause inflammatory processes.
Incorrect treatment of caries
Sometimes pulpitis occurs after caries treatment has been carried out. The reasons for its occurrence may be the following:
- Not all tissues affected by caries have been removed, and they continue to have a destructive effect on the tooth;
- During treatment, the pulp was burned due to insufficient cooling;
- The bottom of the tooth cavity was dried with an air jet before filling.
Tooth injuries
The integrity of the tooth enamel can be damaged due to a blow to it or contact with hard food. If, as a result, the crown splits and the nerve is exposed, inflammation of the pulp in the near future is almost inevitable.
Retrograde pulpitis
Sometimes the infection penetrates into the dental pulp not from the oral cavity, but through the apical foramen in diseases such as periodontitis, osteitis, osteomyelitis.
Indications
- Mechanical damage to the tooth and violation of the integrity of the crown.
- The appearance of complications of deep caries and the penetration of infection into the canals.
- Exacerbation of the disease and pain syndrome.
- Incorrectly installed filling and progression of pathology.
- Detection of inflammation on an x-ray.
Contraindications
- Cardiovascular diseases in the acute stage.
- Pregnancy and prohibition on taking medications.
- Mental and nervous disorders.
- Poor blood clotting.
- Allergic reactions to anesthesia, antiseptics, antibiotics.
Which teeth suffer from pulpitis more often?
Pulpitis can affect any unit in the oral cavity, but on some teeth the disease manifests itself more often. For example, the sixth or first molars are most at risk of developing pulpitis. These teeth are among the first to erupt and are located in an area that makes good hygiene difficult. Moreover, they have a unique structure, which makes it difficult to notice carious damage on them in a timely manner. People often do not notice spots of caries in deep fissures (pits) on the surfaces of the six, and this inattention is quite capable of leading to the gradual development of pulpitis.
If we talk about the front teeth, then the central and lateral incisors will be the most vulnerable to pulpitis.
Pulpitis on fangs is very rare; these teeth are massive and have a unique structure that does not allow caries to develop on them as actively as on other units.
The lower teeth are less susceptible to caries and pulpitis because the units in this area are constantly washed by saliva. Saliva contains useful components that strengthen tooth enamel and protect it from the action of pathogenic microorganisms. However, due to frequent washing of the lower teeth with saliva, another negative phenomenon occurs: hard plaque (tartar) quickly forms. Therefore, you should take care of your dental health equally and thoroughly clean and monitor the condition of all units in the oral cavity, regardless of their location.
Clinical manifestations
Treatment of chronic pulpitis does not always begin on time, since this disease is very insidious. Acute pain is always the reason for seeking professional help, but with chronic pulpitis, pain symptoms are not pronounced and the patient prefers to postpone his visit to the dentist. In this case, the disease develops quite quickly and, at best, will lead to an exacerbation of chronic pulpitis with severe pain symptoms or to the occurrence of periodontitis, in which it can be very difficult to save the tooth from removal. No less pleasant consequences may include the formation of cysts, ulcers, phlegmons and even sepsis. This is why timely diagnosis of chronic pulpitis is so important!
The main manifestation is an acute reaction to cold and hot food. However, it occurs late (sometimes 5-10 minutes after consuming food or liquid). In a calm state, a person experiences heaviness inside the tooth.
The hypertrophied form is not accompanied by severe pain. Overgrown tissue appears that ruptures when eating food. Pain may occur when eating hard foods or when pressing on the inflamed area.
Gangrenous pulpitis causes severe pain when eating hot food, which does not go away for a long time. The pulp begins to rot, which causes bad breath. The color of the tooth enamel changes (it becomes dark gray).
An exacerbation is accompanied by severe pain even without mechanical and thermal effects on the affected area. There are positive symptoms of vasoparesis, swelling of the gums, and pain in the trigeminal nerve.
Symptoms that will help you diagnose pulpitis yourself
Knowing the main symptoms of the disease, it is quite possible to independently diagnose it in yourself and consult a doctor for therapeutic measures. Pulpitis has quite specific symptoms and differs from caries in that pain when the pulp chamber is damaged can occur without external irritants and spontaneously. With carious lesions, pain syndrome always appears against the background of external influences: for example, when eating, as a reaction to sour or sweet foods, to temperature stimuli. Moreover, when the provoking factor is eliminated, the pain quickly subsides (usually within ten minutes). If the factor is eliminated, but the pain does not go away, there is every reason to suspect pulpitis.
Pain with pulpitis usually occurs at night and is not as unbearable as with periodontitis.
Attacks of pulpitis pain can intensify and then disappear, while acute periodontitis is characterized by constant, severe pain, which interferes not only with eating, but even with speaking.
Different forms of pulpitis may have their own unique symptoms. For example, with prolonged attacks of aching pain, you can suspect the development of chronic pulpitis. Symptoms of the chronic form of the disease may be similar to those of chronic periodontitis, however, against their background, fistulas do not form, the gums do not hurt or swell.
When talking about the symptoms of pulpitis, it is important to make the following useful remark: any toothache is already a reason to see a doctor. Teeth don’t just hurt; there is always a reason that needs to be identified and eliminated. This approach will help you avoid complex dental treatment and associated costs and keep your teeth healthy and strong for many years.
Types of chronic pulpitis
It is customary to distinguish the following types of chronic pulpitis:
- Hypertrophic – characterized by the formation of granulation tissue and dentin dystrophy. In this case, the overgrown granulations extend beyond the pulp chamber and enter the carious zone. If the form is polypous, then polyps are formed. Severe exacerbation can provoke pulp gangrene.
- Fibrous - differs from other types in that it leads to the appearance of coarse fibrous connective tissue. When examined, the pulp looks like a scar cord with a color change to white-gray. Gangrene, phlegmon and abscesses develop as complications.
- Gangrenous - represents complete tissue necrosis and tooth destruction (the color changes to gray-black). But in rare cases, it is possible to save small areas of the pulp.
Diagnosis of the disease
Chronic pulpitis cannot heal on its own. The patient may experience acute pain, flux, and progressive inflammation at any time. Which, in turn, leads to the formation of a cyst, phlegmon, and fistula.
Any pain in the teeth and gums should be diagnosed immediately.
The dentist’s task when chronic pulpitis is suspected is to establish the form of inflammation and the nature of the process.
For this use:
- Probing and tapping the tooth. This way you can determine the level of pain sensitivity, and therefore the degree of damage to the nerve bundle.
- Electroodontodiagnosis (EDD) is an assessment of the sensitivity of the pulp to electric current. High sensitivity indicators indicate serious destruction of the vascular bundle, lower ones indicate its viability. This is the most accurate study of the degree of damage to the nervous system.
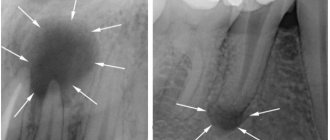
- X-ray. The image shows fibrous growths, calculus deposits and traces of deformation in the root canals.
In difficult cases, the doctor may prescribe a computed tomography scan of the tooth.
Reviews about our doctors
I would like to express my gratitude to the dentist Elena Nikolaevna Kiseleva and her assistant Svetlana - they are real specialists and at the same time sensitive, not burnt out by years of practice.
Thanks to them, I have been coming back here for many years. Thanks to the management for such doctors! Read full review Svetlana Nikolaevna
13.08.2021
I am very grateful to Evgeniy Borisovich Antiukhin for removing my three eights. Especially considering that the lower tooth was not the simplest (it was located in an embrace with a nerve). The removal took place in 2 stages, one tooth under local anesthesia, two under general anesthesia. I had no idea that wisdom teeth could be... Read full review
Sofia
28.12.2020
Complications: pain of a pulpless tooth
After removing the pulp, followed by filling the canals and restoring the crown of the tooth, the patient may still experience pain, especially when biting. If pain goes away within a week, this is normal. If the pain continues to bother you after 5-7 days, this may indicate poor quality treatment and/or filling. For example, the filling material was carried beyond the root apex and got into the soft tissues, or during the removal of pathologically affected tissues, the tooth root was accidentally damaged, or the patient is allergic to filling materials. Also, if the treatment and/or filling of the dental canals is not thorough enough, pulpitis can turn into periodontitis.
Treatment of chronic pulpitis
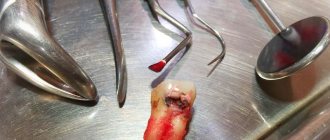
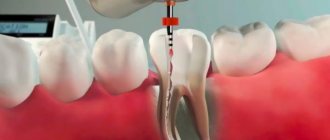
Since chronic pulpitis leads to irreversible changes in the pulp tissue, it is removed from the crown and root parts of the tooth. Treatment involves surgical intervention with depulpation and can be carried out using the following methods:
- vital - the pulp is removed under anesthesia, the root canals and tooth are filled;
- devital - a special paste is applied to the pulp, and then the already dead pulp is removed, the canals and the tooth itself are filled.
Vital extirpation is carried out in one visit and is considered a gentle method, but it cannot be used due to the patient’s allergic reaction to anesthetics or in case of obstruction of the dental canals. It is in these cases that the devital method is used, which requires 2, and sometimes 3 visits to the dentist.
Removal of enamel and dentin destroyed by caries
The doctor must carry out this stage of work carefully and competently: it is important to efficiently remove all tissue damaged and destroyed by caries. Errors in the process are fraught with complications, which will be very difficult to cure. To remove tissue, the dentist will use a drill: with this tool he will remove enamel and damaged dentin, as well as some of the healthy tooth tissue. Healthy tissues are affected as necessary: the specialist must gain access to the pulp chamber and canals.
Recommendations after treatment
The only way to avoid relapse is to maintain proper oral hygiene and visit the dentist regularly. The appearance of pain in a tooth at rest or while eating is a good reason to visit a specialist, as this reflects an inflammatory process in the pulp. Professional cleaning of the oral cavity and visiting the dentist 2 times a year will help you prevent the recurrence of chronic pulpitis. If, after treatment from a specialist, you notice an acute reaction to cold and hot food, experience pain when pressing on your gums and teeth, or notice swelling and discoloration of the enamel, be sure to make an appointment with your doctor.
In the dental department of the CELT clinic, treatment of chronic forms of pulpitis is carried out using modern diagnostic equipment and high-quality filling materials.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
What can happen if pulpitis is not treated?
Since in some cases the disease occurs without pain, many people put off going to the dentist until the last minute. Do not forget that while you are inactive, the disease progresses. Refusal to treat pulpitis can cause serious complications:
- Flux
- periostitis, a pathological inflammatory process developing from the periosteum.
- Periodontitis
- inflammation of the tissue around the root of the tooth with the possible formation of purulent pockets and destruction of the periapical bone tissue.
- Pulp gangrene
(necrosis) is the death of cells in the internal tissue of the tooth.
- Sepsis
- blood poisoning that develops when microorganisms enter the general bloodstream (usually occurs with reduced immunity).
To avoid such dangerous complications, you need to visit the dentist once every six months. Patients at risk should be examined more frequently (once every three months). The risk group includes patients with diabetes, oncology and other diseases that reduce immunity. If you notice symptoms of caries, go to the doctor immediately.
Methods used in the clinic
We are adherents, first of all, of effective and then modern treatment methods that can quickly, efficiently and radically eliminate the cause of pulpitis and its consequences. But, in our work, we always try to “save” the pulp and preserve its viable properties using conservative methods and use them in all cases where possible.
At the same time, if removal of the dental nerve seems to be the only solution according to the indications, in many cases we use effective anesthesia of the “dental nerve”, after which we carry out its removal. We are convinced that advanced methods do not deny classical methods, but only complement, optimize, and improve them. That is why in our clinical practice we always try to follow the “classical” treatment algorithm. Its first stage is a complete comprehensive clinical diagnosis.
Treatment is carried out using a dental microscope and using perhaps the most modern instruments, which makes it possible to eliminate carious lesions without missing a single micron of the affected tissue, flexible and thin endodontic needles for the most effective cleaning of canals, and, of course, the safest filling materials. It is worth noting that filling includes work in the canals and in the crown of the tooth. If suddenly the patient experiences some deviations from the normal course of the adaptation process, patients may be prescribed conservative anti-inflammatory therapy, physiotherapy with ozone or laser treatment.