Implantation with immediate loading is an innovative method of dental restoration that allows you to install any number of teeth in the shortest possible time in the most gentle way. The minimal invasiveness of the procedure reduces not only the duration of the rehabilitation period, but also the number of contraindications to surgery.
Immediate Load implantation is also called one-stage or express implantation. Considering the peculiarities of implant installation, it is also called basal implantation.
For the first time in Russia, basal implantation was used in a metropolitan clinic, where to this day it is a popular method of dental restoration.
Only the ROOTT center has an exclusive franchise for the use of the ROOTT immediate load implantation method in Russia.
Contents of the basal dental implantation section:
- Benefits of the basal method
- Installation video
- Engraftment of implants
- Advantages
- Photos before and after treatment
- Features of the method
- Stages of implant healing
- The history of the implantation method
New teeth in 3 days - all inclusive! And you can chew!
Implantation with immediate loading of a prosthesis - 44,000 rubles. for a unit.
Installation of a complete metal-ceramic bridge prosthesis on one-stage implants of the ROOTT system (1 jaw) - RUB 210,000. 250,000 rub.
Only our center has an exclusive franchise for the use of the ROOTT immediate load implantation method in Russia.
Advantages of the basal implantation method
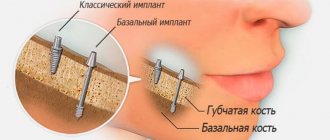
The unique feature of the method is determined by the method of implanting implants into the deep basal layers. These tissues are practically not subject to atrophic processes, unlike the alveolar spongy layer. As a result, it is possible to install implants using the basal method even in complex clinical cases, when alveolar tissues are atrophied, in patients with periodontal disease and other serious diseases.
Installation is carried out using the compression method through a puncture. This is a much less traumatic method compared to the need to saw through the bone for a plate implant or remove a flap of gum for a two-phase implantation.
Basal implantation is performed using monoblock systems, that is, the rod and abutment form a single whole. This made instant loading possible: immediately after implantation, a light bridge-like prosthesis is fixed on the top of the implant and included in the chewing process.
Being correct load conductors, such implants transfer normal pressure when chewing food to the bone layers of the jaw. This stimulates metabolic processes in them and activates osseointegration.
Due to the fact that the implant and abutment are a one-piece structure, FIXED dentures can be installed immediately. A person can forget about missing teeth or removable dentures, returning to a normal lifestyle within 3-4 days. Implants, being conductors, evenly and correctly distribute pressure on the bone and among themselves, while stabilizing each other. The implant healing process is based on stimulating the natural processes of bone tissue restoration during the process of chewing food.
Dental implantation without incisions
Or flapless implantation - some clinics present it as some kind of their own know-how, which makes implant installation a completely non-traumatic procedure, no swelling, pain, etc. what patients are usually afraid of. Here again is the same case of half-truth. This technology for installing implants really exists, but for a very long time, there is no know-how about it.
Indeed, the trauma is somewhat less, and the postoperative period is easier. But! If everything was so chocolatey, then everyone would do it all the time. No one has a goal, believe me, to make the patient suffer more. What pitfalls are hidden in this technique? There are two main ones. The first is that when making a hole for installing an implant, soft gum tissue can get on the cutter and end up in the bone hole. If you then screw an implant in there, there will be pieces of soft tissue between it and the bone. With a high degree of probability, this will interfere with the “engraftment” of the implant. The second “stone” is that without good visualization of the bone, it is difficult for the surgeon to assess the correct positioning of the implant. Such work blindly, by touch, can lead to serious mistakes.
Well, and finally, we must not forget that now, for various reasons, the installation of an implant is increasingly accompanied by bone or gum grafting operations. There are not many patients who do not need this at all. Therefore, incisions are still most often needed. As a result, implantation without stitches and incisions is a more risky procedure, which is also applicable only in a very small number of cases.
Expert opinion
Igor Yurievich Malinovsky
Maxillofacial surgeon, implantologist
Experience: more than 11 years
Implantation with immediate loading combines a number of modern protocols, the essence of which is the almost instantaneous restoration of aesthetic and chewing functions of the dentition, mainly with multiple restorations. When implanting implants, not only cancellous bone tissue is used, but also deeper layers, both of the jawbone and of the skull. Due to this approach, basal dental implantation is carried out without additional osteoplastic interventions.
Contraindications:
- Pregnancy, lactation.
- AIDS, HIV are relative contraindications; implantation is possible in consultation with the attending physician.
- Poor blood clotting.
- Low indicators of bone tissue quality, for example, bone tissue thickness (up to 0.5 cm), are observed by a loose structure or an inflammatory process.
Important! Even if you really want to restore your smile this way, but you know about the presence of contraindications, do not hide it from the dentist! This approach is simply irresponsible, because the treatment will not bring results (the implants will not take root). Money, time and effort will be wasted.
Patient before surgery to restore chewing teeth
FEATURES OF IMPLANTS FOR IMMEDIATE LOADING
HOW IMPLANTS WORK WITH BONE TISSUE
- The cortical plate is a narrow protective shell layer, 95% consists of mineral salts, and accordingly is hard and practically does not dissolve;
- The alveolar region (spongy) is a softer layer of bone, 70% consists of bone septa and crossbars, between which capillaries pass. This section is most susceptible to inflammatory processes and bone resorption in the absence of chewing load;
- The basal section is a deep layer of bone, which is denser and stronger than the previous two and is least susceptible to atrophy. It is this department that is used by specially created implants for cases of severe bone tissue deficiency. Thanks to a special thread, according to indications, the rods are attached, including in the cortical plate, which gives them greater stabilization and uniform load distribution based on the principle of support at 5 points.
Before performing basal implantation, the doctor individually models the structure so that the distribution of pressure during chewing is uniform. In combination with basal implants, compression ones are used, which work with the alveolar region and can be installed at different angles to give the entire structure stability sufficient to withstand immediate chewing load. When such implants are implanted, the alveolar region is subject to compaction (condensation), forming a dense (cortical) layer around the implant. This layer does not dissolve for a long time and serves as the foundation of the product until the new bone absorbs it. The final stabilizer of the structure is the fixation of the prostheses 3-4 days after installation of the implants. This technology allows you to restore the roots of teeth even in complex cases of bone tissue atrophy.
Do not forget that the bone structure of each patient is individual; there are cases of atrophy when the implantation of any implants is not indicated without additional manipulations to build it up (the bone can be atrophied even up to 1-2 millimeters in height or width). Such cases are extremely rare, however, even after bone grafting, the overall period of dental restoration can be significantly reduced, since prosthetics on basal implants is performed after implantation, and not after several months, as with the classic protocol with delayed loading.
One-stage or two-stage dental implantation: what to prefer?
Undoubtedly, to restore teeth located in the anterior region, it is better to use one-stage technology. But, if there are any restrictions, the most effective way to recreate lost units is a two-step procedure. However, there is no clear opinion regarding the choice of one technique or another. In this case, the most important criterion is safety for the patient’s body. Next, we will look at how one-stage and two-stage dental implantation differ from each other. Or rather, let us outline the advantages of the first technique compared to the standard technique. These include:
- Use of local anesthetics only;
- Possibility of carrying out the entire procedure in a minimum period of time;
- The use of minimally invasive methods of intervention with a low degree of tissue trauma;
- The ability to fix dental implants even in the absence of teeth;
- The likelihood of using implantation systems immediately after extraction;
- Installation of dental structures is possible even in the absence of sufficient bone tissue;
- Ensuring chewing load immediately after implant installation;
- Quite affordable price.
BY CHEWING YOUR FOOD YOU HELP THE IMPLANTS TAKE PLACE
Instant chewing load is one of the key points of the technology, since implants act as conductors of chewing load, capillaries in bone tissue are activated, cells begin to receive proper nutrition and self-heal. Thus, in addition to restoring aesthetics and returning to normal food intake, patients also help the process of osseointegration (engraftment of implants in the body). In patients with severe facial asymmetry due to missing teeth, the bite is gradually restored, the facial muscles begin to work as before, and premature signs of aging disappear. Diction is restored, digestion and the general condition of the body as a whole are improved. The fact is that due to the absence of teeth, patients begin to avoid hard foods; as a result, less nutrients enter the body and metabolism is disrupted.
Immediate implantation
The field of dental implantology has changed significantly over the past few years. Major improvements include the development of new materials, technologies and equipment, which together have made immediate implantation (immediate, early) a viable and predictable treatment option with long-term success rates ranging from 90% to 100%. Although this strategy has some important advantages over traditional implant placement protocols, such as time efficiency, immediate esthetics, and improved patient comfort, direct implant placement cannot prevent hard and soft tissue remodeling. Therefore, it is considered a risky procedure by some researchers and clinicians. However, immediate implantation and placement of temporary structures have been used in many patients.
Bruno et al., studying the specific location of the contact zones of temporary crowns in the area of the interproximal papillae, showed that the use of direct treatment methods resulted in the interdental papillae and dental implants being largely preserved. This was associated with less soft tissue remodeling while maintaining gingival level. Esposito et al., Schropp and Isidor systematically reviewed the literature regarding the use of immediate placement of implants in fresh extraction sockets and concluded that this treatment has merit. It can provide better aesthetic results and higher levels of patient satisfaction compared to delayed implant placement methods. The authors also stated that immediate implant placement procedures are technique sensitive and more difficult to perform than conventional procedures. Thus, they suggested that direct techniques should be performed by a well-trained dental team.
Due to the high demands of patients on aesthetics in the smile zone, restoration of extracted maxillary incisors is now considered the main indication for the use of immediate implant placement procedures. Becker et al studied immediate pre-placement of single-tooth implants (5.8 mm or larger) in fresh sockets. They found that pre-insertion of implants is a favorable and predictable treatment option if certain minimum criteria are met (eg, insertion torque = 15 Ncm, insertion stability factor = 50, apical bone amount = 3 mm). Achieving primary stability is now considered the cornerstone of direct treatment modalities. This is an important factor in achieving long-term favorable and aesthetic results.
Other factors such as precise implant positioning and prosthetic use have also been associated with healing and soft tissue preservation in immediate/temporary placement. Malchiodi et al examined the relationship between the interproximal alveolar ridge and soft tissue and its effect on long-term aesthetic outcomes (3-year follow-up). According to their findings, there is a strong relationship between hard and soft tissues, where maintaining tissue architecture (at the surgical site) is key to achieving long-term optimal aesthetic results. In this case, if the bone support is insufficient or its thin biotype is detected before surgery, then a transplantation procedure (in particular connective tissue) is necessary to maintain and stabilize the periodontal tissues. In a clinical and radiographic cohort study by Pozzi and Mura, results showed that direct use of implants with a conical body and an internal moving platform (NobelReplace Conical Connection, Nobel Biocare, nobelbiocare.com) contributed to the maintenance of marginal bone ridge and surrounding tissue esthetics in both the socket and and in healthy bone. Therefore, the primary purpose of this study is to describe a clinical procedure in which a method based on direct implant and graft (bovine bone and connective tissue) placement was used to restore an extracted maxillary incisor with external resorption.
Clinical case
A 23-year-old female patient received dental care at the endodontic clinic at Positivo University (Curitiba, PR, Brazil). The maxillary central incisor was assessed. The patient's main complaint was slight tooth mobility, which was caused by an injury that occurred 10 years ago. The medical history revealed that there were no symptoms of pain at the time of injury or in subsequent years.
Fig.1
Clinical examination
The patient's medical and dental history excluded any contraindications (eg, uncontrolled heart disease or diabetes mellitus) for dental procedures. A general and detailed clinical examination revealed a tooth with preserved anatomy and color and surrounding healthy periodontal tissue (i.e., no pockets or bleeding were detected on probing). The vital test resulted in a negative response to the cold stimulus (-50C, Endo-Ice, Maquira, maquira.com.br). Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) (5 × 5 field of view, 0.14 voxels, 25 seconds) (PreXion3D, PreXion, prexion.com) was performed to further evaluate the periapical bone tissue (Figs. 1 and 2) and revealed the presence extensive external resorption of the tooth neck (NRShz) with the support of interproximal bone ridges. Based on the latest classification of NRS3 proposed by the European Society of Endodontology and the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Patel et al classified the NRS3 observed in this study as 3BP (where "3" means that the height of the lesion extends to the middle third of the root, "B" " means >90 – 180 degrees, and "P" indicates probable endodontic involvement).
Fig.2
Patient Treatment Plan
The proposed treatment plan consisted of atraumatic tooth extraction followed by immediate placement of an implant, together with a bone graft (bovine bone) to fill the gap and a subepithelial connective tissue graft to stabilize the periodontal soft tissue. Restorative procedures included immediate pre-implantation using an extracted clinical crown adapted as a temporary crown. The rationale for the proposed treatment plan was to ensure that the patient's aesthetics were maintained while restoring function to the lost element.
Surgical treatment procedures
Surgical procedures were performed under local infiltration anesthesia (articaine 4% with epinephrine [1: 100,000]), the needle was inserted vestibularly and palatally. An internal incision was made from the distal surface of the adjacent tooth, thereby creating a flap that would allow visual assessment of the area affected by the HRS (Figure 3). Atraumatic removal was performed using a scalpel (n # 15c, SOLIDOR®, solidor.com.br) to preserve the majority of periodontal structures.
Fig.3
A tapered tapered implant (MT, length 3.5 mm x 11.5 mm, Neodent, instradent.us) was placed 3 mm apical to the gingival margin (per manufacturer's instructions) at the prepared surgical site. The establishment of primary stability was confirmed by a torque wrench, which indicated the presence of a torque of 30 N*cm. A 1-mm thick bovine implant (Lumina-Bone, Critéria, criteria.com.br) was then placed between the implant and the buccal bone plate to fill each gap present, while a second graft (from harvested connective tissue) was placed ) over the first graft to serve as a biological barrier during the healing process and to increase gingival volume (Figure 4). The vertical suture was performed using nylon suture (5-0, Ethicon, Johnson & Johnson, ethicon.com).
Fig.4
The selected clinical crown was then separated from the root, prepared and adjusted to fit the prosthetic implant abutment. It was cemented using a light-curing composite (shade A2, Empress® Direct, Ivoclar Vivadent, ivoclarvivadent.com). The adapted crown was screwed into the implant and occlusal adjustments were made to avoid super-contacts (central, lateral and anterior) (Fig. 5).
Fig.5
Postoperative condition
The patient was prescribed a broad-spectrum antibiotic (amoxicillin, 500 mg, every 8 hours, 7 days), an anti-inflammatory drug (nimesulide, 100 mg, every 12 hours, 3 days) and an analgesic (paracetamol, 750 mg, every 8 hours, 3 days) . Postoperative oral hygiene instructions were given to the patient before discharge, and sutures were removed 10 days after surgery.
A follow-up clinical appointment 30 days later showed that a satisfactory short-term aesthetic result had been achieved. After 90 days and 12 months at follow-up clinical appointments, there was a significant improvement in periodontal health with maintenance of gingival volume, increasing profile and interproximal bone ridge, which together contributed to the achievement of gingival esthetics (Figure 6). (Author's note: Rationale for presenting the 12-month follow-up x-ray: The author's CT device was not available at the time, so the 12-month CT is not available).
Fig.6
Fig.7
Fig.8
Restoration of the maxillary central incisor
The purpose of this case report was to describe the restoration of a maxillary central incisor affected by severe NRS. The proposed treatment plan included an immediate implant placement protocol followed by immediate pre-implantation using the crown of the patient's extracted tooth. The treatment plan resulted in immediate aesthetic results for the patient while maintaining the natural contours of the gums and gingival papillae.
The results presented here show that the chosen surgical treatment protocol allowed for correct placement of the implant while ensuring primary stability, as evidenced by torque values (30 Ncm). Using the patient's clinical crown for implantation provided the surrounding tissues with ideal physiological distances between the contact points and the alveolar bone ridge, resulting in periodontal tissues that are well supported and adaptable.
Together, these factors led to optimal gingival aesthetics and minimal disruption to the patient's psychological state in the short and long term. Periodontal biotypic evaluation is fundamental to the success of implants placed using the methods described here. Proper selection and use of biomaterials for gap filling and guided tissue regeneration are critical to achieving sufficient support for both hard and soft tissues. Although the patient's buccal bone plate and gingival tissue were extremely thin, the types of biomaterials used in combination with the placement technique maintained tissue architecture and prevented tissue remodeling and subsequent tissue shrinkage. The results indicate that the use of a tapered implant is a factor in maintaining the gingival bone and improving the esthetics of the adjacent gingival tissues during a 12-month follow-up.
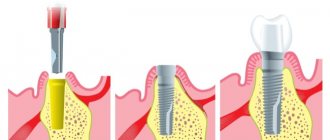
IMPLANTATION STAGES WITH IMMEDIATE LOADING
- preparing the patient and oral cavity for surgery;
- modeling of an individual design of implants to suit the specifics of the patient’s case.
- If there are movable teeth that cannot be restored, they are removed and implants are immediately installed in their place.
- If teeth are already missing, then the bed is formed using a puncture method, and then the implants are implanted into the bone using the compression method;
- The orthopedic doctor makes an impression, models and manufactures the prosthesis;
- the tops of the implants (abutments) are fixed at the required angle for subsequent installation of the prosthesis;
- on the third day after implantation, a permanent metal-plastic prosthesis is installed on the structure, which is adjusted to the patient’s bite;
- the patient can begin to use the new teeth.
VIDEO REVIEWS OF PATIENTS - WATCH HOW THE OPERATIONS GO
In what cases is a one-step technique performed?
This technique is indicated for patients with the following conditions:
- In case of urgent need for tooth extraction;
- Tooth trauma localized in the subgingival area;
- Missing one or more teeth;
- If necessary, immediate fixation of prostheses;
- Urgent need to restore the aesthetic characteristics of teeth after extraction;
- Subject to the necessary conditions: the presence of sufficient bone tissue and gums; satisfactory condition of the patient’s body; good quality jawbone; the presence of nearby teeth near the implant, etc.
DIFFERENCES AND ADVANTAGES OF DENTAL IMPLANTATION WITH IMMEDIATE LOAD
| DIFFERENCES | ADVANTAGES |
|
|
New teeth in 3 days - all inclusive! And you can chew!
Implantation with immediate loading of a prosthesis - 44,000 rubles. for a unit.
Installation of a complete metal-ceramic bridge prosthesis on one-stage implants of the ROOTT system (1 jaw) - RUB 210,000. 250,000 rub.
Only our center has an exclusive franchise for the use of the ROOTT immediate load implantation method in Russia.
Implants for immediate loading
Installation of an implant on the ROOTT system in Russia is carried out only in ROOTT centers. We are official partners of TRATE AG in Russia, installing only high-quality and time-tested implants developed on the basis of research by the European Open Society of Dentistry, with the participation of domestic colleagues from the Russian Association of Implantologists.
The size, shape and method of installing the rods are selected strictly individually according to medical indications. Basal surgery can take place in a one-step format immediately after tooth extraction in 1 appointment.
Read more in the article why the ROOTT implant system. Read more in the article why the ROOTT implant system .
Immediate loading during implantation All on4 and All on6
Good day, Marat Aslanovich is in touch. I want to share with you valuable information and tell you what Immediate loading is during implantation in dentistry.
When crossing the threshold of a medical facility, we all want to feel safe and trust our health and beauty to true professionals in their field. At the same time, each of us should know that the level of development of medicine is growing at cosmic speed. We, in turn, the team of Polar Bear doctors, working with the best equipment and materials, do not lag behind progress, using the most modern and high-quality methods of dental restoration in our practice. One example is Immediate Load.
Immediate loading is a method of restoring teeth with temporary non-removable orthopedic structures supported by dental implants, directly during the operation to install implants.
The main advantages of this technique: - the patient goes home with his teeth - no need to come back for impressions and installation of temporary crowns two more times, all in 1 day. — no pain when installing crowns. — primary load on the implants. — restoration of aesthetics and function. — splinting of implants and distribution of load — supporting the soft tissues of the face and creating conditions for the proper formation of the oral mucosa.
Disadvantages: None.
It used to be like this: The patient came for implantation, the surgeon installed the implants “by eye”, the orthopedist, in the best case, immediately after the operation took impressions for the crowns, and the patient safely went home for two weeks without teeth. A week after the operation, the patient came to register the bite and only another week later the temporary crowns were ready, which the orthopedist fixed to the patient.
I described the cases of all on 4, all on 6. With partial defects and preserved teeth, temporary crowns could be fixed within a week.
Now everything looks a little different: The patient comes for implantation, the surgeon installs the implants according to the template, and the orthopedist reinforces and fixes temporary crowns DURING THE OPERATION. The patient goes home with his teeth intact.
Previously this was impossible. But the development of digital technologies in dentistry has allowed doctors to thoroughly study, clearly diagnose, carefully plan and masterfully implement even the most complex clinical cases. It is the presence of 3D technologies with powerful software that allows doctors, together with dental technicians, to take into account all the nuances, find opportunities and not miss important details in treatment planning. After all, the main determining factor in immediate loading is precisely the primary stability of the implant during its installation, and it, in turn, depends on the quality of the bone. And if previously it was difficult for a surgeon to predict before surgery what stability his implants would have, now he can do this with a probability of 80%. This is exactly the merit of 3D technology.
We plan in advance a surgical template with a clear position, depth and angle of installation of the implants, then we also select multi-units for each implant (I will talk about them in my next article) and in accordance with the location of the multi-units, the height of the bite and the location of the articular heads in the TMJ, the technician models temporary crowns.
You will soon be able to see a more detailed protocol for performing this treatment in our joint clinical case with Alim Timurovich.
HISTORY OF THE IMMEDIATE LOAD IMPLANTATION METHOD
This implantation method originates at approximately the same time as the classical one, but due to the fact that the commercial wave picked up the classical protocol, it is more common these days. But the more people suffer from bone atrophy, as well as the inability to restore teeth in an acceptable short time, the faster new approaches are developed. In 2011, the European Open Dental Society (ODC) together with the Institute. Tramonte, dr. Tomasz Grotowski (follower of the basal implantation school created by Dr. Garbaccio) and other colleagues, adherents of the Immediate load technique, improved the structure and technology of implantation. Their developments formed the basis for the creation of the ROOTT implantation system by the Swiss company TRATE AG. Being a member of ODC and taking an active part in developments, the center became the first clinical base in Russia to use the new technique on an exclusive basis
Advantages of the one-stage implantation method
One-stage dental implantation is widely in demand among patients due to the following positive aspects:
- Eliminates the possibility of additional examination before performing surgery;
- Possibility of performing the procedure in just one visit to the doctor;
- Minimum number of surgical interventions;
- Low degree of trauma, since there is no need to make an incision of soft tissues and suturing them;
- Providing comfortable conditions for the patient with the ability to maintain working capacity;
- Minimal need for the use of anesthetics;
- Reducing the adaptation period to a temporary prosthesis;
- Maintaining chewing functions;
- Possibility of improving aesthetic characteristics in the shortest possible time;
- Eliminates the possibility of facial swelling after the procedure;
- One-stage dental implantation has an affordable price, as does a two-stage technique;
- The survival rate of dental implants exceeds 97%;
- Long operational period of installed structures.
Where to go for basal dental implantation in Moscow
By choosing single-phase dental implants, we can count on a beautiful smile after the first visit to the dentist. Immediate loading implantation provides this unique opportunity.
Compared to classic implants, the basal implantation process takes much less time. Monoblock implants are immediately covered by a temporary prosthesis, so you don't have to wait months for a crown, bridge, or full denture to be placed on the implant. During the procedure, there is no need to cut the gum, and the absence of an abutment adapter between the implant and the crown eliminates possible problems arising from loosening of individual structural elements.
You can consult about basal implantation in Moscow at various dentists. Make your choice consciously, giving preference to the most reputable medical institutions. You can navigate the price level by studying the list of dental implant clinics presented below.
| Name | Clinic address | Service cost |
| ROOTT |
| Installation of a one-stage implant (Switzerland, Trate AG) with an adaptation crown - RUB 38,000. |
| Shandora | Moscow, Kolpachny lane, 6, building 4. |
|
| Dentistry Grand Smile | Moscow, st. Miklouho-Maklaya 43 (metro station Belyaevo, Yugo-Zapadnaya, Kaluzhskaya) | Astra Tech implants (Sweden) from 45,000 rubles |
| Dentistry MEDIKASTOM | Moscow, st. Znamenskiye Sadki, 1, K.1 (M. Dmitry Donskoy Boulevard) | Implantations NOBEL BIOCARE (Sweden) from 45,000 rubles |
| Dentistry "Doctor Martin" |
| From 65,000 rubles per tooth using Nobel screw systems |
We remind you that the success of dental restoration, including using basal implantation, largely depends on the patient’s behavior after surgery. Despite the fact that implantation with immediate loading is as gentle as possible, and the recovery period is fast, there are strict recommendations in this regard:
- After implantation surgery, do not eat or drink for 1-2 hours.
- Proper oral hygiene is extremely important, that is, thorough brushing of the teeth, but being as gentle as possible in the wound area.
- Do not use mouthwash unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
- Do not use any stimulants: alcohol and cigarettes.
- On the first day after the procedure, avoid physical activity, sauna, gym, swimming pool and hot baths.
Other jobs
Is it possible to place an implant at the same time as tooth extraction? If not, then in what cases?
In the language of dentists, we are talking about immediate or delayed implantation. As it is probably not difficult to guess, immediate implantation is done immediately simultaneously with tooth extraction, and delayed implantation is done some time after removal (usually 1.5-3 months).
If you have a situation where a tooth needs to be removed for some reason, do not rush to do it. First, you should think about how you will continue to make up for this untimely loss, if this is not a situation of acute pain in a long-neglected tooth, when there is no time to think. True, it’s better to never let this happen! Why shouldn't you rush to delete? Because it is often possible to combine two, albeit not lethal, but still not entirely joyful manipulations into one. The surgeon can do it carefully! (in this case this is the key word) remove the worn-out tooth and immediately screw an implant into its socket! After all, this is much better than living through the not-so-rosy emotions of meeting a “tooth grinder” twice. However, such a 2-in-1 combination is not always possible. Basically, there are 2 reasons that can interfere:
- active inflammatory process. In this case, after the tooth is removed, an infected wound remains, into which it is better not to put anything immediately, but to let it recover quietly within 1.5-3 months. Then the chances of a smooth engraftment of the implant will be higher.
- when after removal there is a hole that is too large and there is simply nowhere to screw the implant. In order for the osseointegration (i.e. engraftment) of the implant to be successful, it must initially be screwed into the bone tissue with some force. And if the diameter of the hole formed after tooth extraction is too large, then the surgeon simply has nowhere to “screw in the screw.” The same applies to advanced chronic inflammatory processes (cysts, granulomas) around the teeth, which result in the formation of large bone defects. Because the implant cannot simply be “thrown” into the void; in such cases, the implantologist has to abandon the idea of immediate implantation.
lower tooth implantation
Initial situation: the lower 7th tooth is missing, and the 6th needs to be removed
implantation of the 6th lower tooth
Careful (!!!) removal of the 6th tooth. As a rule, the surgeon almost does not use forceps. First, the tooth is sawed into separate roots, and then each root is extracted separately using special tools. It is almost impossible to remove a multi-rooted tooth (and these are all lateral ones) in one fell swoop without damaging the bone partitions.
The tooth has been removed, a hole in the bone tissue is visible what the tooth hole looks like after removal photo
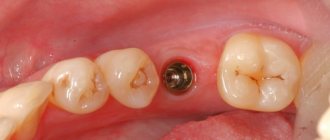
An implant was immediately installed in the socket of the 6th tooth. The implant was also installed in the area of the missing 7th tooth.
Stitches are placed on the surgical wound, which will be removed approximately 7-10 days after surgery.
Examples of work “Before” and “After”
Complex one-stage implantation of the lower jaw
Case: there was a loose bridge of 4 front teeth on the lower jaw; after diagnosis, removal of the remaining teeth and complex basal implantation were prescribed.
Dental restoration using basal implantation method
Case: complete absence of teeth in the upper jaw, bone atrophy.
Restoration of all teeth using basal implantation method (March 2012)
Case: partial adentia, exposed roots of natural teeth, periodontitis, increased tooth mobility, severe atrophy of bone tissue in some places beyond the possible norms for classical dental implantation.
Restoration of anterior teeth using basal implantation method (April 2012)
Case: partial absence of front teeth and destruction of supporting teeth under the prosthesis, the relief of the gums and interdental papillae is disturbed.
Indications and contraindications
The main recommendation for the use of instant implantation technology is advanced atrophy of bone tissue. The technique is also used in the following cases:
- The need to eliminate consistent or complete edentia;
- There are restrictions on the use of the classical technique;
- The need for rapid restoration of dentition.
It is worth noting that the Immediate Load protocol is used for the reconstruction of lateral and posterior units - the restoration of anterior incisors or canines is recommended to be carried out using standard techniques that ensure aesthetics.
General contraindications include:
- Diseases of the heart, immune and nervous system, diabetes;
- Diagnosed mental disorders;
- Oncology, tuberculosis, AIDS, renal failure;
- Bruxism, stomatitis, caries, periodontal pathologies in the later stages;
- Allergy to anesthetics, hemophilia.
The cleft factor is the condition of bone tissue, the minimum permissible thickness of which is at least five millimeters. The procedure is also not allowed in situations where the process of natural formation of the jaw has not yet been completed - this means that the minimum age of the patient must be 22-24 years.