Meet the dentist
Parents should enter the dentist's office with their children, regardless of their age.
The only exception is when the child is over 15 years old. Patients of the pediatric dentistry department are children and adolescents under 18 years of age.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressru
A child is afraid of the dentist - how to establish contact with the doctor, rid the child of dental phobia and cure his teeth?
The need for the mother's presence is justified by several aspects.
- Allergies to medications and other negative reactions when taking them. Have you experienced any symptoms of food or seasonal allergies?
- State of health of the child: presence of chronic diseases of internal organs. It is known about the connection between diseases of internal organs and the condition of the oral cavity, which is especially pronounced in diseases of the digestive tract.
- How did pregnancy and childbirth proceed? Complications of pregnancy, previous illnesses, prescribed medications, and nutritional errors affect the health of the baby’s teeth and gums.
- Type of feeding. Children receiving artificial feeding are considered to be at risk for the formation of caries and other diseases of the maxillofacial area in general.
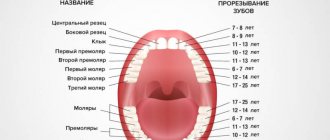
- Timing of teething.
Analysis of the answers to these questions allows us to get a complete picture of the dental status of children. They are also used to draw up a treatment plan and preventive measures.
In addition, children are not always able to describe the symptoms that bother them due to embarrassment, fear, mental and physical development, and even due to age.
- Worrying complaints: when they appeared, what preceded them. If we are talking about the occurrence of pain, the duration of its existence, what measures were used to relieve it.
- Increased temperature and associated symptoms.
Depending on the expected diagnosis, the doctor asks a number of leading questions, the answers to which will determine the further course of research and treatment.
If a child says that on the threshold of the dental office the toothache has gone away, there is no reason to rejoice. This does not mean that the disease went away on its own, but only that it turned into complications.
After collecting anamnesis and complaints, the stage of direct examination follows, during which the presence of the mother is also required.
- Bite pathologies: it is known that about 40% of patients are not even aware of the presence of problems and the need for orthodontic treatment.
- Oral frenulum: there are three of them, and their shortening, which requires surgical assistance, can provoke the development of various pathologies, including bite.
- Caries, the presence of its complications.
- Changes in the mucous membrane.
- Level of hygiene skills.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Vomiting due to stomatitis in children.
In the future, the dentist draws up a treatment plan, which must be agreed upon with the parents, recommendations are given for visiting other doctors, etc.
How is the progression of pulpitis in permanent teeth different in children?
Pulpitis is a serious disease, it must be treated, otherwise you can actually lose a tooth, get gumboil and even blood poisoning.
As in other age groups, pulpitis in adolescents under 14 years of age occurs in 2 main forms:
- Acute, with severe pain at night and in the evening, a painful reaction to temperature and chemical stimuli, an increase in temperature in case of general intoxication and the development of purulent complications.
In the absence of timely adequate treatment, the acute form becomes chronic.
- Chronic. This form of pulpitis can pass painlessly with the appearance of periodic pain reactions to cold, hot, sour, sweet. The acute inflammatory process in the pulp subsides, and the sluggish course of the disease contributes to the development of complications from periodontal tissues. Exacerbations occur periodically.
Attention parents! During adolescence, children may hide the disease and take painkillers uncontrollably.
Therapeutic manipulations
Children 3 years of age should be treated exclusively in the presence of adults, with only a few exceptions when sterile conditions are required.
In the dental chair, the baby is in the arms of his mother or father.
Treatment of children over 3 years of age takes place in the presence of parents, but with its own characteristics: if we are talking about a surgical operation, then the mother may be present in the office, but be at a distance. For some surgeries and conditions, parental presence in the office is prohibited.
- Mother in a chair with a child: the dentist can give this type of treatment based on the baby’s age, characteristics of his behavior or physical condition. One of the parents acts as a guarantor of adequate behavior of the child in the chair, and, if necessary, will hinder the child’s movements. When treating children diagnosed with autism, Down syndrome, mental retardation, cerebral palsy and other movement disorders, treatment takes place with the mandatory presence of the mother.
- Mother next to the child: children after 5-6 years old can sit in the dentist’s chair independently, and the mother plays the role of a dental assistant. The close presence of parents in the office gives children a feeling of security and safety. The specific position of the mother and her role are determined by the dentist; the main thing is not to interfere with the treatment.
- The mother is in the office, but out of sight of the baby. Dentists may ask the mother to leave the baby's field of vision if his behavior is capricious. In the absence of “spectators,” the hysteria stops.
Treating young children is very complex. This is explained not only by physiological characteristics, but rather by behavioral ones. Parents should help the doctor and respond adequately to requests and comments.
We answer basic questions
- Who will receive the 50 ruble allowance in 2022?
Employers will pay a benefit in the amount of 50 rubles to employees on parental leave for a child under 3 years of age in 2022 for children born before 01/01/2020, provided that the benefit is assigned until the end of 2019.
- What is the amount of benefit for children under 3 years of age for low-income families?
If all conditions are simultaneously met, one child's regional subsistence minimum is paid monthly.
- Where to apply for benefits for a child under 3 years of age?
If you are applying for a payment for your first child, then to the social security office at your place of residence, if for your second child, then to the territorial department of the Pension Fund.
VAT – 2022
The best speaker on tax topics, , will prepare you for filing your return on January 14 . There are 10 out of 40 places left on the advanced training course . The flow is limited, as there will be live communication with the teacher live. Hurry up to get into the group. Sign up>>>
How is sedation performed during dental treatment?
The sequence of actions during dental treatment under sedation is as follows: first, the doctor puts the child into a state of sedation, then makes an anesthetic application at the injection site with a special gel.
This is necessary to completely eliminate any discomfort in the baby. The dentist then administers an anesthetic and then begins treatment. Sedation in pediatric dentistry is most often performed using nitrous oxide mixed with oxygen, which is administered through a nasal mask. Oxygen comes in first, then a very small amount of nitrous oxide. This is a sweetish inert gas that begins to act in 2-3 minutes and is completely eliminated from the child’s body within 10 minutes after stopping the supply of the mixture.
Nitrous oxide is completely harmless to the child - to date, not a single case of complications after sedation has been described.
That is why it is so widely used in pediatric dentistry. Nausea or vomiting is very rare, but to prevent these phenomena, the doctor removes the child from sedation gradually, over 5 minutes.
However, sedation or anesthesia does not exclude the need for an adaptation technique. This is a method of working with children in which a friendly, trusting relationship is established between the dentist and the child. The doctor shows the little patient the office, the instruments, the mask and the sedation machine, and explains what it is for. This way the child stops being afraid of the new environment, and the doctor’s actions become clear to him. This reduces the baby's stress and anxiety levels.
When is consultation required?
It is necessary to contact a pediatric dentist if your baby develops pathological symptoms:
- toothache;
- gums bleed when brushing teeth or eating;
- the enamel has changed color;
- dental deposits have appeared that cannot be removed on your own;
- discomfort when eating sweets, cold, hot foods;
- redness, swelling, ulceration of the mucous membranes of the mouth;
- Dark spots and cracks are observed on the tooth surface;
- unhealthy breath;
- delayed teething, etc.
To prevent the appearance of pathologies and identify them at an early stage of development, visit a pediatric dentist every 3 to 4 months (caries in baby teeth progresses faster than in permanent teeth).
Modern pediatric dentistry has a wide range of capabilities and methods that make it possible to treat a child’s teeth without pain, in comfortable conditions. A good pediatric dentist will establish a psychological connection with the baby and try to carry out treatment competently and as quickly as possible. To prevent your child from being afraid of going to the dentist, give him the right motivation and never scare him with the dentist.
What are the responsibilities of a pediatric dentist?
A dentist in a children's office examines the supragingival and subgingival structures of the teeth, oral mucosa, periodontal tissue, bones, jaw joints, salivary glands, tongue, and submandibular lymph nodes. The competence of a pediatric dentist includes:
- taking anamnesis;
examination of the oral cavity using dental mirrors;- identification of defects in crowns, rows, and dental anomalies;
- referral for x-ray examination;
- drawing up a treatment program;
- carrying out planned sanitation (treatment, filling, cleaning, etc.);
- fissure sealing;
- exercises control over the formation of permanent teeth and bite;
- administration of drugs, anesthetics;
- provision of emergency dental care;
- carrying out clinical examination of children with dental and periodontal pathologies;
- referring children (if necessary) to an orthodontist and other specialists;
- interaction with doctors of other specialties, providing them with advisory assistance;
- prescribing therapeutic treatment at home.
The pediatric dentist will teach the child the rules and methods of personal oral hygiene, and explain to the child the need to perform it twice a day.
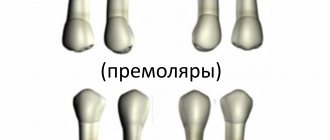
Features of the structure of newly erupted permanent teeth in children.
As we have already said, newly erupted permanent teeth in a child have a number of anatomical features and differ from the teeth of an adult, namely:
- They have fragile, not fully formed and mineralized enamel.
- They have unformed roots that connect to the growth zone.
- The root canals of such teeth are wide, with a funnel-shaped expansion towards the root apex.
- The thin and fragile walls of the dental canals do not have secondary dentin; they are easily injured and destroyed.
- There is insufficient mineralization of dentin in the roots of the tooth.
Therefore, when treating pulpitis of permanent teeth in children, there are a number of limitations and features that the pediatric dentist knows and must follow. Endodontic treatment (root canal treatment) of permanent teeth in children is complex and requires great care.
By the way, for this reason, it is better for adolescent patients to contact a pediatric specialist rather than an adult dentist-therapist.
Why is it important to treat baby teeth?
The permanent tooth germ is located next to the root system of the deciduous segment. Inflammatory pathologies and injuries of the milk segments harm the unformed structures of future teeth (they may die or develop with a defect). In addition, baby teeth must be maintained in good condition for the following reasons:
- if caries begins to progress, pain appears;
- treatment of superficial segment damage is easier to tolerate than complicated pathology;
- inflammatory diseases of dental tissues are a source of infection in the mouth;
- foci of pathological flora reduce immunity, which can cause chronic inflammatory diseases (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis, etc.);
- decayed teeth change the bite. In order to have a beautiful smile and straight teeth in the future, orthopedic correction will be required;
- carious cavities are a source of putrid odor from the mouth.