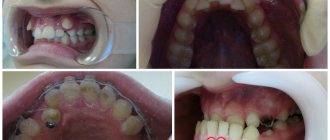
In this article we will look at Stanton-Capdepont syndrome, a disease determined at the gene level. It manifests itself as damage to the enamel and dentin, which results in not only an aesthetic defect, but also a subsequent decrease in the height of the bite. The size and shape of teeth are not affected during eruption.
Discoloration is characteristic - staining the enamel grayish or brown. A medical history test, physical examination data, X-ray examination and EDI can correctly diagnose the syndrome. Its treatment usually consists of complex remineralizing therapy and prosthetics. Let's look at this syndrome in more detail.
Causes of pathology
Stanton-Capdepont syndrome is a hereditary disease that occurs as a result of a mutation in the gene that is responsible for a specific matrix protein. It is transmitted in 50% of cases, both in girls and boys. The disease affects not only temporary teeth, but also permanent teeth.
The cause of irreversible changes is a decrease in the thickness of the enamel layer (enamel and dentin dysplasia), which disrupts the connections between the hard tissues of the tooth. Usually there is no predentin layer. Dentinal tubules are less than normal. The production of replacement dentin leads to obliteration of the pulp chamber and calcification of the root canals.
Stanton capdepon syndrome
Hereditary disorder of the structure of enamel and dentin (Stanton-Capdepont syndrome).
A hereditary disorder of the structure of enamel and dentin (Stanton-Capdepont syndrome) was first described in 1892 by Stanton, and later, but in more detail, by Capdepont in 1905. Simultaneous damage to the enamel and dentin of teeth is more common. This form of dental development disorder is characterized by a change in the color of the crowns, early onset and rapidly progressing abrasion of tooth tissue.
This nosological form has many names (crownless teeth; teeth without enamel; brown or transparent teeth; enamel hypoplasia); defective dentinogenesis; dentin hypoplasia; opalescent dentin; hereditary darkening of teeth; Capdepon's disease; Stanton's syndrome; mesodermal odontopathy, etc. The frequency reaches 33% of all hereditary disorders of dental development.
What provokes hereditary disorder of the structure of enamel and dentin (Stanton-Capdepont syndrome):
This structural anomaly is based, according to some researchers, on a hereditary abnormal function of the mesodermal germinal tissue, and, according to others, on the ectodermal germinal tissue. However, men and women are affected equally often. Appears on temporary and permanent teeth.
Symptoms of hereditary disorder of the structure of enamel and dentin (Stanton-Capdepont syndrome):
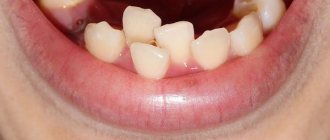
The clinical signs of Stanton-Capdepont syndrome are very characteristic. Teeth are of normal size and shape and erupt in the middle period. The color intensity varies - often watery-gray with a pearlescent sheen or a brown tint. When illuminated by a light guide, the teeth appear to be translucent. Soon after the tooth erupts, the enamel chips off, and its remains have sharp edges. Progressive wear of the enamel and a decrease in the height of the teeth and their volume are possible. Exposed dentin wears off quickly, it is 1.5 times softer than normal, its surface is smooth, shiny, of various colors - from light to dark brown. The contours of the tooth cavity are visible through the dentin. Complaints of pain are usually not due to hyperesthesia, but from trauma to the gums, due to abrasion of the crowns of the teeth or trauma to the tongue and lips from the sharp edges of the teeth. The electrical excitability of the dental pulp is usually reduced, sometimes significantly, and sensitivity to chemical and physical stimuli is also reduced. Dentin contains more water than normal, and significantly less inorganic salts.
Clinically, temporary and permanent teeth with dentinogenesis imperfecta have a characteristic color from reddish-brown to gray, opalescent. Immediately after the formation of a temporary bite, the enamel from the cutting edges of the front teeth and the occlusal surfaces of the chewing teeth chips off. Exposed dentin wears away quickly, sometimes to such an extent that the soft, polished dentin surface is flush with the gum.
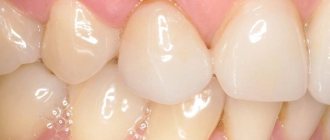
Permanent teeth are usually in better condition and are less susceptible to wear, sometimes looking almost healthy.
Diagnosis of hereditary disorder of the structure of enamel and dentin (Stanton-Capdepont syndrome):
An X-ray of such teeth reveals thin convex roots, a pulp chamber that is small or completely absent, and root canals that are narrow and ribbon-shaped. Due to imperfect dentinogenesis, the mesodermal defect in primary teeth is aggravated. Loss of bone tissue in the periapical region and fractures of tooth roots often occur, especially in older children.
Treatment of hereditary disorders of the structure of enamel and dentin (Stanton-Capdepont syndrome):
Treatment of non-carious lesions of teeth in this group is carried out sequentially, starting with damage to the enamel.
Previously, all types of enamel pathology were not even tried to be treated, expecting prosthetics at the appropriate age. Until recently, the main type of treatment for the development of Stanton-Capdepont syndrome was also prosthetics; in case of damage to the front teeth - cosmetic plastic or metal-ceramic crowns, in other cases - according to indications.
Currently, for the treatment of various forms of hereditary disorders of the development of enamel and dentin, complex remineralizing therapy according to the scheme described above is advisable. The results of such treatment are usually satisfactory and depend on the timeliness of its initiation. If it is started immediately after teething, the results will be quite successful. The fact is that usually restoration therapy, even with modern composite materials, usually leads to rapid further tooth destruction for obvious reasons, which is due to disturbances in the structure and mineralization of enamel and dentin. Therefore, treatment of this group of dental diseases should begin with a fairly long-term complex remineralizing therapy, including the intake of phosphorus-calcium preparations (calcium glycerophosphate), microelements and biologically active substances (clamin), vitamin formulations and local exposure to phosphate-containing toothpastes according to a full yearly schedule, taking into account the age of the patients. This is necessary primarily to prevent tooth decay from caries, abrasion and other unfavorable factors. In addition, with early diagnosis and timely treatment of the 4th variant of amelogenesis imperfecta and Stanton-Capdepont syndrome, very good results can be achieved. If there is no effect in the future, depending on the specific results and age of the patient, dental defects are replaced with GIC (Ionofil, Aqua Ionofil, etc.), and, if necessary, prosthetics are performed.
Symptoms
Stanton-Capdepont syndrome does not prevent teeth from erupting on time. Early or late appearance is rare. A characteristic symptom of the disease is the color of the enamel - from yellow to gray and brown. It occurs due to the filling of the dentinal tubules with blood. When chipped, the enamel exposes the dentin surface.
An increase in water content and a decrease in mineral components destroys the dentin structure, which affects increased tooth wear. A low bite reduces the lower third of the face. Due to chipped enamel, the edges of the teeth become sharp, resulting in painful damage to the mucous membrane. What is glass ionomer cement used for? More on this later.
Diagnostics
Clinical examination and the results of additional research methods, as well as anamnestic data are taken into account when making a diagnosis. During a physical examination, the dentist determines that the pigmented enamel is opalescent, gray or brown. In this case, the shape of the teeth will be correct. The sizes of the crowns are within normal limits. The enamel will be thin and fragile, quickly chipping after eruption, and the dentin layer will be exposed as a result. The dentin is stained and the teeth become dark brown. Due to the fact that there is increased abrasion, sharp edges appear, injuring the mucous membrane in the mouth. With this syndrome, the pulp chambers become translucent.
The radiograph shows a decrease in the height of the roots, the tooth cavity is narrowed, and the root canals of the tooth are obliterated. Also, in patients with this syndrome, radiographic examination often reveals foci of destruction in bone tissue. Cystic formations are associated with disruption of bone formation processes. This is also caused by the penetration of infection transdentally due to decay or inflammation of the pulp. According to the results of EDI, the sensitivity of the pulp decreases.
It is important to differentiate the syndrome from other genetically determined pathologies of hard dental tissues. These include:
- dentinogenesis imperfecta types 1 and 3;
- dentin dysplasia;
- imperfect amelogenesis.
The examination is carried out by a dentist-therapist. To identify hereditary factors of the disease, a geneticist consults.
What is the treatment?
For Stanton-Capdepont syndrome, remineralization therapy is carried out, which consists of restoring enamel and dentin. This method prevents subsequent tooth decay.
Most patients are indicated for endodontic treatment and dental crowning. An effective method is prosthetics. In this case, solid crowns are used, as well as metal-ceramic crowns. Removable dentures help solve problems of replacing dentition. How are tooth canals protected?
The patient is prescribed phosphorus-calcium preparations, vitamins, and microelements for oral administration. The surface of the teeth is coated with products containing calcium and fluoride. Teeth restoration with composite materials that are reflective is carried out in case of the syndrome, but this is a temporary measure, since a strong bond between dentin and the photopolymer material does not occur due to reduced mineralization. Subsequently, the tooth is destroyed.
To restore crowns in childhood, glass ionomer cement is most often used in dentistry due to the good adhesion of the material to dentin and enamel, caries protective effect, and high biocompatibility.
If periapical changes are detected in patients with this pathology, endodontic treatment is carried out with the teeth covered with crowns. These are serious methods.
Symptoms of dysplasia
The main manifestations of dentin and enamel dysplasia are observed in such dental diseases as:
- dentinogenesis imperfecta;
- Stanton-Capdepont syndrome;
- imperfect amelogenesis.
Stanton-Capdepont syndrome
Stanton-Capdepont disease or syndrome is a hereditary disorder of the formation of enamel and dentin tissue. The main symptoms of this pathology are:
- eruption of teeth having a natural shade and shape, and the subsequent change in the color of their enamel to gray;
- gradual destruction and chipping of tooth enamel;
- early, rapidly progressing abrasion of dentin;
- illumination of the contours of the dental cavity through dentin defects;
- decreased sensitivity of the pulp.
Molars with Stanton-Capdepont disease are subject to destruction and abrasion to a lesser extent than milk teeth. In some cases, the disease is completely asymptomatic, while the teeth are in excellent condition and look practically healthy.
Dentinogenesis imperfecta
Dentinogenesis imperfecta is a pathology characterized by a disruption in the formation of a layer of hard dental tissue located under the enamel (dentin). According to statistics, this disease is found in one out of 8,000 babies, with girls being diagnosed more often.
Depending on the symptoms, there are 4 forms of dentinogenesis imperfecta:
- Type I (the disease acts as one of the symptoms of a congenital disorder of bone formation, and its main signs, in addition to dental dysplasia, are bone fragility, changes in the shape of the middle ear and blue coloring of the eye sclera);
- Type II (the main signs of pathology are opalescence (translucency) of the teeth, a change in the natural color of the enamel to dull gray, increased abrasion of the teeth in the zone of closure of the dentition);
- root dysplasia (underdevelopment or complete blockage of dental roots, early loosening and loss of teeth, minimal difference in the shade of dental crowns from the natural one);
- coronal dysplasia (translucency of tooth enamel, frequent injury to the blood vessels of the pulp, accompanied by minor local bleeding, staining of teeth an amber or brownish-gray color by blood breakdown products).
Amelogenesis imperfecta
In turn, amelogenesis imperfecta is a disorder of the enamel formation process, leading to a change in shade and complete or partial loss of dental tissue.
Depending on the clinical picture, there are 4 subtypes of this pathology:
- type 1 (the enamel acquires a brown or yellow tint immediately after the teeth appear, unevenness of the dentin-enamel junction is observed);
- type 2 (1-3 years after the appearance of the first teeth, the enamel acquires a brown tint, becomes rough, matte, and becomes covered with cracks);
- type 3 (at the moment of teething, the teeth are covered with thin white enamel, which quickly disappears, exposing dentin);
- Type 4 (when teething, teeth are covered with matte, chalky enamel, which is easily separated from dentin under mechanical stress).
The sensitivity of the pulp with dental dysplasia is usually significantly reduced. Therefore, pain in people suffering from this disease is mainly caused not by increased sensitivity of the teeth, but by injury to the gums from the sharp edges of damaged crowns.
How can prosthetics help?
Prosthetics is the optimal method of restoring the function and aesthetics of teeth. Solid crowns are made for the lateral teeth, while the front ones are covered with metal-ceramic crowns. Prosthetics can also be carried out by veneering, lamination of the anterior group of teeth and cheek surfaces using ceramic onlays. If the root of a tooth is fractured or if endodontic therapy is poorly effective, the tooth is removed. To replace defects in the dentition, removable dentures are often used.
Treatment of dysplasia
Today, medicine does not have methods that could allow patients to permanently get rid of all manifestations of dental dysplasia. The main goal of treating this pathology is to maximize the preservation of hard dental tissues from destruction by performing the following therapeutic procedures:
- filling;
- remineralizing therapy;
- artistic restoration of teeth;
- vitamin therapy.
In the absence of the expected effect from the treatment, as well as in the case of a significant loss of hard dental tissues, dental prosthetics are performed using the most modern and effective prosthetic devices.
Do not delay treatment, contact the 24-hour A.Dent dentistry and our doctors will provide you with decent treatment.