In many ancient states where medicine was developed, people believed in hidden connections between various organs. Some doctors have tried to find answers about a person's health by examining their tongue. Science has evolved, and many views on diagnosing diseases by language have changed, but even modern doctors are finding evidence of this connection.
Modern doctors believe that certain properties of the tongue do not indicate an accurate diagnosis, but they help to find out the direction of diagnosis . So from time to time it is advisable to look at this organ and consult a doctor if its color or shape changes.
Plaque on the tongue: normal or not?
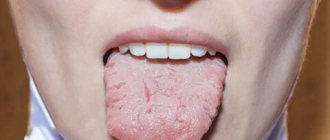
The human language is a kind of litmus test for the health of the entire organism. Normally, a healthy person should have a tongue without plaque, but this is ideal, which is rare today. If the tongue is coated, there are only two cases where you should not worry about it.
- After meal.
Eating foods such as strong tea, black coffee, red wine, blueberries, and beets causes temporary staining of the tongue and an unnatural coating on it, but both phenomena go away on their own and do not cause damage to health. - After the night.
A constant coating on the tongue in the morning is normal. At night, bacteria living in the mouth actively multiply, leaving traces of their vital activity. A thorough morning toilet will put everything in its place.
Tongue care kit from miradent.
Anatomy and functions
The human tongue by its nature is a muscular organ that does not have bones. On top it is covered with a mucous membrane. Tasks and functions it performs:
- participates in the functioning of the speech apparatus;
- determines the taste of the food a person eats;
- is part of the digestive system - it performs primary processing of food, mixes it and forms a food bolus, which pushes further into the esophagus.
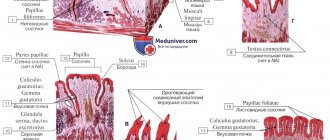
The structure of the language is simple but interesting. This organ is divided into two parts - the back - the root and the front - the body. The upper surface is also called the back and has a velvety structure.
The tongue is covered with papillae, which are divided into 4 groups responsible for recognizing tastes. That is why, with a burn or other injuries to the tongue, a person temporarily loses the ability to perceive one or more tastes.
What if it's a disease?
A strong coating on the tongue and bad breath are already a reason to be wary. An experienced doctor will determine which disease the plaque on the tongue is a sign of, comparing the degree of density of the deposit, color and location.
Glossitis
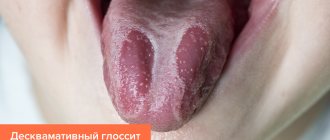
One of the typical diseases characterized by plaque on the tongue is glossitis - inflammation of the tongue caused by injury or of an infectious nature. With glossitis, red spots appear on the tongue, which is why the disease is sometimes called “geographic tongue.” Read more in the article.
Gastritis
If your mouth is sour and there is a coating on your tongue, this is a sign of inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Usually the plaque disappears if you follow a diet.
Thrush
With thrush, the plaque is located under the tongue. It is distributed unevenly and has the character of spots.
Chlamydia
With chlamydia, a sexually transmitted disease, a thick, sticky coating appears on the roof of the mouth and tongue as a result of a malfunction in the immune system after an attack by chlamydia.
Bronchitis and pneumonia
Plaque on the sides of the tongue will indicate an upper respiratory tract disease. In most cases, it is whitish and is easily removed by brushing your teeth and tongue, but also quickly returns to its original place.
Alcoholism
A coating on the tongue after alcohol abuse is common. People talk about this figuratively: “It’s like cats have shit in your mouth.” However, in chronic alcoholics, the dark brown coating never goes away and is localized at the root of the tongue.
Cancer
If the tongue is coated, one cannot say with certainty that a specific type of cancer is present. But it is precisely this symptom, coupled with a number of other characteristics, that indicates a complication of an oncological disease (for example, a malignant tumor in the lungs).
Plaque on the tongue of a pregnant woman, with rare exceptions, is not a sign of illness - it is the result of changes in hormonal levels.
How is the treatment carried out?
The main treatment will be aimed at eliminating the disease or pathology that entails consequences in the form of glossitis. The patient will also be prescribed antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity (for example, “Chlorhexidine”), anti-inflammatory therapy, wound-healing and cell-regenerating ointment (Solcoseryl, vitamin A, rosehip oil), vitamins, anesthetic drugs and applications. The keratinized areas of the affected tissue are removed through surgery. If abscesses and ulcers are present, they are opened and drained. For fungal infections, antibiotics are prescribed.
"Chlorophyllipt" is prescribed for treating the oral cavity
During treatment, it is also necessary to follow a gentle diet, excluding hard, spicy, salty, sour and hot foods, which can injure the mucous membrane and cause additional discomfort.
Main causes of plaque
- Infection.
The main cause of plaque on the tongue in adults is infectious diseases, characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. - Impaired immune function.
When the body's protective barrier cracks, this serves as a catalyst for the activation of pathogenic bacteria, which usually occurs against the background of an increase in body temperature. - Gastrointestinal pathologies.
Various chronic ailments of the gastrointestinal tract caused by Helicobacter. Plaque on the tongue due to gastritis, if the disease is not treated, becomes denser over time and provokes bad breath. A clear sign of enterocolitis in adults is considered to be plaque on the root of the tongue. - Side effect of drugs.
Plaque on the tongue after antibiotic treatment is a common phenomenon. Medicines that include substances that inhibit the growth of certain pathogenic bacteria negatively affect the acid-base balance in the mouth, which entails an increase in the number of microorganisms “responsible” for the appearance of plaque. - The consequences of nicotine.
If you are an “experienced” smoker, then you shouldn’t be surprised by a gray or yellow coating on your tongue. Nicotine abuse has a detrimental effect on the microflora of the body in general and the oral cavity in particular.
Attention!
A provoking factor for the appearance of plaque on the tongue is also helminthic infestations, such as giardiasis. For differential diagnosis in this situation, it is necessary to take a stool test for helminth eggs.
Folded shape
The name speaks for itself. This form of glossitis has the following visual symptoms: folds, grooves, the presence of longitudinal and transverse lines. It is interesting that most patients seek help and undergo treatment only because of complaints of a visual defect and an unusual appearance of the tongue, because The pathology practically does not manifest itself with other signs.
The photo shows a folded tongue
Despite the absence of pain and discomfort, the folded form of the disease must be treated, because grooves and folds are an excellent place for the accumulation of pathogenic bacteria and tiny food particles, and thorough hygiene of these areas is almost impossible. Due to lack of treatment, the patient may develop serious inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and abscesses, the removal of which will require surgery and long-term drug therapy.
Be sure to read the whole truth about the folded tongue and the reasons for its appearance in the feature article on the website.
What does plaque color tell you?
White
As we have already said, a thin white mucous coating on the tongue after sleep is not a deviation from the norm. A white coating of increased density indicates constipation, and a cheesy coating on the tongue indicates the unhealthy activity of yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida.
Yellow
A bright yellow coating on the tip of the tongue indicates hepatitis A (Botkin's disease). If there are problems in the functioning of the gallbladder, a yellowish coating and cracks appear on the tongue.
Dark
A dark coating on the tongue is a sign that something is wrong with the lungs. You don’t often see a completely black plaque: for example, in advanced stages of cholera due to dehydration of the body or in Crohn’s disease.
Diagnosis of internal diseases by tongue color
Characteristic colors , studied over many years, characterize the beginning pathologies of important organs of the human body:
- Red color signals improper functioning of the heart, lungs and other respiratory organs of the system, diseases of the hematopoietic system, and various infectious diseases.
- Raspberry speaks of severe infectious lesions, poisoning with symptoms of chills, complicated pneumonia.
- Dark red characterizes the same diseases as the red color, but they occur in a more severe form or are advanced. Toxic disorders and severe renal pathology occur.
- Alternating red and white areas on the surface of the tongue indicate scarlet fever, a red lacquered organ indicates the development of pellagra.
- A light bluish tint indicates impaired blood circulation and cardiac or pulmonary failure.
- The coloring of the lower area of the tongue in a bluish color indicates heart failure long before the onset of the disease. This indicator is especially typical for middle-aged people who do not expect such changes in the cardiac system, while older people have the opportunity to seriously take preventive measures.
- Purple color indicates severe disorders of the hematopoietic system and pulmonary diseases.
- Black color suggests cholera infection.
- A pale and bloodless tongue indicates anemia and severe general exhaustion of the body. In this case, tooth marks on the lateral surfaces indicate insufficient absorption through the intestinal walls. If discoloration appears only in certain areas of the tongue, then the disease threatens those organs that correspond to the anatomical distribution of surface zones.
What to do?
How to remove plaque from the tongue? To begin with, determine exactly the reason why the plaque occurs and treat the underlying disease by following the doctor’s instructions. For preventive purposes, in order to minimize the amount and density of plaque, you must follow simple rules of personal hygiene:
- brush your teeth in the morning and before bed with toothpaste and a brush that has a tongue cleansing pad;
- use antibacterial mouthwash;
- use a special spoon to clean the tongue, moving from its periphery to the front surface.
For a detailed article on how and how to properly clean your tongue from plaque, read a separate article.
Surface type
In general, the disease can affect different areas of the mucous membrane, but the superficial variety affects only its upper layer. Superficial glossitis of the tongue can be seen in the photo.
The photo shows superficial glossitis of the tongue
It all starts small - the catarrhal stage of the disease. First, the mucous membrane becomes swollen, and upon visual inspection it is noticeable that it is covered with a dense coating. If treatment is not started during this period or the pathology is not completely cured, then an ulcerative form develops - small painful aphthae appear on the mucous membrane, which can bleed.
What is glossitis of the tongue? This is a disease that, like many other dental pathologies, can occur in acute and chronic stages. It can have pronounced symptoms or a sluggish inflammatory process that will go unnoticed for a long time, undermining your health. That is why it is so important to undergo timely preventive examinations with a dentist and therapist.
Possible complications
If the symptoms of glossitis are ignored by a person, then he will certainly develop complications of the disease.
They may show signs such as:
- The pain begins to radiate to the neck.
- Body temperature increases.
- Salivation increases.
- The tongue greatly increases in size.
Inflammation of the tongue can lead to the development of phlegmon.
Symptoms characteristic of this complication:
- Swelling of the mouth and neck.
- Suppuration of tongue tissues.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Refusal to eat, increased weakness.
- Increased body temperature.
The patient's general health deteriorates, and signs of intoxication of the body increase. This complication requires emergency medical care.
External manifestations
In normal condition, the human tongue is clean and moist, with symmetrical edges and a uniform surface. As the disease progresses, these parameters change.
Depending on the pathology, the surface may become dry and glossy . The organ takes on an unhealthy pigmented hue . There is an upward change in size.
When the tongue protrudes, its deviation from the midline is noted. In some cases, pain and a pronounced change in surface relief occur. The epithelium may become covered with cracks and ulcers.