Warts are classified as benign neoplasms.
They can appear on various parts of the skin and mucous membranes.
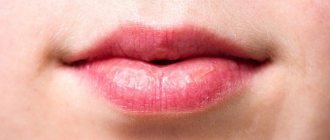
If a wart appears on the lip, it represents a cosmetic defect and can also cause discomfort to its owner, worsening the quality of life.
Forming on the lip, the tumor affects speech and interferes with eating.
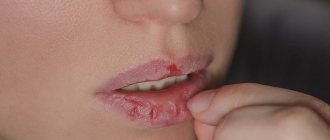
A wart can cause pain, especially if it is localized on the mucous membrane inside the lip.
If measures are not taken to eliminate it, the growth may become injured, which will lead to a secondary infection.
Types of warts
A wart is a growth that rises above the surface of the skin or mucous membrane.
Its dimensions, as a rule, are no more than 1 centimeter in diameter.
The tumor can appear on any part of the body, including the face.
On the face, most often a wart forms on the lip, above or below the lip, on the buccal surface of the oral mucosa.
A warty growth can appear on both the upper and lower lips.
The following types of neoplasms are distinguished:
- Common (vulgar) warts. These are growths that have a dense structure, soft to the touch, flesh-colored or yellowish in color. New growths form on the red border of the lips. They are not painful, but tend to itch. Vulgar warts appear on the lips not only in adults, but also in children.
- Flat- shaped growths may appear on the outside of the lips or on the oral mucosa. Their surface is smooth, oval or round in shape. The color of the growth resembles the color of the skin and almost does not rise above it. The location is also the red border of the lips. Flat warts do not hurt, but they are very itchy.
- Hanging neoplasms are located on a thin stalk. At the beginning of development they resemble a bump. They have a brown, pinkish tint or close to the color of the skin.
- Filiform (acrochords). These are small growths that appear after 35 years, but can occur earlier.
- Genital warts . The localization of such growths is the mucous membrane. The new growths are elongated and arranged in groups, resembling a cockscomb or cauliflower inflorescences. The growths are prone to injury, which causes inflammation and bleeding.
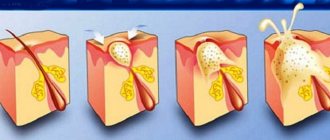
The wart forms gradually and almost imperceptibly.
- At the beginning of development, a small compaction forms, which gradually increases.
- A white dot forms on the surface of the mucous membrane of the lip or in the mouth, which gradually turns into genital warts.
To date, approximately one hundred types of papillomavirus have been discovered.
Some types of growths have a benign course, while others are capable of malignancy.
They can provoke the development of cancer.
In addition to the types of growths listed above, there are also senile warts (keratoma, keratosis).
The difference between keratosis is that its appearance is not associated with papillomavirus, and keratoma does not provoke the formation of cancer.
In their development, senile warts go through several stages:
- ✓ brown spots appear, but the wart has not yet formed
- ✓ formation of papules and nodules
- ✓ appearance of keratoma - when you try to scrape off the scales, bleeding appears
- ✓ transition to the cutaneous horn, which is characterized by excessive growth and keratinization of the neoplasm
According to some experts, keratosis and senile warts belong to different diseases.
Pathogenesis of genital warts
HPV is found in the cellular structures of the skin and mucous membranes, so it can be transmitted from men to women, from adults to children. The long latent period of infection makes early diagnosis of the disease difficult. Condylomas are not immediately visible to the naked eye. To activate HPV, a large number of these pathogens is necessary, only then the papillomavirus “comes out”, represented by genital warts. An increase in HPV may occur due to decreased immunity in women or men. Genital condylomas are caused by the process of atypical reproduction of the human papilloma virus; under its influence, epithelial cells grow and develop with pathology. The skin and mucous tissues change and this is how condylomas appear. Growths in the form of warts and papillae can be single or massive, turning into entire “conglomerates” of condylomas.
The difference between a wart and keratoses and cancer
Keratosis may be similar in appearance to melanoma (a type of skin cancer).
Melanoma can begin as a warty growth or as a seborrheic keratosis.
A dermatologist can distinguish them from cancer.
To exclude an oncological process, a biopsy is performed.
The peculiarity of seborrheic keratosis is that the formation is waxy, flat, and there is no pain when touched or at rest.
With cancer, a growth similar to a keratosis may change shape or color.
In this case, you will need to consult a specialist.
Self-medication is harmful
Do not try to diagnose and treat HPV infection on your own! Firstly, there is a risk of improper use of drugs. Secondly, only a doctor can distinguish papilloma from a malignant tumor. In addition, self-treatment is fraught with consequences.
Today, there are celandine-based preparations on sale that are intended to eliminate warts. Celandine juice is similar in composition to iodine. Therefore, prolonged exposure to the drug causes skin burns. In this case, papillomas are seriously injured and can provoke the development of skin cancer. Cauterization with iodine is even more dangerous - it is more aggressive than celandine. Trying hard to get rid of papillomas with iodine, you can get scars on the skin. Vinegar is no better in this regard. Attempts to bandage warts and papillomas with a thin silk thread often only provoke the growth of these formations.
If you suspect the appearance of warts or genital warts, you should definitely seek advice from a dermatologist, urologist or gynecologist, depending on the location of the source of infection. Only a professional can correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Causes of warts
The appearance of warts is caused by infection with papillomavirus or HPV.
Since the skin on the lips is quite thin, it is therefore easily permeable to viruses.
It should be noted that signs of infection with the human papillomavirus do not always occur.
The better the immune system, the less likely it is that symptoms of the disease will appear.
And yet, most of the world's population is infected with HPV.
The incubation period for the development of the disease can be several months or years.
As soon as the immune system fails, the first signs of infection appear.
Activation of the virus is accompanied by the formation of warts.
As a rule, growths appear on the area of the skin or mucous membrane where the pathogen entered the body.
Infection can occur both through sexual contact and through household contact.
Can the virus be transmitted by kissing on the lips?
The most common cases of infection are:
- intrauterine infection of the fetus if a pregnant woman is infected with papillomavirus
- shaking hands or kissing an infected person (if there are wounds or abrasions, the risk of infection increases)
- the use of personal items of an infected person (toothbrush, dishes, lipstick) is unlikely, since the pathogen is not stable in the environment
- sex accompanied by oral sex
- visiting common areas (swimming pool, sauna, shower)
People at risk are those who:
- patients with diabetes mellitus or other pathology of the endocrine system
- suffer from obesity and metabolic disorders
- taking antibiotics for a long time
- have chronic diseases
- suffer from increased sweating, especially on the feet, as this is where plantar warts often form
A malfunction of the immune system can occur for the following reasons:
- If there is a deficiency of essential substances in the body
- After suffering stress or physical exhaustion
- In case of hormone imbalance: during puberty, during pregnancy, with the onset of menopause, during treatment with hormonal drugs
- In case of chronic lack of sleep and overwork
- Due to a recent infectious disease
- If a person abuses smoking and alcoholic beverages
Stages
The oncologist determines the stage of the disease. This is important for prescribing effective therapy. The stage of the disease must be indicated in the diagnosis. Let's look at the stages using the example of stage III squamous cell carcinoma of the lower lip (T2N1M0). Each sign in the designation has its own role. The letters TNM define the characteristics of a malignant tumor and the stage of cancer:
- T – Tumor, which means tumor size: T1 – no more than 2 cm, T2 – 2-4 cm, T3 – more than 4 cm, T4 – the tumor has grown into surrounding organs;
- N – Nodus. Indicates the degree of damage to the lymph nodes: N0 – lymph nodes are not affected, N1 – enlargement of nearby lymph nodes up to 3 cm, N2 – small lesions in several nodes or a large lesion in one, N3 – enlargement of several lymph nodes by more than 6 cm;
- M - Metastasis. Shows whether the lip tumor has caused the spread of metastases to other organs: M0 – no metastases, M – yes.
Diagnosis of warts
The main diagnostic method is to examine the patient's face for the presence of warts on the lips and oral mucosa.
To confirm or refute the presence of HPV, it is enough to take tests:
- ✓ Blood tests for antibodies
- ✓ To conduct a histological examination (biopsy), a small part of the tumor is taken for analysis
- ✓ The PCR technique allows you to detect the genetic material of a pathogen with one hundred percent probability
Before getting rid of the growth, you should visit an oncologist.
A specialist will use dermatoscopy to determine the condition of the wart to rule out signs of malignancy.
Clinical manifestations of warts on the lip
A wart on the lip does not appear the next day after the papilloma virus enters the body.
The incubation period can last from six months to several years.
This often occurs when the immune system malfunctions.
Having penetrated the skin or mucous membrane, the virus integrates its genetic material into human cells and thus begins to multiply.
As a result, characteristic neoplasms appear at the site of virus introduction.
The pathogen provokes warty growths, disrupting the processes of keratinization of the skin.
Oncogenic strains of papillomavirus change the genetic apparatus of cells in such a way that a malignant formation is formed.
Strengthening the immune system
Modern medicine has not yet learned to kill viruses. But an important fact is that HPV carriage is not lifelong. In addition, medicine has a small number of means at its disposal that allow it to remove some of the viruses from the body. The use of these drugs is fully compatible with immunomodulatory therapy.
The amount of virus in the body is directly related to the state of the body’s immunity - the better the immunity, the less virus. Therefore, the most promising way to reduce the concentration of HPV in the body is to strengthen the immune system. For this purpose, a separate course of treatment is carried out, after which the person begins to feel much better.
Finally, there are very effective preparations for topical use - creams, gels, sprays that increase local immunity and reduce the concentration of the virus in the affected tissues.
Is it necessary to remove a wart on the lip?
Removal of the tumor is carried out if there are indications for this.
The growths sometimes disappear spontaneously.
Therefore, if the wart is small and does not cause much concern, then there is no need for removal.
The decision to excise the growth must be made by a specialist.
If a wart causes discomfort in the form of itching, burning, pain, grows, becomes inflamed, or changes in appearance.
If it has increased in size, changed shape and color, or is bleeding, then it must be removed by resorting to excision by one of the methods.
Removing a tumor at home is not safe.
As a result of incorrect actions:
- It may not be possible to remove the wart completely, which will cause its reappearance
- the risk of injury to healthy tissues that surround the growth increases
- scars and cicatrices may form
Wart treatment
Treatment of any growth on the lips begins with a medical examination and determining whether the growth is malignant.
Next, the doctor selects a method of therapy.
In case of a malignant form, the patient is referred to an oncologist, who will decide how to treat the patient.
Treatment of the disease is complex.
Treatment consists of the main stages: removal of the growth and drug therapy.
Removal of the tumor can be done in one of the following ways:
- ✓ Using pharmaceutical products
- ✓ In a medical institution where modern excision techniques will be used
- ✓ Folk remedies. The use of alternative medicine methods must be agreed with a doctor
Prevention
Since the virus is activated only at those moments when the human body is weakened, patients with HPV will need to constantly maintain their immunity at the proper level. This can be done with proper nutrition, hardening the body and taking immunostimulating drugs. At the moment the formations appear, the patient can infect other people. Therefore, those who are not sick with papillomavirus should avoid oral contact with a person on whose lips neoplasms are noticeable.
You should definitely use protective equipment during sexual intercourse, because the virus is easily transmitted during intimacy. At the same time, the infected person himself may not know that he is sick, which means he can infect his partner unintentionally.
Pharmacy products for removing warts
You can buy medications at the pharmacy that will help you deal with warts at home.
Among them:
- Super clean . The product is an alkaline solution that has a chemical effect on the growth, causing cauterization.
- Cryopharma, Wartner . These agents cause cryodestruction of the wart; as a result of cold exposure, the neoplasm is frozen.
- Solcoderm . A drug containing acids that have a cauterizing and mummifying effect on pathological tissues.
- Immunomodulators – Viferon, Oxolinic ointment will help increase immunity and the body’s fight against the virus.
- Antiviral agents – Isoprinosine, Interferon.
The use of cauterizing agents on the lips and face is extremely undesirable; application of these agents to the oral mucosa is especially dangerous.
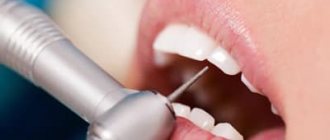
Wart removal in the clinic
The clinic uses modern hardware techniques to excise growths:
- Laser therapy . The method allows you to quickly and without blood remove the growth. There is no discomfort during the procedure, as pain relief is performed. During one session, you can get rid of several tumors in a very short time. The method is suitable not only for adults, but also for children. The likelihood of relapse is minimized. Skin defects in the form of scars after laser use are very rare.
- Radio wave therapy . The technique is considered the safest. When excising a wart using a radio wave, there is no contact with the skin. It is not always possible to completely remove the growth. The procedure leaves no traces of impact.
- Electrocoagulation . The procedure requires anesthesia. Using an electrode to which a high-frequency electric current is applied, the wart is burned out, followed by cutting off the growth with a special metal loop. Scarring may appear after removal.
- Cryodestruction . Liquid nitrogen is used and the wart is treated until it turns white. As a result of exposure to low temperatures, the growth tissues die. There is no need for anesthesia for the manipulation. The disadvantage of the technique is the lack of control over the depth of nitrogen exposure. For this reason, frequent relapses occur.
- Surgical. Removal is done using a scalpel. The disadvantage of the procedure is the formation of a scar, so this technique is used only for certain indications (in case of malignancy of the process and large size of the wart).