06.08.2021
If we talk about the most common reasons for visiting an otolaryngologist, diseases of the throat and larynx are, perhaps, only superior to a runny nose. In most cases, patients struggle with unpleasant symptoms on their own, which often leads to complications and chronic forms of pathologies.
There are many causes of throat and larynx diseases. The lion's share of them are the consequences of the activity of bacteria and viruses, which have similar symptoms to fungal and tumor diseases. There are throat diseases without elevated body temperature; their appearance is provoked by allergens, dry air and substances that irritate the mucous membrane.
Signs and causes
Most diseases of the throat and larynx are infectious in nature. The causative agents are bacteria, viruses and fungi.
The most common bacterial
throat disease - sore throat. Its appearance is caused by streptococci, chlamydia, mycoplasmas, gonococci and tubercle bacilli. Scarlet fever, diphtheria and epiglottitis are also caused by bacteria. All three diseases are manifested by a sore throat, and epiglottitis is generally life-threatening as it can lead to airway obstruction.
Symptoms of bacterial diseases:
- general weakness;
- swelling of the larynx, tonsils;
- high body temperature;
- pain and discomfort in the throat.
For viral
diseases, a sore throat can be one of the symptoms of an illness, for example, ARVI, influenza or measles. Infectious mononucleosis caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (herpes type IV) stands apart. Its development is dangerous due to the rapid spread of inflammation to the spleen and liver, which in turn leads to enlargement of the lymph nodes.
Viral diseases are similar in symptoms:
- heat;
- prostration;
- headache;
- general weakness;
- runny nose;
- cough;
- rash;
- pain and sore throat.
Fungal diseases
genesis - a consequence of the active activity of yeast-like fungi, which looks like a cheesy mass on the mucous membrane during tonsillitis or pharyngitis. Symptoms of a fungal infection of the throat:
- severe sore throat;
- the temperature remains normal.
Fungi quickly multiply in the body during disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, against the background of vitamin deficiency, abuse of antibiotics and hormonal drugs.
A special place as a cause of pain in the throat and larynx is occupied by tumors. It can be primary, that is, formed for the first time, or it can be secondary, the result of metastasis of oncological processes in other parts and organs of the body. The larger the tumor, the more discomfort it brings: the voice changes, becoming hoarse, a feeling of a lump appears in the throat, and it becomes difficult to swallow.
What is more effective: sprays, tablets or lozenges?
The choice of dosage form directly depends on the cause of the disease and the nature of the pain. In particular, if the sore throat is caused by bacteria, then the best choice is a spray with a pronounced antiseptic effect. It is important to consider that with prolonged use, infectious agents develop resistance to the drug, so if after 2-3 days you do not feel relief, the medicine needs to be changed. So, how to treat a throat?
For a disease of viral origin, it is best to choose a throat spray that relieves pain and fights inflammation. In the case of chronic pain, it is necessary to regularly irrigate the throat with a spray with a moisturizing effect that does not contain aggressive substances and carefully relieves unpleasant symptoms.
Many drugs reduce symptoms due to the local anesthetics they contain - phenol, benzocaine or dyclonine. Under their influence, the mucous membrane becomes numb, and the pain noticeably weakens.
Throat tablets can be divided into several groups. For example,
- with enzymes that eliminate viruses and bacteria;
- NSAIDs that relieve inflammation;
- with fragments of bacteria and viruses that enhance local immunity;
- with extracts of medicinal plants that reduce pain.
Throat lozenges are effective only in the initial stages of the disease. They usually contain menthol, which has a distracting effect rather than a therapeutic one. Therefore, you should not get carried away with candies.
TOP 5 sprays against sore throat
- Miramistin is a broad-spectrum antiseptic spray to combat bacterial and fungal infections. Quickly reduces pain. It is odorless and tasteless. Suitable for adults and children from three years of age, as well as for pregnant women. Disadvantage: relatively high price, analgesic effect lasts several hours.
- Hexoral destroys infections of bacterial and fungal origin. It has an analgesic, disinfecting, deodorizing and enveloping effect. The therapeutic effect occurs within 1-2 minutes after treatment and lasts 10-12 hours. Application: twice a day after meals. Cons: components of the drug can cause allergies, read the instructions carefully.
- Yox can be called an analogue of the legendary Lugol's drug. It has a powerful antiseptic, antiviral, antifungal effect. Reduces pain well. Processing Disadvantages: cannot be used for a long time, contraindicated for people with iodine intolerance.
- Proposol contains propolis extract and a large amount of vitamins. Complete disappearance of pain occurs within 5-7 days. It works well as part of a complex treatment of inflammation. Cons: not suitable for people allergic to bee products.
TOP 5 tablets for sore throat
- Faringosept copes well with pain and fights inflammation in the oral cavity. Has a pleasant sweet taste. Recommended course is 3-4 days. Quickly relieves pain and restores voice. The packaging is enough for a full course. There are few contraindications. Disadvantage: effective at the initial signs of the disease.
- Hexoraltabs contain a local anesthetic, peppermint oil and menthol. They have an antiseptic effect. A decrease in pain is observed during the first minute of resorption. Available in different flavors. Cons: the drug only helps with the initial signs of the disease.
- Neo-Angin has a pronounced disinfectant and anti-inflammatory effect, relieves pain well, quickly restores the voice, and relieves coughing attacks. Large packaging. Dosage: one tablet every 2-3 hours. The permissible number of tablets per day is six. Cons: irritates the gastric mucosa.
- Grammidin contains the antibiotic gramicidin C; tablets with lidocaine are also available, which not only destroy pathogens and cleanse the mucous membrane, but also immediately relieve pain. The anesthetic effect lasts about 40 minutes. Enhance the effectiveness of medicinal rinses. Disadvantage: cannot be taken during pregnancy and lactation.
- Lizobakt has a powerful antiseptic effect. The drug contains vitamin B6, which increases local immunity, and the protein enzyme lysozyme, which breaks down bacteria, fungi and viruses. Suitable for pregnant and lactating women. It is used for all infectious lesions of the oral cavity.
TOP 5 lozenges for sore throat
- Strepsils plus. The active ingredients fight bacteria, lidocaine reduces pain, anise and peppermint oils have a distracting and enveloping effect. Dosage: no more than 1 lozenge within 2 hours. Disadvantage: short period of action, effective at the initial signs of the disease.
- Halls. Due to eucalyptus oil and menthol, it temporarily relieves pain, cools a sore throat, and relieves hoarseness. Minus: it is not a medicine.
- Carmolis contains extracts of medicinal herbs, honey, and vitamin C. The drug quickly reduces pain, refreshes the oral cavity, has a pleasant taste, but does not last long.
- Gorpils quickly relieves pain and has a pronounced antiseptic effect. Helps with initial and acute forms of the disease. Available in different flavors. Disadvantage: short period of action.
- Agisept relieves pain, has a pronounced antimicrobial effect, and significantly reduces unpleasant symptoms at the onset of the disease. Disadvantage: not suitable for people with allergies to medicinal herbs.
These recommendations do not replace visiting a doctor. There are contraindications. Before purchasing the drug, be sure to consult with your physician.
Back to articles
Treatment of diseases of the throat and larynx
For any form of the disease, frequent and abundant drinking and rinsing is recommended; this allows you to “wash away” the waste products of viruses and bacteria, relieve inflammation and maintain the mucous membrane in the desired shape (it tends to dry out due to high body temperature during illness).
Most cases respond well to drug treatment if it is started on time. Surgical intervention is sought when purulent or tumor processes begin, that is, the disease takes on a severe form, threatening the patient’s life with suffocation.
What and how to treat:
- ARVI is the most common throat disease. It is characterized by dry throat, sore throat, runny nose, sneezing and coughing. The temperature usually stays between 37–38 degrees. Treated with antiviral drugs based on existing symptoms. Gargling with infusions of chamomile, sage and herbal lozenges helps with sore throat; they relieve irritation and make the treatment pleasantly tasty. Along with this, it is recommended to take vitamin C to support and strengthen the immune system, as well as plenty of warm drinks (herbal teas with honey are welcome);
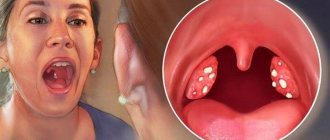
- tonsillitis is an infectious-allergic disease that mainly affects the tonsils. It is characterized by high body temperature, up to 40 degrees, and unbearable pain in the throat. The larynx and tonsils are red - a sure sign of an inflammatory process - and have a white coating. High fever is accompanied by aching joints and headache. Treatment is prescribed by a doctor, since it is important to prevent complications. Drinking plenty of fluids, gargling with antiseptic herbs, and herbal lozenges help with a sore throat. Food should be taken pureed and liquid, not hot, so as not to injure damaged areas of the mucous membrane;
- pharyngitis is an acute inflammatory process in the pharynx, with a characteristic dry cough, soreness, stabbing pain, a feeling of a lump and inflammation in the mucous membrane, developing into purulent processes. During illness, all solid, spicy, sour and hot foods are excluded from the patient’s diet. Treatment is medicinal, the doctor prescribes antiseptics, since the disease is inflammatory in nature. Self-medication in this case is strictly prohibited: the disease develops quickly and becomes chronic;
- laryngitis - inflammation of the vocal cords and larynx is characterized by a barking cough with sputum, a hoarse voice until its complete disappearance, and a scratching pain in the throat. Children often suffer from laryngitis. Laryngitis causes swelling of the throat when lying down, which can lead to suffocation. Therefore, if you find that your child begins to choke while lying in bed, call an ambulance, lift the child to an upright position and take him to the bathroom, under a warm shower, to relieve the spasm. Laryngitis is treated with inhalations, warm compresses, warm drinks and silence. To alleviate the patient's condition, high humidity is needed in the room: a container of water, a diffuser or a wet towel on a radiator;
- Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, which is characterized by high body temperature, acute sore throat, and bad breath due to purulent plaque on the tonsils. The main causes of tonsillitis are viruses and bacteria. The course of treatment includes gargling with a solution of soda and salt - it acts as an antiseptic and “washes away” the pus.
Bacterial throat diseases develop very quickly, within a few hours. Viral ones - a little slower. But only a doctor can determine the real etiology of the disease, and then only based on test results.
Sinusitis.
Symptoms How to distinguish it from a simple runny nose? Why is it dangerous? What will happen if left untreated? How to treat? Prevention. Causes of occurrence.
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus, which communicates with the nasal cavity. Sinusitis can be acute or chronic.
Acute sinusitis most often develops as a complication of acute rhinitis (runny nose), after infectious diseases, and also as a result of inflammatory diseases of the teeth (odontogenic sinusitis). Hypothermia may be a provoking factor due to a decrease in the body's defenses. Sinusitis differs from rhinitis (runny nose): the duration of the disease - a runny nose lasts 6-8 days, and sinusitis - up to 1 month, the presence of purulent discharge, pain in the area of the affected sinus.
Chronic sinusitis is usually a consequence of the transition of acute inflammation to a chronic form. This can be facilitated by thickening of the nasal mucosa, thickening of the nasal turbinates, curvature of the nasal septum, closing or narrowing of the outlet of the maxillary sinuses, and insufficient treatment of acute sinusitis.
Acute sinusitis is characterized by symptoms of general intoxication: chills, increased body temperature, poor general health, headache of varying intensity. In addition to general symptoms, local symptoms are observed: pain in the cheek area. The nature of the pain is intense and constant, accompanied by a feeling of fullness, intensified by tilting the head, coughing and sneezing. Photophobia and lacrimation are sometimes observed. The nose is stuffy, there is copious mucous discharge (catarrhal sinusitis), mucopurulent, purulent discharge (purulent sinusitis). On the side of the affected sinus, the sense of smell may be reduced. When the periosteum is involved in the process, swelling of the cheek and swelling of the lower eyelid are noted.
Chronic sinusitis is characterized by general weakness, malaise, fatigue, headache (usually in the evening), nasal congestion, and discharge. The sense of smell may be reduced. Vasomotor and allergic sinusitis is characterized by an undulating course with periodic remissions. The clinical picture of exacerbation is characterized by the same symptoms as in acute sinusitis.
Treatment is prescribed by an otolaryngologist. As a rule, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis and consists of a course of pharmacotherapy: antibiotics, vasoconstrictor drugs, and decongestants are prescribed. At the final stage, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures.
In case of odontogenic sinusitis, treatment by a dentist is also required.
In severe cases and the presence of complications, hospitalization is indicated.
Treatment of sinusitis is mandatory, because this disease can cause serious intracranial, intraorbital and bronchopulmonary complications: swelling of the meninges, meningitis, swelling of the tissue of the orbits and eyelids, bronchitis, pneumonia and other complications.
Prevention
It is impossible to ensure that your throat never hurts, especially in the autumn-winter period. But prevention can be carried out regularly to reduce the risk of illness and strengthen the immune system. For this:
- stop smoking if you smoke - nicotine irritates and dries out the mucous membrane of the nose and throat, making them vulnerable to pathogens;
- eat a varied and nutritious diet so that the body receives vitamins and minerals in full;
- humidify the indoor air - artificial indoor fountains, aquariums, diffusers, and water containers are suitable for this. Too dry air is a strong irritant to the throat and contributes to the appearance of microtraumas on the mucous membrane;
- wash your hands more often - pathogenic bacteria, as a rule, enter our body from dirty hands;
- take vitamins - they support the immune system;
- dress according to the weather - during hypothermia, blood vessels narrow, which destroys the protective mechanism of the mucous membrane and the person catches a cold. The cold itself does not contribute to this;
- do not self-medicate - there is a high risk of complications, for example, in the form of hearing loss or disease of the ears, lungs, eyes or brain.
If you feel unwell, consult a doctor. You can make an appointment with a multidisciplinary medical otolaryngologist using the feedback form or by calling.
The main causes of inflammation of the throat mucosa
Before treating a sore throat, an otolaryngologist determines the nature of the inflammatory process.
All causes of sore throat can be divided into two groups: infectious causes and non-infectious ones.
In medical practice, we often have to deal with infectious diseases. In this case, the inflammatory process is associated with the activation of pathogenic microorganisms that settle on the mucous membrane of the larynx. Such pathogenic pathogens include staphylococci, streptococci, fungi, herpes viruses, adenoviruses, etc.
The main methods of penetration of pathogenic microflora into the larynx are airborne droplets and household contact. In the first method, infection occurs when communicating with a sick person (during a conversation, sneezing, etc.). In the second method, infection occurs when a sick person shares the same household items (for example, the same dishes or towel).
It is also impossible not to take into account the protective properties of the body. Bacteria and fungi are present on the mucous membranes of every person, but symptoms of the disease are more likely to appear in a person with reduced immunity.
Preventive measures
The best way to combat inflammation of the throat and larynx is to prevent the development of the disease. It's impossible to protect yourself from everything, but your risk of infection will be greatly reduced if you follow these tips.
- Quitting smoking:
smokers are more susceptible to colds, since cigarette smoke reduces local immunity and is an additional irritant, and nicotine constricts blood vessels, interfering with blood supply to the lesions. - Healthy diet:
spicy, fried and highly salted foods irritate the mucous membranes and increase swelling, and also create additional stress on the gastrointestinal tract. You should balance your diet by adding more foods high in vitamins. - Air humidification:
relative air humidity should be 50–70%. Dry air significantly increases the risk of complications and prevents the body from fighting infections. This is especially important for children who are at risk of developing false croup. - Ventilation
will reduce the concentration of microbes in the air and normalize the microclimate. But you shouldn’t keep the windows ajar all the time, creating drafts and the risk of unnoticed hypothermia. In cold weather, you need to ventilate by opening the windows wide several times a day, but only for three minutes, so that most of the air volume is renewed. - Maintaining hygiene
means thoroughly washing your hands, using disinfectants, frequently changing bed linen, avoiding contact with coughing and sneezing people, etc.
Literature
- Delyagin V. M. Fever (new touches on an ancient picture) // Pediatrics. Consilium Medicum. — 2021. — No. 2. — pp. 89-93
- Belan Yu. B., Starikovich M. V. Fever in pediatric practice // Attending physician. - 2021. - No. 1. — P. 40-43.
- Krasnova E.I., Khokhlova N.I., Provorova V.P., Evstropov A.N. Differential diagnosis and therapeutic tactics for acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) at the present stage // Attending physician. - 2021. - No. 11. - P. 58-63.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® solution.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL® aerosol.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL®TABS.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL®CLASSIC.
- Instructions for use of the drug HEXORAL®TABS EXTRA.
Up to contents
come back
When your throat hurts...
And this is how infectious and non-infectious causes of pain in the throat are distinguished:
- Infectious causes:
— Viral 70% (rhinoviruses, coronoviruses, adenovirus, influenza and parainfluenza viruses…) — Bacterial 15%. The most common cause is Group A B-hemolytic streptococcus (GABHS) - Fungal. The main causative agent is representatives of the genus Candida. The most pathogenic Candida albicans is 50% of all cases!
- Non-infectious causes:
— Allergic — Traumatic: cold drinks, ice cream, hot food, tobacco smoke from active and passive smoking, excessive consumption of spices, mustard, horseradish — Burns and injuries of the larynx
— Neuralgic conditions
— Benign and malignant neoplasms;
— Diseases of other human organs and systems
— Exposure to an irritating factor: gastroesophageal reflux, postnasal drip
Infectious causes of pain
Viral causes include primarily acute respiratory diseases, infectious mononucleosis, influenza, measles, and rubella. In addition to pain in the throat, the patient complains of the following symptoms: headaches, runny nose, nasal congestion, cough, fever, weakness, loss of appetite. Etiological diagnosis is difficult, especially in routine practice. In this situation, doctors are forced to rely on literature data. In most cases (20-30%), it is not possible to accurately identify the virus that caused the disease in a given person. Data from successful verification of the diagnosis place rhinoviruses in 1st place in the etiology of ARVI of the upper respiratory tract (30-50%). It should be noted that the influenza virus causes only 5 to 15% of cases of all acute respiratory viral infections.
Lesions of bacterial etiology are the cause of a sore throat in 50% of cases. Bacterial infections are most often localized in the tonsil area (acute tonsillitis). Their characteristic symptoms are: severe pain in the throat; weakness and decreased performance; increased body temperature; redness of the palate, white plaque on the tonsils; enlarged lymph nodes.
Pharyngomycosis in the vast majority of cases is caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (oral thrush). Sometimes the causative agents are mold fungi (aspergillus, penicillin, geotrichum). To trigger the pathological growth of fungi, which leads to an inflammatory process, it is necessary to reduce the body's defenses. Therefore, pharyngomycosis accompanies the following diseases and conditions:
- long-term antibiotic therapy;
- diabetes;
- tuberculosis;
- metabolic diseases (obesity, thyroid pathology);
- oncological diseases (during chemotherapy);
- HIV.
The disease begins in the same way as all pharyngitis - with discomfort in the throat. The fungal nature of the process can be suspected based on the characteristic itching and burning. Patients complain of constant soreness and dry mouth. Pain for pharyngomycosis is very characteristic; it intensifies with swallowing and is more intense than with a bacterial infection.
Non-infectious causes of sore throat
Pain in the throat can be a result of exposure to various allergens: food, pollen, house dust, fur and secretions of pets, etc. In addition to discomfort and pain in the throat, patients are concerned about congestion and clear discharge from the nose, sneezing, itchy eyes .
Various external factors can cause pain: mechanical injuries to the larynx, chemical or thermal burns. Hard pieces of food and bones can injure the larynx. Chemical burns can be caused by inhaling vapors of harmful substances at work or by ingesting harmful substances while eating. Thermal burns most often occur when eating hot foods or drinks.
Pain in the throat may be a manifestation of neurological disorders. Usually this condition is accompanied by a feeling of a lump in the throat, difficulty swallowing, and headaches. This feeling can manifest itself constantly, or maybe with a certain frequency.
Other causes of sore throat accompanied by sore throat and cough: drainage of discharge from the nasopharynx due to adenoiditis or sinusitis, space-occupying formations of the nasopharynx (cyst/bursa of Thornwald); irritation of the respiratory tract by dry air, smoke, including active and passive smoking. In adults, a common cause of such complaints, often with a feeling of a lump in the throat, a “foreign body,” is an exacerbation of chronic pharyngitis associated with pathology of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, esophagitis, gastroesophageal reflux, cholecystitis, gastric ulcer. Severe dysphagia, regurgitation and pain when swallowing can be caused by varicose veins of the esophagus. Chronic pathology of the kidneys, endocrine system, blood, previous radiation and chemotherapy can lead to the formation of a chronic inflammatory and atrophic process in the pharynx. The first manifestation of hyperglycemia (increased blood sugar) may be thirst and dry mouth, accompanied by catarrhal changes in the pharynx. Similar complaints occur with Itsenko-Cushing syndrome. In patients with hypothyroidism, swallowing is often impaired, speech becomes slurred due to swelling and dryness of the tongue and lips, and it is difficult to perform pharyngoscopy.
Hypovitaminosis can also cause discomfort and pain in the throat. Vitamin A deficiency causes dryness and erosion of the mucous membranes. Vitamin B2 deficiency produces a triad of symptoms: dermatitis, cheilitis and glossitis (bright red, smooth and shiny dry tongue), accompanied by burning and pain in the mouth when talking and eating. Vitamin C hypovitaminosis occurs with dietary deficiency of ascorbic acid, inflammatory processes in the intestines and is manifested by pain, hemorrhagic and ulcerative-necrotic manifestations in the oral cavity and in the area of the palatine tonsils, mobility and tooth loss.
Diseases of the spine (cervical osteochondrosis, tuberculous spondylitis, radiculitis) can cause pain in the throat. Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve manifests itself as intense pain in the pharynx, especially against the background of chronic stress in anxious and suspicious patients. Metabolic disorders, intoxication, and trauma contribute to its occurrence. Characterized by unilateral pain in the root of the tongue, tonsil, lasting several minutes, accompanied by dry throat and subsequent hypersalivation. Neuralgia of the superior laryngeal nerve gives similar symptoms, but also includes a painful dry cough and spasm of the vocal folds when inhaling.
Diagnosis and treatment
As we can see, there are many reasons why your throat hurts. And to determine the real cause of this condition, an examination by an otolaryngologist is necessary. If during the diagnostic process with an ENT doctor it becomes clear that the problem is not from the ENT organs, you may need to consult related specialists: a neurologist, gastroenterologist, allergist, endocrinologist. In this case, the patient is sent for CT, MRI, ultrasound of the thyroid gland, gastroscopy, etc.
Every person who has a sore throat needs a medical examination and diagnosis. The sooner you make an appointment, the more effective the treatment will be, and the risk of complications will be minimal.
What to do with a fever with a sore throat
Fever itself is a protective reaction of the body1,2. It triggers a whole chain of immune reactions aimed at fighting infection1,2. As a result, microorganisms lose some of their pathogenic properties, stop multiplying and die.
It is necessary to lower the temperature only in special cases. According to WHO recommendations, antipyretic therapy is indicated for people without chronic diseases only when the temperature rises to 390C1,2. In case of poor tolerance to heat, for example, headache and body aches, as well as severe concomitant diseases of the nervous, respiratory and cardiovascular systems, it is recommended to take an antipyretic drug without waiting for the temperature to rise to 380C2.
The temperature of 380C must be brought down for babies (up to 3 months of life) and children prone to seizures and with severe concomitant diseases2.
Attention! If you have a high temperature, you should definitely call a doctor at home. Only he can evaluate all the symptoms of the disease, make a diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
How many days does a fever last for a sore throat? This largely depends on how quickly the tonsils are cleared of infection and inflammatory products3. To quickly cleanse the tonsils, doctors recommend local procedures, for example, gargling with solutions and dissolving tablets with antiseptics3.
For local treatment of acute tonsillitis, drugs from the HEXORAL® line are intended, which have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects4,5,6,7,8. Cleansing the tonsils, reducing and eliminating inflammation helps normalize the temperature3.
To gargle, you can use HEXORAL®4 solution. It is approved for use not only in adults, but also in children starting from the age of three. HEXORAL® aerosol5 is suitable for irrigating the throat.
Traditional treatment of tonsillitis can also be supplemented with lozenges HEXORAL® TABS6, HEXORAL® CLASSIC7 and HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA8. HEXORAL® TABS EXTRA and HEXORAL® TABS6, in addition to the antiseptic, contain the analgesic lidocaine, which will help fight severe sore throat8.
Sometimes local therapy is not enough to control the infection. Then the doctor prescribes general treatment, which may include antibiotics, antihistamines, anti-inflammatory and other drugs. Strict adherence to the recommendations allows you to successfully cope with acute tonsillitis and prevent the development of complications.
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
Causes of disease development
Acute and chronic throat diseases can occur for various reasons, among the most common are:
- microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi);
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD);
- allergens;
- adverse environmental impacts;
- voice overstrain;
- injuries;
- hypothermia;
- general decrease in immunity;
- smoking.
A combination of several reasons is possible. Their identification and elimination is an integral part of treatment.
Symptoms of throat diseases
Most throat diseases have pronounced symptoms. Moreover, the clinical picture for each disease is individual. Among the common and most basic symptoms it is worth highlighting:
- sore throat that gets worse when swallowing;
- sore throat, dry throat;
- cough;
- hoarseness of voice;
- temperature increase;
- enlargement of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes;
- weakness and general malaise;
- headache;
- bad breath.
The combination of several of these symptoms at once is a reason to immediately consult a doctor. If symptoms increase and health deteriorates, prompt medical care is necessary.
Some throat diseases can cause rapid swelling of the larynx. As a result, without medical assistance, the patient can quickly die from suffocation. If you experience pain, immediately make an appointment with a doctor. This will help quickly and effectively eliminate the disease.