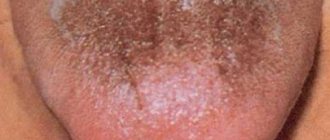
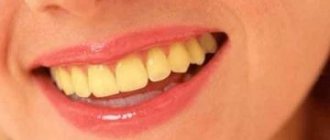
The tongue is an indicator of the health of the whole organism. In an adult healthy person, the tongue is pale pink with well-defined papillae. A small amount of whitish coating on the tongue is normal and not a cause for concern.
The coating on the tongue may vary depending on the time of year. In summer, in hot weather, with a lack of fluid and dry mouth, the plaque becomes denser, acquiring a yellowish tint. Soft temporary deposits on the tongue are not a symptom of the disease, do not cause discomfort to the patient, clean well and disappear quickly.
But if the plaque persists, is poorly separated from the mucous membrane of the tongue, and bad breath appears - all these are signs of the development of pathological processes that require consultation with a doctor.
Norm and pathology
Language is a kind of mirror of the functioning of the body. When it is clean, pink, with visible taste buds, the person is healthy and most likely does not suffer from bad habits. But even a loose white coating, through which the surface of the tongue is visible, is considered as a variant of the norm. It can change shade depending on the time of year: in summer it can be more intense due to hot weather, in winter it becomes white-yellow, in autumn it becomes almost transparent. In addition, a yellow coating on the tongue in the morning appears in heavy smokers and those who drink too much coffee.
However, a change in the color of the tongue may be a consequence of malfunctions in the internal organs, mainly the liver, kidneys, stomach, pancreas and gall bladder. If the plaque has become dense, thick, bright yellow or brownish-yellow, and there is also bad breath, you should consult a doctor and identify the cause of the problem.
Attention!
Typically, “safe” soft deposits come off easily and, if brushed well, will not reappear. But if the plaque returns, we are dealing with pathology.
Diagnostics
To establish a complete picture of the state of the body, the doctor determines the color of the tongue, its structure, position, motor functions, and possible other pathologies in the oral cavity. Among the laboratory and instrumental research methods aimed at clarifying the characteristics of plaque and the reasons for its appearance, the following may be prescribed:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- sowing on flora from the surface of the tongue;
- determination of antibodies to the bacterium Helicobacter pylori;
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- scatological research.
If you are concerned about the condition of your tongue, plaque on it, pain, unpleasant odor, contact the ENT doctors of our clinic. High-precision equipment and the experience of our specialists allow us to quickly make correct diagnoses and prescribe treatment.
Secondary symptoms
- layer thickness. If the natural color of the tongue is not visible through the plaque, we are dealing with severe processes or chronic diseases. A thin layer, on the contrary, indicates an initial stage or a slight deviation from the norm;
- coverage area (fully or partially);
- consistency. It can be thick, soft, dry or flaky;
- ease of removal. Dense thick plaque is usually difficult to remove. A softer, thinner layer is easier to clean, but can quickly reappear.
When is yellow tongue normal?
The appearance of a light yellowish coating in the mornings in summer is normal. This usually indicates a feeling of thirst that the body experiences. This plaque disappears after drinking a glass of water. Plaque formed after eating foods containing dyes: yellow lemonade or ice cream, carrots, sweets, citrus fruits is also considered normal.
The tongue may turn bright yellow from taking certain medications, for example, Furazolidone or Nitroxoline. In pregnant women, yellow plaque may appear in the later stages due to the development of duodenogastric reflux caused by fetal pressure. In all other cases, the appearance of yellowness in the mouth should give cause for concern.
Treatment
To get rid of unsightly deposits, unpleasant odors and other symptoms, you need to determine their cause. To do this, you need to contact a therapist who will conduct an examination and prescribe additional tests and examinations (general analysis and blood biochemistry, throat culture, gastroscopy, ultrasound, coprogram, etc.). Based on the results, he will recommend therapy, diet and, if necessary, give a referral to a gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, dentist or other specialist.
After treating the root cause of plaque, its intensity should decrease. But to speed up the process, doctors recommend paying more attention to oral hygiene, brushing the surface of the tongue twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush (but not a scraper, so as not to cause injury), drinking more water and rinsing your mouth with herbal decoctions.
Prevention
It is not always possible to prevent the formation of plaque on the tongue, especially if it is a symptom of an infectious, viral or fungal infection. But you can reduce the likelihood. The recommendations will not be new: you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, do not smoke, do not abuse alcohol, drink coffee and tea in moderation, exclude too fatty, spicy and fried foods, include more vegetables, fruits, whole grains in your diet, give preference to lean varieties of meat and fish and do not take medications (especially antibiotics) without a doctor's prescription.
When yellow plaque is a symptom
The appearance of a yellow coating should alert you if it has a rich color and the papillae on the tongue are not visible through it. The following signs indicate a developing pathology:
- the plaque does not disappear on its own;
- cannot be cleaned with a brush;
- thickens;
- accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
The tongue is an organ of the digestive system, so if yellowness appears on it, first of all the cause should be looked for there. The sooner you pay attention to the problem, the more quickly you can identify the pathology and cure the disease.
Blue coating on the tongue
A blue tongue is a sign of blood stagnation.
Very often, various diseases of the cardiovascular (congenital heart defects, arrhythmias, heart failure) and nervous system (hemorrhages, cysts, epilepsy) lead to the fact that blood flows through the tissues more slowly than it should - cyanosis or cyanosis appears on the limbs, lips and language. Therefore, if you notice such a symptom in your child, you should urgently contact your doctor for advice.
Read also: Now the beauty and health of your child is completely in your hands
Brown coating on the tongue
A brown tongue in a child is not such a rare occurrence. There can be many reasons for this:
- Severe diseases of the digestive system , accompanied by inflammatory changes, stagnation of bile in the bile ducts, and disruption of the digestive processes.
- Constant dehydration of the child's body due to high ambient temperatures or insufficient fluid intake.
- Insufficient intake of B
- Taking certain medications : antibiotics, antiseptic solutions, concentrated herbal decoctions.
It is very difficult to establish the exact root cause of the appearance of such a dark plaque. This can only be done by an experienced doctor, who, after additional examinations, will be able to prescribe the optimal treatment.
Diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract by language
The tongue will tell you about gastrointestinal diseases.
Modern gastroenterology does not specialize in diagnosis based on the appearance of the tongue. However, an attentive person suffering from such pathologies can distinguish the symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases:
- Acute gastritis - a viscous, dense coating of white-gray color is visible on the entire surface of the tongue, with the exception of the tip and side parts. The mouth feels dry and has an unpleasant acidic taste. Perhaps, instead of dryness, increased salivation will appear. In acute gastritis, similar symptoms include heartburn and sour belching, cutting pain in the epigastric region 1-2 hours after eating, weakness, headaches, diarrhea, heaviness in the stomach. With inadequate treatment, acute gastritis becomes chronic.
- Chronic gastritis - light deposits on the tongue are replaced by occasional dark gray deposits. To the previous symptoms are added such characteristic signs of chronic gastritis as astheno-neurotic syndrome, constant irritation, aching pain that intensifies some time after eating. About 40% of all cases of acute gastritis become chronic. This condition is fraught with the spread of the process to the duodenum and the development of gastroduodenitis.
- A stomach ulcer in combination with gastritis affects the condition and appearance of the tongue - its surface becomes bright red, with gray spots of dense plaque that are difficult to clean. This picture is complemented by signs of stomatitis and cyanosis. The patient feels a burning sensation and the production of saliva increases.
- Oncological damage to the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the presence of internal circulation, is reflected in the condition of the tongue by the appearance of evenly spaced white plaque of increased viscosity, excessive saliva production, and a burning sensation in the oral cavity.
What diseases does yellow plaque indicate?
Pathological yellow plaque can vary in saturation, shade, consistency, and location. Tongue color and pathology:
| Illustration | Description |
| Yellow-green - problems with the outflow of bile. | |
| Yellow-brown is a sign of sore throat. | |
| Yellow-white indicates mainly intestinal infections, poisoning and may be a sign of the presence of parasites. | |
| Pale yellowish and orange - gastritis. | |
| Black and yellow - Crohn's disease or gallbladder pathology. |
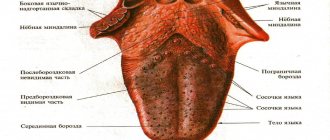
Anatomical structure of the tongue
The structure of human language corresponds to its multifunctionality, which lies in the fact that it participates in the processes:
- chewing;
- salivation;
- taste perception;
- speech.
The body of the tongue consists of striated muscle tissue, which is covered by a membrane of mucous tissue. Its surface, called the back, is conventionally divided into three parts:
- the last third, located near the pharynx, is called the root;
- the first two thirds are the body of the tongue.
A longitudinal groove runs in the middle, which is an external manifestation of the internal septum; it is, in fact, a reduced thyroglossal duct.
The mucous membrane, tightly adjacent to the muscle tissue, is covered on the outside with stratified squamous epithelium. It contains:
- salivary glands;
- taste buds;
- lymphatic ducts.
The mucous membrane of the posterior part forms three supraglottic folds, with the help of which the tongue is attached to the larynx:
- median;
- two lateral.
The tongue is abundantly covered with papillae, including:
- filamentous - act as organs of touch and, thanks to the rough surface, hold food on the tongue;
- cone-shaped – responsible for sensitivity to temperature and pain;
- mushroom-shaped - equipped with taste buds, thanks to them we distinguish many taste sensations;
- groove-shaped - located near the root, have serous glands and are also responsible for the sense of taste;
- leaf-shaped - equipped with lingual glands that secrete a mucous secretion.
The tongue is attached to the oral cavity by a fold of mucous membrane called the frenulum.
Cleaning your tongue with a home irrigator
As an alternative to going to the dentist for professional oral cleaning, you can consider a home irrigator. This is a special device equipped with replaceable nozzles and a reservoir that supplies liquid under pressure to clean the space between the teeth. When choosing an irrigator, you must be guided by the following requirements:
- the number of attachments should be a multiple of the number of family members who will use it, because this is a means of individual use;
- It is highly desirable that the kit include devices for cleaning the tongue and dentures of any configuration;
- it is necessary that the device be equipped with a pressure regulator when supplying liquid, because everyone has an individual level of tooth sensitivity;
- It is better to choose a larger tank volume, this will allow cleaning more efficiently;
- It would be great if it was also equipped with a water supply regulator, that is, it could be a stream of water or a spray.
This device will save you the time and money needed to visit the dentist's office.
Products for daily tongue hygiene
You need to brush your tongue at least 2 times a day. It is not advisable to use a regular toothbrush, since high and medium hard bristles can injure the soft surface and cause a gag reflex. At home, it is safer and more convenient to use special devices. They do not have a significant functional difference, so when choosing, you can only be guided by personal preferences.
Today, you can easily purchase products from well-known brands Curaprox, Dentaid, Jetpik, One Drop Only, Miradent, Pierrot, etc. The range of products from different manufacturers includes everything you need for complete, high-quality oral care.
Scrapers
resemble a spatula. A simple design can be made of silicone or plastic, less often of metal and wood. This easy-to-use device gently cleanses the surface of the tongue without causing a gag reflex. The scraper blades conform to the shape of the tongue and are easily washed with water.
Black coating on the tongue
The presence of a black coating on a child’s tongue looks quite scary, and there may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
Bacterial sore throat is often accompanied by the appearance of dark plaques on the mucous membranes, even black. In this case, the child will have signs of inflammation in the tonsils: red throat, high fever, pain when swallowing, weakness.
Hidden forms of diabetes mellitus, which lead to persistent disruption of the acid-base balance in the body. Excess acid or acidosis will cause darkening of the tongue.
Taking some antibiotics causes the growth of pathogenic microflora in the mouth, which causes the mucous membranes to become permanently stained black.
Treatment of such plaque will consist of eliminating the causes that caused its appearance. After a sore throat is treated, medications are stopped, or diabetes is identified and compensated for, this symptom will most likely go away on its own.
Green coating on the tongue
The appearance of a green coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue often frightens parents, especially if it is found in a newborn or infant.
The most common cause of this phenomenon is candidiasis - a fungal infection of the oral cavity that occurs due to imperfect immune defense in the body of a 1-year-old baby or while taking strong antibacterial drugs.
This plaque has varying color intensities and can spread to other parts of the oral cavity, found on the cheeks, palate and lips. After removing it, you can see the red surface of the tongue with small blisters or ulcers, which cause discomfort to the child.
You should start treating green plaque only after consulting a doctor. Therapeutic measures will consist of taking special drugs with antifungal action and local antiseptics to treat thrush and prevent bacterial complications.
Read also: How bite affects posture and spinal health
How to clean correctly
After the usual hygiene procedure with teeth and rinsing the mouth, they begin to remove plaque. Using smooth but intense movements from root to tip, remove plaque first from one half and then from the other half. The next stage is movements across the tongue. At the end of the procedure, you must rinse your mouth thoroughly.
Persons with digestive diseases and smokers require additional use of paste when removing plaque.
Solving the problem of a coated tongue helps prevent the risk of caries, gingivitis, stomatitis, provide fresh breath and improve the perception of taste.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!