From this article you will learn:
- Why does pain occur after wisdom tooth removal?
- What are the complications after wisdom tooth removal?
- what to do if you have swelling of your cheek or bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth.
After wisdom tooth removal, patients may experience various symptoms - pain, swelling of the gums or cheeks, fever, painful opening of the mouth, painful swallowing, etc. Depending on the initial situation (for example, the removal was carried out against the background of inflammation, the removal was difficult...) - these symptoms may be natural, or they may, on the contrary, signal the development of complications.
Pain after wisdom tooth removal –
1) If the removal was simple - if your wisdom tooth was removed and your gums hurt, then you shouldn’t despair right away, because pain is a normal reaction of the body to any injury. If the removal was simple, then pain occurs immediately after anesthesia and can last from several hours to 1 day (normal).
2) If the removal was difficult - if during the removal the dentist had to make incisions in the mucous membrane, drill out the bone tissue or remove the tooth piece by piece, then you need to be prepared for the fact that the pain can be quite severe and the healing process will take a long time. Normally, after a complex removal, pain may be present even for about a week, but they should gradually decrease, which indicates normal healing and the absence of inflammation.
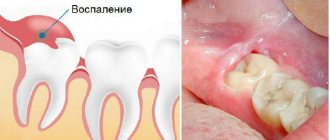
3) When pain should be a cause for concern - pain after wisdom tooth removal should gradually subside - this indicates the ongoing healing process. But, if suddenly the pain does not decrease within 1-2 days after removal, but remains stable or even increases, then you should sound the alarm and run to the dentist. An increase in pain in this case will indicate the development of inflammation in the socket of the extracted tooth, which is called Alveolitis.
Reasons for the development of alveolitis:
- Loss of a blood clot from the socket of an extracted tooth (empty socket) - as a result, pathogenic microbes from the oral cavity and food debris enter the socket, which causes inflammation. By the way, the clot may fall out of the hole as a result of intensive rinsing of the mouth, so you should not rinse your mouth intensively.
- Exposure of the bone tissue of the alveoli in which the tooth was located (Fig. 3) - this can happen for various reasons, for example, when the sutures diverge...
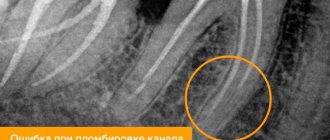
- Suppuration of a blood clot in the socket of an extracted tooth - in this case, the socket will be filled with necrotic decay of the blood clot and food debris (Fig. 4).
Suppuration can occur, for example, if part of a tooth and a mobile fragment of bone tissue were left in the wound. Suppuration is also possible if the tooth was removed due to inflammation or there are carious teeth in the oral cavity - in these cases the clot will come into contact with a purulent infection. However, alveolitis during clot suppuration does not always look like in Fig. 4. Externally, the wound may be quite healthy, for example, only a narrow entrance hole may be visible (Fig. 5), but inside the hole there has been necrosis of the clot and its disintegration.
What to do - alveolitis, exposure of bone tissue requires emergency intervention by a dentist. There is no point in enduring pain, and self-medication with rinses and antibiotics will not help. Also, an unfavorable symptom should be considered if the pain is accompanied by increasing swelling and temperature.
Recommendations for pain relief
Not everyone has the opportunity to visit a dentist immediately when painful symptoms or discomfort appear. Can I relieve pain on my own? How to soothe the mucous membrane, reduce inflammation and bleeding? Before going to the dentist, you have at your disposal traditional medicine recipes:
- Soda solution. Effectively copes with swelling and pathogenic bacteria, prevents infection. used as a rinse.
- A decoction of oak bark and sage. We prepare a complex medicinal product as follows: take 5 tablespoons of each component, add 0.5 liters of boiling water. Let's give it time to brew. Use warm, rinsing your mouth at least 7-8 times a day. The product heals damage, reduces inflammation, and kills pathogenic microflora.
- Turnip decoction. Pour 200 ml of water into chopped root vegetables (3 tablespoons) and boil. Cook over low heat for 15 minutes. Used for rinsing once an hour.
- Saline solution. Dissolve 1 teaspoon of salt in a glass of water. Used for rinsing, without restrictions. It relieves swelling and inflammation well.
- Sea buckthorn oil. This valuable oil is used for applications on mucosal erosions. Quickly restores tissue structure and has regenerative properties.
- Melissa infusion. Take 2 tbsp. spoons of raw materials, add 0.5 liters of boiling water. Wrap the container with the preparation well and let it brew for 4 hours. Recommended for rinsing, up to 4 times a day.
- Chicory root infusion. Prepared similarly to the previous recipe. Has a powerful anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
If the expected effect from using folk remedies is not observed, and the discomfort only intensifies, then use medications from your home medicine cabinet. Most of them are also useful for deep erosions.
- To eliminate intense pain, use Nurofen, Ketorol, Tempalgin, that is, those painkillers that are available without a prescription. However, long-term self-medication with these drugs is not permissible, otherwise addiction or intoxication may occur.
- A more powerful painkiller is Etoricoxib. But it can only be taken once a day - 1 tablet. This is a long-acting drug that also has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Use Chlorhexidine, Angilex and Eludril solutions for antiseptic mouth rinses. Between applications - up to 4 times a day, keep the same intervals.
- Gels "Cholisal" or "Kamistad", which are complex-action preparations based on herbal and medicinal components, will help relieve inflammation of the mucous membrane. Lidocoin, which is included in their composition, will provide local anesthesia.
Once again, we draw your attention: do not put off going to the doctor! Even using all of the above remedies and medications, you will not eliminate the problem, but only temporarily get rid of pain or relieve inflammation. Only a dentist can eliminate the cause itself. Self-adjustment or tooth extraction is not possible.
Removal
Often, the doctor, having objectively studied all the causes of abnormal growth and the impossibility of further correction, decides to remove the incorrectly growing third molar.
For this purpose, the following manipulations are carried out:
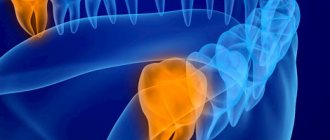
- X-ray diagnostics and computed tomography to clarify the diagnosis and determine the degree of anomaly, the location of the unit and its roots.
- Anesthesia is performed. Due to the fact that the procedure is long and requires surgical intervention, local or general anesthesia is prescribed. The doctor directly monitors the patient both during the operation and in the initial postoperative period.
- The dentist opens the roots of the teeth by cutting the soft tissue in the problem area.
- If required, bone tissue in the root system area is additionally removed.
- It may be necessary to saw the partition, when the roots have to be removed separately.
- The tooth is completely removed from the cavity using instruments.
- The wound is treated with antiseptics and filled with anti-inflammatory drugs.
- The edges of the soft tissues are connected by performing a simple interrupted suture.
- For heavy bleeding, a hemostatic sponge is used.
How quickly and how the operation itself will proceed depends on the complexity of the problem - the location of the tooth and roots, the degree of formation of the unit and its age, depth and other important factors. Sometimes a light incision is required, and the extraction is completed in almost minutes. But the process may drag on if during the operation the doctor needs to perform many complex actions.
Postoperative period
The seriousness of such surgery should not be underestimated. On the contrary, careful preparation for long-term recovery, compliance with medical recommendations and rules, will help prevent possible complications:
- If your doctor has prescribed a course of antibiotics for 5-10 days, strictly follow his directions or instructions. This reduces the risk of infection of the wound surface, suppuration and abscesses, which is often observed with bacterial infection of open deep wounds.
- In the first postoperative days, try not to wash away the blood clot from the bottom of the socket, which performs a protective function, blocking the access of infection deep into the tissues and accelerating the regeneration processes.
- Avoid hard and hard foods for a while so as not to cause irritation or injure the mucous membrane.
- do not use aggressive saline solutions, which is acceptable and justified at the preparatory stage. As recommended by your doctor, use pharmaceutical antiseptics for disinfection and faster tissue healing.
- To avoid hypothermia of nerve endings and to avoid chilling damaged tissues, do not use any ice compresses.
- Temporarily switch to a soft toothbrush; do not touch the damaged area while brushing.
- Control your condition. If it worsens at the slightest level, pain and swelling increase, or fever appears, immediately go to the doctor.
Finally
Do not delay going to the dentist if the problem of wisdom teeth erupting causes discomfort, pain and discomfort. Only competent medical consultation will allow you to outline further tactics of action. In any case, you cannot correct the situation on your own, but you can only harm yourself and significantly complicate the existing problem. Remember that health is most important. Contact the professionals.
Painful sensations will also occur in cases where the figure eight grows to the side or inside the oral cavity.
To get a consultation
Swelling after wisdom tooth removal –
If you have a wisdom tooth removed and your cheek is swollen the next day, then in some cases this is normal:
- When removing an upper wisdom tooth, swelling of the upper cheek may occur (even if the removal was simple).
The appearance of edema in this case is due to the fact that the area where the upper wisdom teeth are located is very richly supplied with blood, and therefore swelling of the surrounding soft tissues occurs. If the removal of the upper wisdom tooth was difficult and was carried out against the background of inflammation, then the occurrence of edema is all the more not surprising. It should be noted that in people whose subcutaneous layer contains more fatty tissue, swelling occurs more often and is more pronounced. - When removing lower wisdom teeth, swelling is natural if the removal was difficult (an incision was made, the bone was drilled, the tooth was sawed) or the tooth was removed due to inflammation. Swelling of the surrounding soft tissue near the removed lower wisdom tooth can lead to painful swallowing or difficulty opening the mouth.
Normally , maximum swelling after removal usually develops the next morning. Over the next 1-2 days, the swelling is stable, after which it begins to slowly decrease. If, against the background of swelling, there is no increasing temperature or pain, but on the contrary, all symptoms slowly decrease, then everything is OK.
When to sound the alarm - if the swelling continues to increase over the next 1-2 days after removal, pain and temperature may also increase, pain when swallowing increases, and the mouth opens less and less - all these are unfavorable symptoms. If you have at least one of the symptoms listed, you need to urgently run to the dentist, otherwise you risk ending up in the hospital.
New over-the-counter pain reliever Pain after wisdom tooth removal? Pronounced analgesic effect!nextpainkiller.ru There are contraindications. Consult your doctor. Does your wisdom tooth hurt? Don't hesitate! Come for a free consultation! We treat teeth and gums quickly and without pain! Our doctors · Reviews · Questions and answers 32dent.ru Moscow 18 + There are contraindications. Consult your doctor.Yandex.Direct
Causes of pain
An erupting tooth hurts for several reasons:
Development of pericoronitis. Above the wisdom tooth there is a hood of soft gum tissue that can completely cover the retracted element. This area is the hardest to clean at home. Gradually, food debris and bacteria accumulate on the gum near the wisdom tooth, triggering the inflammatory process. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, the pathogenic flora spreads to periodontal tissue, causing damage to healthy tissue. The disease requires immediate surgical treatment. The essence of the intervention is that the doctor opens the hood and removes necrotic masses from there. The wound is treated with antiseptic drugs. After the intervention, the patient is prescribed antibiotics to prevent complications.
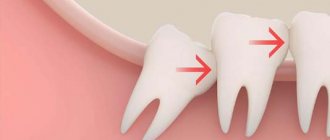
Incorrect growth of the last molar. This is the second most common reason for pain in the gums above the wisdom tooth. If there is not enough space in the jaw for the last element, then it begins to grow sideways, putting pressure on neighboring units or injuring the soft tissues of the cheek. In the second case, stomatitis develops and non-healing ulcers appear on the surface of the mucous membranes. Permanent damage to structures can ultimately lead to the appearance of a cancerous tumor. The treatment regimen in this case is determined by the doctor, depending on the characteristics of the problem.
In the photo, a wisdom tooth injures the mucous membranes of the cheek on the inside
Pain during the eruption of a wisdom tooth is often observed when swallowing, especially if the problem element is located on the lower jaw. At first, the symptom resembles the development of a sore throat, but in this case, discomfort is noted only on one side of the throat. Upon examination, the dentist can easily determine inflammation and swelling of the mucous membranes of the pharynx. On the part of the erupting tooth, inflammation of the submandibular lymph node is noted.
To alleviate the signs of pathology in the first days, it is allowed to use traditional medicine: decoctions of chamomile and sage, tincture of thyme and calendula. It is important that the liquids used are not hot. Heating the inflamed areas leads to the rapid spread of pathogenic bacteria to healthy mucous membranes. The purulent process that begins when heated is often complicated by periodontitis and osteomyelitis. For rinsing the mouth, it is better to use solutions at room temperature.
Why does my ear and head hurt when the last molar erupts? These signs indicate a progressive inflammatory process and the development of severe complications. With pathology, pain radiates to the ear, bridge of the nose, temples and neck. Gels containing lidocaine will help you cope with pain at home. The composition is used to lubricate inflamed gums. Drugs with a powerful anesthetic effect - Nise, Ketorol - can reduce the intensity of headaches.
Due to cutting eights, damage to the trigeminal nerve often occurs. The disease is accompanied by involuntary contraction of facial muscles and headaches. It becomes difficult for a person to talk and eat due to acute sensations. The problem cannot be dealt with at home by rinsing and taking NSAIDs. Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve must be dealt with in a clinic under the supervision of a specialist.
Neuralgic pain will appear until the surgeon removes the problematic tooth. If the unit is abnormally positioned, the roots of adjacent teeth may be destroyed, which can lead to malocclusion. The problem is often observed in cases where the last molar occupies a horizontal position.
Variation of the figure eight arrangement in the oral cavity
Why do my gums hurt when my wisdom teeth grow? In addition to the incorrect placement of the unit in the row, other factors that provoke the problem should be noted:
- Lack of space in the oral cavity. The jaws of modern humans have undergone changes due to dietary habits. Due to the fact that there was no longer a need to chew rough food, the jaw was shortened by 10-12 mm. Often the last teeth do not have enough space to appear on the surface, so they grow incorrectly, putting pressure on other elements, causing swelling of the cheek and an increase in temperature.
- Inflammation of the mucous pocket above the figure eight. Suppuration of the gums leads to inflammation of the problem area and the appearance of throbbing pain in the tooth.
- Secondary infection. Bacteria penetrate into the swollen gums from teething. The situation is noted when there are carious elements in the mouth. Pathogenic flora penetrates into the deep layers of soft tissue, causing gumboil.
- Eruption of caries-affected figure eight.
Why does my jaw hurt when the last molars emerge? The discomfort is due to the fact that eights do not have predecessors, like other molars. The gums in this place are very dense, so wisdom teeth come out very painfully.
Temperature after wisdom tooth removal –
- If the tooth was removed not due to inflammation - If you have a wisdom tooth removed - the temperature can normally rise to 37.5 degrees, but only on the first evening.
The body sometimes reacts to injury with just such a low-grade fever, even if the tooth was not removed due to inflammation. This is especially true if the removal was difficult. Normally, the temperature should disappear the next morning after removal. When you need to sound the alarm - but if the temperature does not subside the entire next day after removal, and even more so continues to increase, then this clearly indicates the addition of an infection. You need to run to the dentist. - If the tooth was removed due to purulent inflammation, in this case the numbers on the first evening may be slightly larger than 37.5. Normally, from the next day the temperature should decrease progressively. If it persists and even increases, then you need to urgently go to the dentist.
When do you need to see a dentist urgently?
Contacting a dentist is required in the following cases.
- Pericoronitis
– the “hood” will be excised. - The figure eight puts pressure on neighboring teeth
- it needs to be removed. - Initial caries
– treatment will be carried out. - Medium, deep caries or rotten tooth
- a clear removal of the figure eight. - The wisdom tooth is loose
- a diagnosis of its condition will be carried out, according to the results of which the molar will be treated or removed. - Pulpitis
– if the root canals are passable, they will be filled.
This list should also include the above symptoms of pathological teething - pain when opening the mouth, swallowing, high temperature. If they appear, you should contact your dentist immediately, since this is a serious inflammatory process, the localization of which requires adequate treatment.
The reason for contacting a specialist may also be the “normal behavior” of the number eight. In this case, the doctor will simply make a small incision on the gum, thereby facilitating the eruption of the wisdom tooth. After a simple procedure, the process will be less painful, and the incision site will heal quickly, after pain for 2 to 4 days.
Bleeding after wisdom tooth removal –
The doctor does not have the right to release you from the clinic if you are bleeding from the socket of the extracted tooth. Usually, in the socket of an extracted tooth, blood clots almost instantly. But with high blood pressure or if a large vessel has been injured, there may be prolonged bleeding.
If significant bleeding occurs during the extraction process, then there is no big problem and the doctor will either suture the wound with suture material, or put a hemostatic hemostatic sponge into the hole of the extracted tooth, or all together (Fig. 8-9).
Often bleeding after tooth extraction occurs after leaving the clinic. Experienced doctors, to be on the safe side (especially if a large tooth is being removed, the patient has a history of hypertension) usually always put 1-2 sutures on the wound to bring the edges of the wound closer together and avoid bleeding. Applying sutures also allows the wound to heal faster.
If bleeding occurs, for example at night, then in this case you need:
- Make a tight gauze swab from a sterile bandage and place it over the socket of the extracted tooth. Clench your teeth so tightly that you feel that the tampon fits tightly to the wound surface.
- Measure your blood pressure. Such things happen very often in hypertensive patients. If your blood pressure is elevated, take the appropriate medication.
- Place ice (a piece of frozen meat in a bag will do) against your cheek, lip - in general, against the area where the removal was performed (Fig. 10). Ice is applied externally; there is no need to put it in your mouth. Usually the ice is kept 2-3 times for 5 minutes (at intervals).
- If none of the above helps and you have to constantly spit out blood clots, and also if you experience weakness or dizziness, then you definitely need to do the following: either feel free to call an ambulance, which will take you to the hospital, where they will put stitches on your wound and let you go home, or independently get to any 24-hour dental clinic, where they will do the same for you (they will put stitches to stop the bleeding).
Prevention of bleeding after removal: you cannot engage in physical labor, take a hot bath, smoke, drink alcohol, make active facial movements (sutures may come apart), and also - hypertensive patients need to control their blood pressure.
For information on how to behave correctly after tooth extraction, read the article: → “Memo on how to behave after tooth extraction”
Hematoma after wisdom tooth removal –
This is a normal phenomenon, albeit an unpleasant one. This is due to the fact that some vessel in the soft tissues was injured. There is no point in blaming the doctor for this, since the doctor, when administering anesthesia, does not see where the vessels pass in your soft tissues. The needle can injure such a vessel. After a few days, the skin may appear blue. Gradually it will pass.
However, the formation of a hematoma may require additional measures. For example, already on this day or the next day after removal, the patient developed swelling of the cheek, a feeling of fullness, pain, and a slight fever. Such symptoms may also indicate the presence of a hematoma. You need to see a doctor; depending on the situation, you may need to take antibiotics, or make a loosening incision along the gum, or both.
If you experience such symptoms, then you should not postpone your visit to the dentist, because... in most cases, swelling and pain in this situation will only increase.
Symptoms
The disease can develop from an acute to a chronic stage and have both purulent and catarrhal forms.
The initial stage is acute catarrhal pericoronitis. It has the following symptoms:
- Local aching pain at the cutting site.
- Swelling of the “hood”.
- Sharp shooting pain radiating to the ear and temple.
- Slight increase in body temperature.
- Headache.
If no treatment is provided at this stage, the disease may progress to the second stage - chronic purulent pericoronitis. In this case, the following signs are observed:
- Improvement in general well-being relative to the first stage.
- Pain when swallowing and chewing.
- The presence of pus at the site where the tooth appears.
- Bad breath.
- Damage to the lymph nodes in the lower jaw.
This stage is the most dangerous and indicates that the inflammation has turned into an abscess and has penetrated deeply into the soft tissue.
The larger the abscess grows, the more difficult it will be to get rid of it completely, which can lead to a cystic cavity.
As a result of these processes, inflammation can also spread to the cheek, causing swelling. At the same time, swelling of the cheek (parotitis) can occur even in the absence of pain in the place where the “third painter” grows. If the wisdom tooth has already erupted and is growing in the wrong direction, then the cheek may also become swollen if it is constantly bitten while eating.