- Laser exposure
Papillomas on the tongue are benign neoplasms that arise from epithelial cells mainly under the influence of the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Most often occur in women over 40 years of age (57%). However, under appropriate circumstances, the disease can manifest at any age (the child has a high risk of infection from the mother).
Papillomas on the tongue according to the classification of A.L. Mashkilleyson (1970) is usually classified as facultative precancerous conditions - the risk of malignancy is up to 10%.
Papillomas on the tongue are caused by constant trauma to the mucous membrane and/or HPV infection
According to the ICD, papilloma is classified as squamous cell formations M 80.5-M 80.8. When examining a patient, the doctor relies on a visual examination, and in doubtful cases, a biopsy of the formation is indicated (differential diagnosis with a polyp, hemangioma).
What is papilloma on the tongue?
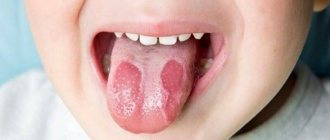
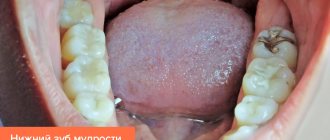
It is not difficult to detect the presence of a growth on the surface of the tongue. This growth is characterized by a rounded shape, protrudes above the mucous membrane and has a wide base.
Papillomas on the tongue are a dangerous manifestation of HPV. Symptoms: growths on the tongue are round in shape, up to 2 cm in size, similar to a nipple, with a soft consistency.
Diagnostics: differential diagnosis with oncological diseases of the tongue. Treatment: antiviral, immunocorrectors, removal.
The size of the formation is from 2 mm to 2 cm. Location: mainly on the back or edges of the tongue. In some cases - at its tip or under it. When the tumor is located near the root of the tongue, it can only be detected during a doctor’s examination or in case of extensive growth.
Removal of papillomas
Papillomas are benign formations.
From the outside, the papilloma looks like a nipple, its color is similar to the shade of nearby tissues, and its structure is soft. Both single and multiple growths form on the surface of the tongue.
Often, the presence of papillomas on the tongue is not given due attention and a specialist is visited if the growths have become impressive in size or their number has increased significantly.
The papilloma itself does not cause pain or itching. But due to frequent injury to the growth, there is severe pain and bleeding. In addition, the growth interferes with chewing, swallowing, talking, and sometimes breathing.
Papilloma on the tongue is often found in the practice of dentists and ENT doctors.
Removal is usually carried out by otorhinolaryngologists. The radio wave method is used more often than others.
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist
Zhikhoreva Inna Viktorovna
6 years experience
Features of the pathogen:
- Laboratory signs noticeable immediately after infection. It will take approximately 3 months before growths are detected.
- The virus can manifest itself in people with reduced immunity. In this regard, experts advise people with HPV to be tested for HIV.
- In some cases, it is possible to recover on your own. During the recovery period, warts can disappear on their own.
- Elimination of external symptoms does not lead to elimination of the viral agent. There is no specific etiological therapy; antiviral agents are used in treatment. They are effective in the presence of herpesvirus, hepatitis and other infections.
Laser removal of papilloma in the throat. Progress in medicine helps.
The main thing is to keep up with it and take advantage of all the new opportunities. In the treatment of papillomatosis, these include the use of CO2 laser, narrow-spectrum endoscopy and certain antiviral drugs. But there is one prerequisite to achieve the best result - everything must be performed by a highly qualified surgeon with extensive experience in treating laryngeal papillomatosis. This is extremely important to understand.
Papillomatosis is characterized by the formation of exophytic growths that affect the mucous membrane of various parts of the larynx and underlying parts of the respiratory tract.
Kinds
Having identified growths on the surface of the tongue or in the throat, you need to establish what type of condyloma this is. They are divided into 2 types:
- Reactive. Papillomas are a consequence of the adverse effects of various irritants. These are mainly mechanical, chemical, thermal or infectious lesions.
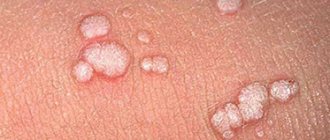
- Neoplastic. Seen extremely rarely. Outwardly they resemble ordinary multiple nodular growths. They are presented in groups or single papules.
Papillomas that appear in children and adults on the surface of the tongue or in the throat are also divided into 2 types.
Pointed
This is a growth under the tongue that has a light pink tint and a sharp shape. In some cases they can grow.
Externally similar to cauliflower inflorescence. A similar neoplasm forms on a stalk. Small in size, but causes significant pain.
Sometimes there is discomfort during swallowing. Acute papilloma gets in the way, rubbing against the teeth and cheeks. The favorite place for this wart will be the area under the tongue.
You need to be extremely careful. Self-therapy is prohibited. Treatment is permissible only under the supervision of a specialist.
Flat
They are characterized by clearly defined contours and protrude somewhat above the surface of the skin. They are located in the throat, on the tonsils, on the small tongue. They do not cause any particular pain. They are extremely difficult to detect.
Why can our articles be trusted?
We make health information clear, accessible and relevant.
- All articles are checked by practicing doctors.
- We take scientific literature and the latest research as a basis.
- We publish detailed articles that answer all questions.
Any examination must be carried out by a doctor in a hospital setting. Self-treatment can have consequences for a person’s life and health. Therapy involves the use of various medications. There is no need for surgical intervention.
When such growths appear in children, their difference will be excessive growth of the tissues of the mucous membrane of the small tongue.
Location zones
The growths select areas on the oral mucosa that are subject to regular trauma. When the stroma is involved in the ongoing inflammation, the growth grows rapidly. This is because the stroma is the basis for the organs.
It is formed from connective tissue, which is saturated with blood and lymphatic vessels with multiple nerve endings. Such an environment is favorable for condyloma. It immediately begins to grow, turns into an ulcer, bleeds and causes severe discomfort.
New growths that are located singly on the surface of the tongue need special attention. Similar symptoms are typical for females. The result will be neuralgia.
Even if the condylomas are in a place where they are invisible, the sensations in the oral cavity cause significant discomfort.
How to identify the disease
If one or more symptoms are detected, it is recommended to consult the following doctors.
The dentist will help identify the presence of diseases of the teeth, gums, etc. Often, precisely because of the neglected condition of the teeth or the presence of inflammation, a person develops growths on the mucous membranes.
The next specialist is an ENT specialist. It is necessary to contact him in order to prevent the growth of formations in the larynx and nasopharynx. Special equipment and the doctor’s experience will help identify the disease at an early stage and prevent infection of other areas.
A gynecologist, a venereologist and a urologist are the doctors who must be visited if you have condylomas in the mouth, because they have the same appearance as warts on the genitals.
After visiting the doctor and being examined, the patient needs to undergo a full examination, including donating blood and urine for a general analysis, bacterial culture to exclude viral diseases, as well as a PCR analysis, the essence of which is to identify the type of warts. If cancer is suspected, the person is prescribed a biopsy of oral tissue. Determining this on your own is quite difficult.
Causes
Papilloma on the tongue is difficult to remain unnoticed. Unpleasant sensations, burning, and pain are concentrated at a certain point on the surface of the tongue.
Test for human papillomavirus
The human papillomavirus (HPV) manifests itself differently in each case.
The patient looks at the affected area and discovers a small white growth that looks like a purulent pimple. The main reason for the appearance of condylomas on the surface of the tongue is human infection with HPV.
This is influenced by a number of provoking factors:
- Reduced functioning of the immune system.
- Tobacco smoking.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Taking drugs.
- Chaotic sex life.
- Constant colds .
- Self-administration of oral contraceptives.
What is HPV
The human papillomavirus affects only humans, and its main mode of transmission is sexual. Therefore, HPV is most common among sexually active people. This explains the fact that most often infection occurs at a young age at the beginning of sexual activity and at its peak, i.e. 15-25 years. Moreover, several strains (types) of HPV can be present in the human body at the same time, provoking the appearance of different types of tumor-like formations on the skin and mucous membranes.
The disease caused by HPV is called papillomatosis.
Infection with the virus occurs when it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes with particles of exfoliated skin or mucous membrane of an infected person. They attach to the membranes of immature epithelial cells, from where they penetrate into the cytoplasm of the cell, and subsequently into the nucleus. It is the cell nucleus that contains DNA, which is damaged by HPV. As a result, when the affected cell divides, the consequence will be the formation of not healthy new cells, but those that already have altered genetic information, which leads to failures in the mechanism of their reproduction and differentiation. This causes the appearance of tumors on the skin and mucous membranes.
HPV infection can lead not only to the formation of papillomas, but also warts, as well as flat and genital warts. However, it can also be asymptomatic. In this case, the patient will not show external signs of human papillomavirus infection, but he will act as a carrier and can infect others through unprotected sexual intercourse or at home.
Thus, HPV infection does not always lead to the formation of papillomas. This depends on the strength of the person’s immunity, but more often the first small papillomas appear 1-6 months after infection.
The human papillomavirus is intracellular. Therefore, with sufficient strength of the immune system, the body successfully suppresses its activity and does not allow it to provoke cell proliferation. But when the immune system is weakened as a result of certain factors, the body’s defenses fall, the virus becomes more active, which leads to the formation of papillomas.
All strains or types of HPV can be divided into 4 groups:
- non-oncogenic – strains 1-5, 63;
- low oncogenic risk – strains 6, 11, 40, 42-44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81;
- medium oncogenic risk – strains 26, 31, 33, 35, 51-53, 58, 66;
- high oncogenic risk - strains 16, 18, 39, 45, 56, 59, 68, 73, 82 (types 16 and 18 are considered the most dangerous).
HPV strains of high oncogenic risk have special genes in their DNA that are responsible for the synthesis of specific oncoproteins (E6 and E7). Therefore, when it is integrated into the DNA of a human cell, its anticancer protection decreases. Oncoproteins destabilize the genome of skin cells, provoke their active reproduction and suppress the ability to differentiate. Therefore, this is fraught with a high risk of developing cancer when infected with strains of the human papillomavirus of high oncogenic risk.
The magnitude of the danger that papillomas pose directly depends on the type of HPV. Infection with strains with a high oncogenic risk is dangerous due to the development of:
- cervical cancer;
- malignant tumors of the anus, vulva, penis;
- oropharyngeal cancer, etc.
70% of cases of cervical cancer are caused by infection with types 16 and 18 of HPV.
But even when infected with strains of low oncogenic risk and the formation of papillomas, they should be treated carefully. Convex neoplasms are often injured by items of clothing, bleed and tend to become inflamed. At the same time, perhaps the greatest discomfort is caused by formations on the genital organs, which cause severe discomfort and complicate the conduct of an intimate life. In such cases, a secondary infection may occur, which can cause the development of purulent-septic complications. In addition, papillomas can form on the mucous membranes of almost any internal organ, which leads to disruption of their functioning. Thus, papillomatosis of the upper respiratory tract often occurs, which causes difficulty breathing.
Symptoms
Before visiting a doctor, a person must discover what worries him. It is necessary to identify the location of unpleasant sensations on the surface of the tongue. In children, this is a shooting or aching pain; in adulthood, it is a feeling of a foreign body or persistent discomfort in a certain place on the tongue.
More specifically, it is possible to establish papilloma based on the following signs:
- The growth is located on the leg.
- The surface of the condyloma is soft.
- The shade of the wart is similar to the shade of the tongue.
- Sizes range from 2 mm to 2 cm.
The favorite place for growth is the side walls of the tongue. Less often - under it or at the tip.
The neoplasm does not provoke severe pain, but discomfort or a feeling of a foreign body exists. Often there is more than one growth; upon careful examination, it is possible to identify a whole group of minor neoplasms.
A proper attitude towards your own health will help you identify papilloma on the tongue in a timely manner.
Diagnostics
The growth on the front surface of the tongue is immediately visible. It interferes with normal eating, conversation, and bleeds due to the fact that it is easy to get caught and damaged.
This provokes unpleasant pain. When the condyloma is located in the oral cavity, for example, on the soft palate or on the back of the tongue, it is possible to notice it by accident when examining the patient by a specialist. Having discovered a growth, the doctor will examine its structure.
Papilloma is soft in structure. And the shade is somewhat lighter than the mucous membrane. When it is in the oral cavity, it will be rough.
What is different is the new growth in the child: condylomas seem to cover the tongue, cover the entire soft palate, and reach the tonsils. It is much easier to detect in children than in adults.
Particular attention should be paid when examining elderly people: they often develop a cancerous tumor resembling condyloma. Only with cancer at the base of the tissue from which the growth is formed is there a clear compaction.
Complications
Complications of benign formations of the ENT organs directly depend on the severity of the process and are caused by disruption of the processes of natural ventilation of the nasal cavities and the free outflow of mucous membranes.
Among the possible complications, the most common are those that occur chronically or frequently recur:
- sinusitis and sinusitis;
- otitis;
- rhinitis;
- tonsillitis.
Complications also include decreased hearing and sense of smell, hypoxia, increased blood pressure and fatigue due to impaired nasal breathing.
Treatment
A neoplasm under the tongue or in the oral cavity is treated under the supervision of a dermatologist. After conducting a thorough and comprehensive examination, he must prescribe medications. In some cases, condyloma can be removed surgically.
Self-medication is dangerous with complications!
Attention
Despite the fact that our articles are based on trusted sources and have been tested by practicing doctors, the same symptoms can be signs of different diseases, and the disease may not proceed according to the textbook.
Pros of seeing a doctor:
- Only a specialist will prescribe suitable medications.
- Recovery will be easier and faster.
- The doctor will monitor the course of the disease and help avoid complications.
find a doctor
Do not try to treat yourself - consult a specialist.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment consists of following the following instructions:
- The use of local therapy with an oil solution of vitamin A in the absence of indications for surgical removal of the growth.
- The use of interferons, which reduce the amount of viral DNA at the site of pathology.
- Simultaneous use of immunostimulating antiviral drugs.
At the moment, there is no effective remedy that could help completely get rid of HPV. The use of any medications must be agreed with a specialist.
Antiviral treatment
Antiviral therapy involves the use of medications to eliminate the development of HPV. Vitamin complexes are prescribed; they help activate the body's defenses. The specialist recommends balancing your diet and leading an active lifestyle.
According to statistics, patients with papillomas have a weakened immune system. People with high immunity are carriers of HPV, but at the same time they do not have any manifestations on the skin.
The specialist prescribes immunomodulating agents, a complex of vitamins and restorative medications. It should be remembered: immunity cannot be increased in one day with pills. Medicines are aimed at maintaining a weakened body during a critical period.
Vaccination
HPV is one of the few strains of viruses against which a vaccine has been developed. It includes organic substances that are similar in structure to the structure of living HPV viruses. Immunity against real pathogens is developed perfectly.
Before vaccination it is necessary to exclude:
- Pregnancy. Get tested or have a blood test.
- Use of serious medications .
- Other vaccinations.
- Serious diseases .
Vaccinations are given intramuscularly. Dangerous side effects are observed extremely rarely.
Drug therapy
Interferon
Treatment of papillomas should be comprehensive, which includes drug and surgical therapy. Before prescribing medications, the doctor cleans the oral cavity, eliminating white plaque and pockets through which infection can enter the body.
For this purpose, the oral cavity is sanitized, and then treated with ointment, which has an antiviral effect. This could be, for example, “Bonaftone”, “Adimal” or “Megosin” ointment. It is necessary to treat the oral cavity from below and from above.
Then the doctor prescribes antiviral and immunostimulating drugs, for example, Interferon or Panavir, and vitamin complexes. Their action is aimed at increasing the body's defenses. The doctor selects medications based on the individual characteristics of the body, taking into account contraindications and side effects.
Removal
The method by which the papilloma will be removed must be chosen by the treating specialist. It depends on the location and characteristics of the body. There are the following ways to eliminate tumors:
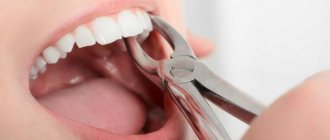
- Surgical excision using a surgical scalpel. After the procedure, “cauterization” is performed. A similar technique is used in the presence of single growths or when they are inaccessible and it is impossible to use other methods.
- Laser elimination. The most effective, painless method with no adverse effects. The disadvantage is the high cost of the procedure.
- Electrocoagulation. The method involves cauterizing the growth with an electric current. The disadvantages include painful manipulation and a long rehabilitation period.
- Radio wave surgery. The technique is similar to the previous one, only instead of current, high-frequency radio waves act on the papilloma. The pain is insignificant, the number of adverse effects is minimal and the rehabilitation period is short.
- Cryodestruction. The most unpopular surgical method for eliminating papilloma on the tongue. The tumor is removed by influencing it with cold. The wart is frozen to liquid nitrogen temperature. The growth will be frozen and die within a week.
If the technique involves excision of the wart, then the biomaterial is sent for histological diagnosis in order to analyze the structure of the growth.
Methods for removing tumors on the mucous membrane of the tongue
Laser exposure
The most effective method due to the selectivity of the tissue being burned. Modern devices are easily adjusted exclusively to tumors with minimal capture of healthy cells. The risk of complications after the procedure is less than 1%. The laser is aimed specifically at the formation and the optimal program is selected (specific wavelength, time and depth of exposure) depending on the type of growth. There are both automatic programs with fixed values, and a number of adjustable parameters for atypical forms of papillomas. The tissues are burned out in layers; in case of pointed forms, the formation is cut off at the very base. Formations of different localizations, including in the area of the frenulum and root, are available for removal.
Electrocoagulation
The method is based on removing the growth using an electric knife. The method is less effective than the previous one, since significant injury to surrounding tissue occurs. Clinical manifestations of a burn do not occur immediately, but over the course of several days, since overheating affects not only nearby cells, but also cells of healthy tissue located at some distance. A wound surface appears at the site of the removed lesion, which must be treated with antiseptics to avoid infection. The tissues are burned in layers, the average exposure time is 20-60 seconds. Electrocoagulation is used mainly for single papillomas localized on the tip or lateral surfaces of the tongue.
Radio wave treatment
A low-traumatic method that allows you to remove several formations at once (important for papillomatosis). The method is based on exposure to a radio frequency wave, which leads to heating and destruction of formation cells. The exposure time is selected individually.
Cryotherapy
In this anatomical area, it is used less frequently than other methods due to the capture of a large amount of tissue. After use, a chemical burn is formed at the site of formation, which takes a long time to heal (about 14 days), which increases the risk of a secondary infection. They are used more often for formations with a large area. The active ingredient is liquid nitrogen. Exposure time from 10 to 50 seconds.
Surgical excision
The method involves removing tumors using a scalpel. They are rarely used due to the high level of trauma, the inability to remove a large number of formations at once and the additional risk of contamination in the case of viral papillomas. Typically, surgical removal is resorted to in case of localization in the area of the tongue root or in case of suspicious neoplasms for further cytological and histological examination. It is performed under local anesthesia. In some cases, sutures are placed after excision for additional hemostasis. Dressings are indicated until the wound is completely healed.
Other methods
The use of ointments or gels for local treatment of papillomas of a given anatomical area is not only ineffective, but is also associated with a high risk of chemical burns of the tongue and oral cavity.
Sometimes, subject to the approval of the attending physician, it is allowed to treat formations with home methods. As a rule, home treatment acts as an auxiliary method that complements the main therapy.
A few recipes as an example:
- Pour 2-3 tbsp. l. celandine and 1 tbsp. l chamomile 300 ml water. Bring to a boil, leave for 1-2 hours. Rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day for 14 days.
- Mix calendula, chamomile and mint in equal proportions. Pour 150 ml of water, boil, cool, strain. Rinse your mouth with the broth for 2 weeks.
Danger
When papillomas occur on the tongue, the patient experiences some discomfort. So, during eating, the growth can easily come off. In addition, the formations are visible when speaking and contribute to changes in speech.
Pointed-type formations cause not only physical, but also psychological inconvenience. Against the background of this condition, a person may experience embarrassment at an appointment with a dentist or ENT specialist. Complexes also appear when communicating with other people.
The localization of growths on the inside of the oral cavity poses a serious danger, since they can provoke the penetration of another infection, resulting in an increased risk of blood poisoning. All this often leads to cancer, which often ends in death.
More than 10 years without recurrence of papillomatosis.
All patients treated by Professor Roberto Pujedo have not experienced a relapse of the disease for more than ten years .
“A comprehensive approach is a key success factor. Starting with detailed diagnostics using cutting-edge technologies, ending with careful monitoring in the postoperative period.”
Along with the expertly performed complete removal of papillomas, Professor Roberto Pujedo carries out targeted administration of antiviral drugs into the mucous membrane of the affected areas of the larynx.
Reliable source:
Enhanced contact endoscopy (ECE) in head and neck surgery
Many patients talk about dozens of surgeries in their history and endless relapses. It seems that it is impossible to cope with this disease. Each time the voice becomes worse, numerous scars form in the larynx.
Now this is history!
Prevention
It is not difficult to take measures to protect against this pathology. The likelihood of HPV infection should be minimized:
- avoid casual and unprotected sexual contacts, use contraception;
- use personal hygiene items;
- Get HPV vaccine
When infection has already occurred, it is necessary to prevent the activation of the viral agent due to weakened immunity:
- consume vitamin complexes;
- get rid of bad habits;
- avoid stressful situations and overwork.
You should not neglect HPV infection and leave its manifestations without proper treatment from a qualified doctor.
Papilloma on the tongue is a dangerous formation that requires a mandatory visit to a highly qualified doctor. The patient’s main task will be to timely detect the growth and seek help from a specialist.