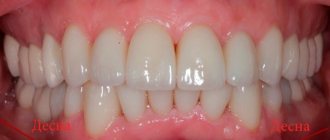
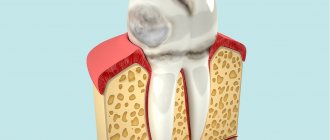
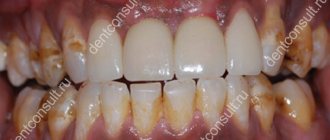
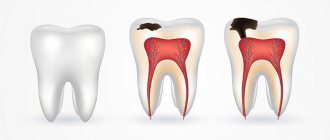
Wedge-shaped defects are defects in the hard tissues of the tooth, located on the vestibular surface of the teeth, most often canines and premolars. Defects are formed in the area of the tooth neck and arise due to trophic lesions of the organic matter of enamel and dentin, usually in connection with past diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system. Often these defects accompany periodontal disease. The pulp remains covered with secondary, compacted dentin and undergoes atrophy and sclerosis. The development of a wedge-shaped defect lasts for years.
Tooth sensitivity
Dental hyperesthesia
– a special disease associated with increased sensitivity of teeth to temperature, chemical or mechanical stimuli. The disease is accompanied by pain that does not allow one to lead a normal life, loss of teeth whiteness, and can lead to dire consequences if treatment is not treated in time.
Forms of the disease
The disease can affect both part of the teeth (limited form) and all teeth (generalized form). The second form occurs in 60-65% of cases, since hyperesthesia is usually associated with common causes. Limited hyperesthesia is ensured by more “narrow” factors, the action of individual exposed nerve endings and areas of worn enamel. Most often, the disease occurs in people with non-carious diseases.
Causes
There are many reasons for hyperesthesia of hard dental tissues. This could be an overly hard toothbrush, exposure of the cervix, periodontitis, or a whitening procedure. Using toothpaste that is oversaturated with abrasives, as well as frequent consumption of carbonated drinks, can also lead to the destruction of the dental structure. Foods with a high acid content have a negative impact on enamel and bone tissue; hyperesthesia is caused by erosions, enamel damage, wedge-shaped defects and dental caries. Pathological abrasion and periodontal disease can also lead to the destruction of enamel and its sensitivity.
Stages of the disease
Conventionally, dental hyperesthesia is divided into three stages. The first stage is characterized by increased sensitivity of teeth to temperature factors, the second - to chemical and temperature factors. The third, in addition to the first two stimuli, also implies a mechanical one. Stages of development are distinguished by the degree of electrical excitability of dentin. The threshold in the first stage is 5-7 µA, in the second stage – 3-5 µA, and in the third stage the dental tissues respond to a current of 0.5-2 µA.
Treatment of hyperesthesia
There are many methods of treatment, as well as the causes of the disease. The first stage of therapy is to identify and eliminate the cause of the pathology. Complete and high-quality treatment can only be carried out by a specialist, so you should not waste time on self-medication.
Usually, to eliminate dental hyperesthesia, a complex of drugs is used to restore enamel. A professional dentist will help determine the root cause of the disease and work on solving the problem. The usual course of treatment (you can find out where to cure your teeth by contacting us) includes the use of medicinal varnishes and toothpastes containing potassium salts, fluoride compounds, strontium, citrates, phosphorus and calcium. A schedule for taking medications is determined for the patient, and special recommendations for dental care are given. There are products that provide exceptional results and excel in the restoration of dental tissue. The action of the selected drugs is aimed at compacting dentin, healing dentinal canals, reducing the excitability of the network of nerve endings, and normalizing the process of restoration and nutrition of enamel.
Treatment of generalized hyperesthesia requires a special approach. The dentist must identify: where to treat teeth and analyze the symptoms in order to establish a connection between dental lesions and disorders in the body systems (central and peripheral nervous systems, endocrine system, etc.). Eliminating the cause of extensive dental disease will give an excellent impetus to the healing process.
Dental varnishes, which are based on sodium and calcium fluorides, act quickly and effectively. To ensure better effectiveness, the varnish is applied to teeth that have already been cleaned and dried, and measures to normalize phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the body will guarantee the preservation of dental health.
Destruction of tooth enamel
Necrosis of tooth tissue
- this is a non-carious destruction of the structure of the enamel and dentin of teeth due to the influence of negative endogenous and exogenous factors, it is considered a very difficult and serious illness, which often ends in a serious deterioration or even loss of chewing function. It should be noted that it has become more common in recent years than 10-15 years ago.
Let's take a look at the most common forms of necrosis of hard dental tissues.
Chemical (acid) necrosis
It can develop as a result of exposure to various acids (acidic products) on dentin and enamel. Tooth decay can go unnoticed, since the enamel is not damaged in the early stages. This happens either as a result of a negative production factor (which is a high concentration of acids and various other substances within the workplace), or due to frequent or constant exposure to acid-containing products, medications, and drinking. The enamel softens and gradually breaks down, exposing dentin, which is a fairly soft tissue.
Getting carried away with drinks like Coca-Cola increases the prevalence of this pathology and complete tooth destruction. Further, pain may occur when exposed to temperature and chemical stimuli. As dentin loses enamel, it becomes dark.
Its treatment depends on the degree of manifestation of chemical necrosis of teeth. When teeth are completely destroyed, implantation is performed. Thus, the scope of therapeutic measures in the initial forms can be limited to stopping or maximally reducing the effect of chemical reagents on the teeth, as well as when carrying out complex remineralizing therapy for a period of 3 to 6 months. Our clinic has developed effective schemes for both treatment and prevention of this pathology.
Computer necrosis of teeth
In recent years, dentists have encountered a completely new and completely unexpected, as well as practically unstudied pathological process in teeth, which is characterized by systemic damage. It is more intense than from radiation therapy.
It is most often observed in young and middle-aged people who have been working with computers of different models for more than five years, in combination with non-compliance with the work schedule, professional protection, and occupational hygiene. Often, the side of the jaws facing the monitor is affected more intensely. The main foci of necrosis can cover both a significant and most of the crowns of the teeth. The lesions are characterized by pigmentation and painlessness, as well as tooth decay.
Is it possible to avoid these defeats?
It is recommended to follow certain standards when working with a PC:
- A workplace area of less than 6 m2 when the volume of the entire room is from 20 to 24 m2 is unacceptable;
- The location of natural light is on the left;
- If there are 2 computers (or more) in the workroom, then the distance between video monitors should be 2 meters or more (if they are directed in the same direction);
- Users should be at a distance of 0.6 to 0.7 m from the screen;
- After 2 hours of work, you should take a 15-minute break and ventilate the room;
- The total duration of computer use should not exceed 6 hours (for adults), and for children and adolescents - 1-2 hours. For women during pregnancy, using a computer is extremely undesirable in order to avoid tooth decay.
If the disease manifests itself, treatment is carried out in accordance with the clinical situation. At the initial stages of the pathology (when the integrity of the enamel is not compromised), deep fluoridation using APF gel is prescribed. In later stages of the lesion, restoration of the shape of the teeth using artistic restoration or orthopedic structures is used. Implantation in case of complete destruction is also practiced. It would not be superfluous to conduct an examination of the whole body.
What factors provoke it?
The development of this pathology can be influenced by a variety of and completely different factors. Dental tissue necrosis can be provoked by both internal and external causes.
Domestic
Internal factors include the following:
- dysfunction of the central nervous system;
- pregnancy period. As a rule, necrosis was observed with frequent pregnancies following one after another;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland, for example, hypothyroidism;
- imbalance of hormone production (especially in adolescence);
- regular human intoxication;
- genetic predisposition.
Internal factors mainly lead to the occurrence of cervical necrosis .
External
External factors include everything that can negatively affect tooth tissue directly :
- excessive or prolonged exposure to substances containing acids or harsh chemicals. For example, medicines, products, industrial substances;
- receiving high doses of radiation. Most often observed in the treatment of cancer diseases;
- constant exposure to electromagnetic radiation.
Loss of dental tissue due to erosion
Tooth erosion
- progressive loss of dental tissue (dentine and enamel) of an insufficiently studied nature.
Some authors suggest that the cause of tooth erosion, like the wedge-shaped defect, arises solely from the mechanical action of the powder and the toothbrush. Others believe that the appearance of erosion is due to the large amount of consumption of citrus fruits and their juices. In any case, our dentists will be able to help in any clinical situation - they will provide high-quality treatment and save you from dental erosion.
A significant role in the mechanism of progression of erosion of hard dental tissues is assigned to increased function of the thyroid gland, and, in particular, endocrine disorders. According to experimentally obtained data, one of the main symptoms of this disease is considered to be a decrease in saliva viscosity and an increase in its secretion. It has been proven that tooth erosion occurs in patients with thyrotoxicosis twice as often as in people with normal thyroid function. At the Dantley Clinic, our dentists will perform remineralization as a treatment option for erosion. The number of patients with erosion of hard dental tissues increases by 20% with an increase in the duration of the disease by just one year.
Erosion is the loss of dental tissue, which will continue to progress without medical intervention. Dental tissues are affected and thinned on one or more sides of the tooth.
Erosion of hard dental tissues mainly manifests itself on the symmetrical surfaces of the lateral and central incisors of the upper jaw, as well as on small molars and canines of both jaws. Erosion practically does not occur on large molars and incisors of the lower jaw. The lesion is most often observed in middle-aged people, and is characterized by a long course - up to 10-15 years. In St. Petersburg, the Dantley Clinic provides remineralization and restoration of teeth to patients of all ages. Over time, a large number of teeth become involved in erosion. Due to the significant impact of adverse factors, including environmental ones (Chernobyl disaster, etc.), the number of cases of dental erosion in fairly young people (18-25 years old) is significantly increasing.
Manifestation of tooth erosion
It is a round or oval enamel defect located in the transverse direction of the more convex part of the labial (vestibular) surface of the dental crown. The bottom of the erosion is shiny, hard and smooth. The gradual expansion and deepening of the boundaries of erosion leads to the loss of part of the dentin and all of the enamel.
There are two transitional stages of damage:
- initial (enamel erosion);
- pronounced (erosion of dentin and enamel).
According to the depth of the lesion, three degrees of the disease are distinguished:
first degree (initial)
- only the superficial layers of enamel are affected;
second degree (medium)
— the entire thickness of the enamel is affected, dentin is not involved in the pathological process;
third stage (deep)
— the entire thickness of the enamel, as well as the surface layer of dentin, is affected.
According to the course of the disease, two stages of erosion are distinguished - active and stabilized, but both of them are characterized by a chronic course. With any type of erosion, our dentists will carry out remineralization or filling, reducing the chronicity of the disease to zero.
The active stage is characterized by:
- rapid loss of hard dental tissues;
- increased sensitivity of the affected area to external irritants (sweet, sour, hot, cold, building up to erosion).
The stabilized stage is characterized by:
- slowly progressive loss of hard dental tissues;
- lack of increased sensitivity of the diseased area;
- possible transition from a stabilized stage to an active one.
Treatment of tooth erosion
Local treatment of the active stage:
- The goal is to stabilize the process. This result is achieved through additional remineralization of hard dental tissues using calcium electrophoresis or applications. Daily applications of a 10% potassium gluconate solution are prescribed for 15 minutes for 15-20 days. After which, for 3 days, a 2% sodium fluoride solution is applied to the area of erosion for 3 minutes. And the treatment is completed by coating the diseased surface with fluoride varnish. A 10% calcium gluconate solution is used for electrophoresis. The duration of the procedure is 5-10 minutes. After the electrophoresis session, a swab moistened with a 2% sodium fluoride solution is applied to the area of erosion. The entire course of treatment is 10-15 procedures.
- Fluoridation - restoration and strengthening of enamel with fluoride-containing and mineral substances.
- Filling erosion with composite materials fully restores the defect, the teeth look beautiful and natural.
- If there is a large area affected by erosion, it is worth making artificial crowns.
Local treatment of the stabilized stage:
- Phosphorus and calcium preparations, microelements and vitamins are prescribed internally.
- The task is tissue depigmentation. For this purpose, over the course of two or three visits, the affected surface is treated with an abrasive paste with a high fluorine content. Whitening, filling and restoration of the defect area are also used.
Diagnostics
Tooth erosion is diagnosed during a dental examination. A clearer localization of the defect is facilitated by drying the surface of the tooth crown and an iodine test. Tooth erosion requires differentiation from wedge-shaped defects, enamel hypoplasia, and superficial caries.
To identify concomitant endocrine disorders, patients suffering from dental erosion may need to consult an endocrinologist, perform an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, and study thyroid hormones. To exclude GERD, examination by a gastroenterologist is recommended.
Treatment of fluorosis
Fluorosis
– damage to tooth enamel, accompanied by the appearance of white, yellow, brown spots on it and destruction of the tooth structure. A chronic disease that does not allow for long delays in treatment and an indifferent attitude towards the destructive process. Fluorosis is a systemic pathology that manifests itself on the teeth.
Causes of the disease: excess fluoride in the human body. The main source of this element is drinking water, so most often the cause of enamel fluorosis is an increased dose of fluoride in the composition of consumed liquids. Obviously, fluoride is found not only in water, but it is absorbed from food in much smaller quantities.
Types of fluorosis
Fluorosis can be divided into two types: endemic (associated with high levels of fluoride in drinking water) and professional (occurs in people who spend a lot of time in enterprises and premises where the fluoride content in the air exceeds the sanitary standard). The concentration of fluoride in water should not exceed 1.5 g/ml. Most often, enamel is affected in children whose skeletal system and enamel are not yet fully formed and who live in an area of water with a high fluoride content. For adults there is a limit - 5-6 g/ml.
Stages of fluorosis and its treatment
- The initial stage of fluorosis is characterized by the formation of white spots on the vestibular surface of the teeth. Treatment is carried out by bleaching, remineralization, fluoridation, and grinding of the affected areas.
- Fluorosis up close! The initial stage, which manifests itself in chalky white spots, smooth to the touch, sometimes light yellow spots.
- The streak form is characterized by the appearance of small white dots and streaks on the teeth. Treatment consists of eliminating the root cause, using filters or bottled drinking water. There are special filters that can be used to reduce the concentration of fluoride in water. Dental treatment is carried out in several ways depending on the manifestation of the disease: whitening, restoration of damaged enamel structure with the help of remineralizing agents, filling defects.
- The spotted form is distinguished by the appearance of light yellow spots. Upon visual examination, the shine and smoothness of the affected enamel is noted. The affected area increases, small spots merge into large ones and cover several teeth at once. The treatment consists of carrying out measures that are used in line form. For significant defects, the doctor may consider it advisable to install veneers.
- The chalky-mottled form provokes the appearance of dull spots on the surface of all teeth, as well as the appearance of dark brown pigmented spots, yellowing of the enamel with the formation of multiple small specks and spots. Treatment is carried out using artistic restoration or installation of veneers.
- The erosive form is characterized by the formation of significant dental defects. Round yellow or brown lesions appear on the enamel, and tissue loss is observed. With such manifestations of fluorosis, remineralization and bleaching will be ineffective. Treatment is carried out by filling with composite materials, installing veneers or crowns.
- The destructive form is the most difficult, as there is rapid destruction of the tooth structure, disruption of the shape of the crowns, fragility of the teeth, and possible chipping and cracks. Multiple aesthetic defects are accompanied by dysfunction and cause pain. Treatment of the destructive form is carried out using therapeutic and orthopedic methods. If possible, teeth are restored using composite materials through restoration. Significant defects and chips of enamel require the installation of crowns or dentures.
How does it manifest?
Various types of this pathology are characterized by some common signs that allow timely diagnosis of the disease.
How tooth enamel hypoplasia manifests itself in children, read in the next review.
In this article we will tell you what a wedge-shaped tooth defect is.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/zubyi/emal/kak-vosstanovit-samyie-populyarnyie-sposobyi.html we will discuss whether tooth enamel can be restored.
These symptoms include:
- increased sensitivity of enamel to hot, cold and sour;
- frequent manifestation of a sore throat for no reason;
- loss of enamel shine;
- the presence of unnaturally white spots on the surface, reminiscent of chalk, with a gradual change in color to a darker one. The spot may even turn black;
- pigmented areas have an uneven color: darker in the center, lighter around the perimeter;
- in the area of change in shade, the enamel becomes rough and heterogeneous;
- when exposed to a probe, the affected tissue crumbles and peels off;
- in some cases, the pathology is accompanied by constant aching pain;
- there is abrasion of tooth tissue in the area of the cutting part of the front incisors and fangs;
- in the presence of abrasion, the edges become unnaturally smooth, and the height of the tooth is shortened;
- If left untreated, complete destruction occurs, right down to the gum line.
Bruxism in adults
Bruxism
is a disease characterized by involuntary, periodic and very strong (spastic) contraction of the masticatory muscles, as a result of which the jaws are clenched to the point of grinding the teeth. Typically, attacks of bruxism last a few seconds, but sometimes it can last much longer - several minutes. At the same time, the pulse may increase, blood pressure may rise, and the respiratory rhythm may become disrupted.
Bruxism can appear in a person at any time in life. According to scientists, bruxism occurs in 15% of adults and approximately 50% of children (childhood bruxism). However, not every person knows about his illness, since it manifests itself at night. Most often, family members and relatives tell him about this.
Scientists have not yet fully determined the causes of bruxism, which significantly affects the prevention of this disease. There is an opinion that the causes of its occurrence may be somnambulism, severe snoring, and nightmares. This disease usually affects people with pathologies of the facial skeleton and temporomandibular joint. They say that bruxism most often occurs in a person whose life is full of stress and great emotional stress.
The danger of bruxism is that it can:
- provoke increased tooth wear;
- cause loosening and damage to teeth;
- disrupt the correct bite;
- increase tooth sensitivity;
- develop pathology of the temporomandibular joint;
- cause headache;
- cause pain in the facial muscles.
In addition, the consequences of this disease can be various mental disorders, since the patient feels discomfort in communicating with other people.
Types of disease
There are two types of bruxism: daytime and nighttime. Daytime bruxism is characterized by the habit of intensively clenching the jaws at a time of strong emotional stress, which causes teeth grinding. With night bruxism, a person clenches his jaw tightly and grinds his teeth while sleeping. Several attacks can occur in one night. Most patients suffer from this type of bruxism.
You should not worry if attacks of this disease do not last long (about ten seconds) and are repeated irregularly. Overcoming this disease on your own will not be successful. As soon as a person realizes that he is suffering from bruxism, he should immediately consult a doctor for advice and begin timely treatment.
Treatment of bruxism
Correct treatment consists of identifying the cause and eliminating it. Since the nature of the disease is not completely clear, bruxism is treated by a general practitioner, a neurologist and a dentist. People visit the dentist most often because of symptoms that arise in the maxillofacial area.
How can a dentist help in this situation? Make special silicone mouthguards that are worn at night and significantly soften the load on the dental system. The specialist will also eliminate diseases of the temporomandibular joints, restore defects in the dentition with orthopedic structures, and sanitize the oral cavity.