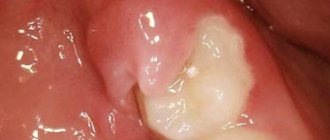
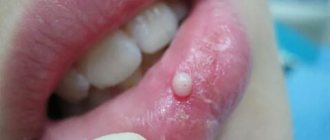
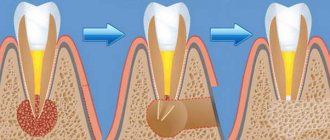
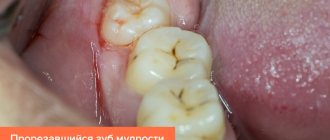
Purulent inflammation can affect the mucous membrane above the root eight that has not fully erupted. Timely removal of the wisdom tooth hood helps prevent the development of pericorontitis, a rather serious disease in dentistry. It is almost impossible to constantly clean this cavity above the molar; it accumulates plaque and food debris, which leads to the active activity of bacteria and the appearance of suppuration (abscess), which is life-threatening. This inflamed focus with pus is located very close to the brain area. Symptoms of the disease:
- Inflammation, redness and swelling in the gum mucosa above the wisdom tooth;
- An unerupted molar is pressed down by a swollen fold of mucous membrane, the process is aggravated by the appearance of pus;
- The swelling spreads to the cheek, causing asymmetrical facial expressions;
- The appearance of pain and tension in the affected area;
- Discharge of pus from under the mucous hood;
- Difficulty chewing food;
- Increased body temperature;
- Bad breath due to suppuration.
If surgical treatment is not carried out, the process will affect deeper and deeper tissues. Pericorontitis can be treated surgically. The radical method involves removing the wisdom tooth. This type of operation is carried out in the presence of appropriate indications, severe destruction of the figure eight or an abnormal location. A more gentle method involves removing the hood of the wisdom tooth with excision of the entire fold of mucous membrane hanging over the root eight. Patients are hospitalized when phlegmon appears. In other cases, the operation is performed on an outpatient basis.
Indications for gum excision
Indications for wisdom tooth removal under the hood
relate:
- The presence of swelling in the cheeks and gums.
- Painful sensations.
- The appearance of lymph nodes.
- Pain when swallowing.
- Increased body temperature.
- Discomfortable sensations when opening the mouth.
Such symptoms should never be ignored. If the patient has indications for wisdom tooth hood removal,
you need to consult a doctor.
Such symptoms should never be ignored. Further spread of the inflammatory process threatens inpatient surgical treatment. Therefore, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor and remove the tooth hood.
Symptoms of pericoronitis
Determining pericoronitis is not very difficult; let’s look at the main signs of the disease:
- Pain in the area of a tooth that is in the process of erupting;
- A noticeable inflammatory process, manifested by redness of the mucous tissues;
- Swelling of the gums in the area of the causative tooth;
- Unpleasant sensations in the area of inflamed gums;
- An unpleasant odor emanates from the tooth due to the pus formed in the hood.
If the signs of pericoronitis are not eliminated in time by cutting the hood, minor symptoms can develop into more serious ones. Over time, it may become more difficult for a person to chew food, as swelling can spread to the muscles of mastication, making it difficult to eat. Additionally, it may become much more difficult for the patient to open and close their mouth due to severe swelling. Acute inflammation can also cause high fever.
If you notice similar symptoms, we recommend that you immediately contact professional and experienced dentists. The infiltrate contained in the hood can develop into an abscess, and rupture of the capsule can lead to phlegmon.
You can make an appointment with a doctor at the Ilatan Clinic by calling the numbers listed on the website. The administrator will schedule you for an initial consultation. The doctor will conduct a thorough examination of your mouth. Make a final diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease. After all the necessary diagnostic measures, the doctor, if necessary, will prescribe you a procedure to remove the hood over the wisdom tooth. In some cases, removal of the entire wisdom tooth is prescribed if it is not of significant value. In addition, such a decision will be made if the x-ray shows that there is not enough space for the tooth in the mouth or if it is growing incorrectly.
It should be noted that the operation to excise the hood over a wisdom tooth is not considered difficult, so the use of local painkillers will be sufficient.
Progress of the procedure
Removing a wisdom tooth hood is not particularly difficult for either the doctor or the patient. The procedure takes a short period of time and causes virtually no inconvenience to the patient. After it is carried out, the tissue heals quickly, and the cavity around the tooth disappears.
Sequence of actions when removing the hood:
- an injection with an anesthetic is given at the excision site;
- cut out part of the tissue that hangs over the wisdom tooth;
- treat the excision site with an antiseptic;
- medicine is applied.
After the wisdom tooth hood is removed, the patient can go home. A control appointment is usually scheduled after 2–3 days.
In some cases, a situation arises that, despite excision, the hood is formed again, and this process can last quite a long time, repeating from time to time. Then the doctor will most likely recommend removing the wisdom tooth.
Removing a hood over a wisdom tooth
If such a situation is left unattended, the consequences may not be the most pleasant. Food may begin to clog into the free space between the crown of the tooth and the marginal area of the mucous membrane, and it may simply be impossible to clean it with a toothbrush. In this case, it is recommended to immediately contact a specialist to carry out a procedure to excise the gingival hood over the wisdom tooth. If this is not done, then favorable conditions for the proliferation of microbes and bacteria may form in the hood, which will quickly lead to an inflammatory process.
The inflammatory process in the hood above the wisdom tooth is called pericoronitis.
What to do after the procedure
The healing process will largely depend on how the patient takes care of the oral cavity and teeth in the days following the removal of the hood.
- During the first hours after the procedure, it is not recommended to eat or drink.
- Within 24 hours after removal, solid foods should be excluded from the diet. Until the wound heals completely, you need to chew food on the other side of the mouth.
- You need to take care of your oral cavity very carefully, use rinsing, and be extremely careful when brushing your teeth so as not to injure the site of the hood excision.
- In addition to medications prescribed by the doctor, cold is indicated on the side where the hood was.
- To prevent the development of the inflammatory process, overheating (hot food, bath) should be avoided.
Stages of the procedure in Clarimed dentistry
Removal of the hood is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Examination of the patient, determining the causes of the problem and the degree of development of the disease, collecting the necessary tests.
- Based on the collected medical history, an anesthetic is selected and anesthesia is administered. Clarimed dentistry uses only modern, certified and safe drugs that reliably protect the patient from pain and discomfort during the operation.
- The dentist uses a scalpel to cut through the mucous membrane and free the molar crown. Excess tissue is removed and the area is treated with an antiseptic.
- In case of critical damage to the wisdom tooth or its abnormal growth, the molar is removed by extraction in whole or in parts. The resulting hole is disinfected, bone shavings are placed in it, and the mucous membrane is sutured.
- A drug is applied to the wound to speed up healing. In case of serious intervention, a drainage is installed to remove the ichor. The patient is given the necessary consultations and is sent home.
After the intervention, it is recommended not to eat for 3 hours, not to smoke or drink alcohol. It is not recommended to visit the sauna, take a hot bath or go to the gym on this day (strong physical activity can lead to renewed bleeding).
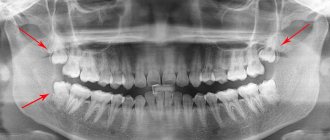
Diagnosis of pericoronitis
Pain in the teeth, the main symptom of pericoronitis, does not directly indicate the disease. This symptom is considered common to dozens of other dental diseases. Only a doctor can make a diagnosis in person.
When examining a patient, the dentist will ask about the nature of the pain, its frequency and duration. This will be followed by a mandatory examination of the oral cavity, perhaps the doctor will use instruments: somewhere he will knock on the teeth, somewhere he will apply a little pressure. If the picture seen remains unclear to the specialist, he will send the person for an x-ray. However, in the vast majority of cases, the doctor immediately determines pericoronitis in the patient, and additional research is carried out when the disease is adjacent to other dental pathologies.
How is the operation performed?
Part of the gum is removed under local anesthesia. An injection with an anesthetic is given into the gum, then the oral cavity is disinfected and an incision is made in the gum. At the end of the operation, the wound is treated with an antiseptic and a gauze pad is placed on the hole to stop the bleeding. In some cases, the wisdom tooth itself has to be removed during the operation.
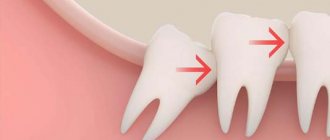
The wisdom tooth is removed then:
- if there is no room for the tooth to grow;
- the incorrect growth of the figure eight interferes with the adjacent tooth;
- if the seventh tooth is missing.
Reasons for appearance
This disease can develop as a result of certain factors:
- eruption of wisdom teeth, which is difficult and prolonged;
- The gums covering the tooth and mucous membrane are constantly injured;
- ulcers that are concentrated on the gums, erosion. This occurs due to the fact that chronic inflammation occurs over a long period of time.
Pericoronitis can also appear as a result of the presence of pathogens and bacteria in the mouth.
Treatment of acute pericoronitis
Treatment of the disease is usually carried out in two ways: removing the hood or removing the tooth. Adherents of unconventional methods of treatment and grandmother's recipes should be reminded that not a single dental disease can be cured using traditional methods. The use of decoctions, tinctures and other methods can only alleviate the symptoms, but without consulting a specialist, it is very easy to let the disease progress until a serious health situation develops. Therefore, going to the clinic is mandatory.
Varieties
The process may differ in its severity, degree of complexity, and location. Taking these points into account, several types of pericoronitis are distinguished - acute, retromolar, isolated purulent, ulcerative, catarrhal.
Catarrhal
This case can be observed in most cases as it is the initial stage of the disease. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, a person can avoid advanced, complex forms of pericoronitis. The symptoms are a little easier here. If a person seeks professional help in time, he will be able to stop the inflammation quickly.
Ulcerative
The reason for the appearance of this type of disease is the gum, which was inflamed and infected with fusosprirochaetes. The main symptom is a necrotic ulcerative rim along the edges of the gums. If a person removes the plaque on the teeth that covers the gums, the bleeding will become stronger. At this stage, surgical intervention is not allowed. Ulcerative pericoronitis should be treated using conservative methods.
Purulent isolated subacute
This type of disease suggests that it is a chronic form. At this stage, in the place where the tooth erupts, there is severe pain of a constant nature. And as a person chews and swallows food, it becomes stronger. Usually the temperature rises, regional lymph nodes become enlarged, and there is an inability to open the mouth. If you press down on the gum hood, pus will flow out of it. With the help of an X-ray examination, you can see that the bone tissue near the wisdom tooth is resorbing.
Retromolar periostitis
An abscess is already forming here. The symptoms resemble the previous version, but they are more pronounced at this stage. The patient's condition becomes much worse. The dentist must examine the mouth visually by forcefully opening the mouth. This type of disease involves inflammation and changes in soft tissues; it is observed in those places where the tooth erupts. If there is an infiltrate there, then the doctor makes such a diagnosis.
Acute periostitis
This type of pericoronitis has all the symptoms listed above. If it is not treated on time, the disease can become chronic. If pericoronitis persists for a long time, purulent periostatitis may occur. This condition usually appears when the lower third molars erupt.
Rehabilitation after tooth extraction from the socket includes
- Rinsing the wound surface with disinfecting solutions according to the rules prescribed by the doctor, always preserving the blood clot;
- Sometimes - taking a course of antibiotics;
- Taking painkillers to eliminate pain after volumetric intervention in living tissue. If the patient’s pain threshold is low, assistance cannot be avoided, because both the jaw bones and injured soft tissues will hurt. After a few days, the sensations become tolerable. Full recovery will take several weeks.
Treatment methods for pericoronitis
After a diagnosis has been made and the doctor has confirmed the presence of the disease, the optimal treatment option is selected. The choice of treatment method depends on the degree of tissue damage in the oral cavity. Two surgical treatment options are used: excision of the hood formed over the erupting tooth and removal of the problematic tooth.
Any conservative methods and traditional methods of treatment can reduce pain, but with their help pericoronitis cannot be cured. Without treatment, inflammation inevitably becomes chronic; in the future, a person is faced with the need for more serious manipulations to treat complications.
Why does the hood have to be excised?
Regular injury to the gums around an erupting tooth contributes to the development of low-grade inflammation, and food particles and bacteria getting between the gum and tooth can cause suppuration. Chronic inflammation and trauma to the hood cause the proliferation of granulation tissue, which leads to the development of the following complications:
- severe pain;
- limitation of jaw mobility;
- violation of chewing function;
- abscess, phlegmon, etc.
To prevent all these troubles, it is recommended to excise the hood. Moreover, this should be done as soon as the symptoms of pericoronitis appear for the first time.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Physiotherapy methods are also used to speed up the healing process:
- UHF therapy - one of the indications for the procedure is the presence of an inflammatory (including purulent) process in the tissues before and after opening the pathological focus. Ultrahigh-frequency therapy has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and resolving effects. The average course of treatment is 5 sessions.
- Microwave therapy is used to treat socket pain and complications of pericoronitis (periostitis and osteomyelitis). Course – 5-7 procedures.
- Irradiation of tissues with low-intensity laser radiation - laser radiation of this type has a local immunomodulatory and analgesic effect, relieves inflammation, and accelerates wound healing. Minimum course – 5 sessions.
How to avoid pericoronitis
As with any other disease, there are a number of preventive measures against inflammation of the gingival hood.
The first and main one is to strictly observe the rules of oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth twice a day, rinsing your mouth after eating, flossing - all these activities are much more pleasant and healthier than chronic pain and the inability to eat your favorite foods.
The second rule that must be followed is to visit the dentist at least once every six months. These precautions may not be a 100% guarantee that you will avoid illness. But you will be able to detect it at an early stage and you will not have to undergo painful and painful procedures. Well, our specialists, in addition to examination and quality treatment, will definitely give you personal advice on dental care.
Competent specialists - the right treatment
On the Internet you can find a lot of advice on how to relieve an acute condition of pericoronitis at home or, even worse, how to treat it using “grandmother’s” methods. All these tips can lead to irreparable consequences. Therefore, the only correct way out in such a situation may be to turn to certified professionals. Doctors at the VivaDent clinic will provide high-quality care and help maintain the health of your teeth.
What treatment is required for pericoronitis? Naturally, everything depends on how the disease progresses. For mild forms, oral rinses and anti-inflammatory medications are prescribed.
But in more severe cases, surgical intervention cannot be avoided. This may be an excision of the gingival hood, aimed at freeing the crown of the tooth and facilitating eruption. Or, if we are talking about more severe forms, the dentist removes the unerupted third molar. After this, treatment is prescribed in the form of taking painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications, as well as rinsing with various antiseptic compounds.
In any case, the decision on treatment should be made only by a doctor! Therefore, it is better to discard the “wise” advice from the forums and trust the VivaDent specialists.
How is the hood excision procedure performed?
Before the operation, the patient's medical history is collected to find out all possible health problems that may affect the course of treatment. You should definitely tell your doctor about diabetes or cardiovascular diseases, as well as hepatitis and AIDS - these diseases can significantly complicate the rehabilitation process.
Excision of the hood is the most common method of getting rid of pericoronitis, which is used in modern dentistry. The operation is virtually painless, and recovery after surgery does not take much time. The effectiveness of the operation is quite high; it allows you to get rid of the problem forever and at the same time preserve a healthy tooth.
Stages of the operation:
- Administration of local anesthesia.
- Cutting the hood with a scalpel.
- Washing the wound with antiseptic solutions.
- Sutures and bandages.
If after excision of the hood a new hood is formed, then excision again will be pointless. In this case, the problematic tooth is removed to get rid of pericoronitis and avoid serious complications. This happens quite rarely; as a rule, excision of the hood during pericoronitis is effective, and the inflammatory process does not develop again.
What else do you need to know?
Removing the formation above the figure eight is not always a panacea for its further painful eruption. Sometimes it happens that the hood grows back. In such a situation, some patients undergo repeated excision, others have their wisdom teeth removed. Still others require both procedures because the hood usually occurs only over units that have not yet erupted. Removing such teeth is a complex dental operation, since there is no access to the tooth using conventional instruments. The doctor has to cut it with a drill and only then remove it.