X-rays allow you to make the correct diagnosis, prescribe appropriate treatment, and also monitor the results of treatment.
Myth about the dangers of X-rays in dentistry
It is important to note that x-rays are an absolutely painless procedure that does not require patient preparation and takes only a few minutes. Many people believe that x-rays are harmful to health. Actually this is not true. Of course, if you take an x-ray every day, there may be unpleasant consequences for the body, but x-rays in dentistry rarely require repeated examination, and therefore are completely harmless to the body.
The X-ray rooms of our dental clinic are equipped with the most modern equipment, which allows you to take an image of the oral cavity without harm to the patient.
When X-rays, OPTG and CT may be required
An x-ray is a targeted photograph of one or more teeth. OPTG or orthopantomogram is a panoramic image that captures both jaws. CT is a computer tomogram. It allows you to obtain three-dimensional or volumetric images of the entire human jaw system. Each of these types of diagnostics is used for certain indications:
- X-rays are performed when treating a specific tooth: in the presence of caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, suspected cyst or granuloma. Allows you to determine the extent of tooth damage, as well as the condition of the tissues around the root,
- An orthopantomogram is indispensable in the presence of inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues and jaw bone. It is carried out both during multiple dental treatment and in preparation for orthopedic, orthodontic treatment or dental implantation. Allows you to assess the condition and volume of bone tissue, clarify the position of the maxillary (nasal) sinuses of the upper jaw, nerves and other anatomically important elements,
- CT scan is performed for certain indications. Most often in the presence of tumors of the jaw system (to determine their volume in all dimensions), as well as before dental implantation, especially in complex cases.
Today in dentistry (and in medicine in general) digital devices are used instead of film ones. They have a much lighter load, and they also use shorter shutter speeds to create a photo. For comparison: a modern digital visiograph takes up to 0.3 seconds to take an image, a film X-ray machine requires up to 1.5 seconds.
The Smile-at-Once clinic uses the latest generation CT-Scan tomograph. It allows you to get both a targeted or panoramic, and a three-dimensional digital image. Thanks to minimal radiation exposure, the equipment is completely safe and allows repeated diagnostics without harm to the human body.
How many times can an x-ray be taken?
If we are talking about analog devices, then experts recommend a break between irradiations of 3 weeks and take one photo per visit.
. However, it happens that it is necessary to increase the number of studies, then they are carried out every couple of days, reducing the negative impact as much as possible. Several x-rays on an analog device in one day can have a bad effect on your health.
The invention of digital equipment has made it possible to greatly reduce risks and allow for more frequent x-ray examinations. There is no longer any need to make compromises between harm and health benefits; doctors prescribe as many procedures as necessary to effectively monitor the progress of treatment.
Is it dangerous to take pictures?
According to SanPiN1, when performing X-ray procedures for preventive purposes, radiation exposure should not exceed 1000 microsieverts (µSv) per year. We are talking specifically about prevention, since for medicinal purposes the indicator can be much higher.
In terms of the number of shots it looks like this:
- 500 targeted shots (1-3 µSv),
- 80 OPTG (13-17 µSv),
- 20 digital CT scans (50-60 µSv).
For comparison, here is a table that shows the radiation doses that a person receives during diagnostic procedures in dentistry, in other areas of medicine and in life in general. The last table shows parameters that are truly dangerous to the body and can be fatal.
| In dentistry | In other areas of medicine | In life | Dangerous indicators |
| 1-3 μSv – one targeted shot | 30-60 µSv – one digital fluorography, 150-250 µSv – old type film FOG | 5 µSv – 3 hours in front of a computer or TV | 750 thousand µSv – minor changes in blood composition |
| 13-17 μSv – one panoramic image (OPTG) | 500-700 µSv – one mammography procedure | 20-30 µSv – one 2-3 hour flight | 1 million µSv – mild radiation sickness |
| 50-60 μSv – one CT procedure in dentistry | 2000 μSv – one head CT procedure | 2000-3000 μSv – natural dose of radiation per person per year (food, solar radiation, air) | 7 million µSv – lethal dose of radiation |
As can be seen from the table, irradiation can cause harm (minor and short-lived) only when a dosage of 750 thousand µ3V is reached, while only one thousand µ3V is allowed for diagnosis. Therefore, 20 CT images or 80 panoramic images will not cause any harm to the body.
X-ray of teeth. Contraindications
Modern equipment gives me confidence to say that x-rays are harmless. The devices installed in our clinics have a low level of radiation exposure. During one visit, the patient can take up to 5 x-rays without harm to health. No more than 100 per year.
The main contraindications for which I do not recommend x-rays are:
– serious illnesses;
– pneumothorax;
– pulmonary hemorrhages;
– decompression diabetes;
– active tuberculosis;
– increased sensitivity to contrast agents used in x-rays.
Is it possible to carry out diagnostics during pregnancy?
According to SanPiN, X-ray examinations are allowed in the second half of pregnancy using protective equipment, provided that the radiation dose does not exceed the same 1000 μSv. However, it is recommended to refrain from taking x-rays in the first and last 12 weeks, i.e. in the first and last trimesters.
Do not be afraid of undergoing diagnostic procedures during pregnancy. Even ordinary caries is an infection that, if not properly treated, can spread throughout the body and lead to infection of the fetus. Therefore, it is better to receive a small and completely safe dose of radiation than to carry out complex dental treatment blindly, not knowing how deep the inflammatory process is.
After the baby is born, i.e. During breastfeeding, dental x-rays can be taken, even more than once (within reasonable limits). Radiation doses are minimal, so radiation does not accumulate in breast milk, and there will be absolutely no harm to the baby. There is also no need to pump or skip feedings.
Advantages of X-rays in dentistry
One of the most common diseases that occurs in almost every patient is caries. If the disease is detected at an early stage and treated, it is not dangerous. But in the absence of timely intervention, caries causes serious complications (pulpitis, periodontitis and others), which are accompanied by severe toothache and the treatment process in such cases takes a lot of time and effort. This is why it is so important to visit the dentist regularly for preventive examinations. It is recommended to undergo an examination every six months, which may include x-rays.
If a root canal filling is planned, the dentist needs to see its structure and possible individual characteristics. After filling, the specialist prescribes an x-ray for control. This is very important, because if a filling defect is not detected in time, inflammation will develop after some time, which can lead to tooth loss.
More information about caries treatment can be found here
Situations when taking photographs is strictly prohibited
Such situations practically never occur. On an individual basis, X-rays are considered in cases where the patient receives radiation in other areas of life: for example, in hazardous work, while undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy. But again, when X-raying the state of the jaw system, the radiation is so small that it will not affect the overall picture.
Thus, you should not be afraid to take photographs - in single quantities they are quite acceptable and will not affect your health at all.
It is important to understand that such diagnostic procedures allow for better treatment, especially with dental implantation, the results of which will last not a couple of years, but for many years of life. 1 Sanitary rules and regulations (SanPiN) 2.6. 2.6.1.1192-03 for the design and operation of X-ray rooms, devices and the conduct of X-ray examinations.
How is the load reduced during x-rays?
All information about the radiation examinations performed, their number and radiation dose is entered into the medical record. If a critical dose accumulates over the course of a year, then prescribing another x-ray is highly undesirable.
To control the workload, the radiographer must have maximum information, so it is important to report all previous examinations and possible contraindications.
To protect the body, three main methods of protection are used:
- Protection by distance. The X-ray tube is placed in a special protective casing. It does not allow X-rays to pass through, which are directed at the patient through a special “window”. In addition, at the exit of the rays from the tube, an X-ray machine diaphragm is installed, with the help of which the irradiation field is increased or decreased.
- Time protection. The patient should be irradiated for as little time as possible (short shutter speeds when taking pictures), but not to the detriment of diagnostics. In this sense, images provide less radiation exposure than transillumination.
- Shielding protection. Parts of the body that are not to be photographed are covered with sheets and aprons-skirts made of leaded rubber. Particular attention is paid to the protection of the genital organs and thyroid gland, as they are the most sensitive to x-ray radiation.
Frequently asked questions from patients
Are x-rays harmful?
Radiography is based on radiation exposure. This sounds quite threatening to the average person. Meanwhile, every person receives a dose of radiation every day, even our bodies are radioactive. The background radiation level per day is 10 μSv (microsieverts). To obtain 4 photos with a bitewing X-ray, the patient receives 20-51 μSv. A panoramic image gives 5-25 μSv. CBCT is accompanied by a higher radiation dose; in one session a person receives from 20 μSv to 700 μSv. The level of radiation will depend on the settings and type of device, and the width of the area being studied.
Thus, there is no direct threat in the procedure. However, radionuclides can accumulate, so diagnostics are prescribed if necessary. After the session, the radiologist must write down how many sieverts the patient received, this will make it possible to calculate the next dosage with minimal harm to the person. After the examination, it is advisable to eat more carrots, apples, radishes, beans and citrus fruits. These products will help remove radionuclides from the body.
How often can it be done
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
The type of x-ray and its frequency depends on the condition of the oral cavity and the complexity of the treatment. It is better to do CBCT no more than 3 times a year. Bitewing film photographs are prescribed no more than 7 times a year; the new technology uses lower radiation doses, so there may be more digital diagnostics. The acceptable norm is 7 diagnostic studies per year. When changing dentists, it is not necessary to take new photographs; it is enough to take the ones you already have with you to the appointment. If digital data has been lost, it can be requested from the clinic that conducted the examination. CBCT results are stored for up to a year in the archives of medical centers.
Where can I do it?
Most dental clinics have an X-ray room where the patient can undergo this procedure without leaving the building and return to his dentist with the images. State clinics also have such installations, but they are exclusively of the old type. This means that you will have to go through the procedure several times and pay less. Old equipment also has high radiation doses. Unfortunately, many private dentistry are also equipped with such equipment. Sometimes a private doctor may refer you to another diagnostic center to obtain data. Cone beam computed tomography is only available in progressive private clinics, but the accuracy of the results fully pays for itself.
The price of the service will depend on the type of examination. Thus, bitewing radiography costs from 3 to 10 dollars, depending on the number of images. At the same time, prices are almost the same in both public and private institutions. A panoramic image will cost approximately $20-25. It can only be done in private institutions, but some clinics can provide this service for free if the patient is being treated by them. The most expensive diagnostic is CBCT, which is done in single diagnostic and dental centers. Its cost will be 50-60 dollars.
Problems with X-rays
In some cases, dental X-rays (the attending physician will tell you how often they can be taken if the first image is unsuccessful) cannot be performed properly due to the patient’s body losing contrast. This can happen for several reasons.
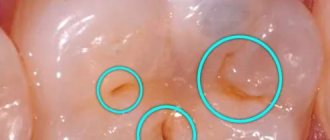
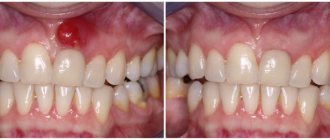
A granuloma, abscess or cyst has developed on a separate part of the jaw
Abscesses, cysts, granulomas can greatly obscure the image, making its accurate description and diagnosis impossible.
A radicular cyst has appeared
A radicular cyst can hide other pathological changes in bone and dental tissues.
Improper canal filling
Incorrect use of filling material or filling of canals after removal of nerves leads to exposure of the image. Accordingly, it is not possible to see anything on it.