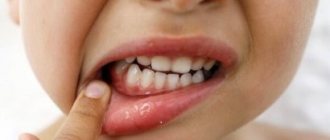
What can a coating on the tongue indicate? Diagnosis of diseases using the tongue.
What health problems can our tongue indicate? Which doctors should you contact if you find a coating on the surface of your tongue? Let's figure it out.
The tongue helps to identify any dysfunctional processes in the body. Since ancient times, doctors examined the patient's tongue to clarify the diagnosis. Nowadays, diagnosing diseases by plaque on the tongue has not lost its relevance. Examining the patient's tongue is one of the doctor's algorithms during the examination.
White coating on the tongue in infants and newborns: causes and treatment
Infant's tongue
- The surface of a small child's tongue is smooth and moist and pale pink. Since the baby's main diet is mother's milk, the baby's tongue may have a slight white coating on the tongue. This is normal if the baby feels great, has a good appetite and sleeps.
- If not only the child’s tongue becomes white, but also the gums and the inner surface of the cheeks, he is capricious and eats poorly, then most likely this is the result of the vital activity of the fungus of the genus Candida. The disease is called thrush .
- White plaque literally envelops the entire oral cavity and tongue of the child. The disease occurs when the immune system is weakened and infection is introduced through dirty pacifiers, pacifiers, toys, or an infected mother.
- Thrush newborn child must be treated under the supervision of a pediatrician, who prescribes treatment depending on the degree of fungal damage. Local medications are usually used. Soda solutions that are used to wipe the affected areas help remove thrush.
White coating on the tongue in adults and children: causes and treatment
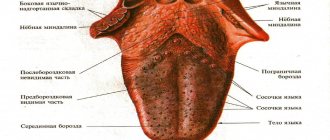
Projection of organs on the tongue
- In a healthy person, the tongue is pink with a slightly whitish tint. The color of the tongue depends on the condition of the filiform papillae of the organ. These are the most numerous papillae that run along the walls and edge of the tongue.
- The body of the papilla is covered with a large layer of squamous epithelium, capable of keratinization. When the epithelium is exfoliated, the keratinized cell remains have a whitish tint, so the tongue has a pink-white color.
- If the digestion process fails for any reason, the epithelium in the form of a stratum corneum lingers on the tongue. Upon visual examination, the tongue becomes white due to plaque in the form of a layer of keratinized epithelium. There is a so-called “coated tongue”.
- Frequent illnesses from viral and microbial infections occur due to low immune status. Young children are especially susceptible to infectious diseases. They have thick white deposits on their tongue. Strengthening the immune system using vitamin complexes and immunostimulants increases the body's resistance to colds.
Symptoms of female sex hormone imbalance
Sex hormones determine a woman’s appearance, her voice, behavior, and are responsible for reproductive function. The most important female hormone, estrogen, is responsible for the soft contours of the body, large mammary glands, wide hips, and a high-pitched voice. Testosterone is also present in the female body, but in less quantity than in men. The female body produces progesterones, prolactin, gonadotropin hormone, and gonadotropin-releasing hormone.
The imbalance is often visible to the naked eye. Here are typical symptoms of hormonal imbalance in women:
- a figure formed according to the male type;
- excess weight, a particularly typical picture is when the stomach is much larger than the chest, and the buttocks are flat (may be a symptom of PCOS);
- hair growth, as in men, for example, hair growth on the chest (single hairs on the nipples do not apply here), excessive hair growth on the stomach, thighs, and face;
- low rough voice.
Acne also indicates that there is a lot of free testosterone in the blood, but this does not always indicate a hormonal imbalance; this is a common situation during puberty.
Most often, the following signs indicate that something is wrong with hormones in a woman’s body:
- menstrual irregularities - too long or very short interval between menstruation, absence of menstruation, heavy blood loss, scanty spotting;
- lack of ovulation, which can be seen on ultrasound;
- early signs of menopause;
- very pronounced premenstrual syndrome - pain in the mammary glands, headaches, nausea, bloating, mood swings;
- infertility;
- miscarriages;
- decreased libido.
If a woman has nipple discharge, this may indicate that she has elevated prolactin due to prolactinoma, a benign tumor of the pituitary gland. Male pattern hair growth, infrequent menstruation, excess weight, and infertility may be signs of polycystic ovaries.
Why is there a white coating on the tongue in the morning, how to remove it?
- A whole world of microorganisms lives in the human mouth. Their waste products accumulate in the form of a whitish layer on the surface of the tongue. During the night, exfoliated pieces of epithelium containing mucoproteins also collect on the tongue. All together layers on the tongue in the form of a translucent white coating.
- This plaque is completely safe and can be easily removed from the surface of the tongue using simple morning hygiene procedures: brushing the teeth and tongue. If the plaque does not disappear within 24 hours and acquires a denser structure, this may indicate a health problem.
Signs of the disease
First news
The first signs of the disease usually appear at 2 months of pregnancy and reach a peak at 8 months. If there are no other aggravating factors, symptoms will regress after childbirth.
Symptoms of gingivitis in pregnant women
Signs of the disease are no different from the usual symptoms of gingivitis and include:
- Loose, red, very sensitive and swollen gums;
- Bleeding gums when brushing with a toothbrush or special floss;
- Unpleasant foul odor or taste in the mouth.
White coating on the tongue during pregnancy: causes and treatment
Pregnant women may have a coating on their tongue
- Pregnancy is a special period in a woman’s life when you should be especially careful about your health. During pregnancy, hormonal changes occur in the female body and the immune system often weakens.
- The expectant mother may develop a white coating on her tongue. If the woman feels well and the pregnancy is proceeding according to the proper scenario, such plaque should not bother the pregnant woman.
- A white, dense plaque with an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity can signal trouble. Most often this is due to insufficient oral hygiene or the presence of carious teeth. In this case, you should visit a doctor and have your teeth treated.
Prevention of stomatitis
During the period of bearing a child, it is very important to be attentive to your health:
- If all dental problems have not been resolved before pregnancy, it’s time to take care of them. Absolutely safe anesthesia drugs have long appeared in the arsenal of dentists, which, unlike stomatitis, will not harm either the mother or the child;
- Buy a good toothpaste, a quality brush and mouthwash. Let oral hygiene become a pleasant procedure that you won’t want to ignore;
- give up the habit of drinking scalding coffee for now and stop biting into ice-cold ice cream. Such rash actions can damage the mucous membrane;
- wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly and eat them without restrictions;
- ask your gynecologist to recommend a vitamin complex for you, and take it without missing a day.
Prevention of stomatitis is, first of all, measures aimed at strengthening the immune system. And it will never fail if you rest on time, get enough sleep, spend a lot of time in the fresh air and set yourself up only for the positive.
Author: Elena Grunina Dentist-therapist, endodontist. Work experience more than 9 years.
The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Yellow coating on the tongue in adults and children: causes and treatment
Liver diseases are reflected on the tongue by a yellow coating.
A yellow coating of a dense structure, which is difficult to remove with simple hygiene measures, can be associated with:
- liver pathology
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas
- taking medications
- infectious and viral diseases
Diseases of the gallbladder and liver often cause a yellow plaque with different shades: from greenish, yellow-orange and brown. Cholelithiasis, hepatitis, liver cirrhosis and other liver pathologies are accompanied by yellow-brown deposits on the tongue.
In this case, the patient complains of morning dryness and bitterness in the oral cavity. These symptoms require a comprehensive examination of the patient's liver. In the early stages of the disease, you can limit yourself to adjusting the diet and prescribing choleretic drugs and medicinal preparations.
Digestive and pancreatic disorders can also cause yellowish coating on the tongue. In this case, there may be bad breath, nausea, and sucking pain in the morning. Such symptoms should be taken into account and examined by a gastroenterologist.
Taking certain medications causes yellow plaque to form. As a rule, after stopping the medication, the tongue becomes clear and acquires a healthy color.
Microbial and viral infections are characterized by the accumulation of a large number of viruses and bacteria in the body. As a rule, all infections are accompanied by fever. Such processes cause the tongue to become coated with a yellowish coating. The higher the body temperature rises, the more intense the color of the coating on the tongue becomes.
Yellow coating on the tongue in children
The following reasons for the appearance of yellow plaque in a child can be identified:
- The introduction of vegetable complementary foods and some types of cereals can cause a slight yellowish coating on the tongue after eating.
- The child’s diet contains a large amount of carrots, persimmons, pumpkins and other vegetables and fruits containing carotene, which can color not only the tongue, but also the skin and sclera of the eyes yellow.
- Sweets in the form of caramels, chewing gums and other children's “joy”, containing a yellow coloring pigment
- If the yellow plaque is associated with a deterioration in the child’s well-being, and the baby complains of abdominal pain and refuses to eat, he may have the initial stage of bile duct dyskinesia or digestive disorders. The child should be shown to a doctor who will adjust the diet and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Diet for stomatitis
In order not to aggravate the situation with stomatitis, you should avoid sweet, spicy and salty foods. It is not recommended to eat mushrooms and legumes. But most importantly, all food should be of a warm, delicate consistency, so as not to further injure the mucous membrane. It is very important that the menu is rich in vegetables and fruits. It is better to stew vegetables and prepare nutritious cream soups from them. And fresh fruits are especially good in the form of smoothies.
In some cases, diet alone will be enough for the expectant mother to forget about stomatitis after 1-2 weeks. But only a doctor can rule out the bacterial, fungal or viral nature of the disease, in which it will not be possible to cope with the disease so easily.
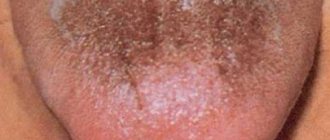
Gray coating on the tongue: causes and treatment
A heavy coating of dark shades on the tongue that is not associated with the use of coloring products is a reason to consult a doctor.
A gray shade of the tongue can be a harbinger of many diseases. You should visit a doctor if:
- gray coating on the tongue is present for a long time
- cleaning the tongue does not eliminate plaque, but deposits cover the tongue more densely
- in addition to changes in the color of the tongue, there are complaints of deterioration in the body’s condition
The gray color of the tongue can be caused by malfunctions of the body for many reasons.
- Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity : the dominance of bacteria and their metabolic products causes thickening of the papillae, which become overgrown with microbial “garbage” and line the tongue with a gray coating. Daily hygienic measures related to brushing teeth and tongue, rinsing the mouth after eating, eliminating foci of infection (sanitation of teeth, treatment of diseases of the gums and oral mucosa) will lead to the elimination of plaque.
- to dehydration of the body . Dry mucous membranes and skin, increased fatigue, frequent constipation are the main symptoms of lack of water in the body, as is a gray coating on the tongue.
- Infectious processes of the respiratory tract : bronchitis, pneumonia, tracheitis. The tongue will turn pink again after complete recovery.
General signs of hormonal disorders
In addition to specific symptoms of hormonal imbalance, there are also less typical ones, which may, however, indicate incorrect functioning of the thyroid gland, or be part of the picture of an imbalance of sex hormones:
- decreased or sharp increase in libido;
- excess weight without diet errors;
- fatigue, loss of strength, tearfulness;
- changes in facial features (bulging eyes with hypothyroidism);
- drowsiness, tachycardia, sweating;
- muscle weakness.
Hormonal imbalance in women is characterized by a pattern in which several alarming signs appear simultaneously. The sexual sphere, appearance, and activity suffer.
Treatment of hormonal imbalance is necessary to restore the normal functioning of a woman’s reproductive system, make conception and pregnancy possible, achieve regular ovulation and simply give a woman a high quality of life. The Dr.AkNer clinic will definitely help you understand the causes of the failure and eliminate them.
Brown coating on the tongue: causes and treatment
Corfe and cigarettes can cause a brown coating on the tongue
IMPORTANT: You should know that strong tea drinkers, coffee lovers and heavy smokers often have brown tongue pigmentation and a yellow tint to tooth enamel.
A brown coating of the tongue usually accompanies the following pathologies:
- diseases of the liver and biliary tract
- diabetic coma
- pellagra (vitaminosis associated with a lack of vitamin PP)
- dehydration in severe intoxication and poisoning
- the use of certain medications: Iodinol, Faringosept, Tetracycline hydrochloride, B vitamins, Lugol's solution, etc.
If the plaque does not cause concern and goes away on its own after some time, there is no need to worry. If you have accompanying symptoms that cause discomfort, you should consult a doctor.
What to add to your diet?
The products in the selection are united by a high protein content - a “building material” for cells, which is useful for the development of the fetus.
Eggs
This product is easily digestible and has unique properties. Eggs contain essential amino acids for humans; it is not for nothing that the World Health Organization has awarded the title of standard to egg white. The product is rich in many vitamins: A, B4, B12, D, E.
Salmon
This fish is useful throughout the entire period of pregnancy, even in the very early stages. In addition to easily digestible protein, it contains a high content of phosphorus, which is involved in the formation of bone tissue in the fetus. Salmon contains omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart and vascular health. Also contains: B vitamins, calcium, iodine, potassium and vitamin D.
Beans
Beans, peas and lentils are very filling foods. Their advantage lies in the large amount of fiber necessary for the normal functioning of the digestive system. It also contains many B vitamins, including folic acid, which is directly involved in the formation of the brain and spinal cord.
Walnuts
Regular consumption of walnuts will charge the body with vitamins and minerals. Walnut kernels contain vegetable protein rich in amino acids, as well as B vitamins and vitamin E. It is believed that walnuts have an antispasmodic effect, which can help a pregnant woman with headaches if she does not want to take synthetic drugs. The immunostimulating and general strengthening effect of nuts on the body is also noted.
Fruits and vegetables
Vegetables and fruits contain a lot of soluble fiber, which regulates bowel function and prevents constipation during pregnancy. They also contain many vitamins that are beneficial for the immune system of the expectant mother.
Orange coating on the tongue: causes and treatment
Fruits and vegetables with orange pigment may cause a coating on the tongue
- Orange bloom is often caused by fruits and vegetables that are rich in carotene and brightly colored. Fans of raw carrots and carrot juice, persimmons, apricots, and pumpkins can observe the coloring of the papillae of the tongue with an orange pigment, which fades over time.
- Some medications can also form an orange coating, which disappears after the end of the medication course.
- A reason to pay attention to your health is an orange coating on the tongue that cannot be removed with a brush or scraper. A change in the color of the tongue may be due to the reflux of gastric juice into the oral cavity. And this could be the beginning of gastroenterological diseases: gastritis, reflux esophagitis, etc. In this case, you should reconsider your diet and, if necessary, undergo an examination.
Which doctor should I contact for stomatitis?
The first specialist a future mother needs to contact is a dentist. It is he who will identify the cause of the disease, choose treatment tactics and select medications that will not harm the baby. If the patient came in on time, and stomatitis manifested itself for the first time, we can say with a 100% guarantee that the result of a visit to the doctor will be detailed recommendations for home treatment.
In addition to prescribing medications, the dentist will teach you how to properly treat the mucous membrane and ulcers with antiseptics and painkillers, and will schedule a follow-up appointment in 5-7 days. As a rule, this time is enough for the disease to subside.
It is much worse if the situation is advanced, and stomatitis appears again and again, after short periods of time. In this case, the dentist will insist on conducting a comprehensive examination and consultation with specialists of another profile: a therapist, gastroenterologist, allergist, infectious disease specialist or hematologist.
Black coating on the tongue: causes and treatment
Black tongue
A thick black coating on the tongue often indicates serious disorders in the body. The presence of such a plaque that does not go away for a long time gives reason to see a doctor and have your health examined. Many problems in the body can lead to a black coating of the tongue.
- Shift in acid-base balance towards acidification. Acidosis of the body can occur with an unbalanced diet, fasting, intestinal disorders, and fever.
- A chromogenic fungus that has settled in the oral cavity can cause black deposits on the tongue and black-green spots on tooth enamel.
- Slagging of the body due to the abuse of “unhealthy” food.
- Long-term viral and microbial infections .
- Crohn's disease is a genetic disease that affects the gastrointestinal tract.
- Problems with the biliary tract and liver .
- Oncological diseases.
Making an accurate diagnosis, treatment and following the doctor’s recommendations will help solve the problem with black deposits.
IMPORTANT: It should be remembered that some medications and products can turn the tongue black: activated carbon, blackberries, blueberries, blueberries, bird cherry, mulberry. This type of plaque usually disappears on its own and does not pose a threat.
Green coating on the tongue: causes and treatment
Basic oral hygiene is the solution to all problems.
Green deposits are not often found on the surface of the tongue. The color range varies: from yellow-green to yellow-brown with an admixture of greenery. Let's consider the reasons for the appearance of green shades of layering on the tongue.
- Elementary disregard for hygiene rules can lead to this type of plaque. Daily brushing of teeth and tongue, rinsing the mouth with refreshing and antiseptic balms and herbal infusions will help eliminate this problem. A visit to the dentist and treatment of sore teeth is an important step towards eliminating plaque.
- Taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs, cytostatics and other drugs can cause plaque to appear.
- Poor nutrition and “starvation” diets with a lack of vitamins and essential minerals are reflected on the tongue in the form of a greenish coating.
- Fungal diseases are often accompanied by plaque of various shades
- Problems with the digestive tract.
- Overeating and consuming large amounts of fatty and high-calorie foods negatively affect the functioning of the liver, and this is manifested in the appearance of a yellow-green coating on the tongue.
Green plaque can only be removed by identifying the cause of its formation and treating the underlying disease.
Why does it appear
The reasons for the problem may vary. If in the morning, after waking up, a pregnant woman sees a thin whitish layer of plaque on the surface of her tongue, this is normal. But if the layer has too thick a consistency, it is difficult to remove it yourself; this is direct evidence of a fungal infection. The fungus Candida Albicans often appears precisely during pregnancy under the influence of hormonal changes and weakening of the body’s natural protective functions (which arise precisely during pregnancy).
If a yellow coating appears on the tongue, this may indicate problems in the digestive system:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the pancreas;
- Congestion in the gallbladder and its ducts;
- Gastritis and other inflammatory processes in the digestive tract;
- Liver dysfunction.
The appearance of a yellowish or yellow-white coating can be caused by an incorrectly formulated diet, which is dominated by coloring foods or foods with a high content of chemicals.
Plaque on the tongue for sore throat and sore throat: treatment
A pale and dry tongue indicates a throat disease.
A yellow-white tongue indicates a disease of the throat and nasal cavity due to a viral or microbial infection. Doctors diagnose ARVI based on the following symptoms:
- chills and fever
- nasal congestion
- a sore throat
- headache and muscle pain
- "coated tongue
A thick white-yellow coating on the entire surface of the tongue with the above symptoms is a sure sign of a cold of infectious origin. A large number of bacteria accumulate on the tongue, forming a dense layer.
At the initial signs of the disease you should:
- take a hot shower or steam your feet (if you don’t have a fever)
- drink plenty of herbal teas with raspberries, lemon, honey and raspberries
- gargle with disinfectant solutions and herbal infusions
- for nasal congestion - use vasoconstrictors
To prevent colds, you should practice prevention of colds and strengthen your immune system:
- rinse the nasal passages with isotonic sodium chloride solution
- apply a contrast shower
- exercise outdoors
Protracted infections with complications associated with the appearance of a dry cough and high fever require treatment with antibiotic and antiviral drugs.
Types of tonsillitis (tonsillitis)
- Sore throat is a serious infectious disease associated with damage to the tonsils by various pathogens. The disease is severe and is accompanied by high fever and severe sore throat.
- Sore throat is characterized by a dense gray-white coating on the tongue with bright red tonsils. In some cases, ulcers or a solid white necrotic coating can be observed. It is important for a doctor to correctly diagnose the disease and differentiate it from ARVI or influenza.
- Depending on the type of sore throat, treatment with antibiotic, antifungal or antiviral drugs is prescribed. Local influence on the source of inflammation, proper oral hygiene, a gentle diet and plenty of warm drinks lead to recovery.
- Untreated sore throat can become chronic and have serious consequences in the form of heart disease, kidney disease and rheumatic complications.
Issues of medical care for pregnant women, women in labor and postpartum with COVID-19, as well as vaccination of pregnant women, were discussed at a national webinar with the participation of leading specialists and experts.
Yuri Gorbich, Head of the Department of Infectious Diseases and Children's Infections of BelMAPO, Candidate of Medical Sciences. Sciences. Head of the Department of Infectious Diseases and Children's Infections of BelMAPO, Candidate of Medical Sciences. Science Yuri Gorbich said that most pregnant women become infected through household contacts, so not only the woman herself, but also all family members should be vaccinated. Typical symptoms: fever, weakness, myalgia, cough.
In addition, pregnant women more often complain of headaches, nausea and vomiting. Complaints about the lack of smell and taste, traditional for the first waves, against the background of the “delta” are much less common. If earlier - in 80% of patients, now in 50%, and according to some data - in 40%.
Features of the “delta” variant of SARS-CoV-2 , which is currently dominant: it is transmitted much faster; people who have already had COVID-19 or have been vaccinated are sick; clinical manifestations are similar to other acute respiratory viral infections; more severe course and outcomes; Young people get sick more often.
Pregnancy is a risk factor for severe COVID-19.
According to an international meta-analysis that combined the results of 192 studies covering 64,000 pregnant women: the incidence of pneumonia is 7.4%, ARDS is 13.4%; 3.3% are admitted to the ICU, of which 1.6% are on mechanical ventilation, 0.11% are on ECMO (the percentage is limited by the availability of the method), death is 0.8%.
Risk factors for severe COVID-19 in pregnant women:
- age 25 years and older;
- work in healthcare (due to high viral load);
- obesity before childbirth;
- chronic lung diseases;
- arterial hypertension,
- pregestational diabetes mellitus.
Yuri Gorbich:
Post-Covid symptoms in pregnant women last longer and are often more severe, especially in terms of psychosocial symptoms associated with psychological and cognitive impairment. The incidence of other symptoms: general - 49.6%, respiratory - 39%, cardiovascular - 13%, psychosocial - 22.7%, alopecia - 28.6%. After 7 months, at least half still have any symptom, and a quarter still have psychosocial symptoms.
Changes in blood flow levels in pregnant women compared to non-pregnant women:
- leukocytosis: 27% vs 14%,
- thrombocytopenia: 18% vs 12.5%,
- increase in CRP: 52% vs 81%,
- leukopenia and lymphopenia: no differences.
Yuri Gorbich:
When assessing the level of D-dimers, one should take into account the natural increase in this indicator during pregnancy. However, a continuous increase of 500–1,000 U per day or a sharp increase during the day cannot be the norm. Another significant difference: the increase in CRP in pregnant women is much less than in non-pregnant women. The most important thing is the absolute level of lymphocytes. If it decreases below 0.8-109/L without signs of bacterial infection, especially from the 4th to the 12th day, then the administration of IL-6 receptor inhibitors should be considered.
Instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods
When assessing changes in lung tissue according to the “ground glass” type, one should not forget that similar changes can be caused by any angioinvasive disease (vasculitis, CMV, influenza, etc.).
When diagnosing an infection caused by SARS-CoV-2, the following are used: PCR of material from the respiratory tract (sputum, endotracheal aspirate, bronchoalveolar lavage); PCR of swabs from the nasopharynx and oropharynx (in the absence of signs of damage to the upper respiratory tract, the impossibility of obtaining sputum); serological methods (testing for antigen (Ag) or antibodies).
Yuri Gorbich:
An important point: when conducting an Ag test, you need to evaluate the results strictly within 15 minutes. If the second line appears later, for example, after 16–17 minutes, then such a test is considered negative. As for antibody tests, their value in the primary diagnosis of COVID-19 tends to zero, taking into account probable re-infections and the fact that their detection is possible no earlier than the 8th day from the onset of the disease.
Clinical and laboratory criteria for establishing the diagnosis of COVID-19:
- single positive Ag or PCR test;
- typical radiological symptoms (according to CT data), clinical picture followed by a positive laboratory diagnostic test;
- one positive serological diagnostic test in combination with the clinical picture.
Yuri Gorbich:
A positive Ag or PCR test, even without a clinical picture, confirms the diagnosis of COVID-19. In other cases, there must be a clinical picture in combination with laboratory and instrumental research methods. In patients with suspected infection, especially those with severe illness or pneumonia, a single test of a negative upper respiratory tract specimen does not rule out COVID-19.
In a pandemic, any acute respiratory viral infection is considered COVID-19 until proven otherwise.
Pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy
At the outpatient stage: prone position, adequate hydration, antipyretics.
Yuri Gorbich:
Additional intake of vitamin D, zinc, ACC is not needed. Hydration is given orally. In late stages of pregnancy, it is difficult to ensure a prone position at home, so a position on the left side with rotation to the right side every 2 hours is allowed. In hospitals, prone positioning for pregnant women is also possible in later stages. Practice shows that with a saturation of 89–90%, a simple turn and laying in a prone position led to a saturation of 96%!
In hospitals: prone position, adequate hydration, LMWH, antipyretics, oxygen support, corticosteroids.
Yuri Gorbich:
GCS are prescribed only to patients on oxygen support. This includes all types - nasal cannulas, face masks, non-invasive and invasive ventilation. If a pregnant woman is transferred to oxygen support, the second step is automatically the appointment of corticosteroids.
In case of an extremely serious condition with a threat of death within 24 hours, on the basis of the conclusion of a medical consultation with the obligatory participation of an infectious disease specialist and an anesthesiologist-resuscitator, the issue of conducting pulse therapy is considered: intravenous methylprednisolone titrated 500 mg on the 1st day, then 250 mg for 3 days, followed by a dose reduction of 50% every 3 days until complete withdrawal.
However, practice shows that in the event of an increase in inflammation and a cytokine storm, the combination of standard doses of GCS (methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg) with tocilizumab (6 mg per kg) is much more effective.
Tocilizumab is a monoclonal antibody to IL-6 receptors, prescribed in dosages of 300 mg for those weighing less than 100 kg, 800 mg for those weighing more than 100 kg. Indications for use: interstitial pneumonia with severe respiratory failure (RF), rapid depression of respiratory function, the presence of extrapulmonary dysfunction (septic shock, multiple organ failure), persistence or resumption of fever, increased levels of IL-6 against the background of RF, signs of cytokine release syndrome against the background DN.
Yuri Gorbich:
Tocilizumab may be considered for the treatment of pregnant women with COVID-19 due to the lack of observations of an increased risk of fetal pathology. But it must be prescribed carefully, strictly according to indications, since the frequency of side effects is quite high. Olokizumab and levilimab are used in our country, but are contraindicated in pregnant women. Baricitinib, which will come to our country, is prescribed to patients on respiratory support, but it is strictly contraindicated during pregnancy.
The etiotropic therapy for pregnant women is exactly the same as for others - remdesivir.
Yuri Gorbich:
Remdesivir is prescribed to pregnant women with minimal signs of DN, as it reliably and significantly reduces the subsequent need for transfer to mechanical ventilation.
Remdesivir is prescribed by a medical council in accordance with the established procedure, obtaining the informed consent of the patient or his legal representative. Dosage: 1st day 200 mg once IV, from 2nd day 100 mg IV once a day. The treatment period is 5 days, but can be extended to 10 days in patients on mechanical ventilation or ECMO, subject to positive dynamics during the first 5 days.
Yuri Gorbich focused on the inappropriateness of prescribing antibiotics for ARVI on an outpatient basis. Nevertheless, for some reason some doctors continue to prescribe them, in particular azithromycin.
Yuri Gorbich:
Azithromycin for SARS-CoV-2 has absolutely no effect on the course of the process, but can lead to serious complications in the form of AB-associated colitis and megacolon.
Overall, the probability of secondary bacterial complications with SARS-CoV-2 is 7%, in patients in the ICU - 14%.
Yuri Gorbich:
Antibacterial drugs of choice if strictly indicated are: amoxicillin/clavulanate or ampicillin/sulbactam or 3rd generation CA + azithromycin. But when prescribing these drugs empirically, it is necessary to perform blood culture and sterility tests, urine and sputum tests. And if the flora in these crops does not grow within 48 hours, there is no point in prescribing AB.
Hospitalization of pregnant women in the ICU
Igor Yalonetsky, assistant at the Department of Anesthesiology and Reanimatology, BSMU. With the advent of the “delta” variant of SARS-CoV-2, the clinical manifestations of the infection develop much faster, sometimes the condition of a patient with a mild course can quickly deteriorate in a matter of hours and become critical. All this forces doctors to change tactics when providing care to patients with COVID-19. Igor Yalonetsky spoke about this .
Igor Yalonetsky:
World practice has shown the importance of an intensive care bed. But we all must understand that the ICU is extinguishing a fire that has already flared up, and some of the patients who end up in the intensive care unit might not have ended up there if there had been more intensive and proper work in the somatic departments.
Patients are admitted to the ICU in four ways: by ambulance in extremely critical or terminal condition; through the emergency department; when transferred from somatic departments within a hospital; during interhospital transfers. At each stage, it is extremely important to adequately triage patients and ensure logistics.
In somatic departments, careful monitoring of patients’ condition, rational therapy, and timely transfer to oxygen beds and back when the need decreases are necessary. Each decision on interhospital transfer must be weighed, with an assessment of the risks of transportation.
Igor Yalonetsky noted that in addition to monitoring the level of saturation, medical staff should pay attention to such points as adherence to the prone position, drinking regime, clarification of diuresis, and also check whether the oxygen mask is worn correctly and whether the humidifier is filled with water. If all this is done regularly, patients get used to it and adhere to the regime more clearly.
Indications for admission to the ICU for pregnant and non-pregnant women differ.
Indications for admission to the ICU: SpO2 <88% with an additional oxygen supply of 5 l/min (15 l/min with severe congestion in the ICU); RR >30/min at body temperature 38 °C; disturbances of consciousness, behavior; oxygenation index (PaO2/FiO2) <250 mm Hg. Art.; systolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg. Art.; decreased diuresis <0.5 ml/kg/hour.
Indications for hospitalization of pregnant women in the ICU: rapidly progressing ARF (RR > 25/min, SpO2 <94%; other organ failure (2 or more points on the SOFA scale); score 2 or higher on the NEWS 2 scale.
Igor Yalonetsky introduced the seminar participants to an overview of recommendations for the management of pregnant women, which were prepared by analyzing 81 guidelines on pregnancy, childbirth and postpartum care from 48 different organizations around the world. The main postulates of this review are as follows:
- Constant monitoring of disease progression and fetal condition is necessary.
- COVID-19 in the mother should not affect the mode of delivery or cause early delivery, unless emergency delivery is necessary due to respiratory problems. It is accepted that there may be a need for a caesarean section.
- For pain management, both regional and general anesthesia may be considered. Preference is given to regional.
- During regional anesthesia, careful monitoring of platelet levels is necessary.
- Decisions about antiviral therapy and the prescription of tocilizumab must be made individually.
- Prevention of venous thromboembolism in pregnant women hospitalized in a hospital is carried out regardless of the severity of the disease.
- Pron position, if impossible - position on the left side.
- Oral dehydration with a conservative fluid strategy is preferred.
Igor Yalonetsky dwelt in detail on the features of rehydration of pregnant women and the step-by-step strategy for hypoxemia.
Vaccinal prevention in pregnant women
Igor Stoma, rector of GomSMU, professor of the department of infectious diseases, doctor of medicine. Sciences. Igor Stoma , Rector of GomSMU, Professor of the Department of Infectious Diseases, Doctor of Medicine. Sciences:
The most effective way to prevent severe COVID-19 is vaccination.
Igor Stoma:
The position of the CDC, the most authoritative organization on vaccination issues, is clear: none of the vaccines registered in the world contains the live SARS-CoV-2 virus, and therefore cannot cause disease.
Given that pregnancy is a risk factor for severe COVID-19, the CDC recommends vaccination for pregnant women. The safety of mRNA vaccines is sufficient for vaccination of pregnant women, including up to the 20th week, and has been shown to reduce the risk of infection. In addition, post-vaccination antibodies are found in umbilical cord blood, which may help protect newborns from COVID-19.
Igor Stoma said that according to the V-safe registry, 168,157 pregnant women have been vaccinated against COVID-19 in the United States. Studies of post-vaccination immunity have shown that antibody titers in pregnant and lactating women are equivalent to non-pregnant patients, and no differences in reactogenicity were found between groups.
As part of observational studies of 35 thousand births, it was shown that the frequency of pregnancy outcomes did not differ in the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups, i.e. vaccination does not affect the frequency of stillbirths, spontaneous abortions, premature births, and congenital anomalies.
The Russian two-component vaccine Sputnik V (Gam-Covid-Vac), which, according to Igor Stoma, is one of the most effective immunogenic vaccines in the world, as well as the Chinese Sinovac CoronaVac (Vero Cell) are currently available in Belarus.
Igor Stoma:
The instructions for Sputnik V indicate that pregnancy and breastfeeding are a contraindication to vaccination. However, our Russian colleagues have changed their recommendations since the summer of 2021, indicating the advisability of Sputnik V vaccination in groups at risk of severe disease from the 22nd week of pregnancy. Risk groups include pregnant women with obesity, chronic diseases of the lungs, kidneys, liver, diabetes, and cardiovascular pathology.
In Belarus, pregnant women use the Sinovac CoronaVac (Vero Cell) vaccine, approved by WHO for use in pregnant women.
Igor Stoma:
The Sinovac CoronaVac vaccine (Vero Cell) is inactivated, grown on cell culture and not on chicken embryos, i.e. it is hypoallergenic. WHO recommends this vaccine for use in pregnant women when the benefits of vaccination outweigh the potential risks, and pregnant women should be informed about the risks of severe COVID-19 during pregnancy to make an informed decision.
WHO does not recommend performing a pregnancy test before vaccination or postponing pregnancy, much less terminating it due to vaccination.
Order of the Ministry of Health of Belarus No. 1257 dated October 12, 2021 recommends vaccination of all pregnant women, regardless of age and the presence of other risk factors for severe disease, however, the priority group is pregnant women aged 25 years and older, working in the healthcare system, having obesity of any degree, chronic lung diseases, Hypertension, pregestational diabetes, etc. As of October 21, 2021, 71 pregnant women and 6 nursing mothers have been vaccinated in Belarus.
“Hemostatic disorders during COVID-19 in pregnant women: why does this happen and what to do”
With severe COVID-19 in pregnant women, the number of thromboembolic complications increases significantly. This is due, on the one hand, to physiological changes in the hemostasis system towards hypercoagulation - a gradual, as the duration of pregnancy increases, an increase in the plasma level of fibrinogen, factors VII, von Willibrand, VIII, and the concentration of D-dimers; antithrombin III decreases slightly, fibrinolytic activity decreases.
On the other hand, SARS-CoV-2 infection also causes a number of pathophysiological reactions that significantly affect the hemostatic system. Thrombosis in patients with COVID-19 is triggered mainly by the extrinsic pathway of activation of the blood coagulation process (through the combination of tissue factor with factor VII).
Olga Svetlitskaya, Associate Professor of the Department of Anesthesiology and Reanimatology of BelMAPO, Candidate of Medical Sciences. Sciences. Damage to the alveolar-capillary barrier
The SARS-CoV-2 virus penetrates the lung tissue by binding to the ACE2 receptor, which is expressed in large quantities on the surface of type 2 pneumocytes and endothelial cells lining the capillary bed.
From the moment the virus enters and begins replication, the cell ceases to perform its inherent functions, begins to produce proteins characteristic of the virus, with the formation of new virions, and then is destroyed. Alveolar macrophages and monocytes circulating in the capillary bed of the lung tissue react to this. They begin to produce large quantities of interleukins IL-1, IL-6 and other pro-inflammatory cytokines.
The more virions multiply, the more type 2 pneumocytes and endothelial cells are destroyed, and the more serious the disruption of the alveolar-capillary barrier, which is clinically manifested by a decrease in saturation. The increase in the production of proinflammatory cytokines by macrophages and monocytes significantly affects the activation of the hemostatic system.
The interleukins produced, in particular IL-1 and IL-6, increase the synthesis of tissue factor on the surface of endothelial cells that are not yet damaged by SARS-CoV-2. In addition, IL-6 blocks the synthesis of tissue factor pathway inhibitor. The accumulation of tissue factor globally activates the process of blood coagulation throughout the vascular bed.
Massive platelet aggregation begins in the lumen of the pulmonary capillaries and the formation of clots. The narrower the lumen of the vessel, the less likely the formation of full-fledged blood clots in it; platelet sludge is more often observed in them. TNF-a (tumor necrosis factor alpha) blocks fibrinolysis.
Thus, with COVID-19, just as with septic conditions, two serious pathophysiological processes occur in parallel in the hemostatic system: global activation of thrombus formation against the background of suppression of fibrinolysis.
Difficulties of anticoagulant therapy for COVID-19
All patients, including pregnant women, should receive prophylactic and therapeutic doses of LMWH calculated for their actual body weight.
It is unacceptable to select the dose of heparin by eye, because this can lead to complications. All patients with COVID-10 upon admission should be weighed at the ED level and weight and height clearly recorded in the medical record.
What to do if it is not possible to determine the level of D-dimers?
Firstly, we must remember that the study of D-dimer levels, which is widely practiced among the general population of patients with COVID-19, in pregnant women has low clinical significance, since the spread of D-dimer levels in normal pregnancy is significant and has not yet been achieved establish reliable reference values for D-dimers during pregnancy. Therefore, the assessment of the level of D-dimers must be carried out in dynamics, paying attention not only to the absolute level, but also to the daily increase.
In situations where for some reason it is not possible to urgently determine the level of D-dimers, the level of LDH (lactate dehydrogenase) should be assessed. A dynamic increase in LDH, especially >1,000 U/L, in a patient with COVID-19 may be an indirect laboratory sign of pulmonary embolism and/or pulmonary infarction. This test is highly sensitive, but non-specific, however, since with COVID-19 the affected area is primarily the lungs, we can assume that the disaster occurs there.
Indirectly confirm the presence of PE: ECG (signs of overload of the right parts of the heart), ultrasound of the heart (expansion of the right parts, increase in the average value of PAP) and veins of the lower extremities (presence of blood clots).
The listed indirect signs allow one to suspect PE or a high risk of PE and promptly prescribe adequate doses of heparins.
What to do if you cannot reach your target RAPTT level?
First of all, you should check the correctness of the nomogram (calculation and correction of the bolus and the administered dose of unfractionated heparin to the actual body weight). If you are sure that you did everything correctly, but the RAPTT still did not reach the target values, determine the levels of antithrombin III and/or anti-Xa activity.
Antithrombin III (AT III) and what to do if it decreases
Heparin is a cofactor of AT III; it transforms AT III into an immediate-acting anticoagulant, enhancing its effects 1,000 times or more depending on the dose and speed at which it is administered. AT III deficiency reduces the ability of heparin to inhibit coagulation factors IIa and Xa.
The average normal AT III level is 80–120%. In pregnant women, it naturally gradually decreases and by the end of the 3rd trimester normally should not decrease to less than 65%. Practice shows that 60–65% is a completely manageable situation. Lower rates (55–50% and below) should alert a specialist.
In acute inflammation, the level of AT III always increases, but with the development of thrombosis, sepsis, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, and the administration of heparins, it decreases. Therefore, a decrease in AT III levels in a patient with COVID-19 is a poor prognostic sign that indicates the development of serious complications and requires action.
In case of AT III deficiency, the decision is made individually.
There are three approaches for coagulation correction of AT III level:
1.Transfer of the patient to therapeutic doses of LMWH. In conditions of AT III deficiency, we focus on factor Xa binding, given the fact that the binding of 1 unit of Xa prevents the formation of 50 units of IIa (thrombin).
2. AT III replenishment with fresh frozen plasma (FFP) or AT III concentrate. Both options are not recommended for COVID-19. Transfusion of FFP in the setting of ARDS increases the risk of further lung damage due to the possible development of TRALI syndrome (acute injury to the lung parenchyma in response to transfusion of blood and its components). The administration of AT III concentrate (in cases where its level has not decreased less than 65%) can lead to increased bleeding, which is undesirable when treating pregnant women in critical condition.
3. Transfer of patients to direct thrombin inhibitors (independent of AT III) - direct factor IIa inhibitor (dabigatran) or direct factor Xa inhibitor (rivaroxaban). This method is used in the general group of patients and is not used in pregnant women.
Determination of Anti-Xa activity (IU/ml)
Currently, the ability to determine anti-Xa activity has appeared in many hospitals, and it is important to be able to correctly interpret the results ( see Table 1 for recommended levels ).
Blood sampling for this study is carried out 3–4 hours after subcutaneous administration of LMWH. It is best to do this after 4 hours, since it is at this time interval that the maximum level of concentration of administered LMWH in the blood plasma (anti-Xa activity) is observed.
Table 1. Classic recommended levels of anti-Xa activity Taking into account the fact that hospitalization of patients with covid pneumonia is generally associated with a high risk of pulmonary embolism, the level of anti-Xa activity should be maintained within the range of 0.5–1.0 IU/ml.
The principle of dose adjustment of LMWH based on anti-Xa activity is given in Table. 2 .
Table 2. Dose adjustment of LMWH for therapeutic concentrations of 0.5–1.0 IU/ml
What to do if D-dimer levels do not decrease?
One of the most frequently asked questions: we are doing everything correctly, but the level of D-dimers was and remains high. Hospitals fall into this trap when laboratories give a D-dimer response of “greater than some value,” for example, “>5,000 ng/ml.”
In this case, you need to contact the laboratory and, if possible, clarify the actual level of D-dimers at the time the patient was admitted to intensive care. It is quite possible that it was 7,000, 10,000 or even 20,000 ng/ml and is slowly decreasing with treatment.
Also, to correctly assess the situation, you should perform: monitoring the level of AT III and/or anti-Xa activity; Ultrasound of the heart with calculation of mean PAP; Ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities (looking for blood clots).
As UFH is titrated, the blood clots gradually loosen and disintegrate, maintaining an elevated level of D-dimers. Therefore, if a pregnant woman has thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities, it is necessary to periodically repeat an ultrasound and check the length of the blood clot. If it decreases, then everything is fine.
We must not forget that sometimes the source of elevated levels of D-dimers can be a hematoma that slowly goes away, sometimes over several weeks.
What should I do if my D-dimer levels start to rise again?
In a situation of sudden growth, it is necessary to carry out diagnostic measures:
- control of thrombus formation: ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities, ultrasound of the heart (dilation of the right cavities of the heart + average value of PAP);
- monitoring the severity of the inflammatory syndrome (the most accessible way is to determine C-reactive protein (CRP)).
An increase in the level of CRP over time indicates the acute phase of inflammation. Under the influence of IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-a, the synthesis of CRP increases after 6 hours, reaching its maximum concentration after 24–48 hours.
If during treatment there is a sharp rise in the level of D-dimers, in parallel the level of CRP begins to increase, correlating with an increase in the level of LDH, this indicates the fact of a catastrophe in the pulmonary vessels.
How to understand whether there is a pulmonary embolism in the absence of CT angiography?
An increased level of D-dimers by itself in this situation does not confirm PE, but the dynamics of this indicator is important. Clinical signs of pulmonary embolism should be assessed, in particular perfusion respiratory failure (decreased peripheral saturation <90%, compensatory tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, etc.).
Apply instrumental research methods available at this level of medical care: perform an ECG (overload of the right chambers of the heart), ultrasound of the heart (dilatation of the right chambers), measure the average value of PAP (with PE it can reach 35–60 or more mm Hg) , Ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities (looking for blood clots).
What to do if the patient “bleeds” or a hematoma appears, and D-dimers are elevated?
In case of active bleeding, it is necessary to stop the administration of UFH and restore normocoagulation. If necessary, compensate for the deficiency of blood coagulation factors by transfusion of single-group fresh frozen plasma or a concentrate of prothrombin complex factors.
Further return to heparins is possible only if normocoagulation is achieved in the screening coagulogram and there are no signs of active bleeding.
The dosage of LMWH is determined individually, taking into account the cause of bleeding (diffuse bleeding, postoperative bleeding, etc.), platelet levels, dynamics and reasons for the increase in D-dimer levels.
Plaque on the tongue after taking antibiotics: how to get rid of it?
Medication treatment may cause a coating on the tongue
- Infectious processes in the body require treatment with antibiotic drugs. Often, treatment uses a combination of different antibiotics, as well as the simultaneous use of other potent drugs: hormones, sulfonamides, nitrofurans.
- Taking medications depends on the severity of the disease; sometimes the course of treatment lasts a long time and leads to an imbalance of normal microflora. Dysbacteriosis is a serious complication after taking antibiotics.
- A dense gray-white coating on the tongue may signal a change in the intestinal microflora in favor of pathogenic flora. The administration of probiotics and immunomodulators will eliminate the problems that have arisen.
Plaque on the tongue with pancreatitis, gastritis: causes and treatment
Diet for gastrointestinal diseases is an important stage in recovery.
An abundant white coating with a yellow tint on the tongue can serve as a “beacon” for the appearance of functional digestive disorders and even indicate diseases such as gastritis and pancreatitis . Gastritis most often occurs due to poor diet, violation of food intake, and consumption of “unhealthy” foods. A thick white coating on the tongue is often accompanied by:
- heaviness in the stomach
- pain in the epigastric region
- unpleasant odor from the mouth
- heartburn
- nausea
Inflammation of the pancreas or pancreatitis occurs when the enzymes of the pancreas, due to the inflammatory process, are not released into the duodenum, but have a “destructive” effect in the pancreas itself.
The process of self-digestion occurs. Toxins and digestive elements can enter the bloodstream and disrupt the functioning of important organs: heart, lungs, liver, brain.
Examination of the patient
Pancreatitis is a serious disease; its acute form requires hospital treatment. The initial forms of the disease can be identified by a persistent white-yellow coating on the tongue with accompanying symptoms:
- pain in the upper abdomen
- vomiting mixed with bile
In diseases of the digestive system, the motility of the intestinal tract is impaired. In order to somehow help the intestines cope with food, the number of villi on its walls for processing food increases.
Papillae also grow on the surface of the tongue, which over time thicken and become clogged with waste products of bacteria. This is how the tongue becomes overgrown with a large layer of white-yellow coating.
IMPORTANT: If you experience periodic pain and discomfort in the stomach area, you should seek help from a gastroenterologist.
The following recommendations will help you get rid of functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, gastritis, pancreatitis, and therefore abundant white-yellow coating on the tongue:
- It is necessary to reconsider your daily routine and analyze your food intake and quality.
- You should eat in small portions every 4 hours.
- It is recommended to exclude “harmful” foods from the diet: fatty, canned, smoked, fried and spicy, fresh baked goods, sweet carbonated water.
- Avoid eating in a hurry.
- Chew food thoroughly.
- Do not eat too hot or cold food.
The problem of jaundice in pregnant women in modern obstetrics
Jaundice refers to the yellow coloration of the skin, sclera and mucous membranes as a result of tissue impregnation with bile pigment - bilirubin. Jaundice in pregnant women occurs with a frequency of 1 in 1500 births and is a symptom of diseases of various etiologies and pathogenesis. In pregnant women, jaundice is most often caused by liver pathology (so-called hepatic jaundice), subhepatic (obstructive) and suprahepatic (hemolytic anemia) jaundice are less common. Jaundice in pregnant women is usually divided into two large groups: I - jaundice caused by pregnancy pathology; II - jaundice associated with concomitant diseases, both acutely occurring during pregnancy and preceding it.
Classification of jaundice in pregnant women
First group. Jaundice caused by pregnancy pathology:
- intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy;
- acute fatty liver degeneration in pregnant women;
- jaundice due to gestosis (preeclampsia, eclampsia);
- jaundice due to excessive vomiting during pregnancy.
Second group . Jaundice caused by various concomitant diseases encountered during pregnancy:
- diseases that occur during pregnancy: acute viral hepatitis (caused by hepatitis A, B, C, D, E viruses, as well as yellow fever, Epstein-Barr, herpes simplex types I and II viruses, cytomegalovirus and some others), medicinal, toxic (alcohol, etc.); obstruction of the common bile duct (obstructive jaundice); some bacterial, parasitic infections, sepsis;
- diseases preceding pregnancy: chronic liver diseases of various etiologies, hemolytic anemia, familial non-hemolytic hyperbilirubinemia and some others.
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy ( ICP) (previously used terms - “cholestatic hepatosis of pregnancy”, “benign recurrent cholestasis of pregnancy”, “adiopathic jaundice of pregnancy”, “pruritus of pregnancy”) is the second most common cause of jaundice in pregnant women (after acute viral hepatitis). , causing up to 20–25% of its cases. The etiology of ICP is unknown; it is assumed that the disease is based on a genetic predisposition to an unusual cholestatic reaction to estrogens produced during pregnancy. ICP is characterized by: onset, usually in the third trimester (less often in the second trimester); an increase in clinical manifestations before childbirth and their disappearance immediately after childbirth; recurrent in nature (not always) with repeated pregnancies; often the presence of skin itching during pregnancy in mothers and sisters. The main clinical manifestation of ICP is itching of the skin, which precedes the appearance of jaundice (jaundice may not develop). Jaundice, as a rule, is not intense, accompanied by darkening of the urine and lightening of the stool. The general condition of the patients does not suffer. Characterized by no more than a 5-fold increase in serum bilirubin levels, an increase in alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels by 7–10 times, gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT), and bile acids; a slight increase in the ratio of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase (AST/ALT). Histological changes in the liver represent simple cholestasis. The prognosis of the condition is favorable, however, the frequency of premature births increases, due to impaired absorption of vitamin K, hypoprothrombinemia and an increased risk of postpartum hemorrhage are possible.
Diagnosis of ICP, as a rule, does not cause great difficulties, especially if there is anamnestic evidence of the recurrent nature of cholestasis or hereditary predisposition. The range of conditions for which a differential diagnosis should be made is limited to diseases characterized by cholestasis syndrome: obstructive jaundice, cholestatic form of acute viral hepatitis, drug-induced hepatitis, and some forms of chronic liver diseases. Obstructive jaundice is excluded based on the clinical picture (absence of abdominal pain syndrome in ICP) and the results of ultrasound examination of the biliary tract. Acute viral hepatitis helps to exclude insignificant changes in cytolysis parameters (AST/ALT) and the absence of serum viral markers in ICP. The greatest difficulties are presented by the differential diagnosis of ICP with the onset during pregnancy of previously latent chronic liver disease (CLD) (primary biliary cirrhosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, chronic hepatitis with cholestasis syndrome). Often, the diagnosis of CKD can be established only after resolution of pregnancy on the basis of the persistence of clinical and laboratory signs of cholestasis, which is uncharacteristic for ICP, and on the basis of a morphological examination of the liver. Carrying out a liver biopsy during pregnancy in such cases, as a rule, is not required, since it does not affect the management of the pregnant woman (in both ICP and chronic liver disease, termination of pregnancy in the third trimester is not indicated; a reduction in the manifestations of cholestasis can be achieved by prescribing cholestyramine).
Acute fatty liver disease of pregnancy (AFLP) - Sheehan's syndrome (previously called "acute fatty liver disease of pregnancy") is a rare complication of pregnancy, occurring with a frequency of 1 in 13,000 births. Etiology unknown; Sometimes there is an association with the use of tetracycline. It usually develops in young primiparous women in the third trimester of pregnancy (from 30 to 38 weeks). Characterized by a sudden onset with vomiting and abdominal pain, then jaundice and fever appear, the development of fulminant hepatic and acute renal failure, blood coagulation disorders (disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome (DIC) in 75% of patients), gastrointestinal and uterine bleeding; the condition is often combined with gestosis. Laboratory tests are characterized by: leukocytosis up to 20–30 thousand, a significant increase in the level of uric acid in the blood serum, severe hypoglycemia, a significant decrease in albumin levels, a moderate increase in the levels of bilirubin, serum aminotransferases. Histologically, small-lobed obesity of hepatocytes without significant necrosis and inflammation is revealed, however, liver biopsy is usually impossible due to severe blood coagulation disorders. The condition is characterized by high mortality for mother and fetus; the prognosis can only be improved by the earliest possible diagnosis of the condition and delivery (caesarean section under epidural anesthesia). The disease may progress within 1–2 days after delivery, then the condition improves. Repeated pregnancies are not contraindicated, since relapses of AFDP are not observed.
The most important differential diagnosis is with the fulminant form of acute viral hepatitis, since management tactics for these diseases are different. The differential diagnosis is based on the clinical and laboratory features of AFDP (characteristic are the time and symptoms of the onset of the disease, leukocytosis and high levels of uric acid in the blood serum with relatively low levels of bilirubin and AST/ALT), the absence of serum viral markers. Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the liver can be useful, revealing a picture of steatosis and a reduced liver size. This study also allows us to exclude the obstructive nature of jaundice, the presence of which may be suspected on the basis of severe abdominal pain and dyspeptic syndromes, leukocytosis.
Jaundice with preeclampsia, eclampsia . In severe gestosis, liver damage is observed, the cause of which is microangiopathy as part of generalized vascular disorders. Histologically, fibrin thrombi are detected in the sinusoids, mainly centrilobular necrosis and hemorrhage; there is no inflammatory reaction.
The appearance of signs of liver damage against the background of a detailed clinical picture of gestosis is typical. As a rule, only laboratory changes are observed (increased alkaline phosphatase, AST/ALT, slight thrombocytopenia). In severe cases, moderate jaundice develops (hyperbilirubinemia within 5-6 times the norm due to conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin), combined with the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, intravascular hemolysis, thrombocytopathy, the so-called HELLP syndrome (according to the first letters of the main manifestations - haemolyas , elevated liver enzymes, low platelet colint). Maximum changes in laboratory parameters are observed in the first two days after birth. Clinically, the condition manifests itself, in addition to the symptoms of preeclampsia and eclampsia, by abdominal pain syndrome (in 65–90% of patients), nausea and vomiting (up to 50%), complications of disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome and may resemble CVD. The condition can sometimes be combined with ACDP, which is proven morphologically by the detection (in addition to the characteristic fibrin thrombi, necrosis and hemorrhage) of small-droplet obesity of hepatocytes. A rare and very severe complication of liver damage in eclampsia is the formation of a subcapsular hematoma with liver rupture and the development of intra-abdominal bleeding.
As with AFDP, the most important differential diagnosis is acute viral hepatitis, which can be excluded by a clear connection of the condition with the progression of gestosis, the absence of a prodromal period, as a rule, a lower level of increase in AST/ALT, and the absence of serum viral markers. Differential diagnosis of severe liver damage in preeclampsia, eclampsia with AFDP can be extremely difficult (especially given the possibility of a combination of these conditions), but it has no practical significance, since in both cases the management of the pregnant woman is the same and consists of urgent delivery .
Jaundice due to excessive vomiting in pregnant women is associated with transient functional changes in the liver caused by malnutrition, protein catabolism, and dehydration. The mechanism of hyperbilirubinemia is not entirely clear. There are no specific histological changes in the liver during vomiting of pregnancy. The development of jaundice is observed in the first trimester of pregnancy against the background of a long period of daily repeated vomiting, weight loss, and dehydration; characterized by a slight increase in the levels of bilirubin (both conjugated and unconjugated), AST/ALT, alkaline phosphatase, a decrease in the level of albumin in the blood serum with a rapid normalization of indicators after cessation of vomiting and restoration of nutrition. The condition usually has a good prognosis and does not require termination of pregnancy. With a typical clinical picture, diagnosing the condition does not cause difficulties. However, with pronounced abnormalities in liver tests, it is necessary to exclude acute viral hepatitis or an exacerbation of unrecognized chronic hepatitis that preceded pregnancy. In difficult cases, when a combination of vomiting of pregnancy and exacerbation of chronic hepatitis is suspected, a puncture biopsy of the liver is indicated, the result of which may affect the management of the pregnant woman (determining indications for termination of pregnancy, for the treatment of CKD).
Among intercurrent liver diseases that occur during pregnancy, the main role in the development of jaundice belongs to acute viral hepatitis (AVH), which causes up to 40–50% of cases of jaundice in pregnant women. AVH can be observed at any stage of pregnancy; its clinical picture is extremely diverse (from anicteric clinically latent forms to severe fulminant hepatitis), which makes differential diagnosis difficult and the need to differentiate AVG from all etiological forms of jaundice found in pregnant women. At the same time, correct and timely diagnosis of OVH is especially important due to the peculiarities of management tactics for pregnant women with this condition. It is known that termination of pregnancy and childbirth aggravate the course of OVH, so management should be aimed at prolonging pregnancy and preventing premature birth.
In the diagnosis of AVH, epidemiological data (risk factors for infection), the presence of a clear prodromal period, a very high level of serum aminotransferases characteristic of AVH, identification of serum markers of hepatitis viruses characteristic of acute infection: anti-HAV IgM in AVH-A may be important; HBsAg, HBcAb total and IgM, HBeAg, HBV DNA in ARV-B; anti-delta IgM, HDVRNA for OVH-D; HCVRNA in AVH-C, anti-HEV in AVG-E (the diagnostic value of anti-HEV has not yet been sufficiently studied), serum and tissue markers of other hepatotropic viruses. It is important to carefully exclude all other possible causes of jaundice in pregnant women.
Chronic liver diseases (chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis of various etiologies - viral CKD, autoimmune hepatitis, drug and alcohol liver damage, primary biliary cirrhosis, liver damage due to primary sclerosing cholangitis, Wilson-Konovalov disease and some others) can be latent for a long time or appear only extrahepatic syndromes, which often makes their timely diagnosis difficult. It is not uncommon to observe during pregnancy the manifestation of a preceding but unrecognized CKD.
Primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis are characterized by exacerbation or the first appearance of clinical signs of cholestasis (itching, jaundice) during pregnancy, which is caused by the action of estrogens. Differential diagnosis is carried out with ICP, drug-induced hepatitis, cholestatic form of AVH. In contrast to the cholestatic form of jaundice in some CKD, which is not associated with a risk to the life of the pregnant woman, non-cholestatic (hepatocellular) jaundice during exacerbation of CKD of viral etiology, autoimmune hepatitis indicates severe damage to the liver parenchyma and is an unfavorable prognostic sign (the possibility of developing liver failure , coma). Differential diagnosis is carried out with OVH, ACDP, hemolytic jaundice and other diseases.
CKD can be suspected on the basis of anamnesis, retrospective assessment of some symptoms that could be a manifestation of liver disease unrecognized at the time of pregnancy (AVG, episodes of jaundice in history, the presence of articular syndrome, relapses of vascular purpura or other most common extrahepatic manifestations of CKD), detection of increased dense liver, splenomegaly, signs of portal hypertension characteristic of liver cirrhosis during ultrasound, esophagogastroscopy. In difficult differential diagnostic cases, especially when the result of the study may affect the management of the patient, a puncture biopsy of the liver is indicated to clarify the diagnosis of CKD.
Subhepatic jaundice in pregnant women is most often a consequence of obstruction of the common bile duct; other causes (tumors, strictures) are extremely rare. During pregnancy, bile becomes more lithogenic, and emptying of the gallbladder becomes more difficult; There are observations of the formation of gallstones during pregnancy. Despite this, symptoms of gallstones are relatively rare during pregnancy. Choledocholithiasis accounts for no more than 6% of the causes of jaundice in pregnant women. Obstructive jaundice in cholelithiasis most often develops after an attack of acute pain in the upper abdomen, often accompanied by vomiting and fever; a blood test reveals leukocytosis; there is no stercobilin in the feces or the reaction is weakly positive (with incomplete obturation); bilirubin (bile pigments) is determined in the urine; in the very first days, an increasing biochemical syndrome of cholestasis is noted; cytolytic syndrome (increased AST/ALT) can be pronounced. The development of cholestatic jaundice during pregnancy (even in the absence of a typical clinical picture of biliary colic) always requires the exclusion of the mechanical nature of cholestasis through the immediate use of ultrasound.
Enzymatic hyperbilirubinemias are rarely a problem during pregnancy. In the most common form of enzymatic hyperbilirubinemia, Gilbert's disease, characterized by an increase in the level of unconjugated bilirubin, a decrease in the level of bilirubinemia is observed during pregnancy. This is explained by the induction of hepatic glucoronyltransferase by estrogens. In rare cases, when unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia is first detected during pregnancy, the differential diagnosis should be made with inactive chronic hepatitis, an erased form of hemolytic anemia. Other forms of familial non-hemolytic bilirubinemia are extremely rare in pregnant women. Of these, only in Dubin-Johnson syndrome, characterized by increased levels of conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin, bilirubinemia increases towards the end of pregnancy, and latent forms may first manifest as jaundice during pregnancy. The diagnosis is reliable only when confirmed by liver biopsy data (the structure of the lobules is preserved, in the hepatocytes there are deposits of dark brick-colored pigment).
Prehepatic jaundice (hemolytic anemia) often occurs during pregnancy. Differential diagnosis from other forms of jaundice, as a rule, is not difficult, based on the presence of anemia of varying severity, signs of irritation of the red line of the bone marrow with reticulocytosis, hyperbilirubinemia due to an increase in the level of unconjugated bilirubin (the level of conjugated bilirubin may be slightly increased), dark color of stool due to stercobilinogen, unchanged levels of cholestasis and cytolysis. One should keep in mind the possibility of autoimmune hemolytic anemia against the background of autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, and the possibility of developing hemolytic crises in Wilson-Konovalov disease.
Ursodeoxycholic acid is used as the main pathogenetic agent for intrahepatic cholestasis.
Ursodeoxycholic acid is a naturally occurring, non-toxic, hydrophilic bile acid that is part of the human bile acid pool. The mechanisms of action of ursodeoxycholic acid are diverse and not fully understood. The main ones are cytoprotective and choleretic effects caused by changes in the pool of bile acids with ursodeoxycholic acid displacing toxic primary bile acids (such as chenodeoxycholic, deoxycholic, lithocholic), the absorption of which in the intestine is inhibited. In addition, ursodeoxycholic acid has an immunomodulatory effect. It has been shown that its use leads to a decrease in the expression of HLA class I and II antigens on hepatocytes, biliary epithelial cells, and to a decrease in the production of proinflammatory cytokines. Ursodeoxycholic acid also has anti-apoptotic and antioxidant effects. By inhibiting the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine, suppressing its synthesis in the liver and reducing secretion into bile, ursodeoxycholic acid reduces the saturation of bile with cholesterol; it increases the solubility of cholesterol in bile and reduces the lithogenic index of bile.
The use of ursodeoxycholic acid in the third trimester of pregnancy not only relieves itching and improves the mother's condition without causing side effects, but also significantly improves the prognosis for the fetus.
Thus, jaundice during pregnancy can be caused by diseases that differ not only in etiology, but also in severity and, accordingly, prognosis for the mother and fetus. The differential diagnosis of jaundice in pregnant women is extremely important, since management and treatment tactics that ensure a successful pregnancy outcome for the mother and fetus are different for various diseases that occur with jaundice.
Literature
- Kuzmin V.N., Adamyan L.V. Variants of the clinical course, diagnosis and treatment tactics of acute fatty hepatosis in pregnant women // Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2009, No. 1, p. 25–29.
- Kuzmin V.N., Serobyan A.G. Acute fatty hepatosis in pregnant women // Issues of gynecology, obstetrics and perinatology. 2008, vol. 7, no. 1, p. 83–87.
- Sherlock S., Dooley J. Liver during pregnancy. In the book: Diseases of the liver and biliary tract. M., 1999, p. 540–549.
- Shekhtman M. M. Extragenital pathology and pregnancy. Medicine, 1987. 295 p.
- Aggarwal R., Ranjan P. Preventing and treating hepatitis B infection // BMJ. 2004. Vol. 329. P. 1080–1086.
- Gambarin-Gelwan M. Hepatitis B in pregnancy // Clin Liver Dis. 2007 Nov; ll(4):945–63.
- Riely CA Liver disease in pregnant patient // Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999. Vol. 94. P. 1728–1732.
- Steven MM Pregnancy and liver disease // Gut. 1981. Vol. 22. P. 592–614.
- Lorente S., Montoro MA Cholestasis of pregnancy // Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007, 30 (9), p. 541–548.
- Pusi T., Beuers U. Intrahepatic cholestasis in pregnancy // Orphanet. J. Rare. Dis., 2007, 2, p. 26.
V. N. Kuzmin , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor
MGMSU, Moscow
Contact information about the author for correspondence
Plaque on the tongue in adults and children and bad breath: causes, treatment
Bad breath is a concomitant symptom of the disease
- Plaque on the tongue is often accompanied by an unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth. This may be due to both a disruption in the digestive tract and insufficient oral hygiene. In any case, you should undergo examination by specialists.
- A general blood test and the procedure for endoscopic examination of the esophagus and stomach (FGS and FGDS) can identify gastrointestinal pathologies.
- You can remove sources of infection in the oral cavity by visiting a dentist. Timely dental sanitation, treatment of caries, gingivitis, stomatitis and other diseases will help get rid of putrid odor and plaque on the tongue.
Putrefactive processes in the oral cavity can be stopped with herbal infusions prepared at home.
Infusion No. 1
Yarrow herb, plantain leaf, linden leaf and oregano herb are mixed equally. A tablespoon of the collection is steamed with 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for 40 minutes. The glass is divided into two servings and drunk throughout the day.
Infusion No. 2
1 tablespoon of oak bark is steamed with 200 ml of boiling water. Rinse the mouth with the resulting infusion several times a day.
Chamomile infusion has antiseptic properties
Infusion No. 3
Mix strawberry leaves, chamomile flowers, sage and mint leaves. A handful of herbs is poured with 500 ml of boiling water. Rinse your mouth with warm infusion throughout the day after meals.
Features of oral hygiene in pregnant women
24.Jul.2017
During pregnancy, problems with the oral cavity increase the risk of developing various diseases for the expectant mother and baby. This can seriously affect the formation of the child’s vital systems. Bacteria that accumulate in the oral cavity enter the gastrointestinal tract. As a result, the immune system of the entire body is weakened. Frequent colds may appear, cardiovascular diseases begin to develop, and problems with the digestive organs arise.
Teeth during pregnancy: first visit to the dentist
Ideally, dental problems should be resolved before the planned pregnancy. But not everyone succeeds in this.
During pregnancy, it is better to postpone serious manipulations, such as caries treatment with anesthesia. Instead, talk to your doctor about the best toothpaste to use to stop tooth decay. In the case of deep damage to the tooth and the need for depulpation (removal of the nerve), you may be offered to install a temporary filling. In the first trimester, dental treatment during pregnancy should be as gentle as possible.
Teeth during pregnancy: treatment and prevention
A very important procedure during pregnancy is professional teeth cleaning. As a rule, the procedure lasts no more than 40 minutes. During this time, the dentist will have time to remove old tartar and plaque. Using special pastes and brushes, he will polish your teeth and cover them with protective varnish. The surface of the teeth will become clean. Smooth enamel will protect you from the new danger of developing caries.
During pregnancy, whitening procedures should not be performed. Teeth whitening comes with the risk of damaging the enamel. In most cases, this is contraindicated during pregnancy, when the load on the enamel is already increased. Teeth become especially sensitive during pregnancy, and the already unpleasant sensations can become very painful.
The second trimester of pregnancy is a suitable period for the treatment of shallow caries and gum inflammation. By this time, all the baby’s main organs have already been formed. The use of mild medications will not cause serious harm.
Teeth during pregnancy: smile more often!
Expectant mothers should choose brushes with medium-hard bristles. This will protect not only the gums from excessive bleeding, but also the sensitive enamel from micro-scratches. You will have to change your brushes more often than before, preferably every month. Your dentist will help you choose the right toothpaste.
A very useful item for comprehensive oral care is an irrigator. With its help, you can more thoroughly clean the hard-to-reach spaces between your teeth. The irrigator perfectly massages the gums, which is the best prevention against gingivitis, which often occurs in expectant mothers. The reason lies in hormonal changes. At the end of the first trimester, if the blood supply to the skin and mucous membranes deteriorates, the gums may suffer. If you notice swelling, bleeding, or pain, you should consult a doctor. In most cases, it will be enough to rinse your mouth with a medicated solution at home, apply ointment to the affected areas and use a soft-bristled brush.
Teeth during pregnancy: proper nutrition
To keep teeth healthy, the expectant mother must monitor her diet during pregnancy. A simple adjustment to your daily diet will do wonders.
Keeping a food diary is very useful. After finishing each meal, write down what you ate and drank in a notebook. At the end of the week, look through your diary and analyze how much protein, carbohydrates and fat you usually eat. You don't have to be a nutritionist to know if you're eating right. By eating a lot of baked goods, you end up with excess carbohydrates. And a lack of red meat, eggs, fish, and dairy products in the diet is a clear sign of an unbalanced diet.
| Dentist visit schedule: 1st visit: 6-9 weeks of pregnancy 2nd visit: 16-18 weeks of pregnancy 3rd visit: 26-28 weeks of pregnancy 4th visit: 36-38 weeks of pregnancy |
Teeth during pregnancy: mouth rinse
Make a decoction of string, chamomile, calamus and licorice rhizomes: place two tablespoons of the mixture in a saucepan, pour two cups of boiling water and simmer over low heat for 15 minutes. Strain and dilute with water to make a glass of liquid. Use after meals to treat and prevent gingivitis.
Plaque on the tongue and dryness and bitterness in the mouth: causes, treatment
Dryness and bitterness in the mouth, accompanied by a coating on the tongue, can occur in a number of diseases.
Plaque on the tongue is often accompanied by symptoms of dryness and bitterness in the oral cavity. This could be due to a number of reasons.
- Eating salty and fatty foods before bed can cause these symptoms. This is a large load on the liver and its reaction to “heavy” foods manifests itself in the form of a yellow coating on the tongue, the appearance of a bitter taste and dryness in the mouth.
- Intoxication of the body can also cause bitterness, accompanied by nausea and vomiting, sweating, headache, dryness or salivation.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract are accompanied by morning bitterness, a coated tongue, belching and heartburn. If such symptoms have become habitual, it is recommended to pay attention to your diet and eating hours.
- It should be taken into account that the initial stage of diabetes mellitus is characterized by dryness and bitterness in the mouth, thirst and the urge to urinate. In this case, the tongue has a dense yellowish coating. Such symptoms require an immediate visit to an endocrinologist.
- Toxicosis in pregnant women is often accompanied by nausea, bitterness and dry mouth. You should be careful about your diet: remove fried and fatty foods, smoked foods and canned food from your diet. The list of necessary products includes vegetables, fruits, and berries in sufficient quantities.
Pay attention to food processing!
It should be remembered that to feed pregnant women, all products must be fresh and well-processed. Remember to wash vegetables, fruits or herbs before eating.
To avoid undesirable consequences, it is necessary to thoroughly heat treat meat, poultry, fish and semi-finished products.
Do not eat raw eggs, meat or fish as this is hazardous to your health. Raw foods that are used in some dishes can cause poisoning and more serious consequences.
Prevention of plaque in children and adults
Oral hygiene
Plaque on the tongue consists of desquamated epithelial cells, accumulated bacteria and their waste products. To keep your tongue clean and healthy, it is recommended to take preventive measures and prevent such “garbage” from accumulating on the surface of the tongue.
Regular tongue cleaning will prevent oral diseases such as:
- gingivitis
- stomatitis
- caries
- periodontitis
Accumulations of plaque block the taste buds, but a “clean” tongue will help preserve the sense of taste.
What can you do to keep your tongue healthy?
- Check your tongue in the mirror every day for plaque.
- You should brush your tongue twice a day: morning and evening. This hygiene procedure should be combined with dental care. It is necessary to clean the tongue with careful movements using special scrapers, a teaspoon or a toothbrush.
- After each meal you should rinse your mouth.
- It is not recommended to eat hot or cold food.
- You should not put sharp or traumatic objects in your mouth.
Tongue cleaning
IMPORTANT: Daily light massage of the tongue (with a toothbrush, a teaspoon, a special scraper) for 2 minutes activates the work of our important internal organs: heart, liver, lungs, kidneys.
Tongue Cleaning Rules
- A scraper or a teaspoon is passed along the surface of the tongue from the pharynx to the tip.
- Such movements are carried out several times throughout the tongue, affecting the lateral surfaces of the tongue.
- Periodically, the scraper or spoon should be washed to remove dirt with clean running water.
- Cleaning the tongue must be done carefully so as not to injure the papillae of the tongue mucosa.