- What does a normal tongue look like?
- White spots on a child's tongue
- Red spots on a child's tongue
- How to treat spots on the tongue
- Imudon® in the fight against inflammatory diseases
The tongue is considered an indicator of health, so the appearance of spots on it should alert parents, even in the absence of other manifestations. However, before you begin to calculate the reasons that caused the formation of plaque, analyze your baby’s diet. Very often, tongue spotting is caused by eating dyes or foods containing chemical dyes3.
Spots in the oral cavity of children are formed from the influence of various factors. This symptom does not always indicate a disease in the oral cavity. Parents' attentiveness to the baby's condition allows the disease to be quickly detected and eliminated.
Classification
The main distribution is related to the location of the resulting rash:
- under the tongue - may be evidence of Kawasaki syndrome or malignancy, pernicious anemia;
- on the sides - the likelihood of herpetic sore throat;
- at the tip - pathologies of the digestive organs or cardiovascular system;
- on the root - a sign of stomatitis.
Rashes on the tongue can take different forms:
- acne;
- inflamed papillae;
- sores;
- swelling;
- spots;
- warts
Based on the color of the manifestations, the following types of rash are distinguished:
- white;
- pink;
- yellow;
- red;
- black.
Probable Causes
In children, the factors that provoke the formation of a rash on the tongue may be the following:
- mechanical damage;
- stomatitis;
- candidiasis;
- sore throat or tonsillitis;
- avitaminosis;
- anemia;
- infectious processes caused, for example, by untreated caries;
- eating too cold or, on the contrary, hot food, eating spicy foods;
- inflammatory processes in the body;
- herpes or other viral infection;
- atopic dermatitis;
- chicken pox;
- scarlet fever;
- allergic reaction;
- leukoplakia;
- pseudotuberculosis;
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome;
- rotavirus infection;
- immunodeficiency;
- pharyngitis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- diseases of the cardiovascular or digestive system.
Prevention of oral diseases
To avoid the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, follow simple recommendations:
- Pay close attention to your oral hygiene. Use a toothbrush with a special surface to clean your tongue. To get rid of food debris, rinse your mouth with water after eating. Do not neglect brushing your teeth before going to bed, otherwise the bacteria accumulated during the day will actively multiply, causing plaque to appear.
- Eat right. Too spicy and hot food injures the oral cavity and tongue. Eat more vegetables and fruits, and less processed food, to get the most nutrients, vitamins and minerals.
- Give up bad habits. These include not only smoking and alcohol - you should also not bite your nails and pencils, eat poorly washed vegetables, and brush your teeth with inappropriate objects. All this increases the chances of infection.
- Visit your dentist regularly. Preventive examinations will help identify any disease at an early stage and begin treatment in a timely manner.
Symptoms
When rashes occur on the tongue, as a rule, the child’s condition is aggravated by the presence of any characteristic signs. Depending on what caused the rash on the tongue, completely different symptoms may be present, ranging from a cough to an upset stomach. As for local manifestations, the following may be observed:
- swelling, hyperemia of the tongue;
- severe itching, burning;
- discomfort in the mouth when eating or talking;
- painful sensations;
- enlarged lymph nodes (regional);
- formation of phlegmon or pustules;
- coating of the surface of the tongue;
- development of crusts at the site of burst pimples;
- growth of formations in the language at high speed.
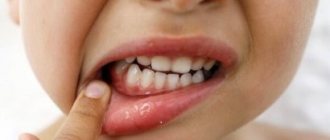
I present to your attention a rash on a child’s tongue, photo:
Candidiasis. Manifestations in the child's language
My son had a rash that was both white and yellowish. In the first case, we encountered thrush before we were even a year old. And in the second, there are problems with the digestive organs.
Diagnostics
The presence of a rash can be evidence of various diseases. Even if there are manifestations of a certain color, it will be difficult to make a correct diagnosis. Therefore, it is very important to seek help from a specialist, undergo the necessary examination and receive appropriate treatment.
- First of all, the doctor will ask the parents, find out the complaints and the nature of the disease, the time of the rash, and examine the little patient:
- evaluate the pain of sensations, the color of formations;
- presence of plaque, its localization;
- pathological changes;
- condition of the papillae;
- presence of hyperemia;
- nature of the rash.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Stool analysis for dysbacteriosis, caprogram.
If a particular disease is suspected, additional studies will be prescribed:
- allergy tests;
- culture from the oral cavity for bacterial flora;
- PCR;
- linked immunosorbent assay;
- sputum examination;
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- ECG;
- biopsy.
Diseases and nature of rashes
As you might guess, various pathologies have specific symptoms. Likewise, the rash can have different colors, be multiple or single, look like pimples or blisters, be large or small. I suggest you consider several diseases, taking into account the characteristics of the nature of the accompanying rash on the tongue.
- Herpes - there is a rash on the oral mucosa, tongue and lips, there are watery pimples with pronounced pain.
- Atopic dermatitis is a white coating with clear boundaries, hyperemia and itching of the skin.
- Candidiasis - white spots spread throughout the oral mucosa, the baby may refuse to eat. The appearance of convex white spots, dense, characterizes the development of ulcers, which can develop into malignant formations.
- Rotavirus infection - in addition to the characteristic red rash, there is a cough.
- An allergic reaction is characterized by the presence of small pimples that spread over the surface of the tongue.
- Scarlet fever is characterized not only by the presence of a rash, which, in addition to the tongue, is present on the child’s entire body, but also by a sore throat and hyperthermia.
- A rash on a child's body and tongue may indicate chickenpox.
- Pharyngitis is characterized by the appearance of dense formations with a cone-shaped top.
Red spots on a child's tongue
The most common type of spots is red, signaling an inflammatory process4. Reasons for such color changes to occur:
- Allergy . When an allergen enters the mouth, such as food or medicine. Sometimes children put animal fur or plant flowers into their mouths, which can also cause spots.
- Herpes . It is quite rare, but a child can develop a herpes infection in the oral cavity. It indicates a weakened immune system. The baby will be bothered by pain and itching. The temperature may rise.
- Scarlet fever . This childhood infection is not identified by spots on the tongue, but they are a specific sign. Key symptoms: high fever, severe pain and redness of the throat, cough, rash all over the body in the form of small dots.
Rash color and diagnosis
You already know that rashes can have different colors. Based on this, the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis of a possible disease.
- A white rash on a child’s tongue is characteristic of the following pathologies:
- atopic dermatitis - there are clearly defined spots, the child has hyperemia and itching on the body;
- Scarlet fever at the beginning of the disease manifests itself as a white rash, which turns into crimson as the disease progresses;
- candidiasis - characterized by the spread of white spots over the entire surface of the oral mucosa, including the tongue.
- A red rash on a child’s tongue may indicate the presence of the following diseases in the body:
- hypo- or vitamin deficiency;
- anemia;
- eating cold or very hot food, spicy foods;
- the presence of a bacterial infection;
- allergic reaction;
- immunodeficiency;
- stomatitis.
- A black rash indicates injury. This coloration is typical for hemorrhage of blood vessels located under the skin.
- A gray-white coating is evidence of pseudotuberculosis. As the disease progresses, the color of the rash changes to a crimson color.
- Yellow plaque will indicate the presence of the following pathologies:
- diseases of the digestive system;
- somatic pathologies, for example, diabetes mellitus and or kidney disease;
- jaundice;
- severe intoxication of the body;
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, for example, gingivitis;
- fever and a rash on the tongue of a child that is yellow or yellow-brown is evidence of the presence of an acute infectious process in the body.
READ ALSO: Herpes on the lip during pregnancy: what to do, how to treat a cold
White spots on a child's tongue
The easiest way to notice the formation of white areas in the oral cavity of children, which can signal the following problems:
- 1 Candidiasis is an inflammation caused by excessive growth of fungi in the mouth. The spots look like cottage cheese flakes. The problem occurs when the body's defenses are reduced.
- 2 Stomatitis is a common inflammation of the oral cavity in children, accompanied by painful white spots. The cause of infection is bacteria1.
- 3 Leukoplakia is a consequence of frequent minor injuries accompanied by infection.
- 4 Diseases of the digestive system: the tongue is often called an indicator of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, so the presence of white areas in combination with symptoms of digestive dysfunction is a reason to worry about the health of the stomach and intestines2.
Treatment
The procedure for getting rid of a rash on a child’s tongue should be based on the correct diagnosis and prescribed only by the attending physician, taking into account the manifestation of symptoms, age and characteristics of the child’s body.
- antihistamines to relieve intoxication and quickly remove toxins from the body, also in the presence of allergies;
- antibiotics if a bacterial infection is present;
- if there is a disease of viral etiology, in particular herpes, antiviral drugs are prescribed;
- probiotics for microflora disturbances or in combination with antibiotics;
- antifungal drugs, in particular against Candida, if the cause of the rash is candidiasis;
- rinsing the mouth or applying ointment for identified stomatitis;
- vitamin therapy, taking microelements;
- immunomodulators.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine may be prescribed as an adjuvant therapy. However, their use is unacceptable without consulting a doctor.
- Preparation of a decoction for rinsing the mouth. You can use a mixture of sage, chamomile, calendula, coltsfoot and St. John's wort. To prepare, you will need one teaspoon of the mixture per glass of warm water. The resulting solution must be steamed for up to five minutes, cooled and strained.
- Soda solution is effective in relieving inflammation. To prepare, take a teaspoon of soda per glass of warm boiled water. Rinse your mouth with the prepared solution.
Preventive measures
- You must adhere to the rules of hygiene:
- wash your hands with soap (before eating, after going outside, after using the toilet);
- brush your teeth, take care of your oral cavity.
- Make sure that your baby does not put various objects in his mouth or lick them, because even his toys may contain pathogenic microorganisms.
- The little one should have individual dishes and hygiene products.
- Eliminate spicy, too peppery, cold or hot foods from your child’s diet. Avoid damaging the surface of the tongue.
- Visit your pediatric dentist promptly and treat any resulting caries.
- Do not forget to regularly treat children's toys with disinfectants, as well as sterilize the bottle and pacifier.
Now you know what causes plaque on your baby’s tongue. At the first manifestations, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Do not forget that you cannot normally diagnose any pathology at home. In addition, there is a need for clinical studies to make an accurate diagnosis. Remember that timely treatment is the key to successful therapy. Do not forget to follow preventive measures to prevent possible illnesses.
It is very often possible to determine the presence of a particular disease by a person’s language, which is what many specialists use when diagnosing. Pimples on a child’s tongue are also often manifestations of certain diseases, but can occur due to injury and for other reasons. In today’s detailed article, we propose to understand what pimples on a child’s tongue mean, why they occur, and how to treat them.
What are pimples on the tongue and the reasons for their appearance?
What can cause pimples on a child’s tongue?
What is it - pimples on a child’s tongue? Pimples or pimples are most often called white rashes, although they can be transparent, as well as red or burgundy. The rash can be not only on the tongue, but also on the inner surface of the cheeks, lips, on the palate or tonsils, in the throat. The rash causes discomfort and pain to the child when eating, brushing teeth or talking. Moreover, pain can appear not only due to irritating factors, but also just like that. The baby becomes capricious, eats and sleeps poorly, and the temperature may rise.
How do rashes form? Due to the influence of certain factors, in some places there is a slight separation of the upper sections of the mucous membrane, under which exudate (liquid) accumulates. It can be transparent, whitish, with inclusions of blood (it all depends on the provoking factor). Next, we will dwell in more detail on which diseases cause pimples of different colors.
Now let's look at the most common causes of pimples in more detail.
Traumatic factors
The symptom may appear after a tongue injury
READ ALSO: Complications after tooth extraction: paresthesia, alveolitis, malocclusion and other problems
Injuries can occur from biting toys, cutlery, careless manipulation of a brush, biting the tongue with teeth, or from pinching by orthodontic plates and trainers in older children. Injury can also be caused by a burn from hot food (including overheated formula), milk or jelly. Cold foods or objects can also cause damage to the mucous membrane, for example, if a child decides to lick metal handrails, swings, etc. in winter. Microbes penetrate into the wounds, causing inflammation and pimples.
Stomatitis of various origins
Stomatitis in children is a very common pathology, which is most often provoked by viruses and bacteria. In general, according to experts, the oral cavity is the most “populated” area of the human body - about 300 million bacteria, and half of them are pathogenic. But there are also viruses and fungi. Most often, children are diagnosed with herpetic stomatitis and candidiasis (thrush).
The photo shows candidiasis of the tongue in a child
Important! In a healthy child, the immune system neutralizes dangerous microbes in a timely manner. But as soon as the immune system weakens, microbial toxins begin to have a stronger effect on the delicate children’s oral mucosa, causing rashes and pain.
Glossitis - inflammation of the tongue
Glossitis is an inflammatory process of an infectious or non-infectious nature, localized specifically in the tongue. It can occur due to trauma, exposure to bacteria and viruses, as well as due to degenerative processes (for example, geographic tongue). Glossitis manifests itself not only as rashes, but also as spots or cracks on the tongue.
The photo shows a geographic tongue
General diseases
There are a lot of common diseases that cause rashes. This, for example, could be chicken pox, Coxsackie viruses, scarlet fever, diphtheria, tonsillitis, mononucleosis and others. Also, pimples on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity can appear due to hormonal disorders or diseases of the endocrine system, gastrointestinal tract (due to gastritis or dysbacteriosis).
Allergic manifestations
A rash on the tongue may indicate an allergic reaction - to food, water (when moving to another region), to medications that the baby is taking. Also, allergies often appear to toothpaste, for example, with a large number of preservatives and dyes in the composition.
The photo shows the manifestation of allergies
Common causes of rashes in young children
White spots or pimples on the tongue of an infant most often appear due to stomatitis - candidal or herpetic. Moreover, candidiasis most often affects children under the age of 1 year, and herpes from 6 months to 3 years. Also, a rash on the tongue in infants and older children can appear as a result of general diseases (ARVI, tonsillitis), chickenpox, allergies to complementary foods, or injuries to the tongue.
Common causes of rashes in teenagers
Rash on the tongue in adolescents most often occurs against the background of hormonal changes. Another reason is mononucleosis, which is also called the “kissing disease.” Mononucleosis is accompanied by a severe runny nose, conjunctivitis, and enlarged lymph nodes. Also, often a rash occurs due to allergies - to “adult” foods (chips, glazed nuts, which contain a lot of preservatives and dyes), to cosmetics. While wearing braces, especially metal or lingual braces, your teenager may experience scuff marks, pimples, or small cuts on the tongue (side or tip).
Types of rashes and their locations
The color of the rash, as well as its location, can tell us what caused the pathological process and how to carry out therapy. However, diagnosis and treatment should be done by a professional as several diseases have similar symptoms but different treatments. But it’s still worth considering what color pimples indicate a particular disease in order to know which doctor you need to see.
Small watery ones
If a child’s tongue is red, covered with small painful pimples and hurts, then most likely the cause is an allergy, burn, or herpetic stomatitis. Transparent rashes of varying sizes with a red border indicate chickenpox. Small, painless, transparent pimples appear due to gastrointestinal pathologies, dysbiosis, or deficiency of B vitamins. You should initially contact a pediatrician, who, if necessary, will refer you to an allergist, gastroenterologist, or dentist.
This is what clear rashes look like
“During chickenpox, not only did the child’s body become covered, but pimples also appeared in his mouth. Why, he scratched his hand and put his finger in his mouth - here’s a hello from where you weren’t expecting it. I didn’t smear them with brilliant green, I was afraid, although the dentist said it was possible. In general, I applied Cholisal in my mouth and Acyclovir on my lips. Our doctor prescribed Acyclovir tablets and we also drank them.”
Ksenia, review from the website stomatology.rf
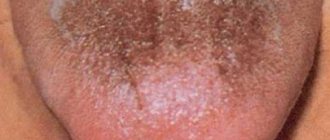
White rashes
The photo shows white purulent pimples on the root of the tongue
White purulent pimples on the root of the tongue and on the tonsils occur with sore throat. Additionally, it is very painful for the child to swallow (it is almost impossible to eat normally and even swallow saliva). Therefore, treatment should be prescribed by a pediatrician or pediatric ENT specialist.
Also, single white rashes located on the tip of the tongue, gums, lips can appear due to injuries (when a child scratches the mucous membrane with a finger or toy), or rubbing. Here treatment is prescribed either by a pediatrician or a pediatric dentist.
READ ALSO: Removal of Bisha's lumps in Moscow
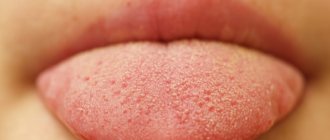
Pink bumps
Pink pimples most often refer to lingual taste buds, which have increased in size due to illness. This happens, for example, with ARVI, stomatitis, gastritis - in addition, there may be a white coating on the tongue. Treatment is prescribed by a pediatrician and pediatric dentist.
Enlarged papillae indicate the presence of a disease
What does the tongue look like normally?
In the absence of health problems, the child’s tongue looks moist, evenly pink, without areas of redness or swelling1. In some cases, parents may see plaque due to the following reasons:
- Insufficient and irregular oral hygiene.
- Eating food with coloring substances (lollipops, chocolate, persimmons, beets, carrots, ice cream, etc.).
- Using seasonings that have a coloring effect (curry) in cooking.
- Taking medications with a coloring effect (iron preparations, activated carbon, iodine sprays, solutions with furacillin and tannins).
- Excessive amounts of fatty foods in the diet.
Whitish spots on the tongue of an infant may appear due to the curdling of mother's milk in the mouth or minor regurgitation.