From this article you will learn:
- What does Lincomycin help with?
- Lincomycin capsules – price 2021,
- how to use Lincomycin in dentistry and for the treatment of purulent-inflammatory diseases.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
Lincomycin is an antibiotic of the lincosamide group, which is quite outdated and does not have a wide spectrum of antimicrobial action. The advantages of this antibiotic are its low price, as well as its effectiveness in treating infection resistance to penicillin antibiotics. Remember that this is a prescription drug that should be used only as prescribed by a doctor, and in addition, lincomycin is strictly contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women, as well as children under 12 years of age.
The antibiotic Lincomycin in dentistry at one time found quite wide use, which was due to its relative affinity for bone tissue. However, it is unlikely that any sane dentist will now decide to prescribe lincomycin for dental implantation or gum inflammation. The range of indications for the use of Lincomycin in dentistry is, as a rule, limited to its purpose - either after a complex tooth extraction, or during tooth extraction due to inflammation, or with purulent periostitis of the jaw (i.e. gumboil).
Lincomycin capsules, ampoules –
If anyone is interested, the chemical formula of lincomycin is as follows: (2S, 4R)-N-[(1R, 2R)-2-hydroxy-1-[(2R, 3R, 4S, 5R, 6R)-3, 4,5-trihydroxy-6-(methylsulfanyl)oxan-2-yl]propyl]-1-methyl-4-propylpyrrolidine-2-carboxamide. In this article we will talk about the optimal indications for the use of Lincomycin, as well as how to avoid the risk of developing a complication almost traditional for lincosamide antibiotics - antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Description:
Hard gelatin capsules No. 00 with a white body and cap. The contents of the capsules are granular powder of white or almost white color.
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
antibiotic - lincosamide.
ATX code:
J01FF02.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
:
Antibiotic produced by Streptomyces lincolnensis
, has a bacteriostatic effect. Suppresses bacterial protein synthesis due to reversible binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and disrupts the formation of peptide bonds.
Sensitive in
vivo
:
Staphylococcus aureus
(penicillinase-producing and non-producing strains),
Staphylococcus epidermidis
,
Streptococcus pneumoniae
.
Sensitive in vitro
: aerobic gram-positive microorganisms -
Streptococcus pyogenes
,
Streptococcus spp
.
viridans
group ,
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
;
anaerobic gram-positive microorganisms - Propionibacterium acnes
,
Clostridium tetani
,
Clostridium perfringens
.
Effective against Staphylococcus
spp .
resistant to penicillin, tetracyclines, chloramphenicol, streptomycin, cephalosporins (30%
of Staphylococcus spp .
resistant to erythromycin are cross-resistant to lincomycin).
Does not affect Enterococcus
spp .
(including
Enterococcus faecalis
),
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
,
Neisseria meningitidis
,
Haemophilus influenzae
and other gram-negative bacteria, as well as fungi, viruses, protozoa. The optimum action is in an alkaline environment (pH 8-8.5). Resistance to lincomycin develops slowly. In high doses it has a bactericidal effect.
There is cross-resistance between lincomycin and clindamycin.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption - 30-40% (food intake slows down the rate and extent of absorption). The time to reach the maximum concentration of the drug in plasma (TCmax) is 2-3 hours. It penetrates well into the tissues of the lungs, liver, kidneys, through the placental barrier, and into breast milk. It is found in high concentrations in bone tissue and joints. Lincomycin penetrates the blood-brain barrier only slightly; in meningitis, permeability increases. However, the concentrations of lincomycin in the cerebrospinal fluid are insufficient for the treatment of meningitis.
Metabolized in the liver. It is excreted unchanged and in the form of metabolites through the gastrointestinal tract and urine. The half-life is approximately 5 hours.
In diseases of the liver and kidneys, the half-life increases, and there is significant individual variability in the dynamics of the concentration of lincomycin in the blood plasma. In case of renal failure (end stage), the half-life is 10-20 hours, in case of liver dysfunction - 8-12 hours.
Elderly patients
Pharmacokinetics in elderly patients with normal liver and kidney function corresponds to the pharmacokinetics of adult patients.
Side effects and contraindications –
Lincomycin cannot be used during pregnancy, because the drug has a toxic effect on the fetus. In addition, it penetrates well through the placenta (the concentration in the fetal blood will be about 25% of the concentration in the maternal blood serum). Therefore, pregnant and lactating women should not use any form of lincomycin, including ointment.
You should also not take the drug if you have intestinal diseases (colitis, enteritis, ulcerative colitis), or if you have allergic reactions to lincosamides or doxorubicin. If symptoms of pseudomembranous colitis (diarrhea) develop while taking lincomycin, it is necessary to urgently discontinue the drug and begin specific treatment. The latter may include prescribing a tablet. Metronidazole or Vancomycin.
Our portal has a separate article devoted to the use of antibiotics in dentistry. A detailed list of the most effective drugs for inflammation of teeth and gums can be seen at this link.
Lincomycin: drug analogues
A semisynthetic analogue of lincomycin is another antibiotic of the lincosamide group - the drug Clindamycin. It should be noted that this drug also has a fairly narrow spectrum of antimicrobial action, but its effectiveness against some types of microorganisms will be 2-10 times higher - compared to lincomycin. Another advantage of this drug is that its absorption in the intestine does not depend on food intake (lincomycin can only be taken on an empty stomach, 1-1.5 hours before meals).
The price of Clindamycin starts from 150 rubles (for a package of 16 capsules of 150 mg). Dosage regimen: 1 capsule 4 times a day, duration of administration is determined by the doctor. To summarize, the effectiveness of clindamycin will be only slightly higher, but taking the drug will be much more convenient. However, the risk of developing pseudomembranous colitis when taking clindamycin will be higher than when taking lincomycin. And remember that antibiotics should not be taken without a doctor's prescription. We hope that our article was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Personal experience as a maxillofacial surgeon, dental surgeon, 3. American Academy of Periodontology (USA), 4. “Antibiotics and chemotherapeutic drugs: a textbook” (Sizentsov, Misetov), 5. “ Sensitivity of microbial associations of periodontal pocket exudate and odontogenic lesion to antibacterial drugs” (Makeeva I.M.).
Indications for use:
Bacterial infections caused by microorganisms sensitive to lincomycin (primarily Staphylococcus spp.
and
Streptococcus spp.
, especially microorganisms resistant to penicillins, as well as allergies to penicillins): sepsis, subacute septic endocarditis, lung abscess, pleural empyema, pleurisy, otitis, osteomyelitis (acute and chronic), purulent arthritis, postoperative purulent complications, wound infection, infections skin and soft tissues (pyoderma, furunculosis, phlegmon, erysipelas).
Lincomycin ointment - application regimen
Lincomycin-AKOS ointment is produced pharmaceutically in Kurgan (Russia). The ointment is for external use only. The tube weighs 15 g. The indication for use is purulent inflammation of the skin and soft tissues, for example: pyoderma, phlegmon, furunculosis, erysipelas.
Scheme of use - lincomycin ointment - instructions for use recommends applying a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 2-3 times a day. If there is no improvement within the first few days of use, it can be assumed that the infection is insensitive to lincosamides. In this case, you must urgently consult a doctor to replace the drug with another antibiotic.
Composition of the drug (per 100 g) –
| Content of active substances – → content of lincomycin hydrochloride (in terms of lincomycin) – 2.0 g, which corresponds to a concentration of 2%. |
| Auxiliary ingredients – zinc oxide, solid petroleum paraffin, potato starch, medical vaseline. |
→ Lincomycin ointment: official instructions (download in PDF)
Directions for use and dosage:
Orally, 1-2 hours before meals or 2-3 hours after meals, with plenty of water, 2-3 times a day with an interval of 8-12 hours. For adults and children over 12 years of age, the daily dose is 1-1.5 g, single dose is 0.5 g. For children from 3 to 12 years old (with body weight from 20 to 40 kg), the daily dose is 30-60 mg/kg.
The duration of treatment, depending on the form and severity of the disease, is 7-14 days (for osteomyelitis - 3 weeks or more).
For long-term or repeated courses, treatment should be carried out under monitoring of liver and kidney function.
Lincomycin in dentistry –
The use of Lincomycin in dentistry was initially justified by the fact that this antibiotic has an affinity for bone tissue.
This means that it accumulates in higher concentrations in bone tissue than in other tissues. But I learned that this is not entirely true only after working as a dentist for 10 years, and until that moment we were never given information that lincomycin is unevenly distributed throughout the bone mass (24stoma.ru). It turns out that its increased concentration is created mainly only in the bones of the small pelvis, and not at all in the jaws. Lincomycin capsules used to be one of the most prescribed antibiotics in dentistry, although I am sure that it is still actively prescribed in remote regions of Russia. The usual regimen of use is 2 capsules 3 times a day (for 5-7 days). The following situations can be considered the most optimal indications for the use of this antibiotic in dentistry:
- if a tooth is removed due to purulent inflammation,
- to prevent complications after complex tooth extraction or tooth root resection,
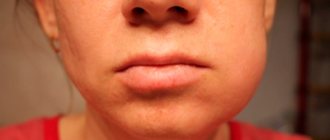
- after opening the flux on the gum (Fig. 1),
- with the development of inflammation of the socket of the extracted tooth (Fig. 2).
Abscess on the gum and inflammation of the socket: photo
It should be noted that in case of a serious purulent infection, Lincomycin, of course, should not be prescribed (otherwise, in any case, it must be combined with other antibiotics, for example, fluoroquinolones). But why do this if you can immediately prescribe an effective broad-spectrum antibiotic - the same antibiotic from the fluoroquinolone group. Lincomycin also demonstrates low effectiveness in the treatment of inflammatory gum diseases, especially in the aggressive course of chronic periodontitis.
Side effect:
Allergic reactions:
itching, urticaria, angioedema, anaphylactic shock, serum sickness.
From the skin:
rash, exfoliative or vesiculobullous dermatitis, erythema multiforme (Stevens-Johnson syndrome).
From the genitourinary system:
fungal infections of the genital tract, vaginitis, renal dysfunction (azotemia, oliguria, proteinuria).
From the digestive system
: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, anal itching, glossitis, stomatitis, jaundice, transient hyperbilirubinemia, increased activity of “liver” transaminases; with long-term use - candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract, pseudomembranous colitis.
From the hematopoietic organs
: reversible leukopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia and pancytopenia.
From the senses
: tinnitus, vertigo.
If any of the side effects indicated in the instructions get worse, or if any other side effects not listed in the instructions are noticed, tell your doctor.
Interaction with other drugs:
Antagonism - with erythromycin, chloramphenicol, ampicillin and other bactericidal antibiotics, synergism with aminoglycosides.
Antidiarrheal drugs reduce the effect of lincomycin (the interval between their use should be at least 4 hours).
Strengthens the effect of drugs for inhalation anesthesia, muscle relaxants and opioid analgesics, increasing the risk of neuromuscular blockade and respiratory arrest.
When used concomitantly with lincomycin, a P450 inhibitor, the serum concentration of theophylline may increase and this will require a reduction in its dose.
Special instructions:
When using lincomycin, official national recommendations on the appropriate use of antibacterial drugs, as well as the sensitivity of pathogenic microorganisms in a particular country, should be taken into account.
During long-term treatment, periodic monitoring of the activity of “liver” transaminases and renal function is necessary (if violations are detected, the possibility of discontinuing the drug should be considered).
Prescription to patients with liver failure is permissible only for “vital” indications.
Lincomycin should be used with caution in patients with a history of gastrointestinal diseases, especially colitis.
If signs of pseudomembranous colitis appear (diarrhea, leukocytosis, fever, abdominal pain, excretion of blood and mucus with feces), in mild cases it is sufficient to discontinue the drug and prescribe ion exchange resins (cholestyramine), in severe cases, replacement of the loss of fluid, electrolytes and protein is indicated, vancomycin - orally, in a daily dose of 0.5-2 g (in 3-4 doses) for 10 days or bacitracin.
The use of drugs that inhibit intestinal motility is contraindicated. Lincomycin is not indicated for the treatment of meningitis because its concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid is insufficient to treat meningitis.
The use of lincomycin in patients with diabetes mellitus is not recommended unless alternative treatment is available, as there are no adequate data on the treatment of patients with endocrine or metabolic diseases.
The half-life of lincomycin may be increased in patients with hepatic or renal impairment, so caution should be exercised when prescribing lincomycin to patients with moderate hepatic/renal impairment and monitor lincomycin blood concentrations during high-dose lincomycin therapy. In such patients, the possibility of reducing the frequency of drug administration should be considered. Use in severe liver/renal impairment is contraindicated.
As with the use of other antimicrobial drugs, when using lincomycin, especially long-term, it is possible to develop a secondary infection associated with the growth of drug-resistant microorganisms (especially fungi), to exclude and confirm which the patient’s condition should be re-evaluated. If a secondary infection occurs during therapy, the necessary measures should be taken to treat it.
Lincomycin should be used with caution in patients with existing fungal diseases, and such patients should also be prescribed antifungal therapy.
Severe bullous reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome have been reported with the use of lincomycin. Patients should be informed that if skin reactions and/or lesions of the mucous membranes develop, they should immediately consult a doctor before continuing treatment with lincomycin. Allergic reactions have been reported with the use of lincomycin, which can progress to a life-threatening condition. In these cases, the use of lincomycin should be discontinued and appropriate treatment should be initiated.
Lincomycin has neuromuscular blocking activity and may increase muscle weakness in patients with myasthenia gravis. The use of lincomycin in patients with an established diagnosis of pseudoparalytic myasthenia gravis is not recommended. Cases of neutropenia and/or leukopenia have been reported during treatment with lincomycin, so periodic monitoring of blood tests is recommended during therapy.
Lincomycin capsules - dosage regimen, reviews
Lincomycin for oral administration is available in 250 mg capsules and is a prescription drug that should only be used as directed by a doctor. The regimen for use in children over 12 years of age and adults is 2 capsules 3-4 times a day (the duration of administration is determined by the doctor, but usually from 5 to 7 days). In younger children and pregnant and lactating women, taking the drug is prohibited.
The drug should be taken only on an empty stomach - approximately 1-1.5 hours before meals (below we will tell you what this is connected with). And this may be inconvenient, but according to the instructions - you should only take Lincomycin capsules with a full glass of water! Failure to comply with this rule will affect the effectiveness, as well as the already low safety of the drug.
Contents of one capsule of Lincomycin:
→ Lincomycin: official instructions for use (download in PDF)
Reviews of lincomycin capsules:
Most modern antibiotics have high bioavailability (absorbed from the intestines quickly and completely), which, for example, allows them to be taken after meals. Taking lincomycin capsules 1.5 hours before meals is associated with low bioavailability of the drug - even when taken on an empty stomach, no more than 30% of the active substance is absorbed from the intestines. At the same time, simultaneous food intake reduces the absorption of lincomycin in the intestine - only up to 5% of the active substance.
Those. simultaneous ingestion of food reduces the effectiveness of lincomycin by 4-5 times, and at the same time, the antibiotic that is not absorbed from the intestine continues to kill all beneficial microflora in the intestine. Poor bioavailability of lincomycin and the inability to combine its intake with food often cause the development of antibiotic-dependent diarrhea in patients. Therefore, a drug such as Lincomycin capsules should be taken only in parallel with taking probiotics.
How effective is Lincomycin as an antibiotic?
Scientific studies show that lincomycin shows good effectiveness only in 36.8% of cases, while in 63.2% of cases, pathogenic bacteria at the site of inflammation have only weak sensitivity to lincomycin. But if you have long-term inflammation (and especially if you have already taken courses of Lincomycin in the past), the effectiveness will be worse.
The same study showed that when it comes to long-term foci of inflammation in the area of tooth roots (for example, in the presence of a fistula, granuloma/cyst), lincomycin will be effective only in 19% of cases. At the same time, in 47.6% of cases, Lincomycin demonstrates only weak effectiveness, and in the remaining 33.4% of cases, patients have complete resistance of the microflora in the inflammation site to lincomycin (it forms especially quickly in staphylococci).
Taking probiotics with Lincomycin:
Antibiotics of the lincosamide group are very often the cause of antibiotic-dependent diarrhea. If you have previously experienced diarrhea while taking antibiotics, or you have dysbiosis or other gastrointestinal diseases, in this case we do not recommend that you take antibiotics such as Lincomycin or Clindamycin. To reduce the risk of diarrhea, as well as reduce the negative impact of the antibiotic on the intestinal microflora, parallel intake of probiotics will help (these drugs contain bacteria beneficial to the intestines). For example, these could be Linex or Bifiform - they are the best, but also the most expensive. However, even simpler probiotics will provide benefits.
Probiotic Bifiform (30 capsules) –
Summary: all this makes the prescription of lincomycin acceptable, for example, when opening a purulent abscess on the gum (flux), as well as when removing a tooth with a purulent granuloma at the root apex. Acceptable simply because in these cases we drain the purulent focus and allow the outflow of pus, and antibiotic therapy in these situations is of secondary importance. But the prescription of lincomycin in the process of treating an exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, or to simply suppress inflammation - all this is ineffective and harmful.
Release form:
Capsules 250 mg.
5 or 10 capsules in a blister pack made of polyvinyl chloride film and printed varnished aluminum foil.
20 capsules in polymer jars made of high-density polyethylene with screw-on lids (top layer of high-density polyethylene, inner layer of low-density polyethylene).
Each jar, 2 or 4 blister packs of 5 capsules each, or 1 or 2 blister packs of 10 capsules each, along with instructions for use, is placed in a cardboard pack.