Chief editor of the site:
Snitkovsky Arkady Alexandrovich
Chief physician of the professorial dentistry “22 Century”, dentist, orthopedic dentist
Author of the article:
Scientific team of dentistry “22 Century”
Dentists, candidates and doctors of medical sciences, professors
Types of veneers
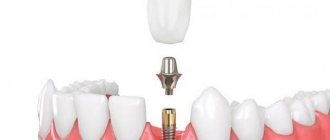
Every year new technical developments appear in dentistry and existing ones are improved. How can a patient who does not have a specialized medical education understand what VENEERS are and why they need them? Veneer (adhesive lining, onlay) is a non-removable microprosthesis that covers the outer (vestibular) surface of the tooth and restores its anatomical shape and color. In this case, the preparation (“drilling”) of dental tissues is minimal or absent . Almost all clinics deal with this type of aesthetic restoration and offer several types of this design.
Historical reference
Composite materials are modified plastics with improved aesthetic, strength and handling properties. Their connection with tooth tissues is due to adhesion.
Adhesion (Latin adhesio - fusion, adhesion) is the phenomenon of adhesion between two surfaces brought into contact. Systems created on the basis of this phenomenon are widely used in dentistry.
Currently, there are seven generations of these systems , with the fourth to seventh being used in clinical practice. They differ from each other in adhesion strength, the relationship of the components (separately or in combinations) and indications for use.
The widespread use of veneers dates back to the 1980s.
Types of veneers
Types of veneers
Direct veneers
Direct – done immediately at the appointment after preparation from composite materials (like a filling).
There are sets of materials specially developed for this purpose that allow layer-by-layer restoration of the structure, taking into account all the color characteristics (hue, saturation, transparency, etc.) of tooth tissue. This is the simplest, fastest and most inexpensive option .
Semi-direct veneers
Semi-direct - like straight ones, are made of composite materials, but not in the oral cavity, but on a model - a plaster analogue of teeth and jaws, obtained from an impression. This is usually done by a technician in the laboratory, but with the appropriate skills it can be done by the doctor himself. Special laboratory composites can also be used as a material.
This design will be more accurate and stronger than direct veneers for the following reasons:
- The ability to compensate for shrinkage - a decrease in the volume of the material during hardening;
- Independence from the conditions of the oral cavity (humidity, the need to isolate the working field, jaw movements, patient fatigue, etc.);
- The ability to more accurately control the color and transparency, fit, thickness of the restoration and adjust them if necessary.
Indirect veneers
Indirect veneers are made only in a laboratory or milling center from porcelain (dental ceramic) or zirconium dioxide (an aluminum compound).
In this case, after preparation and taking impressions, temporary veneers to protect the prepared teeth and provide aesthetic correction. Most often they are made of plastic.
Situation: veneer failed
In practice, there were cases when the veneer fell off. How to fix? You need to assess the situation and carefully study the problem, and the doctor will suggest a solution.
If the material has simply peeled off, then you need to remove it with careful movements (so as not to damage it).
If you see in your mouth that one part has peeled off, then there is a possibility that the device remains intact. If the veneer falls off as a whole, then the doctor will definitely be able to fix it in place.
In case of obvious breakdown of the material, the dentist will have no other solution but to replace it with a new one.
How can you tell if the entire veneer has fallen off? You need to look at the condition of the fallen element. If it has a symmetrical and rounded shape, then the veneer is intact. If you look closely at the tooth and see a residue on it, then the veneer is 100% broken.
In order to help the dentist with further treatment, you must show him the fragments. It is recommended to save all parts of the broken material. To do this, you need to fill a small box with cotton wool and put the debris there.
Next, you need to report the incident to the doctor. The doctor will solve the problem. But in general, the potential risk of such a problem is small. The tooth will remain without protection for some time (two weeks). There will be no significant changes in him for weeks.
Veneer detachment can be detected independently. It happens that you feel a rough surface (as opposed to a smooth veneer) in your mouth. The tip of the tongue undergoes irritation. And yet, a ground tooth will definitely react to temperature changes, since the surface has no protection.
And in the future, carefully analyze the situation and determine what actions you took could cause the breakdown. Once you find the answer, never repeat such actions again. If you cannot determine, consult your dentist.
Methods for making veneers
- Injection pressing followed by sintering of ceramic mass (Dicor, IPS Empress);
- Vacuum firing on a refractory model (refractor);
- Milling on a computer-controlled machine from ready-made factory blocks - CAD/CAM (computer aided design and manufacturing). These are systems such as Cerec, Everest Procera, Cercon and In-Ceram, Vollceram, Hi-Ceram masses.
Advantages and disadvantages of veneers
Advantages and disadvantages of veneers
Let's look at the advantages and disadvantages of veneers
Advantages of ceramic cladding compared to composite ones
- Color stability – resistance to coloring;
- Resistant, long-lasting surface shine;
- Possibility of color modification due to fixing cement;
- Fluorescence (“internal glow” due to the transmission of part of the light);
- High strength;
- Compatibility with dental tissues, oral cavity and body;
- Durability (resistance to abrasion and wear);
- Resistance to solvents (including oral fluid), cosmetics and drugs;
- Do not absorb moisture;
- Greater variation in the shape and/or color of the anterior teeth.
Disadvantages of ceramic adhesive overlays
- Difficulty of repair;
- Complexity of manufacturing technology;
- Inability to change color after fixation;
- In some cases – the need to prepare (grind) the hard tissues of the tooth (teeth);
- High price.
Disadvantages of composite veneers compared to ceramic ones
- Less wear resistance;
- Less solvent resistance;
- Moisture absorption.
This design is distinguished by gentle preparation (within the enamel) and use in the so-called. aesthetic zone - the area of the dental arch visible when talking and smiling. The thickness depends on the material, manufacturing technology and clinical situation, varying from 0.3 to 1 mm.
Veneers: service life, reviews
Dental patients often have doubts about the strength of veneers, because their thickness is very small. Porcelain is one of the highly durable materials, but it is fragile. In order for the veneer to gain durability, it is fixed to a strong base of natural tooth enamel. This allows for a strong, durable and reliable design.
Experts conducted studies that allowed them to evaluate the “survival” of veneers. After 7 years of use, in 86% of cases, veneers that do not overlap the cutting edge of the tooth retained their appearance unchanged. For veneers that covered the incisal edge of the tooth, the survival rate reached 96%. this indicates the incredible reliability of ceramic veneers and the minimal likelihood of problems with them. More often, dental patients complain about braces than they experience difficulties with veneers installed on their teeth.
Often, braces and veneers lose their characteristics due to the fault of the clients themselves. Violation of oral hygiene, sudden severe injuries, and exposure of teeth to critical temperatures are unacceptable.
Composite veneers: reviews
The service life of composite veneers is limited to 2-3 years. In an ideal situation, if the dentist strictly followed the technology, the period of use of veneers will increase to 4 years. Like braces, they require periodic maintenance. Composite veneers need to be polished regularly. This will not stop the gradual fading and darkening of the surface.
Indications for the use of veneers
Indications for the use of veneers
- Changes in tooth color (discoloration);
- Tooth surface defects – stained cracks, non-carious lesions extending beyond the middle of the vestibular surface;
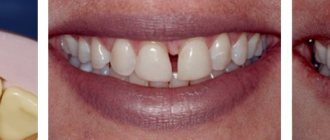
- The presence of gaps between teeth with a sufficient area of remaining healthy enamel and refusal of orthodontic treatment;
- Dental trauma;
- Abrasion along the cutting edge.
Contraindications to the use of veneers
- Inability to preserve more than 50% of the enamel during preparation;
- Teeth with removed pulp;
- Parafunctions of the masticatory muscles - non-functional contractions (bruxism - grinding teeth at night and/or daytime or clenching - strong clenching of teeth);
- Pathological types of bite (for example, straight, when the cutting edges of the front teeth are connected end-to-end);
- Carious lesions and/or fillings/restorations;
- Poor oral hygiene;
- Temporary teeth;
- Teeth after intensive fluoridation (relatively temporary).
The depth of preparation depends on the clinical situation. Thus, changes in color require an expansion of the boundaries of the preparation (greater coverage of contact surfaces, overlap of the incisal edge) compared to a change in tooth position (dystopia, for example, palatal inclination or position, a thin layer of enamel).
Indications and contraindications for the manufacture of lumineers
Lumineers (Hollywood veneers, ultra-veneers, nano-veneers) are veneers that do not require grinding of tooth tissue.
General indications for lumineers are similar to those for traditional veneers.
- Minor defects of the crown part of the tooth (chips, enamel cracks, wedge-shaped defects);
- Anomalies in tooth shape;
- Anomalies in the structure of hard dental tissues;
- Change in color of hard dental tissues;
- Relapses after orthodontic treatment (displacement of the central incisors to the sides with the formation of a gap).
General contraindications to the manufacture of lumineers
- Anomalies in the position of the teeth (the thinness of the design will not significantly change the situation);
- Anomalies in the closure of the dentition;
- Non-functional muscle activity and bad habits;
- Significant defect in the coronal part of the tooth (inlays or artificial crowns are shown);
- Acute or exacerbation of the chronic form of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity (it is impossible to ensure dryness of the field during fixation due to leakage of inflammatory fluid and/or blood);
- Allergic reaction of the patient to any component of the adhesive system;
- Amelogenesis imperfecta (inherited defective structure of hard tissue).
Care
If you take special care of your veneers, you can wear them for decades. In this case, of course, it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations. What are the care activities? They need to be cleaned thoroughly twice a day. You can use both a brush and paste.
Veneers are installed for cosmetic purposes. It should be remembered that the strength of the material is low, so you need to take care of their condition. It is necessary to ensure that bad habits (for example, biting nails) do not find a place in the patient’s life. In addition, you should not consume foods that are colored (for example, coffee, tea).
Sources used:
- “Aesthetic dentistry and ceramic restorations (Tuati B.)
- Criteria for evaluating composite dental restorations / A.I. Nikolaev and others - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2015.
- “Adhesive ceramic restorations” (Manier P.)
- National Library of Medicine (USA)
Advantages and disadvantages of lumineers
Advantages and disadvantages of lumineers
Benefits of using lumineers
- Gentle method (the principle of preserving healthy tissue);
- No need to make temporary restorations;
- The ability to achieve maximum aesthetic results with minimal impact on the hard tissues of the tooth.
Disadvantages of Lumineers
- Inability to radically change tooth color;
- A change in tooth shape is not always indicated;
- Plaque can accumulate at the lumineer-tooth interface and pigmentation and enamel caries can develop;
- The edge of the lumineer “hangs” over the gum, which can lead to the development of inflammatory periodontal diseases - gingivitis and periodontitis;
- Lumineers are very fragile due to their thinness (up to 0.3 mm) and require extremely careful handling at all stages - from manufacturing to use (unreliability of the design).
Author's veneers at NKclinic
Few people in the modern world can say that they are satisfied with their natural smile. Some defects, such as malocclusion and underdeveloped teeth, are congenital. During life, teeth are also exposed to negative environmental influences, including harmful industries, injuries and bad habits, which can lead to cracks, chips, and slight discoloration. Incorrect bite, without timely orthodontic correction, leads to increased tooth wear, which is a direct indication for reconstructive orthopedic dentistry.
For NKclinic specialists, making veneers is a responsible as well as creative process. At the same time, the finished product is inimitable and unique. Despite the large-scale introduction of digital technologies, doctors at our center exclude the use of template, standardized methods for manufacturing ceramic structures.
At NKclinic, the main principle of the work of the chief physician, Grigory Georgievich Kyalov, is to create teeth of natural beauty, taking into account the optical properties of hard dental tissues: light transmittance, brightness, transitional shades of color, like natural teeth. This makes it possible to emphasize your individuality, place the right accents and add charm to your smile.
The key to achieving maximum aesthetic results is individualized, multidisciplinary treatment planning. Often, in addition to the orthopedic stage, the patient needs surgical correction of the gingival margin, which allows the formation of the correct gingival contour. Get proper periodontal care.
Aesthetic and functional analysis of the dental system as a whole consists of a comprehensive study of each clinical case individually. This takes into account the structural features of the skull, the trajectory of the lower jaw, as well as facial features.
To achieve the most predictable and accurate results, we use digital technologies in combination with the practical and clinical experience and knowledge of our center’s professionals.
Orthopedic treatment planning:
- Medical photography to assess the aesthetic parameters of the patient’s face and determine individual anthropometric data.
- Creating 3D photographs of a face.
- Digital scanning, which, in combination with the manual skill of the doctor, allows you to obtain highly accurate three-dimensional digital models of the jaws and bite in a matter of minutes.
- 3D modeling makes it possible to compare medical photographs of a patient with digital models of the jaws, combined with computed tomography and 3D photography to predict the outcome.
- Digital modeling of teeth according to the patient's smile to achieve facial harmonization. The use of a virtual articulator allows you to build a physiologically correct bite.
- Making a 3D model on a 3D printer.
After this, our doctors make a mockup, i.e. transfer of a prototype of future orthopedic structures into the oral cavity.
At this stage, the design of future teeth is agreed upon with the patient, namely the color, shape, size and other nuances of the future smile.
This layout allows the orthopedist to prepare the teeth in such a way as to correctly convey the optical effects for maximum naturalness of the smile, as well as to easily install the ceramic structure in the oral cavity at the fixation stage, while maintaining the maximum thickness of the natural tooth tissues. Kyalov Grigory Georgievich individually selects materials for each specific case. Our goal is not to sell the most expensive technology. We work for high results and select the best solution for our patients.
Ceramic veneers are made from sintered ceramics, which has maximum aesthetic properties close to the properties of natural tooth enamel, therefore an important condition is the preservation of the enamel layer of the tooth.
NKclinic doctors work at the intersection of scientific and practical dentistry and art. Our approach will certainly be appreciated by people who want to achieve a truly unique smile.
Veneer manufacturing sequence
Veneers require individual care! Avoid lever-like movements when biting food
- Determination of indications;
- Cleaning teeth from plaque, determining color;
- Photographic registration of images of the patient's face in front and profile with the mouth open and closed in the anterior region (this information helps the technician in planning future restoration);
- Taking diagnostic impressions and making models, recording central occlusion (habitual closure of the dentition);
- Wax planning of future restoration (WaxUp);
- Production of temporary veneers (if preparation is planned);
- Preparation with depth marking (the goal is to remove only the minimum volume of enamel necessary for applying and fixing the facets;
- Taking final working impressions, re-registration of central occlusion, temporary fixation of temporary structures made of composite or acrylic plastic;
- Production of veneers in a dental laboratory or milling center;
- Removal of temporary restorations;
- Application and fitting of the finished structure, assessment of quality, accuracy of marginal fit, contact with adjacent teeth and antagonists (teeth of the opposite jaw);
- Cleaning and preparing the tooth surface and veneers for permanent fixation;
- Isolation of the working field;
- Fixation with dual-curing composite cement (light and chemical);
- Removing excess material;
- Check and, if necessary, correct contacts.
Total etching
Total etching for 30 seconds using phosphoric acid.
Rice. 8
Rice. 9 In any technique for etching tooth tissue, the most important point is the complete removal of acid from its surface. To clean the tooth from all decay products of the etching agent, we recommend rinsing it off for 20 seconds. It is worth remembering that overdrying the dentin surface can lead to the collapse of collagen fibers, so it must be dried carefully. And if you need absolute dryness, you can always choose the self-etching technique.
Rice. 10 Clean matte tooth surface after the etching stage.
Rice. 11 At the same time, the feldspathic veneers were treated with hydrofluoric acid. Depending on the concentration, the acid exposure time changes: 1.5 minutes for 10% and 3 minutes for 5%. A sign of high-quality processing is the surface of the veneer - uniform, matte and clean. Otherwise, this stage should be repeated or (if the desired effect is persistently absent) sandblasting should be used.
Application of adhesive
Apply adhesive within 20 seconds using ScotchBond Universal, which can be used as either a self-etch agent or a total etch technique.
Rice. 12
Rice. 13 The next step is to distribute the adhesive with an air stream over the surface of the tooth so that its excess does not affect the fixation of the veneer.
Adhesive polymerization
Adhesive polymerization stage. Manufacturers recommend carrying out this process for 20-30 seconds, but it is better to increase this time to form a strong hybrid layer even in places farthest from the lamp.
Rice. 14
Rice. 15 The inner surface of the veneer must be treated first with silane (a substance that enhances adhesion), and then with an adhesive. In this case, the silane application step can be omitted, since it is present along with the phosphate monomer (MDP) in ScotchBond Universal. Both of these approaches (using silane before applying the adhesive or using only a silane-containing adhesive) have a scientific basis. In this case, we preferred to pre-treat the veneer surface with silane.
Rice. 16 Carefully distribute the adhesive with an air stream so that its excess does not interfere with the fixation of the veneer.
Rice. 17 The polymerization strategy is the same: increasing the time will improve the quality of the hybrid layer. Polymerization for one minute is justified only with a very thin layer of bond.