In recent decades, therapeutic dentistry has received a significant impetus for development. This is due to the emergence of new materials and working methods, with the help of which it has become possible to restore the crown of a tooth even in the presence of significant defects .
At the same time, it is possible to repeat the smallest individual features of the patient’s dental apparatus. It is thanks to the precise recreation of the anatomical shape of the damaged tooth that structures made of composite materials are harmoniously combined with the environment in the oral cavity.
Restoration of the tooth crown
Indications for restoration
There are quite a few situations that will require you to resort to a restoration procedure. The main reasons include:
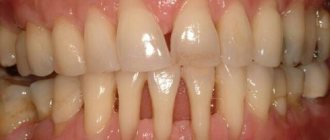
- Congenital anomalies of dental development, too wide interdental spaces.
- Minor injuries to hard dental tissues.
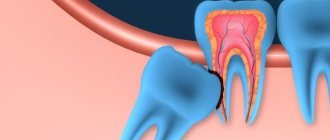
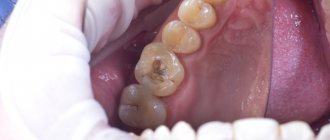
- Destruction of enamel as a result of the carious process and other reasons.
Various circumstances can lead to the formation of defects in the hard tissues of the tooth, for example, poor-quality water, lack of vitamins and minerals in food, even improper brushing techniques.
Small defects may not be detected by the person for a long time, which leads to the gradual destruction of increasingly large volumes of enamel and dentin. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly (at least 2 times a year) be examined by a dentist. This will allow restoration of the crown part of the tooth in the early stages and prevent further aggravation of the situation.
Causes of destruction
Even if the rules of hygiene are observed, teeth can be destroyed under the influence of unfavorable factors:
- caries;
- injuries – chips, cracks, fractures;
- unhealthy food - sweets, soda, baked goods;
- metabolic disorders as a result of endocrine pathologies, kidney problems, gastrointestinal tract;
- abrasive cleaning agents and aggressive methods of enamel whitening;
- lack of nutrients necessary for dental health - calcium, phosphorus, fluorine, vitamins, protein;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- living in an environmentally unfavorable area.
In some people, the development of pathologies is caused by genetic abnormalities or disorders of intrauterine development. Teeth also suffer during pregnancy, when the body’s main reserves are spent on the development and nutrition of the fetus.
Basic restoration techniques
In modern dentistry, many methods are used to eliminate hard tissue defects. This allows you to apply an individual approach to each patient and choose the most effective ones depending on the condition of the tooth. The most common methods include:
- Filling. The filling materials currently used make it possible to reliably eliminate even large defects and restore not only the chewing function of the tooth, but also the aesthetic appearance of the entire dentition.
- Veneers. These are thin ceramic onlays; they are widely used to correct defects and compensate for wide interdental spaces.
- Crowns. An old but reliable method of restoring teeth. Thanks to the use of new technologies, even very large imperfections (loss of 70% of tissue) can be eliminated with the help of crowns.
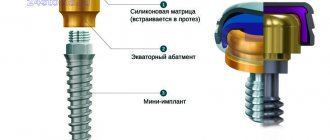
- Fiberglass reinforcement. Used to compensate for the loss of one tooth. Its artificial counterpart is built onto a base made of fiberglass threads, which are attached to adjacent teeth. There is no need to sharpen them.
Restoration of the tooth crown
The technology of stump overlays is also widely used. It consists of inserting a pin into the surviving root. A crown is then installed on it or a composite material is applied layer by layer. The method allows you to restore even a completely lost coronal part, if you managed to save the root.
Contraindications
Fortunately, there are not many absolute restrictions, but you need to know about them in advance. This usually includes intolerance to the materials and substances used for pain relief, as well as serious diseases of the heart, respiratory system, problems with blood clotting and mental disorders, due to which the patient cannot remain stationary for a long time. However, in the latter case, a solution can still be found, for example, by using general anesthesia instead of local freezing.
There may be more temporary contraindications; first you will have to deal with them, only then can you talk about restoration. This usually includes the presence of caries, thyroid diseases, problems with the immune system, and oncology. Also questionable is the possibility of treatment during pregnancy and breastfeeding, during radiation therapy, when diagnosing alcohol and drug addiction, etc.
Difficulties may also arise when a person takes certain medications, for example, blood thinners, cytostatics and others. You will also have to temporarily refuse intervention if there is severe stress, cachexia, that is, exhaustion of the body against its background, as well as fear of doctors. In the latter case, you can try the introduction of sedatives, which have a relaxing and calming effect.
Crown extension algorithm
In the process of building a crown using composite materials, it is especially important to accurately replicate the natural anatomical shape of the tooth surface. The chewing surface of molars is particularly complex. It is diamond-shaped and includes four tubercles:
- Paracone.
- Metacone.
- Protoconus.
- Hypocone.
Additional tubercles may also be present, for example, the Karabel tubercle. Between the tubercles there are grooves separating them from each other. The dentist must reproduce all these structures as accurately as possible, using composite materials and special instruments. Due to this, the chewing load will be evenly distributed, which will prevent further tooth decay.
To simplify orientation, a special coordinate system is used, which divides the tooth into four sections:
- Medial.
- Vestibular.
- Distal.
- Palatine.
This division makes it possible to more accurately calculate the pattern of tubercles and grooves on the functional surface of the crown, which significantly facilitates the formation of a new surface.
The restoration algorithm looks like this:
- Cleansing teeth from plaque and other contaminants. Then a material of a suitable color is selected and a local anesthetic is administered. In essence, this is a preparatory stage at which everything necessary for further actions is prepared.
- Tooth preparation. It involves the removal of parts of the crown that are injured or affected by caries. It is performed within the boundaries of healthy tissues that have retained their natural characteristics.
- Application of materials. To imitate dentin and enamel, the same composition is used, differing in color. A darker shade is selected for dentin, and a lighter shade for enamel, corresponding to the color scheme of the remaining teeth.
- Formation of a new chewing surface. It involves the artificial recreation of anatomical structures such as tubercles and grooves. This is a difficult stage, since the quality of the specialist’s entire work largely depends on it. To perform it, you will need to use several types of bur (ovoid, needle-shaped, No. 3, No. 4).
Different burs are needed to repeat the shape of the microrelief of the chewing surface, which will fully correspond to the structure of the lost area. After the process is completed, the crown is polished. To do this, use polishing heads made of silicone or circular brushes with polishing paste.
Restoration of the tooth crown
Polishing significantly improves the smoothness of the crown surface. In addition to additional comfort for the patient, polishing serves as a preventive measure for the development of caries and plaque deposits. It will be much more difficult for food debris and bacteria to attach to a smooth surface.
Stages of dental restoration
1.
Treatment planning.
At the initial appointment, a visual and instrumental examination and analysis of the oral cavity are performed. The topographic position of the elements of the dental arch, the shape of the vestibular surface, the cutting edge/dental contour, the length of contacts between units of the row, and individual characteristics are determined. After diagnostics, the optimal shade of the material is selected to recreate transparency/natural shine;
2.
Sanitation
. During preparation, hygienic teeth cleaning, removal of stone/plaque, and treatment of diseases are performed: filling carious cavities using local anesthesia;
3.
Fixation of the pin in the root canal
. The pin is fixed in case of significant loss of tooth tissue; in the future, the rod structure serves as the basis for the formation of a new organ;
4.
Regeneration of tooth shape with filling material
;
5.
Finishing
: polishing and grinding.
Features of composite materials used for restoration
There are many different composites that are suitable for restoring the crown of a tooth. These materials are characterized by high strength, durability, are easy to use, and have a moderate cost. This combination of characteristics has made them very popular among both dentists and patients.
The basis of the composite is an organic or modified matrix in which the filler and other components that make up the material are evenly distributed. Inorganic microparticles of different sizes (from 0.01 to 100 μm) are usually used as fillers. Most often these are compounds of barium, aluminum, and silicon dioxide.
In addition to the filler, dyes, stabilizers and other functional additives are added to the composite composition. There are several main types of composite materials:
- Microfilled. Contains many particles of the minimum available size. They have high aesthetic qualities and excellent wear resistance. They are used to work on front teeth and install veneers.
- Macro-filled. They are distinguished by increased strength, but low aesthetics. Large particles create a matte effect and rough texture. Suitable for working with lateral teeth.
- Mixed. Universal compositions that combine the positive qualities of the above varieties of composites. The main disadvantage is that they cannot be used to eliminate cavities.
There are many other types of composite materials, but they are used less frequently, mainly for solving highly specialized problems, for example, keromers, ormokers.
One of the promising modern developments is nanocomposites, which consist of extremely small particles. They have the best performance in all areas. The only drawback of nanocomposites is the high cost associated with the complex and expensive production process, so they cannot be found in all cities; even in Moscow, not all clinics offer such materials to choose from. But over time they will become much more accessible, since this is a new technology that has only recently begun to spread.
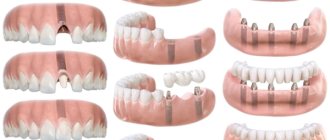
Types of dental crowns
Rules of care
Oral care after dental restoration involves following the rules of hygiene and the following recommendations:
- after the procedure, you should not eat foods containing dyes, drink coffee, or strong tea for 18-20 hours;
- eliminate high stress on the teeth, use soft brushes, non-aggressive pastes, gels with neutral PH;
- You should not use rinses that contain chlorhexidine - it can change the color of the restoration;
- patients with bruxism need to use special mouth guards to prevent chipping of orthopedic structures;
- adjust your diet: avoid eating nuts, hard vegetables/fruits, colored carbonated drinks, beets, quit smoking and alcohol, too cold/hot food, which can cause chips and cracks in the material and loss of its snow-white color.
If external changes, increased sensitivity and pain occur, you should immediately contact your dentist to eliminate serious complications. For the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to visit a doctor twice a year.
Types of artificial crowns
Restoration of the coronal part of a tooth is often performed by installing an artificial crown. This technique is used when the destruction process has affected more than half of the tissues. The most commonly used types of crowns are:
- All metal. They can be stamped or cast; their surface is often coated with decorative plating, for example, gold. Although this method of producing crowns has become significantly outdated, it is still popular. This is due to the affordable price and fairly long service life of such structures.
- Metal-ceramic. They are also made from metal, but the top layer is formed from ceramic materials. This significantly improves the properties of such crowns and increases their aesthetic qualities.
There are also completely ceramic crowns. They are made from porcelain or zirconium ceramics.