Today, dentists successfully treat almost any disease of the teeth and gums. Their arsenal includes advanced technologies and modern techniques that allow them to find a way out of the most difficult situations. But sometimes the only possible solution is removal - this is a drastic measure that is resorted to in desperate cases. The procedure is ordinary, and therefore complications after it occur quite rarely. It is important to contact an experienced surgeon and conscientiously follow all his recommendations in the postoperative period. Today we’ll talk about how tooth extraction in the upper jaw differs, what difficulties there may be and how the procedure is carried out.
Removal of upper teeth - what are the features?
The upper jaw has its own anatomical features. So, for example, implanting upper teeth is somewhat more difficult. The bone tissue is looser, which is why the implanted rods take several months longer to take root. Low jawbone density is due to less chewing load that falls on it. Therefore, after removal, it atrophies faster. But if implantation becomes more complicated, then with surgical extraction of teeth things are different - here the procedure is easier and simpler than on the lower jaw.
Choice of anesthesia - general or local
As noted above, the bone tissue here is less dense. It is covered by a thin membrane called the “cortical plate”. It contains a large number of openings for nerves and blood vessels. Due to this, there are no problems with the administration of local anesthesia. Removal of the upper teeth is usually easy and quick, without any discomfort. In this case, there is no need to consider general anesthesia as an alternative option for pain relief.
Local anesthesia is most often used on the upper jaw.
Risk of injury to the maxillary sinus
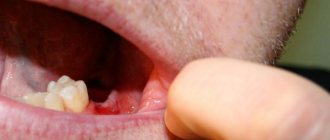
The maxillary sinus is located in the internal structures above the upper jaw. Often its shell is located in close proximity to the roots. If the extraction technology is violated, the sinus can be damaged, which will lead to its perforation or rupture. This complication is typical for the procedure for extracting chewing elements and wisdom teeth. It causes a number of symptoms indicating sinus injury. For example, when you eat or drink, ingested liquid and air may exit through the nose. Sometimes foam appears in the vacated hole, and during probing the instrument penetrates much deeper than it should.
This complication is a consequence of medical errors. To correct the situation, the injured membrane will have to be sutured. Sometimes perforation of the sinus leads to increased temperature, suppuration, and the development of sinusitis and sinusitis. In serious cases, the patient may be hospitalized, undergo a full-fledged operation and be prescribed a course of antibiotics.
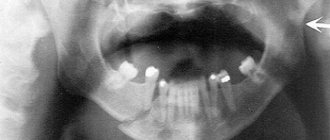
Entry of part of the root into the sinus
Sometimes, when the maxillary sinus is damaged, part of the root penetrates into it. And this is again a medical error caused by incorrect advancement of the tooth at the time of its extraction. Often such a complication occurs against the background of thinning of the bone plate. Simply put, the tooth breaks and part of its root system “slips” into the sinus.
Among the characteristic symptoms, dental experts identify fluid and air entering the nose through the mouth, severe runny nose, high temperature, and pain in the nose. To clarify the diagnosis, the patient is sent for an X-ray examination. Next, he is prescribed a full-fledged operation, which is carried out in a hospital setting.
When removing teeth on the upper jaw, there is a risk of injury to the maxillary sinus or particles of the tooth root getting into it
Types of teeth and their location
The lower and upper teeth of the six are dentin (the hard part of the tooth) with a cavity, covered with a layer of enamel. It has a characteristic shape, is built from several special tissues, and also has its own nervous system, circulatory and lymphatic system. Inside the tooth cavity, contrary to general belief, there is loose tissue permeated with nerves and blood vessels.
Normally, a person has from 28 (full set) to 32 teeth (full set + 4 wisdom teeth). Each tooth has its own name and performs a specific function.
Incisors are teeth whose function is to bite food. These are the front teeth that erupt first (4 at the bottom, 4 at the top).
Fangs are cone-shaped teeth, the functions of which are to tear and hold food (2 below, 2 above).
Premolars are small milk teeth, and then small molars, following the canines, a pair on each half of the jaw. There are 4 at the bottom, 4 at the top. This is the 1st, 2nd premolar, or if you give serial numbers - the 4th and 5th tooth.
Molars are teeth whose functions are the primary mechanical processing of food. These are the largest molars. They are located next to the premolars, a pair on each half of the jaw (4 below, 4 above). 1st and 2nd molars or teeth six and seven. If in adulthood, after 20 years, an additional molar or wisdom tooth is formed, then their number becomes 6 at the bottom and 6 at the top. The wisdom tooth is the 3rd molar or the number eight tooth.
Sixes, as well as 7s and 8s, do not have milk teeth. They erupt immediately as radicals.
If today many have seen what a separate molar six looks like from a photo on the Internet, then few know in what order the entire bite is located and what place this molar occupies.
Based on their type, teeth are divided into primary and permanent teeth.
In the temporary primary dentition of children, there are only 20 teeth: these are all 8 incisors, 4 canines, and 8 premolars.
In the permanent dentition there are 20 replaced and 8 original molars, for a total of 28: these are 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars and 8 molars immediately cut through by the molars. An additional 4 molars – wisdom teeth – may also appear. Then the bite will have 32 teeth.
How painful is it to remove upper teeth?
Today dentistry has all the capabilities to treat any complexity without pain and discomfort for patients. Even complex removal of the posterior destroyed element, including the figure eight, can be carried out quickly and completely painlessly. When working on the upper jaw, local anesthesia is usually sufficient. If desired, the patient can insist on the use of general anesthesia, for example, if he has a panic fear of dental treatment. Here you need to understand that the use of such powerful anesthesia has a whole list of contraindications and requires serious preparation.
Sedation may be used to eliminate fear during the procedure.
An excellent alternative can be sedation, which involves placing the patient in a semi-conscious state. Fear and anxiety disappear, the person feels completely calm and relaxed, and can respond to simple requests from the doctor. It is noteworthy that after the sedation ends, the patient may not remember how the procedure took place. It should be understood that sedation is only an addition to pain relief and does not exclude the use of local anesthetics.
Molars and permanent teeth. What are the differences?
Many people are accustomed to thinking that a baby tooth is temporary, and a molar tooth is permanent, already having a nerve. However, it is not. The correct division of teeth involves milk and permanent teeth, which replace them.
But molars are those teeth that never had predecessors, that is, molars: the 6th, 7th, and 8th tooth (1st molar - tooth six, 2nd molar - tooth seven, and 3 1st molar – tooth number eight).
And the premolars (4th and 5th teeth, or 1st and 2nd premolars) are first deciduous, and then permanent, and also molar, because they replaced the deciduous predecessors.
Contraindications to the procedure
The extraction procedure (that’s what it’s officially called) has its limitations. It should be noted that almost all contraindications are relative, which means that after eliminating limiting factors, removal can be carried out. These phenomena and conditions include the following:
- acute infectious diseases,
- blood clotting disorders,
- first and last trimester of pregnancy,
- 2 days before and after menstruation,
- diabetes in an uncompensated stage,
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels,
- mental illnesses in aggravation.
It is not advisable for pregnant women to perform the procedure.
Sometimes emergency removal is required, and then there is simply no time left to eliminate the above-mentioned obstacles. In this case, the doctor takes on additional risk and performs the procedure as carefully as possible. It is better if it is a truly experienced and qualified dental surgeon.
Indications and contraindications for removal
The absolute indication is acute purulent inflammation with the possibility of developing osteomyelitis or phlegmon.
Relative readings:
- development of a cyst at the root;
- destruction of the outer part of the tooth without the possibility of restoration;
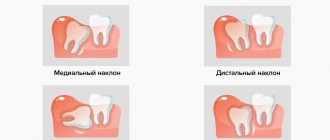
- dystopia or incorrect position of the tooth in the gum;
- malocclusion;
- periodontitis of the third and fourth degrees;
- dental inflammation caused by tuberculosis or actinomycosis;
- supernumerary six teeth, upper or lower, which cause malocclusion;
- damage to the tooth root during dental surgery.
Description of the procedure: how it is carried out
If the patient is undergoing a planned operation, then first he is sent for an X-ray examination and tests. After studying the diagnostic results, the doctor begins the procedure or prescribes it for the next free time. Complex extraction is recommended to be carried out at the beginning of the day. It is better not to eat or drink immediately before visiting the doctor - this will help enhance the effect of the anesthetic. If the patient suddenly catches a cold before removal, it is better to reschedule the procedure.
An X-ray examination is performed before removal.
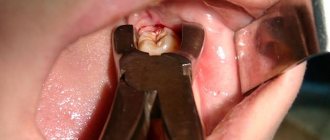
First, the specialist administers anesthesia. If a simple operation is to be performed, its duration will be no more than 20 minutes. Using special forceps, the doctor carefully clamps the crown, rocks it with a special movement, and then sharply pulls it out of the socket. Lightly compresses the edges of the wound until the hole is completely filled with blood and a blood clot is formed - protection against infection and mechanical damage. Next, the doctor treats the injured tissue with an antiseptic, prescribes painkillers, and in some cases antibiotics, and gives detailed instructions about the postoperative period.
Symptoms of molar eruption
As a rule, the sixth teeth emerge from the molars first.
During the teething period, the immune system's defenses are weakened, and the following symptoms similar to colds may appear:
- elevated temperature;
- runny nose;
- and most importantly – increased salivation.
And since the teeth appear in pairs, that is, the canine on the upper right side erupts at the same time as the canine on the upper left side, then the six teeth in children come out together, which can aggravate the process.
These teeth are the very first molars to erupt. To ease the symptoms of a small child and relieve some of the pain, you can massage the gums with your finger, but be sure to wash your hands thoroughly before doing so. Otherwise, it will not be difficult to get an infection. And older children can chew hard vegetables or fruits: apples, carrots and other hard foods.
Difficult removal of a wisdom tooth (eight) - what are the features?
Complex removal usually concerns teeth with a branched root system, impacted, dystopic, destroyed elements, and figure eights. In this case, the procedure looks like this:
- the specialist makes an incision on the gum, peels off a flap of the mucous membrane,
- if the tooth is located under a layer of bone tissue, it is literally cut out using a special bur,
- then the element is carefully removed in parts, for which special forceps are used,
- the doctor cleans the hole and treats the tissue with an antiseptic,
- the resulting cavity is filled with osteo-replacing material and covered with a protective membrane to prevent the growth of the mucosa,
- the wound is tightly sutured.
Most often, wisdom teeth are difficult to remove.
The procedure can last 40-60 minutes. A few days later, the patient is invited to a second visit so that the specialist can assess how successful the healing process is.
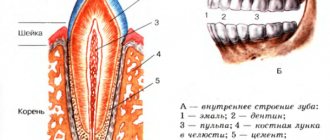
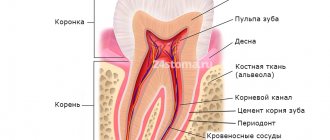
Tooth structure
The teeth are located on the upper and lower jaws. They consist of hard and soft tissues.
Solid:
- tooth enamel – the outer shell that protects the tooth;
- dentin – hard tissue, the basis of the entire tooth;
- Dental cement is the tissue covering the neck and root of the tooth.
The soft pulp includes the loose tissue inside the dental cavity, which has a large number of vessels, both blood and lymphatic, and nerve endings.
Anatomically, a tooth can be distinguished into three parts:
- crown - the part protruding above the gum;
- root - a part located deep in the alveolus of the gum;
- neck of the tooth - part of the actual transition of the tooth enamel into cement, that is, the place in the gap between the root and the crown.
Possible complications
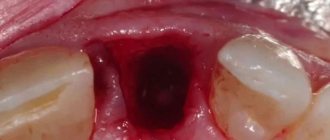
Complications are more typical for cases of complex removal. And even with the extraction of a wisdom tooth, if the operation is performed on the upper jaw, the risk of developing undesirable consequences remains minimal. A dangerous complication after removal is alveolitis - inflammation of the socket with possible suppuration. The mucous membrane in the area of the defect turns somewhat red, swelling appears, the blood clot disappears, and instead a yellowish coating with an unpleasant odor appears. There may be discharge of pus and increased body temperature.
The photo shows inflammation of the socket after tooth extraction
Important! When answering the question about how long it takes for a wound to heal after removal, it should be noted that pain and swelling usually go away within 3-4 days. If during this time the pain only intensifies, consult a doctor immediately.
Another possible complication could be injury or perforation of the nasal sinus, or penetration of part of the root into it. Typically, this situation occurs due to the fault of the doctor if he pressed too hard on the instrument. To avoid such troubles, it is important to take the choice of a clinic and doctor seriously, as well as follow all the specialist’s recommendations after the procedure until the tissues are completely restored.
Changing baby teeth
The process of changing the bite begins much earlier than the first tooth falls out. Over time, baby teeth no longer hold tightly to the gums and begin to loosen. And this happens due to the fact that the roots of such teeth are formed from tissue that can dissolve over time. But only if the germ of a permanent tooth appears.
The germ of the future tooth is separated from the root of the milk tooth by just a thin bone plate. If it forms, it will begin to put pressure on this bone septum. Osteoclasts will begin to appear in the surrounding tissue, which are designed to destroy it.
From this moment on, the process of changing one tooth to another occurs from two sides: the permanent one destroys the enclosing plate, and the pulp of the baby tooth begins to turn into tissue rich in blood vessels and the same osteoclasts that destroy the dentin of the baby tooth. As a result, the root is absorbed, and only the neck with the crown remains, which are easily removed during the growth of a new tooth.
Is it possible to perform prosthetics immediately after root removal?
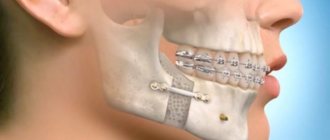
Single-stage implantation is a technology that allows you to restore a tooth immediately after its extraction. This technique makes it possible to significantly reduce treatment and restore the aesthetics and functionality of your smile in the shortest possible time. This concept includes immediate loading protocols, but in some cases a classic implant is fixed using standard two-stage technology.
With single-stage implantation, implants are installed in the socket immediately after tooth extraction
However, today experts prefer one-stage methods. According to the results of numerous clinical studies, implantation using a one-stage technology immediately after tooth extraction protects bone tissue from atrophy and reduces treatment time with a guarantee of long-term results of up to 96%1.
“I needed to remove one decayed tooth, but the problem was that it was in sight. I wanted to do everything right, but I was very worried that I would have to walk around with a hole while the implant took root. And then I came to you, and they offered me a one-step implantation. The tooth was carefully removed and an implant with a crown was immediately placed in its place. The procedure went quickly, completely without pain, although I still had doubts about local anesthesia and thought about going under anesthesia. I am immensely grateful to your specialists!”
Lyubov Vyacheslavovna K., 46 years old, review on the website of a Moscow dental clinic
After extraction, restoration of bone tissue is not required - the implant is implanted into the vacated socket and can be additionally strengthened with bone replacement powder. In this case, a temporary crown is immediately fixed, and after a few months, when the implant has fused with the jawbone, it is replaced with a permanent single prosthesis. A temporary crown is created from a lightweight material – plastic. It turns out to be slightly shorter than the neighboring elements, which avoids intense mechanical impact and displacement of the artificial root.
Important! Single structures are fixed only in place of single-rooted front teeth (incisors and canines), which are not subject to intense exposure. Their main function is to restore the aesthetics of the row.
The photo shows a diagram of a tooth implantation with immediate loading.
But this procedure is not possible in all cases. Implantation is a serious operation that cannot be performed without careful preparation. It is necessary to study the clinical picture, exclude possible contraindications, and select an implant model. Most patients turn to dentistry when emergency removal is required, and there is simply no time left for preparation.
Biochemical composition of the tooth
Since the parts of any tooth differ in their functions, they will also differ in their biochemical composition.
The main composition of the entire tooth is water, organic and inorganic compounds. In particular, individual important components are mineral components.
Enamel is a hard, mineralized tissue. Its strength is determined by a high degree of mineralization.
Dentin is a mineralized tissue that does not have cells or vessels. Forms the bulk of the tooth. The structure is similar to both enamel and bone tissue of the body.
Pulp is a connective tissue consisting of cells and intercellular substance. The pulp performs one of the important functions: it participates in the formation of dentin and provides the central nervous system with the necessary information about the condition of the enamel and the tooth as a whole, which explains the high sensitivity of the teeth.
Mineralization is a process by which an organic base is formed and saturated with calcium salts, if present in the body. This is an intensive process that occurs during the period of teething and the formation of dentin and enamel, since initially the tooth has non-mineralized enamel.
Estimated cost of the procedure
According to the compulsory medical insurance policy, a tooth can be removed completely free of charge, in a state clinic. In private clinics, the procedure will cost from 1,500 to 3,000 rubles, depending on the degree of complexity. In some situations, the cost of the operation can even reach 15 thousand rubles or more, for example, with a complex extraction of the figure eight using sedation.
As for immediate recovery, the cost of such treatment using inexpensive brands will cost approximately 30-50 thousand rubles - this includes x-ray diagnostics, 3D planning and tests. Restoration with the installation of a more expensive Nobel Biocare implant and an adaptation crown will cost approximately 70-90 thousand rubles.
- Drobyshev A.Yu., Matytsin O.M., Dronov M.V. Modern approaches to immediate dental implantation, 2004.
How much does it cost on average in Moscow?
Prices for economy, business and premium implants (in rubles):
| № | Brand of implant | Economy | Business | Premium |
| 1 | Alpha Bio | 15000 | 20000 | 25000 |
| 2 | Dentium | 15000 | 20000 | 30000 |
| 3 | M.I.S. | 17000 | 20000 | 23000 |
| 4 | BioHorizons | 25000 | 30000 | 35000 |
| 5 | Ankylos | 30000 | 35000 | 40000 |
| 6 | XIVE | 30000 | 40000 | 50000 |
| 7 | Astra Tech | 50000 | 60000 | 70000 |
| 8 | Nobel Biocare | 50000 | 60000 | 70000 |
| 9 | Straumann | 50000 | 60000 | 70000 |
Implantation by stages: economy, business, premium class:
| № | Type of work | Economy | Business | Premium |
| 1 | Anesthesia | 500 | 700 | 1000 |
| 2 | Bone grafting | 15000 | 20000 | 30000 |
| 3 | Implantation of 1 tooth | 15000 | 20000 | 30000 |
| 4 | Abutment installation | 10000 | 15000 | 20000 |
| 5 | Crown installation | 15000 | 20000 | 25000 |