Tumor of the lower jaw involves complete or partial resection of the lower jaw. If reconstructive surgery is not performed, the person becomes disabled and drops out of society.
Reconstructive surgery is the restoration of the form and function of a body part using a person’s own tissue.
Reconstruction of the lower jaw allows you to completely restore the patient’s appearance, chewing and speech function, without resorting to removable dentures.
Cut options
There are three options for accessing the tumor:
- The classic approach involves an incision along the chin and along the neck fold;
- In most cases, an incision along the chin can be avoided and the operation can only be performed through an “invisible” incision in the neck fold;
- In the case of marginal resection of the lower jaw, the operation can be performed transorally - access through the mouth, without external incisions.
Incision options for resection of the lower jaw
The classical approach is becoming a thing of the past, but in Russia it is still widely used, because Most surgeons do not have the necessary skills to perform an operation only through an incision in the cervical fold.
In my practice, I use all access options depending on the indications.
What are the consequences after tooth root apex resection surgery?
Apexectomy can result in various complications, for example, soft tissue swelling (this is a temporary reaction to injury) or even recurrence of the cyst. All negative consequences are usually divided into two types: conditionally normal and pathological.
Fever
This is the body's natural reaction to injury during surgery. An increase in temperature occurs on the first day after apexectomy. Typically varies between 37.5°C and 38°C. In the evening the temperature rises and drops in the morning. It normalizes on its own in 1-2 days. It is not recommended to knock it down if the mark on the thermometer is below 38°C. But if you feel very unwell (general weakness, dizziness, body aches), you are allowed to take an antipyretic drug. Sometimes fever and chills signal the development of serious complications. In this case, the high indicator lasts 2-3 days after the operation, increases every day and is not knocked down by pills. If there are complications, it is accompanied by additional symptoms:
- pain;
- severe swelling of the soft tissues of the face;
- putrid odor from the mouth;
- the presence of purulent plaque on the wound;
- pressure instability.
With such a set of symptoms, you should immediately contact the dentist.
The tooth is loose
result of tooth root resection
Resection involves removing the tip of the root, which often leads to a decrease in the stability of the tooth. If the root is destroyed during surgery, the tooth will become very loose and may fall out. Also, tooth instability is caused by the patient himself if he loads the operated area with solid food.
The dentist returns the stability of the tooth if you contact him immediately after the problem occurs.
To avoid such a complication, it is necessary to follow a gentle diet in the postoperative period. The tissue healing process lasts 4-6 months, during which time the cavity formed during the operation will completely heal, and then the stability of the tooth will become the same. Until this moment, you should not chew nuts, dry foods, or hard candies on the operated side.
White gums
White plaque can be a sign of a natural healing process or complications: gum inflammation, purulent infection:
- A day after surgery, a white fibrin coating forms on the gum.
- After two to four days, the plaque becomes most noticeable.
- By day 7, swelling subsides, pain disappears, but the gums remain white.
- By day 14, the plaque disappears, new mucous tissue forms underneath it, and the gums acquire a normal color.
The following symptoms indicate the development of a purulent infection:
- severe increasing pain;
- bleeding or profuse ichor (the wound is bleeding);
- rotten smell;
- swelling and redness of the gums for more than a week;
- change in color of plaque to yellowish, gray, brown;
- poor general condition.
This consequence will have to be treated with anti-inflammatory and antibiotics, and can be prevented by rinsing with antiseptic solutions (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine).
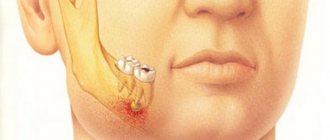
Polypous purulent sinusitis
Apexectomy of the upper dental units is accompanied by the risk of breaking through the wall of the maxillary sinus. If this happens, a fistula forms between this cavity and the vestibule of the mouth, which subsequently provokes purulent polypous sinusitis. Its symptoms:
- pain in the lower part of the eye sockets;
- nasal congestion;
- speaking through the nose (nasality);
- it hurts to chew, press on the disturbing area and move your mouth;
- constant headaches;
- weakening or loss of sense of smell;
- purulent fluid from the nose;
- sensation of the presence of a foreign object in the nasopharynx.
This complication is treated with conservative and surgical methods. Conservative treatment consists of taking antibiotics and intranasal hormonal medications (such medications include Mometasone furoate). Surgical treatment involves closing the fistula.
Bleeding from the nose
Nosebleeds during surgery or immediately after indicate perforation (break through) of the bone of the nasal sinus. It can open during resection of the upper teeth, since the roots in the jaw are located close to these sinuses, which is why the sinuses are easily injured at the slightest careless movement of the doctor. If a sinus perforation occurs, the doctor must stop the bleeding, make sure that nothing gets into the hole (perhaps a piece of the root has fallen off and pressed in there), disinfect and close the resulting wound. Then antiseptics for rinsing, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. If fragments and foreign objects get into the sinus, a more serious operation will have to be performed.
Painful sensations
The resection itself is completely painless thanks to anesthesia, but when it wears off (2-3 hours after the procedure), the patient may experience soreness, which is a natural reaction to injury. In the first few hours after surgery, the gums ache very much. The drugs Diclofenac, Dicloberl, Ketanov and the like, which will be recommended by the dentist, will help relieve pain. With each subsequent day, the severity of pain decreases. After 3-5 days it goes away completely. If the pain throbs, the sensation does not go away after 3-5 days, you need to contact the dentist again.
Damage to the maxillary, nasal sinuses, and blood vessels of the jaw
problems associated with resection of the roots of teeth
Damage to the nasal maxillary sinuses during resection of the roots of the upper tooth is manifested by severe bleeding with air bubbles in the blood, a nasal voice of the patient and bleeding from the nose. This postoperative complication is eliminated on the spot. Damage to large blood vessels is manifested by prolonged bleeding from the wound. Stops with sterile swabs with vasoconstrictor medications. If it opens at home, you need to apply a gauze swab to the wound, press it and change it periodically. If the bleeding does not stop within 2-3 hours, you should seek help. To prevent bleeding, you should stop taking blood thinning medications before surgery and not take them after the procedure.
Numbness of the face
This symptom is possible when the trigeminal nerve and its branches are damaged or irritated. Main symptoms:
- nagging pain;
- burning sensation in soft tissues;
- numbness of the soft tissues of the cheek (the cheek hangs and cannot be felt);
- weak sensation when touching the cheek.
Damage to the trigeminal facial nerve is extremely rarely caused by an instrument. More often, irritation occurs due to the pressure that the filling material exerts on the branches. If there is numbness in the face, a course of neurological treatment should be carried out in combination with addressing the cause of the nerve damage.
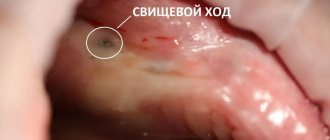
Suppuration, fistula, lump, abscess
A fistula is a channel connecting foci of infection to the surface of the gum, through which pus comes out. Its appearance indicates poor quality cleaning of the dental canal and wound during the operation. This can be avoided by sealing the perforated area with a special filling, which the dentist must do. Also, the complication is often provoked by the patient by improper oral care in the postoperative period. To prevent gum decay (formation of a purulent lump), it is necessary to regularly disinfect the oral cavity after surgery: rinse with antiseptics (for example, Chlorhexidine) or soda solution. Treatment of complications in the form of a purulent fistula is carried out in two ways:
- Medication with antibiotics (Levomekol, Lincomycin, Metranidazole).
- Surgically (the seal is opened and cleaned so that all the pus comes out).
The success of resection depends not only on the professionalism and experience of the dentist, but also on the patient’s compliance with all prescriptions during the rehabilitation period.
Operation
When reconstructing the lower jaw, a flap from the leg is usually used - the fibular flap. The operation is planned on a computer: the surgeon determines how to correctly select the flap, how to remove the tumor, and how to implant the flap.
Computer-aided planning of mandibular reconstruction
If the patient plans to install dental implants, then an implant surgeon is involved in planning and performing the operation. Tumor removal, reconstruction and implantation are performed in one operation.
Without nutrition, the transplanted flap dies. To avoid this, the feeding vessels of the flap must be sewn into the bloodstream. Since the feeding vessels are very small and fragile (less than a millimeter in diameter), to work with them the surgeon must have microsurgical equipment - be able to suture microscopic vessels under a microscope so that they do not bleed or become clogged.
What causes complications?
Negative consequences often arise either due to medical error or the fault of the patient during rehabilitation. Causes of resection complications:
- Late filling. This procedure is carried out 1-2 days before the apexectomy, otherwise there is a risk of inflammation occurring after the operation as a negative reaction.
- Poor quality filling. The canals inside the tooth must be sealed, otherwise an inflammatory process will occur if the infection continues to spread.
- Tooth decay. If the treatment is handled incorrectly during surgery, there is a risk of damage to the tooth, which will lead to its loss.
- Unprofessionalism. Sometimes serious damage during surgery is caused by the doctor due to improper use of the instrument or careless handling of it.
- Incomplete resection. If the inflamed tissue and source of infection are not completely removed, then a recurrence of the cyst is possible in the future.
- Tissue infection occurs during surgery due to incomplete sterility or after improper oral care.
- Root destruction. The operation involves removing only the tip of the root, a minimal part of it, but if the dentist makes a mistake, the root can completely collapse, causing the tooth to become loose.
- Failure of the patient to comply with postoperative appointments. Proper care, lack of physical activity, diet and other medical prescriptions speed up the rehabilitation process.
Symptoms
Exostosis of the tooth appears in the form of a convex growth that appears for no apparent reason. Main symptoms:
- Sensation of a foreign body in the mouth;
- discomfort when eating, talking (with large osteophytes);
- pain when pressing on the tumor;
- redness, thinning of the mucous membrane in the pathological area.
A small anomaly can only be detected during a dental examination, since visually it does not manifest itself in any way.
Treatment of dental cyst: methods
Most often, treatment of dental cysts is carried out jointly by dentists - a therapist and a surgeon.
Therapeutic treatment of a dental cyst is aimed at sanitation, or cleaning of the root canals - it is necessary to remove the source of infection and the cause of the cyst. First, the dentist-therapist processes the root canals and fills them with antiseptic paste for a period of 1 week to 1 month, as in the treatment of periodontitis. Then he fills the root canals with gutta-percha and sealer. Sometimes, especially in young patients, therapeutic treatment of the cyst is quite sufficient.
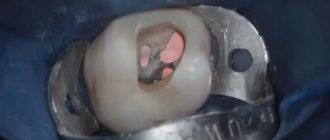
Surgical treatment is an operation to remove a cyst from bone tissue, sometimes this operation is accompanied by resection of the apex of the tooth root. The technique of apex resection is generally simple, but the operation is a complex surgical procedure and, like any operation, it must be taken seriously.
If resection is not done in time, the infection will spread upward through the root canals and can spread to the entire jaw. The consequence is that you may have to schedule the removal of all inflamed teeth. Therefore, you should not joke with such inflammations!