Facial nerve neuropathy is a disorder in the transmission of nerve impulses along a nerve due to the death of its fibers. Paresis is weakness of the facial muscles , i.e. a consequence of nerve problems. Nervous eye tics are a common reason why patients visit a doctor in search of treatment. Treatment of nervous tic (hyperkinesis) of the eye in our clinic will be based on the cause of hyperkinesis. We specialize in treating neurological problems, including facial nerve treatment.
- Treatment of the facial nerve at the Echinacea clinic
- Restore the functioning of the facial nerve: the sooner, the more completely
- Symptoms of neuritis, neuropathy, inflammation of the facial nerve
- Neuralgia of the facial nerve
- Examination for facial nerve disease - find and eliminate the cause of the disease
- If treatment does not bring results. Synkinesia and facial contracture
- Facial hemispasm. Paraspasm. Blepharospasm
Treatment of the facial nerve at the Echinacea clinic
The treatment will be structured like this:
- Find and eliminate the factor that damaged the nerve (viruses, for example);
- Stimulate nerve regeneration.
If you neglect the first point, the chances of restoring the nerve are reduced, and the risk of facial contracture increases. The average duration of treatment is 2 months; you can complete most of the course at home on your own.
The planned result is restoration of the functioning of the facial muscles. Possible difficulties are advanced disease, significant narrowing of the facial nerve canal, damage to the myelin sheath of the nerve, leading to the appearance of a nervous tic of the eye, which to some extent complicates the treatment process. Read more about the causes and treatment of nervous tics.
Restore the functioning of the facial nerve: the sooner, the more completely
The sooner the cause of death of nerve fibers is eliminated, the faster the restoration of facial muscles will occur. Modern diagnostic methods almost always make it possible to find out the cause of the suffering of the facial nerve. We will perform almost any necessary examination.
| The cause of the girl's facial nerve paresis was an infection (asymptomatic sinusitis). On a computed tomogram: 1 – clean maxillary sinus (the air looks black on the image); 2 – the maxillary sinus is filled with pus. | The cause of facial nerve paresis in the man was foci of cerebral circulatory disorders. On an MRI scan, areas of impaired blood circulation appear lighter than healthy brain tissue and are marked with numbers 1 and 2. |
Simply stimulating the regeneration of the facial nerve is risky: facial symmetry may not be restored, facial contracture and synkinesis are possible. Finding and, if possible, eliminating the cause of nerve death is a condition for successful treatment .
Most often, we find one of four causes of facial paresis:
- Neuritis – inflammation of the facial nerve (usually involving viruses);
- Insufficient blood supply to the facial nerve or its brain centers (nuclei);
- Compression of the facial nerve in its bony canal (tumor, edema or injury to the temporal bone);
- Injury to the nerve or its brain centers.
Treatment of the facial nerve should be aimed at eliminating the cause of its suffering . Methods:
- In case of inflammation and swelling of the facial nerve, it swells and compresses itself in its narrow bony canal, and then dies from compression. This is precisely what is a common cause of facial paralysis. Therefore, in the acute period, we perform powerful anti-edematous treatment . Medicines can be prescribed orally, intravenously, or in the form of local blockades.
- Antiviral treatment and restoration of the immune system will help stop the destruction of the nerve when it is inflamed.
- The damaged area of the nerve needs building material for restoration. We will select medications that promote the supply of blood and nutrients to the nerve and its centers in the brain stem.
- Treatment by an ENT doctor if necessary (purulent or sluggish inflammatory process in the tonsils or ear, with damage to the nearby facial nerve).
For the most complete restoration of the facial nerve, it is very important to perform facial gymnastics and massage. Gymnastics and facial massage are needed daily. We will teach you to perform them yourself.
Prevention
Taking into account the main causes of the disease, its prevention includes protection from colds, hypothermia, as well as timely treatment of diseases of the ENT organs. It is useful to harden the body, treatment in sanatoriums on the seashore, and a diet rich in B vitamins.
After suffering from facial neuritis, self-massage of the face with essential oil of fir or cedar is useful to prevent recurrence of the disease. It can be done at night during the cold season.
The paid services department of NIKIO invites patients with neuritis and neuropathies of the facial nerve for treatment. The patient is examined by an experienced doctor; a consultation with a candidate or doctor of medical sciences is possible. The clinic uses modern physiotherapy equipment. If necessary, the patient undergoes surgery to quickly restore the function of the damaged nerve.
Symptoms of neuritis, neuropathy, inflammation of the facial nerve
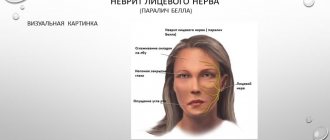
The essence of the symptoms is the disconnection from the brain of those areas whose function is controlled by the facial nerve:
- Weakness or paralysis of the facial muscles of one half of the face, which is expressed in the inability to raise the eyebrows, close the eyes, blink, wrinkle the nose, smile, puff out the cheeks (sail symptom); sometimes you feel the chin being pulled down, tension in the subcutaneous muscle of the neck;
- As a result of the disconnection of the facial muscles, a drooping of the corner of the mouth and smoothness of the nasolabial fold may be noticeable;
- As a result of the shutdown of the cheek muscles, it may be difficult to eat liquid foods;
- Sometimes the symptoms described above are accompanied by dry eyes or lacrimation, increased sensitivity to sounds (booming in the ear), decreased taste sensitivity, increased or decreased sensitivity of the facial skin on the affected side.
Neuralgia of the facial nerve
Neuralgia is a pain syndrome. The diagnosis of “facial neuralgia” is usually made incorrectly instead of the diagnosis of “trigeminal neuralgia”. The facial nerve contains only motor nerve fibers and does not transmit sensory impulses. Therefore, neuralgia, i.e. There is no pain in the facial nerve system. The facial nerve transmits commands from the brain to the facial muscles, and the symptoms of its suffering are weakness or paralysis of the facial muscles (facial nerve paresis).
Read more about trigeminal neuralgia
Causes
Facial neuritis occurs under the influence of the following etiological factors:
- in 15% of patients this is damage to the branches of the nerve during surgical interventions on the middle ear, mastoid process, and also associated with otitis media and other lesions of the hearing organ, for example, cholesteatoma;
- in rare cases, the disease is caused by infection - herpes virus (Hunt syndrome), mumps, polio, influenza, as well as Lyme disease, transmitted through tick bites;
- in 75% of cases, the cause of neuritis of the facial nerve cannot be determined; in this case, they speak of Bell's palsy, which worsens after hypothermia and colds.
Other causes include head trauma, surgery on the salivary gland, and removal of an acoustic neuroma.
Examination for facial nerve disease - find and eliminate the cause of the disease
The symptoms of facial nerve pain are almost the same in all cases, but its causes are different and require different treatments. Treatment “blindly” can delay the healing process. Therefore, in our clinic everything starts with searching for the exact cause and location of the nerve damage.
MRI of the brain, temporal bone. MRI scans show the brain centers of the facial nerve and its area of exit (root) to the base of the brain, blood vessels, and temporal bone. Circulatory disorders, cysts and tumors are easily recognized.
Blood tests to check for infections, biochemical changes that damage the facial nerve. The trigeminal nerve is a favorite area of attack by the herpes virus group. The suspicion of the presence of the virus and its activity can be easily verified using a blood test.
Electromyography, Blink reflex - measurement of electrical potentials of facial muscles. Helps assess the function of impulse transmission along the facial nerve, the degree of its impairment, judge the effectiveness of treatment, the presence of complications, and help in choosing the correct treatment tactics.
Stimulation electromyography of the facial nerve (electroneuromyography, myography of the facial nerve)
general information
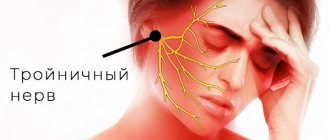
The trigeminal nerve consists of sensory and motor fibers. It originates in the structures of the brain and is divided into three branches:
- ophthalmic: responsible for the eye, forehead and upper eyelid;
- maxillary: innervates the area from the lower eyelid to the upper lip;
- mandibular: involves the chin, lower jaw, lips and gums.
With neuralgia, one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve are affected, which determines the main symptoms of the pathology. People over 45 years of age are most susceptible to the disease, and women get sick more often than men.
Make an appointment
If treatment does not bring results. Synkinesia and facial contracture
Facial symmetry returns in an average of 3 months. If your treatment has not brought results, facial asymmetry persists, pain or other symptoms appear, you should immediately clarify the cause of the dysfunction of the facial nerve. The location and cause of the nerve injury may not have been recognized and treatment was prescribed blindly. Perhaps little attention was paid to restorative procedures.
Facial synkinesis is a condition when, for example, closing the eye is accompanied by movement of the mouth and cheek, and smiling is accompanied by closing the eye, etc. Synkinesis occurs more often in cases of long-term, chronic disease of the facial nerve. Most often in these cases we find a chronic inflammatory process in the area of the nerve bed.
The most problematic complication of facial paralysis is contracture, i.e. cicatricial degeneration of facial muscles. The result of contracture is loss of elasticity and immobilization of the facial muscles, even after the function of the facial nerve itself has been restored. Contracture appears as a result of prolonged untreated paralysis of the facial muscles and/or as a result of inadequate recovery procedures (insufficient intensity of exercise or, conversely, excessive stimulation of the facial muscles). Facial contracture is partially reversible. We usually use local injections of the anti-scar drug Longidaza: we inject it with a very thin needle directly into the area of scarring of the facial muscles.
Nervous tics in children
There are several types of such disorders in childhood.
Transient tic disorder begins to manifest itself during early school age. Its duration ranges from 1 month to 1 year. Motor types of tics occur more often. Mainly typical for children with developmental delays and autism.
Chronic disorder occurs before age 18. And lasts from 1 year and above. In this case, either motor or vocal tics develop. The earlier the pathological symptoms appear, the easier and faster they pass.
Tourette syndrome is a multiple tic disorder characterized by both motor and movement types. A serious disease, which, however, softens with age.
A special type of disease, which is also characterized by signs of the nervous type, is minor chorea. It develops against the background of infections caused by streptococcus: sore throat, tonsillitis, rheumatism. Accompanied by pathological changes in nervous tissue.
Along with hyperkinesis, emotional instability, irritation, restlessness and anxiety, this condition corresponds to neurotic changes in the face. They are expressed in tension and spasms of the facial muscles, which is often mistaken for grimacing. There is also a spasm of the larynx, manifested in inappropriate screams.
At school, such children, not knowing the true cause of facial hyperkinesis, and even in combination with increased activity, are reprimanded and kicked out of class. Such an attitude towards the child forces him to miss school classes and avoid going to school. Treatment for chorea minor, along with sedatives, includes antibiotics to fight infection and anti-inflammatory drugs.
A nervous tic leaves a heavier imprint on a child’s psyche than on an adult. It often causes anxiety and detachment, withdrawal, and even provokes depressive disorders. Causes sleep disturbances, speech difficulties, and learning difficulties.
Tic disorders lead to distorted self-perception and decreased self-esteem.
Parents of such children are advised not to focus the child’s attention on the problem. On the contrary, they recommend finding ways to shift attention and increase self-esteem. A special place is given to support groups for such people and communication in general.
Facial hemispasm. Paraspasm. Blepharospasm
These are diseases similar to diseases of the facial nerve. Even doctors often confuse them. We will definitely understand the causes of the disease and provide the necessary treatment.
Facial hemispasm is attacks of involuntary contraction or twitching of the facial muscles on one side, similar to a nervous tic of the eye (read more about the causes and treatment of neural tics (including the eyes) here). It may look like squinting, closing your eyes, retracting the corner of your mouth or tip of your nose, or lowering your chin. More information about nervous tics (including the eyes and its causes)
Facial paraspasm is an attack of involuntary contraction of facial muscles on both sides. It occurs much less frequently than hemispasm and more often has common causes with it. More details
Blepharospasm is a disease that begins with rapid blinking, which subsequently develops into intense uncontrolled squinting of the eye or both eyes. More details
We will be happy to help you find the cause and treatment of facial hemispasm (nervous tic of the eye), facial paraspasm, blepharospasm.