The quality of dental treatment depends on the accuracy of the diagnosis. A panoramic photograph of teeth helps to find the cause of dental diseases. However, some patients are concerned about X-rays, fearing harm to their health. In the article we will consider the need for such images, harm to the health of the body and other issues related to this procedure.
What is an orthopantomogram?
A panoramic photograph of the teeth, or abbreviated as OPTG from the word “orthopantomogram”, is a two-dimensional cross-sectional image of the patient’s jaw. In fact, this is an ordinary x-ray, since it is x-ray radiation and an orthopantomograph x-ray machine that is used to take the picture. This is where patients begin to fear for their health, because X-ray radiation is harmful to the body.
What you can see in the image:
- both jaws;
- all teeth including roots;
- condition of bone tissue;
- jaw joints;
- maxillary sinuses.
The doctor receives a panoramic picture of the patient’s skull and can make the most accurate diagnosis.
However, a panoramic image still differs from the usual x-ray and other hardware diagnostic methods: teleradiography, tomogram.
When an X-ray is taken, a visiograph works. With the help of such hardware research, you can see a maximum of two adjacent molars. That is, a targeted image is obtained in a two-dimensional plane. An x-ray can be taken at any public clinic.
Orthopantomogram
An orthopantomogram is done using a computed tomograph. The result is a panoramic image of the jaw in two dimensions. Diagnostics can be done in any public or private clinic. The price is several times more expensive: from 1000 rubles.
Teleradiography
Teleradiography is also performed on a computed tomograph. However, compared to an orthopantomogram, the doctor already sees the entire skull in front and profile. Accordingly, this is a more informative diagnosis than the first two. The examination method is used to resolve surgical and orthodontic issues. The procedure costs from 2000 rubles.
Tomogram
A tomogram (or computed tomography, CT) is also performed on a CT scanner. However, the doctor already sees a three-dimensional three-dimensional image: not only bone tissue, but also soft tissue. This examination is carried out to resolve issues regarding implantation and surgery. The photo is taken in private clinics, the price for the work starts from 1,500 rubles. You can do a segmental tomogram (a separate section of the jaw): it will be cheaper.
Which method is better
Which examination method is preferable? It depends on the issue that needs to be resolved. To place an implant, it is better to take a 3D image. If only one molar needs to be treated, a simple x-ray examination is sufficient.
In private clinics, patients are offered a panoramic photo at their first appointment. This is necessary to track the dynamics of changes in the condition of the jaw and teeth. The image will be stored along with the patient's record. Sometimes this service is provided free of charge, it all depends on the clinic.
Decoding the results
An x-ray of an adult's jaw is usually interpreted by a radiologist.
Other specialists may also be involved in this work: dentist, facial surgeon, otolaryngologist. Specific pathologies of the upper and lower jaws have certain radiological features:
- Chronic osteomyelitis. Depending on the type of disease, the images may show foci of resorption of various shapes with a shadow of necrotic masses inside. In more severe cases, communication of the sequestra with the oral cavity is visualized.
- Acute osteomyelitis. When examining the image, you can see areas of bone tissue resorption that do not have clear boundaries.
- Fractures or cracks in the jaw bones. This pathology reveals itself by the fact that thin, elongated shadows are quite clearly visible in the photographs. In such cases, it is important not only to identify the fracture, but also to see the bone fragments, if any, and to understand how much they are displaced.
- Chronic periostitis. In the image with such a pathology, periosteal thickenings will be visible. If the disease has become severe, areas of ossification of the periosteum and new bone tissue along the edge of the jaw are visualized.
Minuses
Every medical procedure has its pros and cons. Let's consider them in relation to panoramic diagnostics:
- OPTG does not always provide accurate information, since the image is not three-dimensional, but two-dimensional. In this regard, CT is still much more informative.
- Sometimes image distortion reaches 30%, which negatively affects the diagnostic accuracy.
- OPTG does not provide complete information about the three root teeth, as it produces a two-dimensional image in a slice. The roots of such teeth are located in three planes at once, and the image is only two-dimensional.
Accordingly, many dentists refer to OPTG as a rough diagnosis that only gives a general idea of the condition of the teeth and jaw. When it is necessary to see a crack in a root canal or to fill a curved root canal, they resort to other forms of examination.
Examination of children
Dental x-rays are often prescribed for young children. You should not be afraid of this, since children sometimes need such examination more than adults. Baby teeth are often subject to carious problems, and caries appears in inaccessible places. As with an adult, the dentist cannot fully assess the condition and depth of the problem in a child. To accurately assess the situation, treat and prevent diseases, X-rays are needed. Also, a photo of baby teeth helps determine the process of eruption of molars, the quality of bone tissue, and the formation of a bite. In childhood, it is easiest to prevent improper formation of the dentition. If such problems are not resolved in time, in later life this will happen longer and more severely.
For small patients, only minimal doses of radiation are used. The doctor builds treatment and diagnostic tactics so as not to expose the child to radiation again. The procedure is the same as for adults: the rest of the body is covered with a protective apron, the session lasts a couple of minutes, no pain or discomfort occurs. In addition, some clinics use a collimator - a tube that is attached to the device. This device shrinks the X-ray beam and changes its contour, so children receive even less radiation.
Indications
In what cases is it necessary to do without an x-ray? There are several such situations:
- before starting orthodontic treatment;
- for detailed diagnostics of the maxillofacial apparatus and dentition;
- before planning an operation;
- to detect the localization of the focus of the inflammatory process;
- when diagnosing periodontitis;
- in implantology.
Orthodontic treatment
Orthodontic treatment is always preceded by an examination of the jaw apparatus. The image clearly shows the root system and its condition. Based on the information received, the orthodontist will select a bite correction method. A panoramic photograph of the teeth must be taken for children, since the doctor must see the anatomical features of the structure of the jaw system and the rudiments of unerupted molars. It is important to see in advance in which direction the teeth will grow, in what condition the root system is - its stability.
In what cases is a comprehensive diagnosis of the entire dental system performed? This examination method allows:
- identify malocclusion pathologies in young children;
- promptly detect hidden foci of the inflammatory process and unmanifested problems;
- detect the beginnings of the formation of tumors and neoplasms;
- control the quality of filled root canals;
- check the condition of bone tissue;
- see other hidden problems.
It is very important for adult patients to undergo annual examinations and take panoramic photographs in order to promptly identify pathology.
Hidden caries can also be seen on the x-ray.
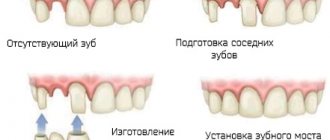
Before surgery
Radiographs are extremely important before planning dental surgeries. The surgeon needs to see nearby molars, the condition of their roots, and the proximity of the nerve endings of neighboring molars. Also, before the operation, it is necessary to identify the presence of root fractures, foci of the inflammatory process and other nuances. Otherwise, the surgeon will operate “blindly”. So it is in the best interests of the patient to go and take a panoramic photo.
Tumor detection
Detection of the localization of the inflammatory process is of particular interest to the doctor and the patient himself. Because in most cases, patients complain not about a bad tooth, but about nearby healthy molars.
A panoramic photograph is also taken when wisdom teeth are difficult to erupt.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a dangerous gum disease that also destroys bone tissue. A panoramic (circular) image allows you to see the depth of tissue damage, the depth of periodontal pockets and make the correct diagnosis.
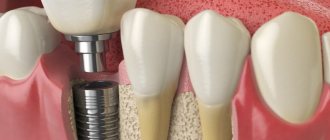
Implantation
Implantation is a modern method of restoring the smile line and functionality of the jaw system. Panoramic diagnostics (it is better to do a computed tomogram) before implantation will help identify pathology of the maxillary sinuses, in which implantation is strictly prohibited.
CT scans are also performed after implantation to monitor the quality of work. The image shows the condition of the bone tissue, which is especially important when implanting titanium elements.
Multislice tomography or MSCT
This is the most modern and advanced type of 3D research today, thanks to which very high quality images are obtained. The method allows you to most accurately assess the situation in the oral cavity. To perform MSCT, you need very powerful and expensive equipment; this is not used in dentistry. However, dentists in some cases refer patients to specialized centers to obtain such images. For example, if it is planned to carry out zygomatic implantation using elongated zygomatic implants against the background of acute atrophy of the upper jaw bone.
This type of tomography is the most modern and accurate
Multislice tomography, unlike all the previously listed research methods, is performed not standing, not sitting, but lying down. The patient is placed in a closed space, with the apparatus arch rising above him like a dome. The main contraindication to the study is pronounced claustrophobia.
The photo shows a multislice tomograph
The cost of 1 photo is from 3000 rubles.
As for the cost of different types of research, you need to understand that everything is rarely limited to just one image. For example, if you are restoring teeth with implantation, then diagnostics will have to be done at least at the treatment planning stage, after installing implants and prosthetics, as well as during the rehabilitation process. This measure may seem expensive to many patients, but saving on this particular expense item is not advisable, because radiography is the key to your safety. However, you can reduce costs if you choose clinics that perform dental implantation on a turnkey basis.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
prevention
- Petrenko K.A. Promising methods of X-ray examination in dentistry. International Journal of Humanities and Sciences, 2021.
Expert “Radiography today is inseparable from modern dentistry, as well as from other areas of medicine. It is constantly being improved, new methods are emerging that significantly improve the quality of service provision. This is a tool that helps patients be more confident in the outcome of treatment, trust the specialist and understand the nuances that the dentist is talking about, because the doctor often uses pictures as visual aids to more clearly explain what the problem is.” Dentist-therapist Elena Vladimirovna Orlova
Consulting specialist
Orlova Elena Vladimirovna
Doctor rating: 9.5 out of 10 (2) Specialization: Dentist-therapist Experience: 32 years
How pictures are taken
The pantomograph diagnostic procedure does not take much time and is easy to perform. A special stick made of medical plastic is placed in the patient’s mouth, which he must squeeze with his teeth. Before the procedure, you must remove all metal accessories: rings, earrings, watches, necklaces. The patient is asked to wear a lead apron, which protects against harmful radiation.
After turning on the device, a digital sensor begins to rotate around the patient’s head, which scans the jaw and temporal area. The whole procedure takes no more than a minute. Then the doctor analyzes the data received, enters the information into a computer or onto a flash card, and takes a picture.
Other types of diagnostics
An image of the jaw is taken using a special device called an orthopantomograph. This device is an X-ray mechanism for scanning the entire jaw and temporal area. There are two types of pantomographs: digital and film (analog). Film mechanisms require a darkroom, while digital mechanisms require a computer. Digital pantomographs are more convenient to use, and their radiation dose is several times lower.
In modern dentistry, film orthopantomographs are used less and less often, since the pictures are unclear and quickly erased. The latest equipment is based on digital technology, and examination methods do not harm the body. The resulting digital image can be printed on photo paper or saved on any medium.
However, some public clinics still have old film-type equipment. If you take a panoramic photograph of your teeth under compulsory medical insurance, be prepared for such a turn of events.
The image can also be obtained using other hardware tools. Therefore, a panoramic test is also done using:
- computed tomography;
- teleroentgenograms.
CT scan
Cone beam tomographs allow you to take panoramic images of the jaw, which facilitates the work of dentists and orthodontists. A panoramic image of the entire oral cavity helps to make a correct diagnosis, prescribe bite correction and implant implants. However, this type of diagnosis is contraindicated for persons suffering from claustrophobia and pathological mobility (cannot sit quietly in one place). Pregnant women should refuse this procedure; breastfeeding women should refrain from breastfeeding for two days after the examination.
Teleradiogram
Teleradiography is prescribed when installing braces or implants, bridges. The procedure is also part of orthodontic treatment and surgery. The radiation exposure during this type of examination is minimal and does not pose a threat to the patient. This procedure is performed even on young children if there is a suspicion of an anomaly in the structure of the dental system.
Types of teleroentgenogram:
- frontal;
- lateral;
- axial
In frontal diagnostics, images are taken from the front and back. A lateral teleroentgenogram is done in case of malocclusion; this procedure is mandatory when installing braces. The chin (axial) radiograph is clarifying (additional). It is necessary for a complete picture of the structure of the patient’s skull in a three-dimensional image. This procedure is mandatory when installing upper jaw implants.
Advantages of teleradiography:
- the resulting image is as close as possible to the actual dimensions of the patient’s skull;
- the result of the study is ready within a few minutes after the image;
- The radiation dose to the patient is negligible.
This type of examination is preferable for patients with claustrophobia who are frightened by the appearance of the tomograph cabin. This type of diagnosis has virtually no disadvantages. However, the doctor’s literacy factor should also be taken into account: you need to be able to correctly decipher an x-ray.
Electroradiography
In another way, this image of the oral cavity is also called xeroradiography. This is a complementary test that is most commonly used in orthodontics, but is also quite effective in detecting bone lesions and soft tissue lesions.
In electroradiography, the image is printed on paper.
Electroradiography images are obtained by passing x-rays through a selenium plate (it is used instead of x-ray film). Next, the image is developed on paper. At the moment, the method is rarely used, for narrow indications.
Common Questions
How safe is X-ray diagnostics?
Doctors responsibly declare that this diagnosis can be carried out several times a year without harm to health. A lead apron does not mean that the examination is mortally dangerous for the patient. The apron is worn to protect the thyroid gland from radiation. It is customary to wear aprons in dentistry, traumatology, etc., since the patient receives a dose of radiation annually during a fluorogram.
How often is irradiation allowed?
Since the radiation exposure to the body during an orthopantomogram is small, studies can be done as needed. That is, how much is needed for treatment. However, there is a limitation: no more than 80 images per year. This figure takes into account preventive fluorograms, and not just dental photographs.
How dangerous is x-ray for pregnant women?
X-rays are taken for pregnant women only as a last resort, if it is required to save the life of the woman and the fetus. However, in the first trimester, any manipulations with X-rays are prohibited: this will negatively affect the condition of the embryo. The second trimester is relatively safe, when all the internal organs and systems of the baby are formed. In the third trimester, taking an X-ray is very dangerous, as it can lead to premature birth.
Do children get x-rays?
In dental practice, photographs of baby teeth are taken if a cyst or a hidden source of inflammation is suspected. For diagnosis, a targeted image is sufficient, the radiation dose at which is extremely small. For the body to suffer harm, you need to make 100 such diagnostics in a year, or more than five in a day. Teenagers can already undergo OPTG, as they understand the requirement to stand still and not cry during the procedure.
Concept and purpose
Performing a targeted shot involves solving several main problems:
- Accurate diagnosis. It is almost impossible to do this by visual inspection.
- Choosing a treatment plan.
- Monitoring ongoing treatment.
- Monitoring the development of existing pathologies.
- Assessment of the quality of canal filling.
- Assessment of the condition of the internal elements of the tooth.
- Diagnosis of hidden deviations.
- Determination of the size of caries lesions or inflammation.
To take a targeted photo with a low level of radiation, a digital camera is used. It is called a radiovisiograph. Examination with such a device is safe, since the beam of rays is directed only at the selected dental unit.
Indications for this procedure are:
- Pain in the tooth area.
- The presence of deep caries, purulent discharge, periodontitis, periostitis, pulpitis.
- Signs of disease on the gums.
- Injuries.
- Determining the quality of wisdom teeth growth.
- Upcoming prosthetics or implant installation.
- Bite correction.
- Upcoming surgery.
Bottom line
To properly treat teeth, you need to have an idea of the condition of the jaw and skeletal system. This information can be provided by an x-ray, which is taken with a special orthopantomograph or computed tomograph. The picture is taken in every private clinic and government institutions. The cost depends on the equipment and tariffs of private clinics. In a government institution, you can get an X-ray done free of charge upon referral or for a small fee of 300 rubles.
Orthopantomography is a panoramic image of both jaws in a section in a two-dimensional plane. The absence of a three-dimensional image is a common reason for an incorrect diagnosis. Also, a two-dimensional image does not allow one to see microcracks on the roots of teeth, and in three-rooted teeth only 2 roots are visible. The listed disadvantages speak in favor of computed tomography, although it costs several times more.
Panoramic diagnostics are recommended not only during dental treatment and implantation: it must be performed annually for preventive purposes. This will allow timely detection of hidden caries, internal foci of inflammation, cysts, tumors, and neoplasms.
Sources used:
- Abolmasov N. G., Abolmasov N. N. Orthodontics. – 2008.
- American Academy of Implant Dentistry (AAID)
- Distel V. A. Dental anomalies and deformations. Omsk — 2004.
- “Orthopedic dentistry. Textbook" (Trezubov V.N.)