What is pipun in language
Depending on the cause and form, glossitis can be an independent disease, or a symptom of general disorders of the body. This means that the pathology develops against the background of infectious and non-infectious genesis as a result of the addition of bacteria and viruses of the oral cavity. It is also a manifestation of dysfunction of organs and systems.
When affected, the tongue changes color, shape, unpleasant sensations appear, including severe pain, burning and itching, as well as growth. Symptoms appear both from irritants and are independent in nature.
Attention! Pip begins to develop with inflammation of the papillae of the tongue. The initial forms are easily treatable with timely consultation with the dentist. Without therapy, the disease becomes chronic and cannot be cured in the future.
It is impossible to determine whether tongue tip is contagious without laboratory tests. The risk of infection exists only with a viral etiology of the disease.
Peck on your tongue - what does it mean, the meaning and origin of the phraseological unit
A growth on the tongue is considered a disease of birds. Birds have a tubercle on their beak that helps them consume food. It happens that inflammation of this formation occurs and characteristic symptoms appear.
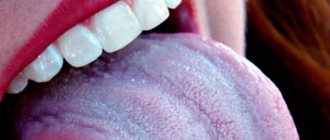
Pip in humans is a hard formation on the tongue due to damage or decreased immunity.
According to popular beliefs, tipun is found among people prone to foul language or deception. Therefore, the appearance of phraseological units is associated with people’s observations. If a person expresses himself poorly or is deceiving, they say: “Tip your tongue.” This means that the formation of a growth will prevent a person from conducting a conversation in this way.
Origin of phraseology
Linguists have several assumptions about where the word “tipun” came from in our language. In the etymological dictionary of M. Vasmer we find a hypothesis according to which “pip” comes from the German “pips” (“disease”).
F. Milosic suggests that the common Slavic designation for a bump, a bulge (“pip”, “pipot”) is taken as a basis. In V. Dahl’s dictionary the verb “tip” is recorded - that is, “peck”, “pinch”. It is derived from the name of the hard part of a bird's tongue, with the help of which chickens and the like grind up swallowed grains.
A pip is an overgrown seal that can be regarded as a disease of poultry.
From the second half of the 16th century, purulent ulcers on the tongue began to be called pipunami. The reason for their appearance was considered to be foul language and any other verbal intemperance or impurity.
If a person gossips, slander, slander, wishes harm to others, lies and distorts other people’s statements, he cannot avoid sores in the mouth. Our ancestors firmly believed in this.
The wish for a tap on the tongue is of an abusive nature and comes from a pagan ritual of scaring away evil spirits. However, the idea of the material embodiment of everything bad and retribution for it was also reflected in the folk-Orthodox picture of the world.
Causes and symptoms of glossitis
Etiological factors are varied and are important in the development of the clinical picture of the disease. In many cases, once the cause is eliminated, tongue tip goes away on its own or with the help of simple therapy. Common causes of glossitis are:
- Tongue injury. Damage occurs most often from fish bones, seed husks, candies or nuts. Injury from a toothpick or fork is possible. In addition, hot and spicy foods can also cause damage.
- Decreased immunological status. In the language, tipun is diagnosed after a severe course of acute respiratory infections or influenza. Against the background of other infections, glossitis can be a separate symptom.
- Getting infected. Pathogenic bacteria enter the oral cavity with dirty food and unwashed hands. Against the background of minor damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue, rapid infection occurs.
- Pregnancy. During this period, hormonal changes are observed in the female body. The appearance of pipun during pregnancy requires consultation with an endocrinologist.
- Lack of vitamins. Glossitis is caused by a lack of vitamin A, group B and C.
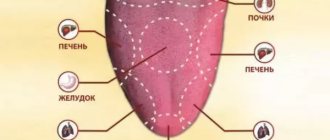
- General pathology of the body. Against the background of tuberculosis, diabetes, rheumatism, diphtheria and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, changes in the tongue are observed.
- Bad habits. Ethanol and tobacco combustion products cause severe irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Oral problems. If there are uneven edges of the filling, poorly installed orthopedic structures or a malocclusion, then such dental problems will lead to the formation of not only pipunitis, but also more severe diseases in the form of candidiasis or periodontal disease.
- Heredity. There is not only a disease of the tongue, but also developmental anomalies. Rhomboid glossitis is a form of pathology that is inherited and difficult to treat. This manifestation can be noticed on the tongue of a child at an early age.
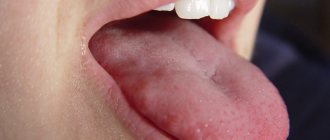
The clinical picture of glossitis is varied and the first thing that is noticed is burning and itching, as well as the presence of a foreign body in the oral cavity. Gradually, the pathology begins to give the following symptoms:
- hyperemia of the tongue mucosa;
- presence of swelling;
- white coating;
- pain at rest and from irritants;
- decreased sensitivity mainly at the tip of the tongue.
If the disease is not treated, it becomes chronic. Pip looks like a foreign body with such manifestations as:
- taste disturbance;
- hypersalivation;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- difficulty eating;
- a sharp change in the color of the tongue;
- taste disturbance;
- the appearance of a pronounced growth on the surface of the tongue;
- speech problems.
Attention! The further course of the disease leads to the spread of inflammation to the upper respiratory tract. Pathological foci can merge into a single formation and form a retropharyngeal abscess.
Types of glossitis
In order to get rid of pipun in a timely manner, the form of the disease should be determined. It is customary to distinguish 9 types of inflammation of the tongue:
- Candida. It occurs more often than other forms. It is formed against the background of a violation of the local immunity of the oral cavity due to infection with candida fungi.
- Diamond-shaped. A pathological focus resembling a tubercle, square or diamond is found in the middle of the tongue. Infection of the mucous membrane of the tongue occurs through microcracks. There are lumpy, smooth and papillomatous forms.
- Catarrhal. Characterized by swelling and hyperemia. Qatar takes over the entire tongue, causing an increase in its volume.
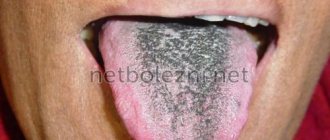
- Exfoliative. It is distinguished by structural and color changes in the area of the tip of the tongue and the back. The defeat resembles a geographical map. Glossitis develops against the background of blood disease and endocrine pathologies.
- Ulcerative. Develops due to dental problems. Small ulcers may appear on the mucous membrane, which quickly disappear after the cause is eliminated.
- Villous. This type of tip resembles hair on the tongue. These are overgrown filiform papillae of a dark brown color. It occurs mainly in men due to bad habits.
- Folded. Refers to an anomaly of language development. But with this form, the soft organ is susceptible to infection due to food debris and plaque in the folds.
- Phlegmonous. Distributed in the deep tissues of the tongue. It requires constant attention from a doctor, since over a long period of time the pipun can become malignant.
- Atrophic. The surface of the tongue becomes smooth and unnaturally red. Characterized by bad breath and grouped painful ulcers. The origin of glossitis is not completely known. A multifactorial ethological theory is proposed.
Candidal glossitis
Synonyms
When we want to ask someone not to predict failure in advance, we can use one of the following expressions:
- don't croak;
- so that your tongue dries up (dries to the roof of your mouth);
- don’t worry, Emelya;
- shut up the fountain;
- stop talking nonsense.
Foreigners stop people who speak intemperately like this:
- bite your tongue (English) - bite your tongue;
- Halt Maul (German) – stop your face.
Rough, but very intelligible. Nobody wants to hear bad things addressed to them. Well, this just means that people have not stopped believing in the power of words.
Sometimes it’s better to keep your mouth shut than to feel the pain in your mouth of a pip that someone sent onto our tongue in indignation.
How to cure a pip on the tongue
The therapeutic course is determined by a dentist, therapist, and sometimes an endocrinologist, as with a gastroenterologist. Initially, the cause of the pip is identified and eliminated.
How to remove a pip on the tongue quickly and without consequences? If glossitis has formed due to dental problems, then the oral cavity is sanitized. In the presence of concomitant diseases, a general therapeutic course of treatment using antibacterial and antiviral drugs is required. Symptomatic effects are indicated in the oral cavity.
General principles of therapy
In medical practice, it is customary to treat pipun with the following methods:
- conservative;
- surgical;
- folk.
Conservative treatment of pipuna involves the use of certified medications both locally and in the form of tablets for oral or intramuscular injection.
Radical surgical treatment is rarely used. This treatment is indicated when the tongue hurts for a long time, and the growth has a pronounced outline. Basically, removal of overgrown papillae or neoplasms occurs by cryodestruction or diathermocoagulation.
Drug treatment depending on the form of glossitis
With timely treatment, the pip is quickly cured and does not occur again. The following drugs are used for therapy:
- Antiseptics. Chlorhexidine, Iodinol, Furacilin and potassium permanganate are mainly used. Suitable as a rinse for all forms of pipun.
- Ointments and gels. Cholisal, Levomikol and Kamistad are prescribed for severe forms of inflammation and to reduce the pain reaction of the tongue. If after examination a viral etiology of the disease is revealed, treatment with oxolinic ointment is recommended.
- Antibiotics. Required in the presence of bacterial flora of inflammation.
- Antifungal drugs. Prescribed in case of pip appears against the background of a fungal infection.
- Retinol acetate. Provides wound healing for folded, catarrhal and atrophic glossitis.
- Sprays. Lugol, Tantum Verde, Hexasprey are prescribed for local treatment of the tongue in the presence of a bacterial infection.
- Immunoglobulin and Viferon. It is an immunomodulator that is necessary for all forms of glossitis in case of severe chronic course. In addition, if pip has formed, it is necessary to take vitamin-mineral complexes, change the diet in favor of gentle food and at least temporarily give up bad habits.
How to treat pip at home
Folk remedies are always used to treat dental diseases. Today, official medicine uses natural ingredients as additional substances to eliminate oral pathology. Tipun on the tongue at home is affected by such means as:
- oil solutions of rose hips, peach and sea buckthorn as compresses;
- decoctions of chamomile, St. John's wort, calendula or nettle for rinsing the mouth for non-healing wounds;
- oak bark as an antiseptic and hemostatic agent;
- propolis as an application to the tip area;
- eucalyptus juice, which can be used to anoint wounds to heal and relieve pain;
- a decoction of horseradish leaves for the regeneration of ulcers;
- compress of raw potatoes and sunflower oil;
- rinsing with a baking soda solution to eliminate candidal glossitis;
- a decoction of coltsfoot and raspberry leaves as mouth baths for inflammation and open wounds.
Attention! It is strictly forbidden to cauterize the tipun with chemicals or using high temperature. Such exposure will cause extensive damage to the mucous membrane of the tongue and aggravate the presence of the underlying disease.