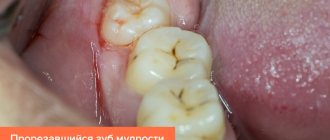
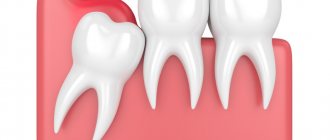
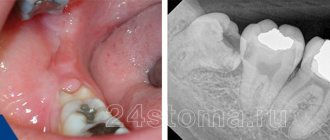
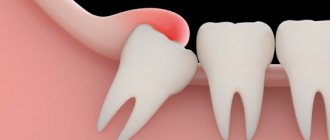
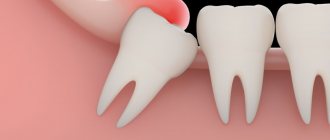
Removal, or scientifically extraction of a wisdom tooth, is a rather responsible and complex process due to the fact that the roots of the eighth molars in most cases have a massive and curved root system. They are also characterized by a non-standard location in the bone tissue of the jaw, so dentistry classifies such operations as complex.
A reasonable question that arises in every patient with indications for extraction of the eighth molar is whether it hurts to remove a wisdom tooth? Today we will talk in detail about the stages of extraction, the new generation of anesthetic drugs used and whether the removal is painful.
Out of fear of the dental chair, many people prefer to delay a visit to the doctor, thereby achieving serious complications in the form of purulent contents sinking to the root, the formation of phlegmon, and even the development of blood poisoning. Therefore, it is worth overcoming your fear, realizing that dentists now use high-quality painkillers and are constantly improving their professional skills so that the removal procedure goes as smoothly and comfortably as possible for the patient.
Indications for figure eight removal
To remove a wisdom tooth or try to save it is a question that only an experienced dentist can answer, based on the clinical symptoms that concern the patient, the direction of tooth growth, the presence of an inflammatory process and other factors. Here is a list of indications in the presence of which it is worth getting rid of a problematic molar:
- abnormal location of the figure eight in the jaw bone - when the wisdom tooth grows evenly, this is rather an exception than a common situation. More often, the figure eight erupts at an angle, damaging the tissues of the cheek and tongue, destroying the roots of neighboring healthy teeth (sometimes they grow horizontally, without even appearing on the surface of the gum; a molar can only be detected on an x-ray);
- pericoronitis or too slow eruption of a molar is an indirect indication for removal; if the tooth is simply covered with a hood, then the doctor can remove part of the soft tissue to avoid the inflammatory process. Removal is carried out only when the patient has taken too long with his visit to the dentist;
- carious process - since it is difficult to fully care for eighth molars, this often leads to the development of caries due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque in the gingival hood;
- inflammatory process - if the infection has also affected the soft tissue of the gums, then it is better not to delay the removal of the problematic tooth, this can lead to the development of gumboil or the formation of a purulent cyst.
Complicated eruption of wisdom teeth
As already mentioned, whether it is worth removing a tooth is up to the attending physician to decide. The practice of foreign and Russian dentists differs; while European doctors prefer to extract eighth molars right away, Russian doctors are in no hurry to remove them (if the tooth has grown, it means it is not superfluous). Therefore, if the dentist insists on immediate surgery, it means there is a strong indication for it.
The role of the wisdom tooth
Third molars are considered to be rudiments left after a change in the shape of the jaw due to a change in diet; they do not bring any benefit.
But while the eights are being cut, the patient is bothered by pain, the mucous membrane regularly becomes inflamed, which can lead to various complications. Therefore, dentists recommend removing wisdom teeth. Wisdom teeth do not perform any functions. They do not participate in the chewing process, as they are located very deep. At the same time, the last molar creates favorable conditions for the formation of tartar and caries, since cleaning them is inconvenient and difficult. If the patient does not clean the figure eights diligently enough, the plaque persists.
The third molars do not participate in the formation of the bite, since they grow at a fairly mature age, when the jaw has already grown and formed. And if a wisdom tooth begins to erupt at the age of 15, it can negatively affect the bite and cause a shift in the dentition.
Removal process
Whether it is painful to have a wisdom tooth pulled out depends not only on the psychological mood of the patient himself (if he is tense, scared and does not want to cooperate with the dentist, the process may indeed not go so smoothly and may cause pain). Another factor influencing the course of the operation is the type of removal; whether a simple procedure will be performed or a complex one. The first step to consider is simple wisdom tooth extraction.
Easy removal
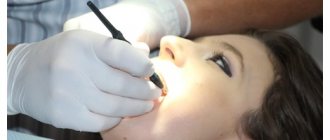
Simple extraction involves the use of only dental forceps and elevators; the process does not involve cutting the soft tissue of the gums, does not separate the roots, and does not use a drill to drill out the bone. Such a procedure, especially if carried out efficiently and carefully, is not accompanied by pain during and after extraction. Simple removal takes place in several stages:
- Anamnesis collection. The doctor asks the patient about complaints, conducts an external examination, and, if necessary, x-rays. The medical history is studied, allergic predisposition is assessed, concomitant diseases are determined, and blood pressure levels are measured. All of these factors can directly affect the course of the operation.
- Conducting anesthesia. Most dental clinics prefer to remove wisdom teeth using local anesthesia. Extraction under general anesthesia is carried out for critical indications and only in a hospital setting, under the supervision of an anesthesiologist.
- Extracting the tooth from the socket using elevators and forceps. An elevator is a special device consisting of a pear-shaped handle, a rod and a working part that acts as a lever. It is applied to the molar being removed, resting on the wall of the socket or adjacent tooth. A simple extraction lasts from 5 to 15 minutes, sometimes the process can take 30-40 minutes, after which the final stage begins.
- Removing the remaining parts of the tooth from the socket and washing the wound with antiseptic solutions. If there is evidence for this, the doctor will inject an anti-inflammatory drug.
After tooth extraction, dentists try to suture the gum to reduce the risk of wound infection and bring its edges closer together.
The process is not accompanied by pain, since the anesthesia is still in effect. Next, the doctor gives recommendations on proper care of the socket during the recovery period.
Difficult removal
For patients who had to have their wisdom teeth pulled out during Soviet times, the fear of dentists remained for many years, because previously the procedure was painful and lasted for several hours in a row. In modern clinics, a drill with a special bur, forceps, elevators and other equipment are used to separate the roots of the eighth molar and reduce the volume of bone tissue.
Previously, dentists' offices were poorly equipped; the doctor had to separate the roots with a chisel and hammer. The coronal part of the tooth was first broken off, and the tip of a chisel was placed on the interroot septum, which was hit with a hammer. If the dentist had the skill, he could divide the root in 1–2 strokes; in difficult cases, the procedure was delayed for several hours.
Perhaps this fact, preserved in the memory of many patients when removing figure eights was very painful, still frightens them, forcing them to delay a visit to the doctor.
Most often, the wisdom tooth is positioned incorrectly and grows at an angle, so an x-ray is necessary before removal. Almost no dentist will undertake an extraction without examining an x-ray, unless the situation is critical, when there is no time or opportunity to conduct an examination. The doctor will also pull out the complex figure eight in several stages:
- Anamnesis collection.
- Preparation for extraction - removal of hard dental plaque, rinsing the oral cavity with antiseptics.
- Carrying out anesthesia in the required dosage so that with the injection the patient does not feel pain for 2-3 hours in a row.
- Cutting the soft tissue of the gums, separating the roots using a drill and extracting them.
- Cleaning the hole from remnants of bone tissue, roots and sawdust.
- Smoothing the sharp edges of the socket using a drill or bone nippers.
- Wash the wound with antiseptic solutions and inject an antimicrobial drug (as indicated).
- Suturing the edges of the wound to avoid infection.
Particular attention is paid to patients whose eighth molar is impacted, that is, has not erupted
Many people face this problem when the dentition does not have enough space for full eruption. In this case, sharp pain occurs in the gums, since the molar growing sideways or horizontally is not visible above the soft tissue, but pushes the neighboring tooth from the inside. If the tooth still erupts on top, but is covered with a hood of gums, this often causes serious suppuration. Such situations require immediate surgical intervention.
Pericoronitis: treatment
If you have inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth, the treatment most often consists of a dental surgeon removing the hood over the wisdom tooth. However, if severe purulent inflammation is observed, then complete excision of the hood is undesirable immediately, because this can lead to various inflammatory complications.
In case of severe purulent inflammation, the hood is first only dissected to facilitate the outflow of purulent discharge, and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed. And the doctor will prescribe you for its complete removal after the active inflammation has subsided. Also, in some cases, the doctor may recommend immediately removing the wisdom tooth (24stoma.ru).
Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth –
Removing the hood of a wisdom tooth involves excision of the overhanging mucous membrane over the erupting eighth tooth. Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth leads to the elimination of conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. This minor surgical procedure is usually less traumatic, but in some cases a large amount of gum tissue must be excised.
Excision of the hood over the wisdom tooth is performed by a dental surgeon under local anesthesia. The procedure is completely painless if you see a good specialist, if the anesthesia is administered correctly and a good anesthetic is used, and not something like novocaine. Pain will appear only after anesthesia has passed (after 30 minutes), so it is worth taking an analgesic even before the pain appears.
- Hood removal: price for 2021 in an economy class clinic in Moscow, a similar service costs about 2,500 rubles. In the regions, the cost of the procedure may be 2 times lower. By the way, in the clinic at your place of residence (if you have an insurance policy and a passport), you should undergo this intervention completely free of charge.
Stages of excision of the hood –
- Conducting local anesthesia,
- Using a scalpel and surgical scissors (less commonly, a surgical laser), the dental surgeon excises the gum overhanging the tooth.
- Treating the wound with antiseptics.
- An iodoform turunda is usually placed in place of the excised hood.
- The doctor gives recommendations and schedules a re-examination.
Removing a wisdom tooth hood: video
Please note that both hood excision operations are performed with a surgical laser and not with a scalpel. Using a laser avoids bleeding, swelling and severe pain. In Russian dental clinics, lasers are practically not used (due to their absence), and only a few clinics can boast of their presence.
After the intervention, the following are prescribed:
- Antiseptic baths with chlorhexidine solution 0.05% (3-4 times a day);
- Antibiotics are not prescribed in every case;
- for pain - good tablet analgesics.
Usually this is enough for you to completely forget what wisdom tooth pericoronitis is after 4-5 days.
However, if the doctor performed the operation traumatically, the pain may last for 7-10 days. If you want to remove inflammation as quickly as possible, then after antiseptic rinses, you can additionally apply CholisalGel to the hood 2 times a day in the morning and evening (it has a pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect). Remember that if you put gauze soaked in iodoform on the wound surface, you need to remove it yourself no later than the next day. Then it itself will become a breeding ground for infection. After you take out this turunda, it may cover a little. Then it is advisable to treat the wound with a gauze swab soaked in 3% hydrogen peroxide.
Important: in some cases, the hood may form again, in which case either a repeat operation may be required, or the issue of tooth extraction will be decided. Often these teeth are in an incorrect position. An experienced doctor can quickly determine the chances of the eighth tooth taking the correct position using an x-ray and external examination of the tooth.
In what cases is it better to immediately remove a tooth with a hood -
If your gums near your wisdom tooth are inflamed, the most radical treatment method will be the removal of the 8th tooth, above which the ill-fated hood appears.
This will solve the problem permanently, but you must be prepared for the fact that the eighth teeth may have curved roots (this can be checked by taking a photo) and then removal may be difficult. Situations where deletion is the best solution to the problem -
- Firstly , when the lower jaw is insufficiently long, which means there is not enough space for the eruption of a wisdom tooth. Removal in this case will prevent the remaining teeth from being displaced by the erupting tooth, and will prevent the development of crowding of teeth in the anterior part of the lower jaw.
- Secondly , if the 8th tooth has a strong inclination towards the cheek or the seventh tooth, then it will still have to be removed sooner or later, because it will injure either the buccal mucosa or the root of the 7th tooth, respectively.
For more information about the difficult eruption of wisdom teeth, read the article: → “Features of the growth and eruption of eighth teeth”
Removal methods without pain
To ensure that the removal of problematic eighth molars is painless, dentists have a number of anesthetic drugs that are selected depending on the clinical situation. Previously, extraction was carried out using the drug Novocain, which was a good pain reliever and was considered a low-toxic substance. However, during the tests, a large number of various complications after its use were confirmed, from allergic reactions to anaphylactic shock.
Anesthesia for wisdom tooth removal
Today, there are much more effective and safe drugs that allow extraction to be carried out quickly and painlessly. Lidocaine is also a common drug - it is used in most budget dentistries; the drug shows good results in pain relief, which are several times higher than those of Novocaine.
There is rarely an allergic reaction to the product, however, during prolonged manipulations, doctors have to administer a large dose of the substance from 3 to 10 ml. To administer Lidocaine, plastic syringes with not very sharp needles are used, which is why the patient feels severe pain after the operation. This explains the fact why it is painful to swallow after extraction, and the discomfort intensely radiates to the ear and throat.
To avoid pain and discomfort for the patient during removal, dentists give preference to articaine drugs, such as Ultracaine, Septanest, Ubistezin
They are administered using carpule metal syringes, the ampoule does not need to be opened, contact with air is excluded, and the dose of adrenaline intended to extend the freezing period is precise. This reduces to zero the risk of complications such as rapid heartbeat, dizziness and panic. For weakened patients, disabled people, pregnant women and adolescents, Scandonest injections are more suitable - this drug does not cause vasodilation and does not contain adrenaline.
Why does pain persist after extraction?
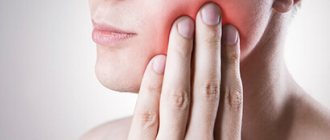
Many patients, after wisdom tooth extraction, experience intense pain during the recovery period, but they do not know why the discomfort occurs and how long it will last. The severity of the pain syndrome here may depend on whether the lower or upper wisdom tooth was removed, a simple or complex procedure was performed, and also what the patient’s individual pain threshold is.
It should be clarified that when a tooth is removed from below, the pain in the recovery period will be more pronounced. The lower jaw is more massive than the upper jaw, and the molars have a more curved and thicker root structure. Therefore, extraction on the lower jaw is often carried out in complex versions, and damaged soft tissues hurt more.
The reason for the pain lies in the fact that the removal procedure itself is an injury; it is associated with an inflammatory process that occurs against a background of tissue swelling and discomfort. The symptoms cannot be called pleasant, but with normal healing of the hole, the signs disappear after 2-3 days. To do this, it is enough to follow medical recommendations.
In some cases, severe pain persists for up to a week, and to relieve it the patient must constantly take anesthetic drugs
If dangerous signs appear 2-3 days after removal, you should contact your dentist again. Such symptoms include severe swelling of the soft tissues, increased body temperature, the appearance of a sharp unpleasant odor from the socket, acute pain in the jaw, radiating to the temple, throat, ear, and neck.
Most likely, the patient has developed alveolitis - inflammation of the socket. A problem arises if a person did not take antibiotics prescribed by a doctor after extraction, began rinsing his mouth on the first day after extraction, or constantly touched the hole with his tongue. The doctor will determine the cause of the symptoms and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Is it possible to treat a wisdom tooth?
It makes sense to treat caries on figure eights if the tooth is in the correct position and is not severely damaged. Third molars are often affected and are located deep, making cleaning difficult.
Plaque accumulates between the seven and eight; in some people, the third molars do not fully erupt and a pocket is formed in which food particles constantly accumulate. This creates favorable conditions for the growth of bacteria.
Treatment of wisdom tooth caries depends on the stage at which the pathology was discovered. Often, deviations are detected when tissue is severely damaged, and the deep location of the molar does not allow the doctor to use the full range of therapeutic measures.
Whether it is possible to treat figure eight, only a doctor will say after assessing the condition of the patient’s oral cavity.
Features of treatment
If treatment is possible, it is carried out in the following order:
- cleaning the crown from affected tissues;
- if the canal is affected, it is also cleaned and washed;
- the doctor restores the integrity of the crown using filling material.
There is no point in treating a severely damaged figure eight. It will be difficult for the doctor to clean out the affected tissue so deeply. And if the bacteria remain under the filling, damage to the adjacent sevens and jaw bone will begin. To play it safe, it is recommended to remove the third molar.
Removal is carried out in the following order:
- The doctor conducts an examination, collects anamnesis, and prescribes tests if necessary. If general anesthesia is indicated, you will need to take a blood test, do an ECG, and consult with a therapist.
- An anesthetic drug is selected and administered to the patient.
- Once the anesthesia has taken effect, the surgeon removes the third molar along with the root. If the wisdom tooth is under the gum, it is cut.
- The hole is washed with an antiseptic and Alvogil paste is applied - it is an antiseptic and hemostatic agent.
- If necessary, the wound is sutured and covered with a gauze pad to stop bleeding.
After a complex operation, you will need to take antibiotics and painkillers.
How to prevent pain
To reduce the risk of inflammatory processes in the socket and the development of pain, the doctor gives the patient recommendations on how to behave immediately after extraction:
- hold a sterile swab between the teeth, which is placed to stop gum bleeding for at least 20 minutes;
- refrain from eating for 2–3 hours after removal;
- take a painkiller tablet in the first 1–2 hours after the wisdom tooth root has been removed, Ketorol, Ketanov, Baralgin are suitable;
- avoid smoking, alcoholic beverages, spicy foods, hot and cold drinks, physical activity on the first day;
- rinse with antiseptic solutions Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, chamomile decoction, starting from the second day after extraction (this cannot be done earlier, so that a blood clot will form in the hole, it will protect the wound from infection);
- apply antiseptic ointments and gels to the affected area - Metrogyl Denta, Asepta, Cholisal, Solcoseryl.
Antibacterial drugs are usually prescribed in cases where a tooth has been pulled out, surrounded by suppuration or with flux located nearby. Then the patient is required to take the drugs for at least 5–7 days in a row, in order to avoid recurrent complications
As you can see, modern dentistry has stepped far forward, giving patients the opportunity to remove problem teeth painlessly and with the least risk of complications. The drugs used today for anesthesia do not cause side effects or allergies, have a quick and long-lasting effect, allowing you to reduce discomfort to a minimum. After extraction, you do not need to go to the dentist to remove the sutures again - doctors use self-absorbing threads, as they save the tissue from additional trauma.
An important point is the psychological mood of the patient himself. Having read and heard stories about terrible pain during tooth extraction, a person delays a visit to the doctor, provoking complications that can be avoided by seeking help in a timely manner. Therefore, you should not be afraid of the dental chair - the doctor will do everything possible to ensure that the patient does not experience discomfort, and the fear of dentists is a thing of the past.
How long does it take to heal?
In the first days after surgery, it is difficult to understand whether the gums are healing normally or with complications, because the blood clot has a whitish tint, similar to pus, and the gums can be very painful. To avoid mistakes, dentists recommend an examination 3 days after surgery. The doctor will evaluate the healing process of the wound and give recommendations for treatment.
Partial healing of the wound occurs 10-14 days after surgery, and complete recovery takes 20-30 days. Difficult figure eight removal may result in a longer recovery. Reasons for prolonged healing:
- severe injury to bone and gums;
- absence of a clot in the socket;
- inflammation of the socket;
- the presence of a foreign body in the wound, a bone fragment;
- the patient did not take antibiotics;
- old age of the patient;
- if the doctor did not stitch the wound.
The best way to speed up healing after major surgery is to place stitches in the gums. The suture will prevent infection, and the edges of the mucous membrane that are fastened together will quickly recover.
The patient is advised to follow these rules:
- the cotton or gauze swab is removed after 10 minutes;
- It is forbidden to eat for 3 hours after the operation, you can drink clean water;
- You cannot play sports for 2-3 days after surgery;
- Until the wound heals, it is forbidden to drink alcohol and smoke;
- It is forbidden to chew on the operated side.
If improvement does not occur 3-5 days after surgery, your health worsens and your gums hurt, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Reviews
Olesya: I was terribly afraid to go remove the wisdom tooth from below - I rinsed my mouth with chamomile, took painkillers, but the pain did not go away. After 5 days of torment, I finally decided to go to the appointment, the doctor scolded me that I provoked inflammation of the gums. After the removal, my entire jaw hurt, I again took painkillers, and also antibiotics, since I myself started the infectious process. After 2-3 days everything returned to normal, the pain went away, but I still regret that I didn’t go to the doctor on time - pulling out a tooth with an injection was not scary at all, I didn’t feel anything.
Oleg: Two years ago I had my upper wisdom tooth removed, then everything went smoothly, the whole process took literally 5 minutes. After the anesthesia wore off, my teeth hurt, but not too much - I took only one tablet of Ketorol. Recently I had to remove a figure eight from below - the process took much longer (as the doctor explained, the tooth had thick, curved roots). During the removal, I didn’t feel anything, it didn’t hurt, but then I couldn’t sleep for two nights - my gums were severely injured. Now everything is fine, it has healed, there were no complications.
Irina: My first wisdom tooth at the bottom grew straight and didn’t cause any problems, but a year later it was struck by caries. The hollow grew very quickly, and soon severe pain began. I went to the doctor, he said that the caries was already very deep, and there was no point in treating the tooth - the eights very quickly collapse and rot, and he suggested removing it. I was very afraid, but the doctor sent me for an x-ray, the roots turned out to be smooth and thin, so it didn’t hurt when removed. My jaw ached for about two days, but then the discomfort went away, so I shouldn’t have worried that something would go wrong.