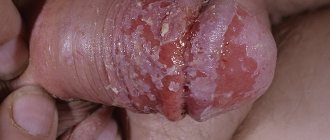
Like other parts of the body, there are sebaceous glands called Tyson glands on the head of the penis and the inside of the foreskin.
They produce a thick secretion - spegma - the purpose of which is to protect the penis from friction against the foreskin or other damage. Normally, this lubricant has a milky color, but some physiological reasons or pathological processes can provoke a change in its consistency and the formation of a white coating on the head of the penis.
Attempting to cope with this problem on your own is dangerous and can lead to the development of serious complications. Therefore, if this symptom occurs, you should immediately seek the help of a urologist.
Spots on the skin of the penis - reasons for their appearance
White spots on the penis may indicate the following diseases and conditions:
- Allergies are the most common cause. The white spots are usually itchy. Symptoms often do not appear immediately, but several hours or even several days after skin contact with the allergen.
- Vitiligo is areas of depigmented skin. As a rule, they are found not only on the penis, but also on other areas of the skin. But such spots appear gradually. They may appear first on the skin of the penis. In the future, their growth is observed. The spots become more numerous, they merge, appearing on the scrotum, pubis, as well as areas of the skin remote from the genitals.
- Lichen sclerosus is a precancerous pathology. The spots are localized on the head. This is a type of limited scleroderma. Synonyms: guttate morphia, Tsumbusha's lichen alba, white spot disease, lichenoid scleroderma, atrophic punctate leukoderma. The inflammation is autoimmune in nature. It is not spots that appear, but plaques – that is, they are dense and characterized by thickening of the skin.
- Hypertrophy of the sebaceous glands - small white spots appear on the penis. This is the norm, not a pathology. Hypertrophic sebaceous glands are unsightly, so they are sometimes removed for aesthetic reasons. But they do not threaten health.
- Psoriasis is a systemic disease that can begin in the genitals. Silvery plaques with peeling appear. Often found on the head.
- A tumor can look like anything, including a white spot on the skin of the penis. The growth of the spot and especially its manifestation should cause oncological alertness.
- Setton's nevus is a pigment spot that looks like an area of hyperpigmentation (mole) in the center and a focus of lack of pigment on the periphery. It looks very similar to vitiligo. Treatment is required only for aesthetic reasons.
- Scars - if the skin was damaged and then restored, then it is lighter than the surrounding skin. The cause may be injury, chafing, previous herpes or other inflammation, surgery and minimally invasive procedures. A white ring around the penis may appear when rubbed with a condom. Small spots form after acne resolves.
Diagnosis of pearly papules
The diagnosis is made based on a clinical examination by a urologist or dermatovenerologist. If the change is accompanied by symptoms of inflammation - redness, swelling and itching - another etiology should be considered.
They are often confused with condylomas (genital warts), which are sexually transmitted diseases caused by HPV infection. The misconception can be easily eliminated with the help of a biopsy and microscopic examination of this change - a different number of dilated thin-walled blood vessels, proliferation of fibroblast cells and connective tissue are observed.
What does a white spot on the penis look like?
For different diseases, white spots on the penis look different:
- vitiligo - spots of different sizes with clear boundaries, irregular shape, can merge, are multiple, do not rise above the skin level
- Setton's nevus - looks the same as vitiligo, only there is a mole in the center (sometimes the mole disappears, but the depigmented spot remains)
- psoriasis – silvery, dense plaques with small scales
- scars - may be denser than the surrounding skin, rise above it or fall below the level
- lichen sclerosus - multiple small (no more than 1.5 cm) white papules rising above the skin level (can merge into irregularly shaped plaques)
Causes
There are several factors that can provoke the inflammatory process. In most cases, the causes of the disease are:
- wearing tight synthetic underwear, which can injure the delicate skin in the groin area;
- allergic dermatitis, which develops when choosing inappropriate intimate cosmetics, lubricants, condoms;
- failure to comply with intimate hygiene rules;
- complications of diabetes and other endocrine diseases;
- obesity, which provokes a decrease in the body's defenses;
- alcohol abuse and frequent smoking;
- frequent stress, overwork, nervous tension.
Often inflammation occurs not as an independent disease, but as a complication of balanitis. The risk of developing an inflammatory process also increases if the frenulum of the foreskin is too small. During intimacy, tears or microcracks appear on it, in which pathogenic microorganisms can begin to multiply.
Are white spots on the penis dangerous?
Usually white spots on the penis are unpleasant, but not dangerous. The exceptions are:
- psoriasis
- lichen sclerosus
- penile cancer
Psoriasis is dangerous in itself. Spots on the testicles or penis do not directly pose a threat to life. Psoriasis can affect large areas of the skin as well as internal organs.
Lichen sclerosus on the penis is not dangerous for 95% of people. But in 5% of cases it transforms into squamous cell skin cancer.
The most dangerous white spots on the penis are associated with a malignant tumor. It is rare to die from this type of cancer, as there are effective surgical treatment methods. But partial or complete removal of the penis dramatically reduces a man’s quality of life.
Signs of wound formation
During the formation of pathology, the inner wall of the skin is damaged, which contributes to some manifestations:
- the formation of wounds of various sizes as a result of the development of pathology, which cause acute pain, causing discomfort for the patient;
- redness and formation of an inflammatory process around existing wounds;
- small wounds are formed as a result of complications after mechanical trauma, gradually destroying the internal covering and forming large wounds;
Characteristic signs of the presence of wounds on the foreskin, without visual manifestations, are pain when urinating and exposure of the head. Sexual intercourse is also accompanied by discomfort and pain.
Patients experiencing such problems should not aggravate the situation and, if possible, protect themselves from provoking factors in order to avoid serious complications.
Useful information on problems related to the foreskin and urology:
- Calling a urologist to your home
- Balanitis
- Balanoposthitis
- Frenum plastic surgery
- Urethral swab
- Prostate massage
- Circumcision
- Tests for STIs
- Treatment of sexually transmitted diseases
- Ultrasound at home
- Frenum of the penis
- Pyelonephritis
- Ultrasound of the bladder
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections
- How to prepare for an appointment with a urologist?
- How to get tested for urological diseases?
- What tests can be done by a urologist?
- What diseases does a urologist treat?
- What symptoms should you consult a urologist for?
- How to make an appointment with a urologist at the clinic?
- Consultation with a urologist
- Diagnosis of urological diseases
- Examination by a urologist
- Treatment of urological diseases
- Appointment with a urologist
- Urology - the science of men's health
- Pediatric urologist
- Male doctor
- Paid urologist
Treatment of papilloma virus in men
If a man has condylomas on the head of the penis, treatment is carried out in two directions:
- Remove growths.
- Conduct shock antiviral therapy.
None of them have any advantages, since the doctor prescribes treatment based on their examination data and the tests obtained. Often these treatments are complementary to each other.
Drug therapy complements the process of removing papillomas in men. With its help, the immune system is strengthened to avoid relapse, since removal of papillomas again brings the patient to the doctor with the same symptoms of the disease in 30% of cases.
The patient is prescribed immunostimulants: polyoxidonium, immunal, cycloferon, etc. These drugs are prescribed only by a therapist or urologist.
Ulcers caused by oral diseases
White sores in the mouth can appear due to diseases of the oral cavity. The most common cause is stomatitis. It comes in several types:
- aphthous;
- herpetic;
- bacterial;
- fungal.
| White ulcers in adults and children occur with aphthous and herpetic stomatitis. This disease can appear due to stress, untreated caries, lack of vitamin C, or overexertion. It is better not to self-medicate, but to immediately consult a doctor. Recommendations, in addition to medications, may include treatment of caries, a balanced diet, stress reduction, etc. |
| There are two separate forms of stomatitis - Bednar's aphthae and Setton's aphthae. The former develop only in a child due to injury to the mucous membrane or poor oral hygiene. Such rashes are also called erosions. Setton's aphthae is a more complex and painful phenomenon. It begins with the appearance of compactions, which then develop into painful ulcers. They most often form on the inside of the cheeks, in the corners of the lips and on the sides of the tongue. |
| Another cause of white sores is gingivitis. In smokers, such rashes are much more common due to the effects of nicotine on the mucous membranes. Those who have poor oral hygiene, reduced immunity and hormonal imbalances are also at risk of encountering gingivitis. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis: when the tissue that supports the tooth is affected. And this is a direct path to tooth loss. |
Types of frenulum diseases
There are a certain number of pathologies that require medical intervention and a certain course of therapy:
- accumulation of growths of different shapes and sizes;
- papillomas are an infectious disease that spreads sexually; without timely treatment, the entire penis may be affected;
- rashes indicate a disruption in the functioning of certain organs or the development of an allergic reaction to certain external irritants;
- swelling occurs due to damage to the genital organ;
- itching can be caused by a variety of external factors and accompany the development of other pathologies;
- frenulum rupture.
If any symptoms indicating the development of pathology occur, you should immediately seek medical help to avoid subsequent complications and injuries.
Symptoms and diseases of the frenulum of the penis:
- Rupture of the frenulum of the penis
- Removal of the frenulum of the penis
- Growths on the frenulum of the penis
- Soreness of the frenulum of the penis
- Papillomas on the frenulum of the penis
- Rash on the frenulum of the penis
- Itching of the frenulum of the penis
- Frenum of the penis
- Inflammation of the frenulum of the penis
- Swelling of the frenulum of the penis
Important
If papillomas appear on the head of a man’s penis, then curing them will not be easy, and the removal procedure will be painful.
First of all, doctors recommend that a man avoid promiscuous sex and use barrier contraception.
With early prevention and a negative test for the virus, a healthy man is offered vaccination against HPV. If the virus is detected, but papillomas have not yet had time to manifest themselves, it is advised to strengthen the immune system in order to avoid their growth.
There are several ways to strengthen your immune system:
- Improve your diet, add a vitamin-mineral complex or foods enriched with beneficial microelements and substances.
- Exercise.
In winter and in the off-season, immunologists advise strengthening the immune system with vitamin complexes and antiviral drugs.
Preparing for treatment
Before starting treatment for papilloma, the doctor conducts a thorough examination of the man’s groin under magnification, makes a diagnosis, and studies tests.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the correct diagnosis:
- Oral interview with a venereologist, taking an anamnesis.
- If the head of the penis, urethra or urethra is affected, consultation with a urologist is indicated.
- You need to be tested for HPV using the PCR method (scraping from the genitals), for AIDS, HIV and syphilis.
- Examination of the anus by a proctologist.
- Getting tested for STDs.
After all the tests are ready, the doctor will select the appropriate method for treating and removing papillomas for the man. Tumors can be removed only if the man does not have infectious or viral diseases in the acute stage.
Symptoms of condylomas
Single neoplasms are difficult to detect and there is no pain syndrome. Condylomas do not bother the patient and do not affect the quality of sexual life. Formations are detected by touch or upon examination.
Papillomas in the urethra in men, around the head of the penis, around the anus and on the scrotum are common places for growths to occur. HPV is found in warm, moist places, so the folds of the genitals and anus are likely places where growths are found.
If the disease is not treated, it will progress, eventually the papillomas will grow together, protrude more above the surface of the skin, and the appearance will resemble cauliflower.
Fused papillomas affect a large area on the genitals, and then the symptoms of the disease become obvious:
- Pain during sexual intercourse. Growths on the head of the penis interfere with penetration and cause discomfort to partners.
- Itching, redness of the affected area, irritation. During friction, the growths become injured, bleed and itch.
- Difficulty urinating. Those papillomas that have grown in the urethra will interfere with normal urination.
If a man develops condylomas on the head of the penis, this is the first sign that the human papillomavirus (HPV) has entered the body.
You can get infected in several ways:
- sexual intercourse – this includes vaginal, oral or anal intercourse. When healthy mucous membranes come into contact with infected genitals, infection occurs;
- at home, 20% of those infected caught the virus due to insufficient hand hygiene, sharing personal hygiene items (washcloth, toilet rim, underwear, towels);
The absence of tumors on a man’s genitals does not mean that the person has not become a carrier of the HPV virus. If a person has a strong immune system and leads a healthy lifestyle, the body resists the virus, stopping the progression of the disease.
Decreased immunity often causes growths to appear. There are factors that negatively affect the body's immune system:
- recurrent colds;
- hypothermia;
- unbalanced, meager, monotonous nutrition;
- regular neuroses, stress, overwork, lack of sleep;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
Doctors recommend regular examinations to ensure the absence of the virus, and that the man’s sexual partner also be examined.