12/06/2018 Dentistry combines several areas of narrower specialization: dentofacial surgery, therapy, orthodontics and orthopedics. All of them are aimed at diagnosing diseases of the teeth and oral cavity, maintaining and restoring their health and beauty. However, each section has its own specifics and a set of techniques used.
For example, orthopedic dentistry deals with the treatment and prevention of congenital and acquired anomalies of the dental system. What diseases does an orthopedic dentist work with and in what cases is it necessary to contact this specialist? We will consider in more detail in this article.
- Modern orthopedic dentistry: tasks and goals
- Microprosthetics
- Fixed prosthetics
- Removable prosthetics
- When to contact an orthopedic dentist?
Content:
- Consultation with an orthopedist
- Making a treatment plan
- When to visit a specialist
- Popular Orthopedic Treatment Options
- Preparation for installation of prostheses and restorative procedures
- Why is it important to see an orthopedist on time?
Orthopedic dentistry is a field that specializes in detecting and eliminating violations of the integrity of the dentition and restoring the functions of the dentofacial apparatus.
Orthopedic dentists are involved in the installation of removable and fixed dentures, aesthetic structures (veneers, lumineers, etc.), special leveling devices and systems. Dental orthopedics today includes many in-demand medical services. If earlier it meant only prosthetics, now doctors include in this area also measures aimed at preventing the development of various types of dental deformations.
Microprosthetics
Microprosthetics is a technique for restoring a dental unit when it is partially destroyed, provided that the root and nervous systems are preserved. Most often, teeth chip when chewing hard food or mechanical injuries. This violates the integrity of the dentition and increases the load on neighboring units. In addition, a chipped incisor or fang is a visible cosmetic defect.
To correct it, an orthopedic dentist may suggest:
- Dental onlays or veneers. They are made from high-strength ceramic compounds that are visually indistinguishable from natural enamel. They are installed using hypoallergenic dental cement, which firmly fixes the onlay to the front surface of the tooth. The thickness of the veneer is up to 1 mm; before fixation, the orthopedic dentist removes part of the hard tissue. The microprosthesis is durable and beautiful, completely restores the functions of the tooth, and does not require special care. This design is used not only for the restoration of chips, but also in the case of darkening of the enamel, the appearance of cracks or areas of discoloration on it.
- Dental inlays. They are made from the same material as fillings, but are made according to an exact impression of the tooth, returning it to its original shape. The products are used primarily for the restoration of chewing teeth. Installation requires minimal preliminary preparation of the oral cavity, for example, no grinding of hard tissue is required. The procedure is painless, does not cause discomfort to the person and is performed in one visit to an orthopedic dentist.
Regardless of the technology chosen, microprosthetics remains one of the most gentle methods of restoring dentition. During the manipulations, the orthopedic dentist does not damage the surrounding tissues, since no grinding of adjacent units occurs. Other advantages of microprostheses include:
- Minimal adaptation period - after recovery there is no sensation of a foreign object in the mouth, diction is not impaired, and there is no need to change eating habits.
- Short production time - unlike other types of dentures, veneers and inlays can be produced within 1-2 days after contacting the dental clinic.
- Long service life - the linings last for decades without requiring restoration or replacement. They also do not need special care - normal oral hygiene is sufficient.
- Maximum aesthetics - products are cast from materials that are externally identical to natural enamel. They do not have a metal frame or fastenings that would be noticeable after installation.
The disadvantages of microprosthetics include the fact that this technique is suitable for correcting only minor defects. If a tooth is completely lost or its nerve tissue is damaged, orthopedic dentistry offers other methods of restoration.
Consultation with an orthopedist at the Smile Line clinic
By undergoing treatment with our specialist in the field of orthopedic dentistry, you can install dentures and restore the integrity of the row. These concepts are not identical. The fact is that if the roots are destroyed, fixation of the crowns is impossible. Then we are no longer talking about prosthetics, but about implantation (restoration).
It is a mistake to believe that a doctor of the named specialty works only with the goal of restoring beauty to the patient’s smile. Of course, the activities he performs have a positive effect on the client’s appearance. But first of all, the specialist takes measures to restore the functionality of the jaws. They help avoid bone tissue atrophy, movement of neighboring units, and problems in the gastrointestinal tract.
Specialty sections
QUESTION 1
The subject of orthopedic dentistry, its goals and objectives. Specialty sections
The founder of scientific orthopedics is considered to be the French surgeon Nicolas Andry (1658-1742), who in 1741 published a two-volume work “Orthopedics, or the art of preventing and correcting body deformities in children.” The term "orthopedics" is made up of two Greek words: ortho" - direct and padel - education. In introducing this term, Andry meant “proper education of children” (physical) and defined orthopedics as “the art of preventing and treating deformities in children.”
Currently, orthopedists treat diseases of the musculoskeletal system in children and adults, using functional, hardware, surgical methods and prosthetics.
Orthopedic dentistry is a branch of general dentistry and an independent part of general orthopedics. Orthopedic dentistry
the science of diagnosis, prevention and treatment of congenital anomalies and acquired defects, injuries and deformations of the organs of the dental system. For these purposes, it has functional (myotherapy, mechanotherapy), prosthetic, hardware and hardware-surgical methods of treatment.
The main place in orthopedic therapy is occupied by prosthetics. Its task is not only to replace defects in the dentition or alveolar process, but also to prevent further destruction of the organ or relapse of the disease. The prosthesis is thus considered as a medical device, the reasonable use of which makes it possible to solve therapeutic and preventive problems.
Specialty sections
Currently, prosthetic dentistry is a rigorous scientific discipline, consisting of general and private courses. The general course is propaedeutic, i.e. preparatory. The private course includes three main sections: dental prosthetics, maxillofacial orthopedics
and
orthodontics.
The propaedeutic course of orthopedic dentistry outlines a brief anatomical and physiological outline of the masticatory apparatus, general and special methods of examining the patient (diagnosis), assessment of the signs of the disease obtained in this case (symptomatology or semiotics), clinical materials science, as well as laboratory technology (methods for making dentures and various orthopedic devices).
Dental prosthetics deals with the diagnosis, prevention and replacement of defects in teeth and dentition that arise as a result of any pathology. Maxillofacial orthopedics studies the diagnosis, prevention, prosthetics, and correction of jaw and facial deformities resulting from injury, disease, and various operations. Orthodontics is a branch of orthopedic dentistry that deals with the study, prevention and treatment of persistent anomalies of teeth, dentition and other organs of the dental system.
Drawing up a treatment plan
You usually have to visit an orthopedist more than once. During the first consultation, the doctor examines the client’s oral cavity, determines the existing disorders and their severity. To study the location and condition of the roots, a computed tomography or radiography is performed.
The plan may include the following steps:- Choosing a method to eliminate the defect that has arisen.
- Preparation for prosthetics.
- Manufacturing and installation of prostheses.
- Assessing the dynamics of the patient's oral cavity.
When to visit a specialist
You should take advantage of the progressive possibilities of orthopedics (dentistry) in the following situations:
- the crown is very badly destroyed due to caries and it is not possible to restore it with filling material;
- the roots have completely collapsed and cannot serve as support for a future external structure;
- Dangerous pathological processes and necrosis have been identified in hard tissues;
- there are diseases that have caused a change in the shape of the crown part of the molars, incisors, and canines;
- advanced periodontal disease was detected.
Also, the help of an orthopedic dentist will be needed if there are chips, cracks, deep scratches, or individual units are positioned incorrectly in relation to their “neighbors.”
The doctor is responsible for:
- making the correct diagnosis;
- carrying out preparatory activities, preparing for planned therapy;
- choosing the optimal prosthetic method;
- installation of removable/fixed dentures.
Removable dentures
If the patient is not satisfied with fixed prosthetics for various reasons, the orthopedic dentist selects removable analogues to replace the lost teeth.
It can be:
- Nylon prostheses.
- Clasp dentures.
- Acrylic products.
- Zirconium “teeth”.
Each type is made using a special technology from various materials and differs in its characteristics. For example, “clasp” and artificial teeth made of zirconium dioxide are considered to be the most beautiful. They perfectly imitate natural enamel and look organic in the mouth. However, their production is a difficult task, so the cost of the finished product is quite high.
A more affordable option is acrylic products. Acrylic looks good, is not stained by food coloring, is durable and lasts for 10-15 years. Its main disadvantage is that it causes gum irritation in some patients. In this case, the orthopedic dentist suggests a hypoallergenic material – nylon. It is softer than acrylic, but wears out faster and requires more frequent replacement.
Each type of removable dentures has its own advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, in orthopedic dentistry there is a wide variety of different technologies and materials that allow us to choose the optimal solution for each client. To choose a design that is right for you, you must consult with a qualified physician. An orthopedic dentist will examine the current state of the dentofacial apparatus, soft tissues of the oral cavity and recommend an appropriate way to compensate for missing teeth.
Popular Orthopedic Treatment Options
Each situation has its own optimal prosthetic option. There can be no universal solutions here. Orthopedic dentistry today offers many ways to treat dental disorders and anomalies.
The most popular are:
- Tabs. Replace fillings. Made from individual casts. They fill the existing carious cavity and fit tightly to its sides. They make the tooth beautiful and very durable, do not shrink over the years, and do not change the original color.
- Veneers. Overlays glued to the front surface of the crown. Requires minor preliminary grinding. They only cope with minor changes - chips, cracks, unsightly fillings, changes in the shade of enamel.
Prosthetics on implants. This type of dental orthopedics is indicated for complete or partial loss of fangs, molars, and incisors. It makes it possible to restore chewing function, eliminate problems with “lisping” diction, and make the smile area beautiful.- Crowns. Optimal if the crown part is severely destroyed and the roots are in satisfactory condition. They are made from metal, plastic, ceramics, zirconium oxide, and precious metals. The material is selected taking into account the required strength and the desired visual effect.
- Dental bridge. Used if there is no one or several adjacent units. Its edges are crowns, and the center is artificial teeth. Requires, as a minimum, two reliable supports.
- Removable structures. They can be lamellar or clasp. They are used if there is no large number of dental units. They are usually preferred by older people due to their low cost and ease of use.
Orthopedic dentistry is rightfully one of the most popular dental branches. After all, even children with primary malocclusion often become clients of an orthopedist.
Fixed prosthetics
In case of complete destruction of one or more teeth, the orthopedic dentist selects a fixed prosthesis for the patient - a structure that replaces the missing units. Products differ in material of manufacture, cost, fixation technology, service life, ease of wearing and indications for installation. The most popular options in prosthetic dentistry are:
- Crowns.
- Bridges.
- Implants.
A crown is a kind of “cap” that is placed on the frame of a tooth or an implanted metal rod. The operation is carried out in several stages:
- Sanitation of the oral cavity - an orthopedic dentist treats foci of caries, inflammation of the gums, and, if necessary, carries out hygienic cleaning.
- Tooth preparation – part of the enamel and dentin is removed. If the tissue is severely damaged, the unit is removed and an implant is installed in its place - a metal rod implanted into the jaw bone.
- Making a crown from an impression. The orthopedic dentist creates a model of the prosthesis, which he sends to the dental laboratory. The technician makes the crown using the technology chosen by the client. The cost of the product, its aesthetics, and service life depend on this.
- Installation of the prosthesis. The crown is placed on a pre-ground base (or implant) and fixed with dental cement. At first, the patient may experience minor discomfort while the chewing apparatus adapts to the prosthesis. In the future, the crown is not felt and completely replaces the lost or damaged tooth.
Orthopedic dentistry is aimed not only at restoring the functionality of the dental system, but also at maintaining the beauty of the dentition. Therefore, crowns are not only reliable and durable, but also aesthetically pleasing. The appearance of the product depends on the selected material. An orthopedic dentist can offer the following types of prostheses:
- Metal.
- Metal-ceramic.
- Ceramic.
The most popular is metal ceramics. The crown has a metal frame onto which dental porcelain (or other ceramic composition) is applied in layers. As a result, the finished structure is durable and outwardly indistinguishable from a regular tooth. In addition, metal ceramics are more affordable than their counterparts made entirely of ceramics.
If not one, but several units are missing, bridge-like fixed prostheses are installed instead of crowns. They are several crowns combined into one design. The two outermost ones are fixed on previously prepared teeth, the rest fill in the missing units. The “bridge” has no visible metal fasteners, so it is invisible when eating or smiling. However, it has a drawback - wearing a bridge increases the load on the supporting teeth, so they are subject to accelerated wear. To avoid this, you can use implantation.
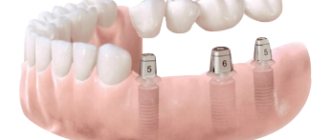
Implantation is another type of permanent prosthetics in orthopedic dentistry, which involves the implantation of a metal rod into the jaw bone, onto which a crown is subsequently placed. A good solution for filling both one and several missing teeth without increasing the load on neighboring units. But implantation is a complex procedure and can only be performed by an experienced orthopedic dentist. In addition, the cost of the operation is quite high and it cannot be performed on people with chronic diseases. In this case, removable dentures are used - metal or ceramic structures that imitate the tissues of teeth and gums. This is one of the most reliable and proven options that orthopedic dentistry can offer.
Preparation for installation of prostheses and restorative procedures
Before installing any type of prosthesis, the doctor carries out preparatory measures. During them:
- Treats caries. All carious cavities must be closed.
- Provides therapy for detected oral diseases. It is important that the gums are in satisfactory condition and the patient is not bothered by pain.
- Eliminates anomalies. It happens that before receiving prosthetics, a person is sent for a consultation with an orthodontist so that the existing curvatures can be removed.
- Provides professional hygiene. During this procedure, it removes soft plaque and hardened stone. This measure is preventative - it eliminates gum inflammation in the future and promotes the speedy healing of implants.
- Prepares supports for crowns. To do this, the teeth are ground, treated and the canals are filled.
Only after preparation can you proceed to prosthetics and implantation.
Why is it important to see an orthopedist on time?
Let's not dwell on the unsightly appearance of the smile of a person who has missing teeth. Although this fact is very important. Let's talk in more detail about the problems that result from complete and partial adentia. Among them:
Difficulty chewing food. Because of this, the load on the gastrointestinal tract increases. If a patient has a predisposition to stomach diseases, they will certainly arise.- Changing the position of the “neighbors”. As soon as voids appear in a row, neighboring units try to occupy them. Because of this, the bite changes and the teeth become crooked. Such changes complicate hygiene procedures, which is fraught with caries, pulpitis, and gum inflammation. They also have a bad effect on the appearance of the smile and facial proportions.
- Atrophy of bone tissue. If teeth are missing for a long time, the jaw bone in the area where they were previously located begins to sag. This occurs due to the lack of chewing stimulation. Subsequently, atrophy causes difficulties in preparing for implantation - the patient has to undergo a complex osteoplasty operation.
Don't forget to take care of your oral health and restore missing teeth in a timely manner. However, do not give preference to the cheapest techniques. Ideally, after applying dental orthopedics, the functions of the tooth will be completely restored.