Benign tumors of the oral cavity - These are neoplasms of various nature located in the mouth. Tumors of this localization do not tend to develop into malignant ones; as a rule, they have limited growth. The following neoplasms fall into this category:
- Papilloma;
- Myxoma;
- Cyst;
- Fibroma;
- Fibromatosis;
- Hemangiomas;
- Lymphangiomas.
The most common tumors are of epithelial origin, that is, they originate in glandular or squamous epithelium. In rare cases, tumors appear from muscle fibers or adipose tissue. A benign neoplasm can be localized on the tongue, on the inner surface of the cheeks, on the palate (hard and soft), in the area under the tongue, on the lips and on the gums.
The causes of benign tumors are currently not fully understood. Among the dominant risk factors are bad habits, various injuries, one-time (as, for example, during tooth extraction) or permanent (microtrauma caused by the edge of a broken tooth).
Causes of oral tumors
The origin of benign tumors has not been fully studied, but today there are several possible causes or predisposing factors that influence the formation of formation:
- bad habits - smoking, alcohol abuse;
- oral cavity trauma (including tooth extraction, permanent mechanical trauma to the mucous membrane from sharp edges of teeth or fillings, dental structures);
- viral infection - may cause the formation of some forms of benign tumors;
- disruption of tissue differentiation during intrauterine development of the fetus (as a rule, tumors formed for this reason manifest themselves already in childhood - within 1 year of the child’s life).
Treatment of benign neoplasms of the oral cavity
When a benign tumor grows so much that it interferes with eating or speaking, as well as in cases where permanent trauma to the tumor is possible (for example, when it is located near the sharp edges of the teeth), a decision is made on surgical intervention.
The process of tumor removal is multi-stage. Fibromatous growths are excised along with the periosteum. The destroyed bone tissue is excised using the coagulation method. If the surgery is performed well, the prognosis is usually favorable.
Epithelial tumors of the oral cavity
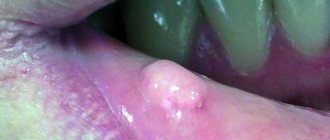
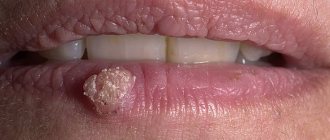
- Papillomas. Tumors formed by stratified squamous epithelial cells and most often localized on the tongue, lips, palate (hard and soft). They look like a protrusion above the surface of a healthy mucous membrane; the surface can be smooth, but more often the formation is covered with papillary-shaped growths. Most often they are observed in the singular, but multiple forms of the disease also occur. Over time, a tumor of this type becomes covered with keratinized epithelial cells and becomes whitish and also acquires a rough surface.
- Nevi. Most often, an intramucosal nevus is found in the oral cavity, which consists only of ovoid nevus cells located in the thickness of the connective tissue. Typically, the neoplasm has the appearance of a brown formation protruding above the level of the mucosa, on average 4 to 8 mm in size, but nevi of a different pigmentation - light pink in color - are often observed.
- Glands of Serres. Most often, such tumors are localized in the area of the hard palate and alveolar process. They look like hemispherical formations up to 10 mm in size, with a fairly dense consistency and a yellow tint. Such formations often occur in multiple forms in children and, as a rule, go away on their own during the first year of the child’s life.
Treatment of inflammation
Removal of a lump with pus on a child’s gum should be started immediately. Only a dentist can help the baby.
IMPORTANT! Self-medication, as well as piercing and squeezing are strictly prohibited! Such an intervention will lead to serious complications.
When an abscess forms over a baby's baby tooth, the doctor most often removes it. Such measures are necessary to exclude the possibility of destruction of the rudiments of the root. If a child has a lump on his gum next to a permanent tooth, treatment begins with a thorough examination. Sometimes the dentist will send you for an x-ray to assess the extent of the damage. Removal of a permanent tooth is carried out in extreme cases.
Connective tissue tumors of the oral cavity
- Fibroids. A distinctive feature of fibroids is the lack of expression of color - they have the shade of healthy mucous membrane. Most often they are localized on the lower lip, palate, tongue and have the appearance of a round or oval formation with a smooth surface. In some cases, pedunculated fibromas occur.
- Fibromatosis of the gums. Some experts argue that gum fibromatosis is a consequence of the inflammatory process. Such growths have a dense structure and are local or diffuse in nature, that is, they are located around several teeth or cover the entire lower or upper jaw. They are painless, but formation occurs in the gum papillae, which can lead to complete overlap of the tooth crowns. There are difficulties in diagnosing gingival fibromatosis, since the clinical picture is similar to the symptoms of the hyperplastic form of gingivitis.
- Myomas. Formations are formed from muscle tissue cells. There are several forms of oral fibroids:
- rhabdomyomas - such formations are formed by cells of striated muscles, often localized in the thickness of the tongue in the form of single nodes;
- leiomyomas - this type of fibroids is formed from smooth muscle fibers, the most common location is the palate;
- myoblastomas are a consequence of disembryogenesis, therefore they are observed in newborns and have the appearance of a shiny, round formation measuring up to 100 mm.
- Myxomas. They consist of connective tissue and have jelly-like contents. They are more often found on the hard palate and in the area of the alveolar process; they have the appearance of a rounded formation with a papillary, tuberous surface.
- Pyogenic granuloma. It is formed from cells of the mucous membrane, connective tissue elements, and has an elevated shape. It can be caused by increased capillary growth, swelling of the surrounding tissue, and is often formed due to trauma to the mucous membrane. It is characterized by intensive growth and size up to 2 cm, has scarlet, brown, blue-black color.
- Epulis. Located on the gum. There are fibromatous (round shape, location on the vestibular side), angiomatous (finely tuberous surface, location at the neck of the tooth) and giant cell (round shape, tuberous surface, bluish color) epulis.
- Neuromas. They are formed from the sheath of nerve trunks, have a dense structure and are painful. They can reach 100 mm in size and have the appearance of a limited node (there is a capsule inside).
Symptoms of an abscess
The initial stage of the formation of a white bump on the gum may be asymptomatic. The abscess gradually increases, leading to the following symptoms:
- formation of a painful protrusion;
- smell from the mouth;
- bleeding from gums;
- pain when eating.
If you do not help the child at this stage, further development of inflammation will lead to intoxication. The baby's temperature will rise and signs of weakness and malaise will appear.
Vascular tumors of the oral cavity
- Hemangiomas. Classified into the following types:
- capillary - formations from red to bluish in color, protruding above the mucous membrane (can be of different sizes);
- cavernous - formations with clear boundaries 1-2 cm in diameter, have a bluish color, most often formed on the mucous membrane of the cheeks;
- capillary-cavernous;
- mixed.
- Lymphangiomas. The cause is a violation of embryogenesis, so diagnosis is most often carried out in early childhood. They have the appearance of a limited tumor. Lymphangiomas are classified into the following forms:
- cavernous;
- cystic;
- capillary-cavernous;
- cystic-cavernous.
They are characterized by blanching and reduction in size when pressed; injury to these formations can cause bleeding.
These neoplasms are characterized by a tendency to inflammation: it can often be triggered by trauma to the oral mucosa and exacerbation of chronic inflammatory processes in the upper respiratory tract. The tumor is prone to rapid growth, but its distinctive feature is its spread over the surface without penetrating deep into the mucous membrane. Lymph nodes may also be enlarged. In the absence of inflammation, the formation is not filled with lymphatic fluid, however, experienced dentists diagnose the disease at this stage.
Reasons for the formation of an abscess
Young children do not properly care for their oral cavity. Poor brushing of teeth promotes the accumulation and proliferation of bacteria. Penetrating into the tissue, they provoke the development of inflammatory processes, including a purulent lump.
Other factors also influence the formation of an abscess:
- New teeth.
In some babies, the eruption of baby teeth is preceded by the appearance of small tumors filled with white fluid. If such a lump on the child’s gum does not hurt, then there is no reason to urgently consult a doctor.
- Gum injury.
Damage occurs due to the active lifestyle of babies, solid foods or accidental biting. The injured area becomes red and inflamed. Usually everything goes away on its own, but sometimes, when an infection occurs, ulcers and lumps appear.
- Oral diseases:
- caries;
- pulpitis;
- periostitis;
- cyst;
- fistula;
- gingivitis;
- periodontitis.
Inflammatory processes on the gums are often accompanied by abscesses. Purulent complications can be avoided by promptly consulting a doctor.
Diagnosis of oral tumors
Benign tumors of the oral cavity are diagnosed through a visual examination by a specialist, and cases of diagnosis are not uncommon during a planned, preventative visit. Also, in the process of treating other diseases of the teeth and oral cavity, a diagnosis can be established, but an accurate determination of the shape and type of tumor is possible only after laboratory analysis - histological examination of tissues. It can be carried out either after complete removal of the tumor, or through a biopsy - partial sampling of material.
To determine the depth of tumor growth, an ultrasound diagnostic method is used - this makes it possible to assess the condition of the soft tissues.
The condition of bone tissue is assessed using radiography.
In case of fibromatosis of the gums, the doctor prescribes an orthopantomogram - a panoramic image to diagnose the destruction of the alveolar process.
Angiography is used to assess the condition of tumors of a vascular nature.
Diagnostics
Benign neoplasms in the oral cavity are diagnosed during a routine examination by a dentist. An accurate diagnosis is established by an oncologist who first performs tests: a biopsy, listens to the patient’s complaints and collects an anamnesis.
To clarify the type of tumor, the following are prescribed: ultrasound, x-ray, orthopantomogram and angiography.
If you detect at least one of the symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor:
- detection of swelling in the neck;
- sensation of a foreign object in the throat;
- thickening or swelling of the cheeks;
- pain in the mouth;
- a wound in the mouth that does not heal for a long time;
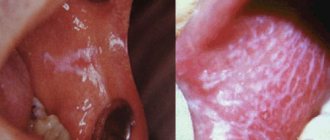
- whitish or red spots on the tongue, tonsils and gums;
- sudden change in timbre and pitch of voice;
- numbness of the tongue;
- weight loss;
- difficulty swallowing or chewing;
- difficulty breathing.
Diseases in which a lump on the gum does not hurt
There are diseases in which the resulting compaction does not bother the patient with pain. It is because of this that people are in no hurry to see a doctor, which can subsequently complicate treatment. In what diseases does a lump that appears on dental tissue not hurt?
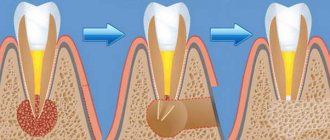
Fistula
If a lump with pus appears in the gum, for the flow of which there is a hole in the gum, we are talking about a fistula. The formation is a growth 3-5 mm in size with a white tip. When the outlet is not blocked by compacted exudate and pus flows freely, such compaction, as a rule, does not hurt. The reason for the formation of a fistula is a complication of periodontitis, in which the tissue grows and becomes infected by accumulated bacteria. Despite the fact that pus periodically flows out and does not accumulate in large quantities, if left untreated, an acute fistula becomes chronic. If the fistula is not treated, there is a risk of infection spreading through the periodontium and tooth loss.
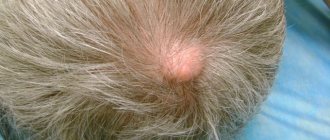
Exostosis
Exostosis is a type of jaw abnormality when the bone protrudes slightly to the surface. Such a lump is hard and painless to the touch, since it is, in fact, a bone or osteocartilaginous growth of a benign nature. The causes of occurrence are hereditary predisposition, congenital pathology or consequences of injury. With such an anomaly, prosthetics are difficult or even impossible: the prosthesis will rub the skin on the bone growth, which can cause injury and infection.
Important! Exostosis is determined by x-rays. The decision to remove is made by the patient, but it is worth considering that such growths can become malignant over time.
Epulis
If a lump appears above the gum, shaped like a mushroom on a stalk, pale pink or red in color, we are talking about epulis - a pathological formation, common mainly in women, and also occurs in children when their first teeth erupt. The reasons for the appearance of epulis are often post-traumatic in nature (large filling, tartar, chips), however, a pathological growth can also appear due to malocclusion, hormonal disorders or wearing low-quality dentures. The symptoms of epulis are similar to those of gingivitis, so for an accurate diagnosis, the doctor uses radiography or a histological test.
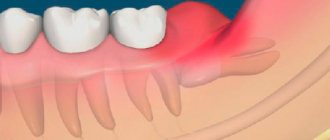
Periodontitis
You should think about periodontitis if a lump has formed on the gum - hard to the touch, up to 10 mm in diameter. The causes of inflammation of the periodontal tissues are usually unsealed dental canals and their infection. An abscess forms at the root apex. A characteristic sign of the disease is that when you press vertically on a tooth, pain appears. If the pus has already drained, there may be no pain, but the disease cannot be ignored, as it can lead to tooth loss and further spread of infection.
Attention!
If a seal appears on the gum, under no circumstances should you apply a warm compress or hot rinses: this can aggravate the course of the disease!
Hematoma
A soft-to-touch swelling with watery contents – a hematoma – is formed as a result of tissue injury during tooth extraction. This bump, as a rule, does not require special treatment, dissolving a few days after its appearance.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.