Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
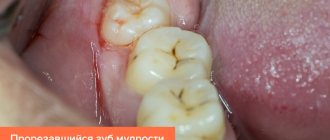
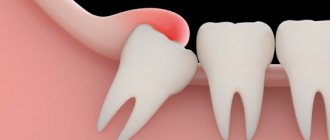
Pericoronitis is a popular dental disease that most often affects the gums of the lower jaw near the wisdom tooth. This is an inflammation of the gingival structures that occurs due to teething. The main thing is not to confuse periodontal disease. As a rule, the pathology occurs in people of older age groups and is accompanied by very unpleasant symptoms.
“Eight” is considered one of the most problematic teeth. Not surprisingly, these teeth appear later than all others, there is little space left for them. Therefore, often the wisdom tooth remains in the jaw without erupting. Sometimes the “figure eight” rests on neighboring teeth and cheeks, grows at an angle and causes a lot of unpleasant sensations.
Causes of pericoronitis
The disease most often results from:
- epithelial injuries due to difficult long-term tooth eruption;
- impacted (formed, but not erupted outward) teeth;
- atypically located tooth roots;
- thickening of the gum mucosa;
- accumulation of soft plaque under the hood and, accordingly, infection of tissues;
- reduction in the size of the dental arch, lack of space for teething;
The catalyst for pericoronitis of wisdom teeth is often a source of infection in the oral cavity. Very often the disease is provoked by caries, stomatitis or periodontitis. Sometimes the disease occurs against the background of ignoring the rules of personal hygiene, prolonged stress, hypovitaminosis and other conditions accompanied by decreased immunity.
Symptoms of tooth pericoronitis
The main clinical manifestations of dental pericoronitis may be the following symptoms:
- swelling of the soft tissue of the gums in the area of the growing tooth;
- redness of soft tissues;
- pain that worsens when eating and brushing teeth;
- pain radiating to the temple, ear or eye socket (on the affected side);
- Difficulty opening the mouth and talking due to pain and swelling;
- bad breath;
- purulent discharge from under the gingival hood;
- increase in body temperature to 37.5 degrees.
If the disease has acquired a serious form, an increase in the submandibular and parotid lymph nodes (on the affected side) is observed, as well as a significant deterioration in the patient’s well-being.
Meanwhile, the most characteristic manifestations of wisdom tooth pericoronitis are:
- swelling of the gums;
- redness of the gums;
- pain in the gum area.
Often, with acute pericoronitis, the swelling is so severe that the patient has difficulty speaking and it becomes difficult to open and close his mouth.
Removal Features
As a rule, operations to remove third molars are always considered difficult, since these are the teeth that usually cause more problems. The operation can be simple, provided that the “figure eight” is located on the upper jaw and does not have pronounced developmental abnormalities. In all other cases (as well as in situations where the tooth is in the upper jaw, but has strong, curved and branched roots), the operation is considered complex and must be performed by a qualified dental surgeon.
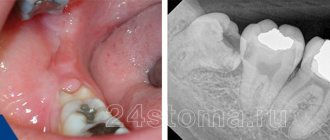
Before performing an intervention, the doctor determines possible contraindications for a particular patient, examines an x-ray of the problem area and determines the optimal tactics for the operation. The duration of the procedure ranges from 1-10 minutes for simple removal and up to 20-120 minutes for complex removal, requiring a series of manipulations and suturing of the hole.
Types of pericoronitis
Depending on the complexity and localization of inflammation, pericoronitis is divided into:
- Spicy.
The initial stage of the disease, which is characterized by pain, hyperemia and swelling of the gums. In case of acute pericoronitis of a wisdom tooth, there is no purulent discharge and the general condition of the patient does not suffer. With proper timely treatment, this type of disease disappears in 3-5 days.
- Ulcerative.
The disease develops against the background of epithelium damaged by fusospirochetes. A characteristic symptom of ulcerative pericoronitis is the appearance of a necrotic rim along the edges of the gums. Small ulcers form on the mucous membrane. When plaque is removed from the gum surface, bleeding begins.
- Purulent
Pericoronitis, as a rule, occurs in a subacute form and is manifested by severe pain. Pus is released from the source of inflammation, and the temperature rises. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease can provoke the formation of abscesses, phlegmon and periostitis.
- Posteriormolar.
The disease develops when molars erupt incorrectly. A gingival hood forms, which then becomes infected due to the active proliferation of bacteria.
What are wisdom teeth?
Dentists and scientists call them a vestigial organ, the need for which disappeared when people learned to heat food. Eights, like all other human teeth, consist of roots, a neck and a crown, but despite this they have certain anatomical features.
Here are the main differences:
- they are only indigenous and do not come in milk;
- their eruption is often accompanied by pain;
- have a larger number of roots - from 2 to 5;
- bent and twisted roots.
Treatment of pericoronitis
Treatment by a dentist and surgeon should be aimed not only at eliminating the symptoms of the disease, but also at eliminating its causes. As a rule, for wisdom tooth pericoronitis, drug therapy and surgical intervention are used.
Drug treatment is the fight against microorganisms that caused the development of the infectious process. The doctor also prescribes medications that reduce pain and inflammation symptoms.
As a rule, the following groups of drugs are used to treat wisdom tooth pericoronitis:
- antiseptics, mouth rinses. The products reduce the microbial load and wash away bacterial and purulent particles.
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Ibuprofen, Ketorolac.
- antimicrobial, broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory drugs, for example, Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Azithromycin.
Surgical intervention for wisdom tooth pericoronitis usually involves excision (removal) of the gum hood over the wisdom tooth. This tactic is chosen in case of frequent relapses of the disease, pronounced pain syndrome, and spread of the purulent process to surrounding tissues. When an area of soft tissue is excised above the surface of the crown, plaque stops accumulating, which prevents infection and progression of the disease.
Excision of the hood takes no more than 10-15 minutes and is performed under local anesthesia.
If removing the hood and conservative treatment does not lead to an improvement in the condition, it is possible to remove the wisdom tooth. Removal is also carried out in case of incorrect tooth position or significant deviation of the “figure eight” from its physiological axis. In rare cases, not only the wisdom tooth is removed, but also part of the bone tissue. After removal, in almost 100% of cases, the patient recovers completely.
It is worth noting that many patients often insist on maintaining the “eight”. Many believe that in the future a wisdom tooth may be useful if prosthetics are needed. However, such an opinion is wrong. The wisdom tooth is located the farthest away and does not bear a significant functional load, taking only 2% of the total load on the dentition. When installing a crown, the wisdom tooth will not withstand the pressure, and the prosthesis will have to be replaced very soon.
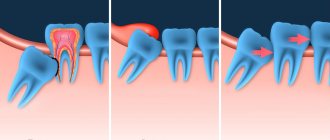
Method for removing a horizontally lying figure eight
Any position of a wisdom tooth identified as a deviation from the norm implies an unambiguous recommendation for complex removal. The operation falls into this category because it requires a series of traumatic actions for the patient to extract the tooth completely.
The intervention can be complicated by various unpleasant consequences, so before the operation the surgeon carefully prepares and calculates possible options for the development of the situation. An X-ray is mandatory.
Most dentists vote for early removal of the impacted figure eight. Over the years, the molar roots grow strongly and the jaw bones become denser, which prevents the tooth from being quickly removed from the socket. In youth, tissues are restored faster, and discomfort is experienced more easily.
However, the complexity of the operation is quite surmountable, and it occurs under strong anesthesia. The patient does not experience pain during removal.
Can you put a crown on a wisdom tooth?
Step-by-step method for extracting a horizontally located wisdom tooth:
- The use of an anesthetic, the drug “Ultracaine” is mainly used;
- Making an incision in the gum to expose an impacted wisdom tooth;
- If access to the roots is difficult, sawing the bone is necessary. The manipulation is performed extremely carefully, without the risk of damaging the adjacent tooth;
- Application of forceps and removal of the figure eight using loosening technology;
- When the third molar is in a recumbent position, the dentist first saws the tooth into pieces and removes them piece by piece;
- Suturing the incision on soft tissues with the application of a cotton-gauze swab. If self-absorbable suture material is used, no further treatment of the wound is required. In case of direct suturing, the sutures are removed at a doctor’s appointment in the clinic.
At the last stage of the operation, ice is applied to the extraction area, thus preventing the formation of severe swelling of the gums. The doctor discusses the possible consequences of the intervention: increased temperature, tissue soreness due to injury, bleeding. In this case, the normal limits are indicated, if exceeded, you should immediately contact the clinic.
Rinse
Special rinses will help relieve pain and swelling at home. However, such treatment is symptomatic. If inflammation progresses, in no case should you limit yourself to rinsing only.
The treatment for inflammation recommended by dentists is ASEPTA Active mouth rinse. This unique two-component product with a combination of “chlorhexidine + benzydamine” has an antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory effect and provides an immediate analgesic effect.
To eliminate inflammation and relieve discomfort during wisdom tooth pericoronitis, it is possible to use such medicinal herbs as:
- chamomile;
- sage;
- calendula.
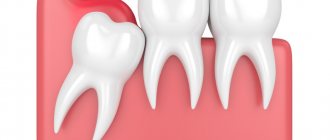
Symptoms and signs of abnormal growth
It is extremely rare for eights to appear without any complications. This is due, first of all, to the fact that wisdom teeth grow in adulthood, when the jaw is already formed. Even with proper teething, discomfort may still be present for several weeks or months. If a wisdom tooth grows incorrectly or has an abnormal location, then certain symptoms indicate this.
Let's take a closer look at the types of pathologies and symptoms associated with the growth of wisdom teeth.
- Retention is a pathology in which the third molar is located under the mucous or bone tissue. The main symptoms are severe pain in the gums, as well as the development of an inflammatory process in the gum pocket.
- Dystopia or abnormal position of the tooth. It manifests itself as severe pain, affecting adjacent teeth, and the development of inflammation, including phlegmon or osteomyelitis.
The initial alarming symptoms that a patient may identify when a wisdom tooth grows are:
- Swelling in the cheek area.
- When swallowing, severe pain occurs, radiating to the throat or ear.
- Purulent or bloody discharge.
- Injury to the mucous membrane.
If you detect at least one of the above symptoms during the eruption of figure eights, you must seek the help of a dentist as soon as possible. The doctor will conduct an x-ray and determine whether the wisdom tooth is growing correctly.
Possible consequences
Pericoronitis of the wisdom tooth in the lower jaw is a rather dangerous disease, ignoring which can lead to very unpleasant consequences.
Possible complications of the disease may be:
- abscesses, phlegmon of the vestibule of the mouth, buccal area;
- periostitis;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- periodontitis;
- ulcerative stomatitis;
- actinomycosis;
- paradental cysts.
In addition, if wisdom tooth pericoronitis affects the lymph nodes, if inflammation develops, the lymphatic system may become a victim of infection.
And, of course, without proper treatment, the disease can become chronic and periodically “harass” the patient with unpleasant symptoms. Inflammation can spread to neighboring healthy teeth. Therefore, in order to avoid complications, treatment of the disease should be carried out as early as possible.
Function of the eighth molars
Dentists call them spares. Where does the wisdom tooth grow? It stands on par with the others, is classified as molars, but is practically not used for chewing food. The main purpose is to hold teeth so that they do not become loose and move apart. If a nearby molar is lost, it will take its place and perform the necessary functions. During dental prosthetics, the figure eight can become a support. During development, the human skull has changed, the jaw has become smaller and there is no room for a molar. Young people do not have such a tooth even in its rudiments.
Prevention
As you know, it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. The main disease prevention measures are:
- annual dental examinations;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of impacted molars;
- maintaining oral hygiene;
- timely treatment of caries, gingivitis, periodontitis and other dental diseases;
- Regular (once every six months) professional teeth cleaning in a dental clinic.
Remember: pericoronitis without proper treatment can cause very serious complications. Therefore, if you suspect inflammation, do not delay your visit to the dentist. The doctor will help you cope with unpleasant sensations in a matter of days and prevent the development of the disease.
What to do: treat a wisdom tooth or remove it?
Many people are often interested in the question: is it better to use the services of a dentist at the stage of intramaxillary development and remove a rudimentary tooth so that it does not create problems later?
However, most experts agree that preventive removal of eights is unacceptable. When the tooth has erupted correctly and does not cause any discomfort, it can be preserved. The main thing is to carefully observe the rules of hygiene and visit the dentist on a regular basis to monitor and perform hygiene procedures.
Removal is resorted to in cases where conservative treatment methods cannot achieve the desired result.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- The role of hygiene products in the treatment of periodontal diseases (S.B. Ulitovsky Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Honored Dentist StAR Prof., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Department of Preventive Dentistry of Pavlov Pavlov State Medical University, St. Petersburg) S.B. Ulitovsky - Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Honored Dentist of StAR, Prof., Doctor of Medical Sciences; E.S. Alekseeva - associate professor, candidate of medical sciences; A.A. Vasyanina - associate professor, candidate of medical sciences; V.A. Grigoriev - Associate Professor, Ph.D.
- The use of drugs from the Asepta line in the complex treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (N.V. Berezina E.N. Silantyeva S.M. Krivonos, Kazan State Medical Academy. Kazan.) N.V. BEREZINA, E.N. SILANTIEVA, S.M. KRIVONOS Kazan State Medical Academy
The best dental clinic in Ivanteevka
Specialists at Sanident comprehensive dentistry in Ivanteevka offer a wide range of dental services: from caries treatment to prosthetics and restoration. We have innovative equipment, highly experienced staff, high-quality consumables, and at the same time quite affordable prices and promotions. We give a healthy and beautiful smile to everyone!
You can make an appointment with a dentist at our clinic by calling the phone number listed on the website or by visiting us in person at the following addresses:
- Ivanteevka, st. Novoselki, 4 (Ivanteevka railway station);
- Shchelkovo, st. Central, 80 (railway station Voronok).