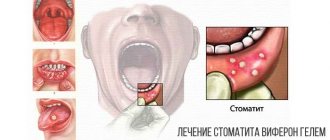
Stomatitis is one of the most common dental diseases, which is expressed in damage to the oral mucosa. It occurs in both adults and children and requires urgent treatment. Treatment of stomatitis in children is usually required for children with weakened immune systems. There are many ways for infection to enter a small organism.
Urgently contact the dental department of the CELT clinic if your child exhibits the following symptoms:
- increased temperature;
- no appetite;
- a white coating appears on the gums;
- ulcers appeared in the mouth;
- lymph nodes hurt.
We have everything to carry out effective, prompt and painless treatment of stomatitis in children of any age. Bring to us children under one year old, 2-3 years old and older - and we will select effective treatment for him in each individual case.
Consultation with a pediatric dentist (pedodontist) - RUB 1,000.
Apexification with the application of a temporary filling (1 channel) - 1,500 rubles.
Filling the root canals of baby teeth - 4,000 rubles.
Installation of insulating gasket "VITRIBOND" - 800 rubles.
At CELT you can get advice from a dental specialist.
- Cost of consultation with a pediatric dentist (pedodontist) – 1,000
Make an appointment
Causes and types of stomatitis
Treatment of stomatitis in young children is carried out by treating the affected areas with special medicinal compounds, the choice of which is carried out in accordance with the etiology of the disease. Treatment is prescribed by the pediatric dentist after examining the small patient and identifying the cause and nature of the disease.
The disease can develop due to bacteria entering the mouth through dirty hands or cutlery, as well as due to a weakened immune system. The spread of pathogenic bacteria in a child’s body occurs at extreme speed due to the vulnerable mucous membrane. An additional factor is weak salivation, which causes a lack of hydration. Excessive dryness leads to cracks into which bacteria penetrate and cause disease.
Stomatitis often develops while taking pharmacological drugs. To avoid progression of the disease, you need to stop taking antibiotics. During the consultation, the decisive factor is the observations of the parents. They are the ones who can explain the cause of the disease (injury to the mucous membrane, allergies, taking antibiotics).
Aphthous stomatitis
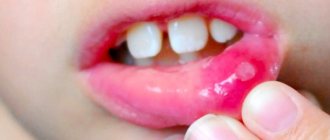
Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of a large number of aphthous stomatitis on the oral mucosa. These are round or oval ulcers covered with plaque. The causes of this disease are as follows:
- past infectious diseases: influenza, measles;
- lack of vitamin B12 and microelements in the body;
- oral injuries;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
For the most effective treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children, our specialists pay special attention to identifying the cause that caused it. Treatment of acute stomatitis in children is simply necessary, since the disease itself is very difficult. Its characteristic feature is unpleasant pain symptoms, which intensify when the ulcers are touched with hot or sweet food.
Treatment of purulent stomatitis in children requires an integrated approach. It consists not only in local treatment of ulcers with medications, but also in proper diet, frequent drinking and regular oral hygiene.
Causes and prerequisites for the development of aphthous stomatitis
The etiology of aphthous stomatitis has not yet been clarified. In the course of specially conducted studies, it was possible to establish only the factors contributing to the development of the pathological process. These include:
- inadequate immune response to the action of certain substances (components of hygiene products, dust, medications, waste products of bacteria and parasites);
- food allergies (potential allergens in such situations are buckwheat, rye, wheat, barley, pineapples, citrus fruits, tomatoes, strawberries, apples, seafood, figs, spices, cheeses, chocolate and food additives);
- mechanical damage to epithelial tissues of the oral cavity;
- neuropsychic stress;
- deficiency of nutrients in the body;
- menstruation in women;
- poor nutrition;
- immunodeficiencies;
- genetic predisposition;
- systemic blood diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- long-term use of antihypertensive, antiarrhythmic and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- functional disruptions in the nervous system;
- chronic inflammatory lesions of the nasopharynx (tonsillitis, rhinitis, otitis).
Viral stomatitis
The name of viral stomatitis speaks for itself: it is caused by influenza, herpes, measles and chickenpox viruses.
Symptoms of the disease at an early stage include weakness, lethargy, a slight increase in body temperature, and pain in the mouth. When examining the oral cavity, you can see the appearance of small red ulcers on the mucous membrane and tongue. Treatment of viral stomatitis in children depends on the age of the child, the state of his immunity and the stage of the disease. As a rule, our experts recommend treating the oral mucosa with anti-inflammatory drugs and decoctions, and lubricating the affected areas with vitamin A.
Briefly about stomatitis. Dentist Marina Khrunitskaya says
Children's dentist Marina Yurievna Khrunitskaya tells.
Stomatitis is a disease of the oral cavity, an inflammatory process that is localized on the tongue, gums, and inner surface of the cheeks. It looks like small sores.
Course of the disease
The disease is infectious in nature. It requires treatment for 4-14 days, depending on the type and extent of the disease. Healing of ulcers usually proceeds calmly, and practically no traces remain at the site of the wounds.
People who have had stomatitis at least once in their lives are at risk of recurrence of stomatitis. If new sores appear before the old ones have completely healed, it is necessary to consider stomatitis as a chronic disease.
Causes of stomatitis
- mechanical trauma: scratches, cheek biting;
- stress;
- unhealthy diet: deficiency of vitamins A, C, group B and some microelements;
- allergic reaction to food;
- hormonal changes, more often during pregnancy;
- poor oral hygiene or incorrectly selected care products (usually lauryl sulfate);
- poor-quality or incorrectly installed crowns and dentures;
- passion for alcohol and smoking;
- dehydration of the body.
Stomatitis in children is almost always a “disease of dirty hands.” The incidence of stomatitis decreases as soon as the child stops trying everything he can get his hands on. At a more conscious age, the habit of schoolchildren biting their nails and pens can lead to frequent and chronic stomatitis.
Types of stomatitis
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the type of stomatitis. Stomatitis happens:
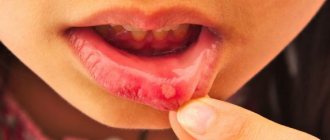
- catarrhal - redness and swelling of the mucous membrane,
- erosive-ulcerative - the formation of blisters, followed by ulcers,
- traumatic or bacterial - infection as a result of injury,
- herpetic - manifests itself on the oral mucosa,
- allergic - manifests itself against the background of allergies and is part of an allergic reaction,
- fungal - candidiasis, or oral thrush.
What can it be confused with?
It is necessary to differentiate oral stomatitis from other diseases, such as:
- oncological diseases,
- venereal diseases,
- retention cysts of the mucous membrane,
- inflammatory diseases of the major and minor salivary glands.
When diagnosing stomatitis, the doctor will necessarily examine the patient’s medical record for previous diseases and conduct a visual examination of the oral cavity. There are currently no specific medical tests that can detect stomatitis. The main sign of the disease is the presence of ulcers, the characteristics of their appearance and location, and the frequency of recurrence. If the tissue surrounding the ulcers is healthy and there are no pronounced systemic symptoms, we have every reason to diagnose stomatitis.
Stress can cause stomatitis
Prolonged nervous tension leads to weakened immunity.
You can't kiss if you have stomatitis
A kiss can injure the healing mucous membrane. In addition, you can infect your partner.
Follow a diet
Avoid hot, scratchy, spicy and sour foods
How to treat stomatitis in children and adults?
Several methods are used to treat stomatitis. The doctor chooses one or a combination depending on the complexity of the case and the cause of the disease.
Local medicinal treatment of stomatitis: rinsing, medicinal dressings, film with a medicinal solution.
Hardware treatment: laser treatment of affected tissues.
General treatment: selected based on the specific form of the disease and its characteristics, may include hormonal drugs, antibiotics, etc.
Diet: the mucous membrane is inflamed, so you should avoid aggressive foods. Chocolate, coffee, sweet, spicy, coarse meat, hot food are excluded. Soups, vegetable and fruit purees are recommended. It is important to fill your diet with vitamins - this will allow you to achieve a speedy recovery and healing of ulcers.
Which doctor treats stomatitis?
The disease is classified as dental, despite the various causes that provoke it. If symptoms indicating stomatitis appear, you should consult a general dentist or periodontist. If stomatitis occurs in a child, contact a pediatric dentist.
Candidal stomatitis
Candidal stomatitis is known as thrush. It can appear in children even in infancy, and it is caused by saprophytic fungi, which become pathogenic when immunity decreases. With this type of stomatitis, white spots appear in the child’s mouth. In addition, there may be an occasional increase in temperature and the appearance of photophobia. Infection of a child can occur through contaminated dishes, toys or pacifiers.
Treatment of candidal stomatitis involves undergoing daily procedures in the dental office, rinsing the mouth with alkaline solutions, and taking vitamins.
Treatment of stomatitis in a child cannot be delayed, otherwise this may lead to relapse of the disease. CELT pediatric dentists recommend regular preventive examinations that will help prevent the development of serious dental diseases, including stomatitis!
Treatment of stomatitis in a child
The main rule is to immediately contact a specialist and not use any gels or ointments based on recommendations from the Internet. Each type of pathology is treated differently, so the dentist conducts a comprehensive examination. Additional consultation with an otolaryngologist or dermatologist is often required.
In complex therapy, proper oral care is prescribed and professional toothpaste is selected. Solutions and gels are required. If the form is viral, then antibiotics are used, and if it is allergic, then antihistamines are used. If necessary, medications are used to reduce the temperature (if there is fever and chills).
How does furatsilin work?
Furacilin, consisting of nitrofural and sodium chloride, has pronounced antiseptic properties, so many believe that this is the best remedy for stomatitis. One of its main features is the ability to act on most bacteria known to medicine. For this reason, it is widely used for a variety of purposes, from treating wounds to gargling.
The drug not only eliminates symptoms; upon contact with pathogenic microflora, it dissolves the cell membrane, which leads to their death and a reduction in the number of colonies.
Several forms of the drug are used in different fields of medicine:
- solutions (alcohol, water);
- pills;
- ointment;
- aerosol.
In dentistry, solutions are most often prescribed - ready-made or prepared independently from tablets.
Prevention of stomatitis in children
- Be sure to clean all cutlery, bottle and pacifier. Boil periodically.
- You need to brush your baby teeth 2 times a day. Cleaning should be carried out by parents up to 6 years of age, and then show all the movements to the child and teach him proper oral hygiene.
- After eating food, you need to rinse your mouth with boiled or filtered water that is well removed from bacteria.
- Wash your hands and all toys regularly. Children often put their fingers or toys in their mouths - wean them off this (many pathogenic bacteria get into the mucous membranes).
- Visit your dentist 2 times a year for a visual examination and disease prevention.
- Do not give your child too hot or cold food. Avoid hard, spicy, sour and very salty foods. This will lead to injury to the oral mucosa.
- Avoid foods that cause allergies.
- Provide a healthy diet rich in minerals and vitamins. It is advisable to walk outdoors more often. All this helps strengthen the immune system and protect against stomatitis.
How to care for a child after stomatitis appears?
Without the help of parents, a child will never get rid of the disease, because strict discipline is needed. You must follow all the requirements of the pediatric dentist and pay special attention to diet and pain medications.
Prefer soft food with a temperature of no more than 28o C. It is important that it has a balanced composition of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. Allergens, as well as spicy, sweet, sour and very salty foods, must be excluded from the diet. It is advisable to exclude citrus fruits due to their high acid content. After eating, rinse your mouth with filtered or boiled water.
Treatment includes the use of painkillers. The child will feel severe pain at first, which will interfere with sleep. Therefore, you need to regularly rinse your mouth not only with clean water, but also with medicinal balms. The affected area should be smeared with medicinal gel. All recommendations for treatment and pain relief will be given to you by your pediatric dentist during your consultation.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Furacilin solution for stomatitis
Ready-made formulations can be purchased at pharmacies. Once opened, they can only be stored in the refrigerator for no longer than ten days. The second option is to prepare the solution yourself from tablets. The procedure is as follows:
- Take a 0.02 gram tablet (or two 0.01 grams each) per glass of water.
- The tablets need to be broken into several parts, then ground into powder.
- The water is heated to a temperature of 30 degrees. If the temperature is higher, the medicine will lose some of its properties.
- Dissolve the drug in water.
The prepared solution can be purchased at the pharmacy.
It is not recommended to use the prepared liquid immediately. It should stand at room temperature for 3-4 hours, after which it must be filtered using cotton wool or gauze folded in several layers. Before use, the required amount of solution is heated, but not more than 40 degrees.
There is no need to prepare a large volume of solution at once! The shelf life is 10 hours; it must be stored refrigerated in a closed glass container.
Another method is treatment with an alcohol solution, recommended for the formation of ulcers (ulcers). It contains ethyl alcohol (70%) and furatsilin (three tablets). The resulting liquid is infused for at least three hours. You cannot rinse your mouth with this composition; it is used to cauterize ulcers with a cotton swab dipped in the solution.
The use of an alcohol solution is contraindicated for children, pregnant and lactating women.
To increase efficiency, other components can be added to the solution:
- calendula tincture (a few drops);
- hydrogen peroxide (teaspoon per glass);
- essential oils of juniper and tea tree.
"Furacilin avexima" are effervescent tablets that dissolve quickly.
Due to the popularity of the drug, other forms are also available. Not long ago, the drug “Furacilin avexima” appeared, which is an effervescent tablet designed for rapid dissolution. They contain auxiliary substances - sodium carbonate and bicarbonate, tartaric acid and others that facilitate dissolution.
One tablet of the product is diluted in 100 ml of water. It is advisable not to store the resulting solution, but to prepare it before use. To prepare an alcohol solution, mix two parts alcohol and part water. The tablet is diluted in 330 ml of the resulting mixture.