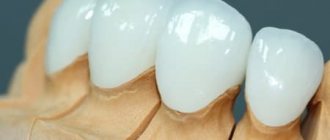
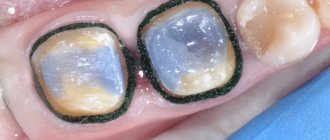
Coagulation is used in dental practice in the treatment of both benign and malignant tumors. Using a coagulation apparatus, the specialist excises the tumor with the highest level of accuracy. The patient does not feel pain and does not experience psychological discomfort at the sight of a surgical instrument.
Pulpitis of the tooth and its treatment
A characteristic sign of this pathology is inflammation in the pulp, which is located inside the tooth cavity, where blood vessels and nerves are concentrated. The cause of inflammation is the penetration of harmful bacteria into the cavity due to damage to the external dental tissues (enamel and dentin). This is the destruction that we most often owe to untimely treatment of deep dental caries: pulpitis becomes a consequence of the carious process. Much less often, it appears due to mechanical damage to the pulp, poor preparation of the tooth for filling, and unprofessional installation of orthopedic structures.
Treatment methods for pulpitis
In dentistry, two main methods are used to treat dental pulpitis in adults and children:
- biological - drug treatment of pulpitis with antibiotics and medications;
- surgical - treatment of pulpitis by amputation (partial removal of the pulp) or extirpation (in which the nerve of the tooth is completely removed).
The choice of technique remains with the dentist. The doctor studies X-ray diagnostic data, interviews and examines the patient. Based on these data, he selects the most rational method of treating pulpitis for a particular case.
When removing a dental nerve, the following methods are used:
- vital extirpation, which involves complete removal of the pulp from a patient under local anesthesia, - devital amputation, in which partial mummification of the nerve is performed using a special drug, - diathermy (diathermocoagulation), during which the pulp is killed using an electric discharge, after which the doctor removes the non-viable nerve.
Vital extirpation
This technique allows the patient to get rid of the diseased nerve in one visit to the dental office. The use of vital extirpation is possible for acute or chronic pulpitis in a tooth with well-passable canals. Depulpation by vital extirpation occurs in 10 stages, during which antiseptic treatment of adjacent teeth is performed, administration of an anesthetic, cleaning of the diseased tooth from caries, opening of the pulp and amputation of the nerve, after which the tooth is filled. The entire procedure takes no more than 2 hours, but requires careful preliminary preparation and diagnosis of the tooth.
Devital amputation
Devital amputation is practically not used in modern medicine, since it is associated with multiple complications and the occurrence of necrotic phenomena in the nerves located in close proximity to the pulp removed by this method.
Diathermocoagulation
The essence of diathermocoagulation is to insert a microscopic electrode into the pulp cavity and apply a small current charge, which kills the nerve and cauterizes the resulting wound. Diathermocoagulation requires minimal doctor intervention in the jaw bone, so the depulpation procedure is almost bloodless. Occasionally, bleeding occurs when a nerve is removed from large molars.
After tooth nerve removal, many patients will experience pain for several days when closing their jaws or when hot or cold food enters the mouth. The pain is relieved with analgesics and does not require additional treatment.
Thanks to qualified treatment, a pulpless tooth can last for several years, especially if it was subsequently covered with a crown.
Biological method of treating pulpitis
If the disease has become chronic, a biological method or conservative treatment of pulpitis with calcium is used. The process involves applying therapeutic pads containing calcium preparations. The technique is also used in the following cases:
- if the pulp was accidentally exposed during the caries treatment procedure;
- when you need to strengthen the bone partition between tooth enamel and pulp.
The specialist applies a drug for the treatment of pulpitis to the site of thinning bone tissue and thereby strengthens it. Next, the tooth is filled and monitored over time, conducting X-ray examinations at certain time intervals. The method is suitable:
- children with baby teeth;
- patients under 30 years of age during the treatment of reversible pulpitis;
- everyone who takes special care of their oral cavity.
If, after treatment of pulpitis, the tooth aches, hurts when pressed or bitten, and the pain remains for a long time, intensifies at night, and becomes long-lasting, you must return to the clinic. Aching pain during the treatment of pulpitis indicates that more radical, that is, surgical, methods are needed.
Types of coagulation (cauterization) of gums
Monopolar technology
A special return plate is placed on the patient’s body, which is responsible for closing the electrical circuit. A weak electrical impulse is passed through the patient's entire body and through the surgical instrument. With this procedure, you can get rid of even large neoplasms and tumors located in the deep layers of tissue. Due to its effectiveness, this method is used more often than others.
Bipolar technology
An electrical discharge is passed locally, only through the part of the body in which the tumor or inflammation is located. Therefore, the end plate is not used. This method is effective for the treatment of mild dental diseases.
The gum cauterization method is widely used in dental practice and shows good results in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
Before performing the operation, the doctor examines the patient’s oral cavity for injuries to the mucous tissues, since their presence can cause complications.
How is pulpitis treated surgically?
As we have already noted, there are two possible options for surgical intervention:
- treatment of pulpitis using the amputation method with partial preservation of the pulp;
- treatment with complete removal of soft tissues, blood vessels, and nerves.
If there is an objective possibility, the doctor will remove only the top of the pulp - from the crown, leaving the root part. The blood supply and sensitivity (innervation) of the tooth will be preserved. The technique is used in the treatment of children - for milk or permanent teeth that have not yet fully grown. This allows them to form normally in the future. Treatment for pulpitis can be carried out in one visit.
Cervical caries - causes, treatment, prevention
Despite the obvious good visualization of the defect, the treatment of cervical caries is by no means simple due to several reasons:
- proximity of the gum edge to the working field, the likelihood of blood/pus from inflamed soft tissues getting there;
- the need for gum retraction to access the gingival wall of the carious cavity;
- difficulties in instrumentation of the cavity due to the proximity of the pulp, high risk of opening the pulp chamber;
- the problem of complete isolation of the working field from saliva, especially if the defect extends to the root part of the tooth;
- poor adhesion of the filling material to the gingival surface, especially since the adhesion of the filling to root dentin is much worse than to coronal dentin;
- the need to ensure macromechanical retention of the installed filling, because Adhesion alone is not enough to achieve reliable fixation of the restoration.
Therapeutic manipulations in the cervical area are quite painful, so the preparation of deep cavities and their filling takes place under anesthesia. In children, the injection site is first anesthetized by applying a gel.
Treatment at the spot stage
At the very beginning of the disease, when the enamel began to lose its shine and a stain appeared, you can do without using a drill, trying to stop demineralization with special preparations. Remineralizing therapy is carried out through applications to the cleaned and dried surface of the teeth.
Popular means:
- enamel-sealing liquid from HumanChemie (Germany);
- Gluflutored;
- foam “Flairesse” (Germany)
- "Topical APF Gel" (USA).
- Tyc Mousse (Japan) and others.
The preparations contain fluorine and calcium in the form of ions. Treatment of cervical caries is complex. About 10 procedures are required (the doctor alternately applies calcium compounds and highly active fluoride to the enamel). To consolidate the result, products containing fluorides are prescribed - toothpastes, mouthwashes. With proper therapy, the enamel restores its structure and shine. After 1-2 months, it is recommended to visit the dentist to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.
Treatment at the superficial stage
When cervical caries passes into the superficial stage, it is sometimes possible to get by by grinding off the rough layer and carrying out remineralization therapy, but such tactics are more suitable for children. As a rule, patients rarely go to the dentist in the first stages of carious disease, so the doctor prefers to carry out full treatment with cavity preparation. At the superficial stage, the specialist cleans the tooth of plaque, removes the rough layer, and etches the enamel with gel to improve its susceptibility to the restorative material. A liquid composite of a suitable shade is applied to the surface, which fills the voids of the changed enamel. The doctor polymerizes the material with a lamp, it hardens, being completely invisible on the tooth. This treatment will take about 15-25 minutes and no anesthesia is required.
Treatment at the middle and deep stages
Therapeutic measures for diagnosing mid-stage cervical caries include:
- anesthesia;
- isolation of the working field;
- opening the cavity with a drill;
- removal of changed (softened) tissues;
- antiseptic treatment of the cavity;
- drying the bottom and walls;
- application of insulating and therapeutic pads;
- filling the defect;
- grinding and polishing of the filling.
In modern clinics, for the treatment of cervical caries, complex technologies are used, involving the use of several materials and adhesive systems, which makes it possible to successfully fill gingival and subgingival defects with the restoration of the tooth’s functional properties.
Treatment of acute pulpitis
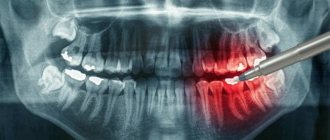
The above methods are ineffective in treating exacerbations of chronic pulpitis, an acute disease when the tooth becomes a source of unbearable pain radiating to the ear, temple, and back of the head. With these symptoms, endodontic treatment of pulpitis is carried out - with cleaning of the root canals and complete removal of the pulp.
In dentistry, two modern methods of treating tooth canals for pulpitis are used: devital and vital.
- Treatment of pulpitis using the vital amputation method is carried out by removing the nerve, washing, cleaning and filling the canal.
- Devital treatment of pulpitis involves the use of medicinal pastes and requires several sessions.
These treatment methods are most often used for pulpitis on permanent teeth.
What complications may arise after surgery?
Many patients note that their gums hurt in the first few days after coagulation. This phenomenon is considered a completely natural consequence of the intervention. To reduce discomfort, you can take painkillers that you usually use and keep in your medicine cabinet.
If the pain does not disappear after some time, and additional alarming symptoms appear (inflammation and redness of the mucous membrane, the appearance of bad breath, discharge of pus), then be sure to visit a doctor. The specialist will tell you what to do to make the gums suppurate go away: for these purposes, antibiotics that destroy pathogenic microflora and treatment of the mucous membrane with antiseptics are most often prescribed.
Stages and stages of tooth treatment for pulpitis using the devital method
- Stage I.
The tooth is anesthetized and the carious cavity is cleaned. The pulp cavity is opened. - Stage II.
A devitalizing paste is placed into the exposed pulp and the tooth is filled for 3 to 7 days. People still call the paste “arsenic,” although it has nothing to do with this substance. - Stage III.
During your next visit, your dentist will clean the root canals according to medical protocol. - Stage IV.
If there is a risk that the tooth will crack, it is covered with a crown. If the hard tissues are well preserved or only slightly damaged, they are restored. The tooth is strengthened with a fiberglass or metal anchor pin and securely filled with photopolymer material.
The treatment time for pulpitis depends on how damaged the tooth is, the age of the patient, whether there are complications, and how many root canals should be treated.
How to prepare for the procedure
There is no need for special preparation before coagulation, but you should do the following:
- visit different specialists: before the procedure, if necessary, the doctor may refer you for a consultation with other specialized specialists (infectious disease specialist, oncologist, periodontist),
- Avoid drinking alcohol several days before the procedure, as well as on the day of coagulation: it negatively affects blood clotting and the effect of medications and anesthetics used during the procedure,
- have a snack before the procedure: the snack should not be heavy, but you should not completely refuse food, because After the operation, you will not be able to eat for at least another 1-2 hours.
Is it painful to treat pulpitis?
Many patients believe that treatment for pulpitis is painful. In fact, pain accompanies the disease itself, and not the procedure for its treatment. The pulp tissue and nerves become inflamed, which causes unbearable painful sensations comparable to an electric shock. Pulp removal is absolutely comfortable, because high-quality anesthetics completely relieve the patient of pain while the doctor prepares the canals. During treatment or after treatment of pulpitis, the tooth hurts when the internal tissues are severely inflamed. Then safe painkillers are prescribed while healing occurs (1 - 3 days).
Why is the gum most often cauterized?
Most often, patients are recommended to apply electric shock to the affected areas due to hyperplasia or overgrowth of soft gum tissue, also called papillae. They fill the interdental spaces and are very sensitive to any impact. Their excessive enlargement and inflammation are caused by household injuries (occurring when using floss to remove plaque, toothpicks, brushes with hard bristles, or eating hard foods), dental diseases, poor oral hygiene, malocclusions, or hormonal disorders.
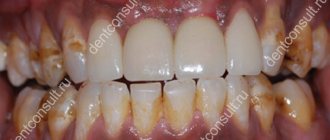
In the absence of proper treatment, the area of the interdental papillae increases, the soft tissues begin to become inflamed and bleed, causing pain and discomfort. In addition, the formation of such growths can cause problems with the correct pronunciation of sounds, impaired blood circulation in the gums, lack of adequate nutrition, and the appearance of complexes (overgrown mucous membrane can completely cover the crown part of the tooth, which looks extremely unaesthetic), so dentists recommend cauterizing them in a timely manner.
Possible complications
If you delay visiting the dentist, inflammation can spread to the bone tissue of the tooth - periodontium. This is how one of the most common and dangerous complications of this disease begins - periodontitis, which can lead to tooth extraction. Periodontitis also occurs due to an unskilled approach to cleaning root canals.
If you are concerned about an elevated temperature after treatment for pulpitis, urgently contact a more reputable dentist, as the inflammation is progressing. Professional clinics use modern methods of canal treatment using microscopes, binoculars, visiographs, endomotors, and apex locators. These instruments prevent the risk of complications.
Unfortunately, pulpitis remains a common occurrence after caries treatment. The reason for its appearance is the same - the unprofessional actions of a doctor who violated medical protocols and made mistakes when filling. Perhaps he accidentally opened the pulp and gave bacteria access to it.
Advantages of hot filling
An experienced doctor can perform equally high-quality fillings using any of these methods (“cold” or “hot”). However, the hot gutta-percha method is still less labor-intensive, filling occurs faster, and the probability of error is even lower.
But still, the main advantage of hot filling is the ability to fill all, even microscopic microchannels, which the cold gutta-percha method is not able to fill. Each tooth is unique, as are its root canals. Seeing them, an experienced dentist will always recommend to the patient the optimal filling method.
How much does tooth treatment for pulpitis cost?
The final cost of pulpitis treatment is influenced by many factors: the degree of destruction of hard tissue, the number of canals in the tooth, the presence of complications, concomitant diseases, and the chosen treatment method. If the tooth is permanent and has one canal, then the procedure in Moscow clinics will cost from 5,000 rubles. This amount includes a full range of services: x-ray diagnostics, application of anesthetic, installation of a rubber dam, treatment of caries, treatment of dental canals with cleaning, installation of a filling. Price may change if multiple sessions are required.
Coagulation methods
There are several options for treating the affected mucosa. Depending on which device is used, the following methods are distinguished:
- cauterization with a metal instrument with a hot tip: the instrument is considered obsolete and is rarely used nowadays - the procedure using it is quite traumatic, and the subsequent rehabilitation period is quite long,
- excision with an electrocoagulator: here, with the help of a device, electrical energy is converted into thermal energy. High-frequency alternating electric currents supplied through the tool “dry” and destroy damaged areas,
- treatment with a laser device: damaged tissues are “burned out” with a beam of intense light.