Syphilis is one of the most dangerous sexually transmitted diseases. But not everyone knows that it can manifest itself not only on the genitals, but also on the skin and in the mouth. Syphilis, formed in the oral cavity, is a very common disease that is caused by infection of the body with Treponema pallidum.
The mucous membranes of the mouth are very vulnerable, and this pathogen easily affects them. Because of this, you can become infected with oral syphilis not only through sexual contact, but also, for example, through unsterile medical equipment or utensils.
Insidious disease
This pathology is very insidious and is not completely cured in all cases. Lack of treatment leads to the development of very serious complications and can even cause the death of the patient. This disease can be either acquired or congenital. In the latter case, the infection is transmitted from mother to unborn child through the placenta. And with acquired syphilis, infection is transmitted through the skin or mucous membranes, as well as through household means.
In addition to infection of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, there are lesions of the lips, larynx, throat, cheeks, palate, tongue, gums and tonsils. The course of this disease is characterized as chronic.
Known since ancient times
This pathology has been known since ancient times; mentions of it can be found in the records of such ancient healers as Avicenna and Hippocrates. But, despite the study of the disease, it is impossible to completely cure it, even in our age of high technology.
There are many reasons why a person becomes infected: kissing, oral sex, contact with sick people, household items or medical instruments. You can get the disease even at a dentist’s appointment if the latter uses instruments that are not properly disinfected.
Let's look at how syphilis manifests itself on the lips.
Oral syphilis
At all stages of this disease, rashes appear, localized on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. The cause of infection can be unsterile medical devices, and if there are wounds on the skin or mucous membranes, this will make it easier for the infection to enter the patient’s body. Even invisible abrasions, microcracks, etc. are enough for infection. Treponema pallidum can also enter the bloodstream as a result of surgery or injection. The pathogen is transmitted from mother to child in the womb. Doctors, especially gynecologists and dentists, are at risk for increased risk of infection.
Almost always, secondary syphilis manifests itself in the mouth area - both inside and on the lips. The infection affects the tonsils, mucous membranes, gums, tongue, etc. The disease has several successive stages, and each of them has its own symptoms.
Risk factors for oral lesions due to STDs
There are several conditions in which the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases through the oral route is significantly increased. These include:
- Sexual intercourse during menstruation.
- Oral-genital contact in the presence of dental diseases with damage or inflammation on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, gums, tonsils, and throat.
- Ingestion of infected body fluid.
It is not necessary to have a pathological process in the mouth to become infected with an STD [3].
Primary stage
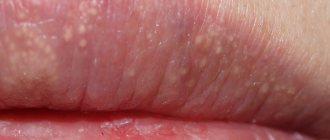
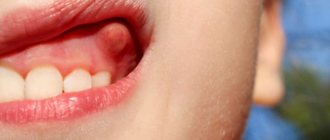
The incubation period is followed by the primary stage, characterized by the formation of chancre. A chancre is a painless ulcer that lasts about one and a half to two months. Hard chancre begins its formation with the formation of an area of hyperemia on the mucous membrane or skin. This redness gradually turns into thickening; this occurs due to the formation of an inflammatory infiltrate. It increases in size, reaching several centimeters. And in its center a bright scarlet erosion forms. These are the manifestations of syphilis on the lips. At the stage of completion of its development, the chancre looks like a dense erosive island rising above the mucous membrane. If there has been injury, or a secondary infection has occurred, then a painless ulcer with clear boundaries of a round shape is formed in its place.
On the lips, chancre can have a round shape or form in the form of cracks in the corners of the lips.
Secondary stage
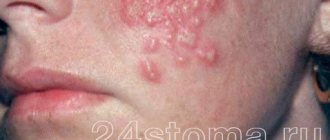
In the secondary stage of syphilis, the patient develops roseola. This occurs two months after infection and only if the patient has not received treatment. During this period, papules and roseola appear in the patient's mouth. From a medical point of view, this stage is the most dangerous. Roseolas look like bright red spots, clearly visible against the background of the mucous membrane. If treatment is not carried out, this stage will last about a month.
Papules are the most common symptom of the secondary stage of this disease. It can also occur due to relapse of the disease. These rashes are present over the entire surface of the oral mucosa.
Papules are round in shape, they are dense and of different sizes, they are covered with plaque, under which, when scraped off, red erosion is revealed. When papules appear, the papillae on the tongue disappear, and the skin becomes uncharacteristically smooth. Also, these formations can be concentrated locally, forming large foci. At the same time, in addition to erosions, jams may appear in the corners of the lips, which are accompanied by very painful sensations.
How to treat syphilis on the lips? We'll talk about this below.
Symptoms
What does syphilis look like? The first sign of infection is a chancre, which often appears on the injured lip. The infection in men does not spread immediately; the following main stages can be distinguished:
- Infection during the incubation period - for one it lasts two weeks, for another - about a month. If a person takes antibiotics for too long, the disease does not manifest itself for a long time;
- The formation of a hard chancre, which resembles a subcutaneous pimple, is easy to feel. At an early stage of the disease, the patient rarely goes to the doctor immediately, because he is not bothered by the pain, he thinks that the pimple will go away on its own;
- Rash inside cracks on the lip after mechanical damage. As you can see in the photo of syphilis, chancre is not so easy to detect. It can be seen if you open the wound. The patient may feel a foreign body inside the wound;
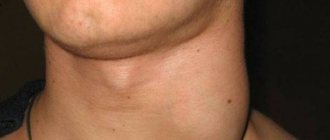
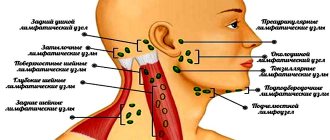
- Spread of infection to other parts of the body. This stage is typical for those who do not treat the disease. In addition to all the symptoms described above, the submandibular lymph nodes become very inflamed. Chancre turns into roseola, papules. It is during this period that the patient infects others. The photo shows that the lips are covered with a red border. Sometimes papules appear in the corners of the mouth. At the same time, an unpleasant burning sensation is felt, the lips are very peeling.
Tertiary stage
At the tertiary stage, the patient develops so-called gumma and tuberculate rashes. Gummas spread throughout the oral cavity, but are more often localized on the lip, tongue or hard palate. They begin without pain, imperceptibly and gradually forming a deep knot in the mucous membrane. It increases in size and acquires a brown tint. The central part of this formation is destroyed at the stage of ulcer formation.
When gummas affect the lips and tongue, no pain symptoms are observed, and there are no acute inflammatory processes. And when the ulcer heals, a retracted scar appears in its place. This whole process takes place over several months.
Very often, tubercular syphilis appears on the lips. At the same time, these tubercles are dense, painless and quickly collapse, forming small but deep ulcers. This stage of the disease can last from several months to several years if the patient does not receive treatment. Once the ulcers heal, the scars remain forever.
Possible symptoms of oral STDs
These infectious processes do not always have obvious signs. The most studied in this regard are gonorrhea, in which the pharynx is most often affected, and syphilis with its typical course and appearance of symptoms - chancre, enlarged local lymph nodes, rash.
You should pay attention to manifestations that arose some time after unprotected oral contact.
- Mouth ulcers, one or more.
- Manifestations of stomatitis, which can be very painful, or can proceed almost unnoticed.
- Herpes-like rashes on the lips and the inside of the mucous membrane around the mouth.
- Difficulty swallowing, especially if it is not associated with other symptoms of a cold.
- Redness of the back of the throat.
- Angina-like symptoms.
- A plaque like a sore throat or diphtheria on the surface of the tonsils.
- The formation of tonsilloliths in large quantities (unpleasant-smelling, dense, yellowish-gray formations that fly out of the mouth when coughing).
- Saliva takes on a different color, such as yellowish or streaky [2, 3].
Manifestation of syphilis on the lips
The lips are one of the most typical localizations of syphiloma. As already mentioned, it all starts with a red, swollen spot, in the middle of which erosion gradually forms, and then an ulcer. The diameter of the latter can be from 0.5 to 2 cm. Its edges are smooth, bright red and rising above the level of the mucosa. The bottom of the ulcer is smooth, dense and red. Also, chancre can look like a long-lasting lesion that does not heal. Sometimes syphilis on the lips manifests itself as a thickening in the form of a mushroom cap, the size of which can reach two centimeters.
What happens in later stages?
In the secondary stage of this disease, papules form in the mouth, affecting the pharynx, hard and soft palate, and larynx. The patient also experiences bouts of prolonged and dry cough. Damage to the larynx causes hoarseness and hoarseness.
At the tertiary stage, gummas on the lips look like purple bumps, which, after healing, turn into deep scars, often in the form of stars.
The problem is how to distinguish a cold sore from syphilis. Many people do not know how the latter manifests itself, confuse it with other diseases characteristic of the oral cavity, for example, herpes, and try to treat it themselves. Because this treatment is ineffective against Treponema pallidum, syphilis continues to develop.
What happens if syphilis is not treated?
If this disease is not treated, the consequences will be severe. The infection affects internal organs, most often the upper respiratory tract. The patient feels worse and worse. Necrosis begins at the site of syphiloma. Bones, internal organs and tissues are increasingly destroyed by Treponema pallidum. The vascular system is destroyed, facial and cervical tissues begin to rot, and the brain is also affected.
If all or some of the symptoms listed above appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. A specialist will be able to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the most effective treatment. The sooner it starts, the less complications there will be in the end. What tests should I take for syphilis on the lips?
Diagnostics
As a rule, the diagnosis is confirmed if the pathogen is detected on syphiloma or in the lymph nodes closest to it. Serological reactions will give a positive result for the presence of treponema, but only a few weeks after the onset of chancre, whereas during the incubation period and at the beginning of the primary, the results of this analysis will be negative. Diagnosis is also carried out using: the Wasserman reaction, the immune fluorescence reaction, the test for the presence of Treponema pallidum and the reaction to the immobilization of these microorganisms.
Primary syphilis on the lips is also manifested by weakness, headache, aching bones, leukocytosis and fever. To distinguish a chancre from a traumatic ulcer, it is examined for compaction (it is not present in case of injury). It will differ from herpetic erosion by the absence of pain, swelling, reactive flow and pimply formations. Also, sometimes chancre resembles pyoderma, but the latter is characterized by purulent discharge, pain and duration of occurrence. In addition, chancre can be similar to a disintegrating malignant tumor, but its infiltration is usually much deeper than syphilis on the inside of the lip of the primary stage.
Diagnosing secondary syphilis is usually much more difficult. One of the main signs is the absence of pain at the affected sites, resistance to the effects of drugs and the stability of the clinical picture of the disease. The main criterion for making a diagnosis will be the identified pathogen found in scrapings from plaque on the papules, as well as the corresponding serological reaction. Usually at this stage the doctor is faced with the task of differentiating syphilis from leukoplakia, lupus, and lichen ruber. This disease differs from candidiasis in the absence of eroded mucosa. It is also necessary to exclude exudative erythema and allergic stomatitis - in these diseases there are disturbances in the general condition of the patient, and erosions will be without infiltrates, superficial. Papular manifestations of syphilis may also resemble the course of leukoplakia and HIV.
The tertiary stage is even more difficult to diagnose. The main problem is that it is very difficult to detect the presence of Treponema pallidum in the contents of gummas. Therefore, doctors are guided by the readings of RIF and RIBT - if a microorganism is present, they will show the corresponding result. Gummas resulting from syphilis must be differentiated from diseases such as tuberculous or traumatic ulcers, tumor ulceration, and aphthous stomatitis.
Syphilis
Syphilis is caused by Treponema pallidum. Despite the certain “familiarity” of the name of this disease, it is not the most common. The pathogen penetrates the skin and mucous membranes, causing a cascade of manifestations. When infected through oral contact, it affects the mucous membranes of the mouth, throat, and lips [4]. Symptoms of syphilis develop in stages. In the first stage, one or more ulcers form in the mouth and throat - chancre. They are round, slightly recessed, the edges are smooth, the bottom is shiny, pink, sometimes with a grayish coating and the release of a translucent liquid. As a rule, the lymph nodes become inflamed at the same time, in this case the cervical ones. If the infection is not treated, it progresses to the stage of secondary syphilis, during which a skin rash appears. In this case, the lymph nodes swell strongly and painfully, not only regionally, but also distantly. Sometimes this stage occurs latently, without manifestations, and then, over time, syphilis spreads and affects other organs and systems of the body [6].
In the presence of erosions or ulcers, repeated studies should be carried out in a dark field of view of a microscope to separate them for treponema pallidum.
Its detection is decisive in the diagnosis of primary syphilis, since specific serologies become positive only 2–3 weeks after the onset of primary syphiloma. Dyadkin Yu. V., Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Department of Dermatovenereology KSMU [6]
To detect syphilis, various laboratory diagnostic methods are used: PCR, RPGA, ELISA, RIF, RMP and others. Blood or scrapings from the chancre may be used for testing. Antibiotics are selected for treatment depending on the stage and location of the process and manifestations. During treatment, complications may develop, including the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction - a sharp and severe exacerbation of the disease due to the rapid disintegration of treponemes and severe intoxication [6].
Treatment of syphilis on the lips
Treatment of this disease, when chancre appears on the lips or in the oral cavity, is aimed at destroying the infection in the body. Therapy is also aimed at combating complications and symptoms. A set of measures aimed at treating the disease must be started as early as possible.
The main drugs in the fight against Treponema pallidum are bactericidal drugs of various groups. It is also important to increase the patient’s body’s resistance to infection. Treatment is carried out in stages, with long intervals between courses. The general condition of the patient is of great importance for its success. To increase resistance to infection, the patient is prescribed medications that help increase the body's immune strength. After each course, clinical and serological tests are carried out.
Gonococcal infection
It is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae and is one of the most common STDs [4]. When infected through the oral route, it occurs as gonococcal pharyngitis with subtle symptoms: a feeling of dryness in the mouth and throat, difficulty and pain when swallowing, slight hoarseness. There may be redness and areas of swelling with whitish films on the mucous membranes of the mouth and pharynx. Diagnosed by culture (culture), treatment is carried out with specially selected antibiotics. If necessary, symptomatic therapy is prescribed - pain relief for sore throat, rinsing for dry mouth, etc. [5].
Complications
Why are ulcers on the lips caused by syphilis dangerous? If left untreated, the disease affects not only the tissues, but also the patient’s organs, which naturally affects the general condition of the body for the worse. After some period, the symptoms may subside, which creates the illusion of a cure, but in the future the disease progresses sharply. Necrosis, deep damage to bones, organs, tissues, bleeding resulting from the destruction of blood vessels, and brain damage may be observed.
Now you know what syphilis looks like on the lips.
Treatment methods
The venereologist prescribes antimicrobial drugs, and always regulates the dosage. After a course of medication, the patient undergoes a blood test. The drug is administered invasively after an equal period of time.
During treatment with antimicrobial drugs, the patient’s blood must be examined step by step. The drug is administered after the same period of time.
Of no small importance is a restorative course of therapy so that the patient is rehabilitated after prolonged use of antibiotics, which destroy not only pathogenic flora, but also beneficial microorganisms. In this situation, lactobacilli and vitamin complexes are prescribed.
During treatment, you should avoid sexual intercourse. Only after repeated tests show the absence of infection in the blood can we talk about a complete cure. If a pathogen is identified, it is imperative to inform your sexual partner about this, and he must also undergo a course of therapy. It happens that in men the symptoms are not expressed, and subsequently he infects his partner.