The lips have very thin skin, so they are practically not protected from external influences. Because of this, every person has to deal with various lip diseases at least once in their life. In medicine they have a common name - cheilitis.
. There are about a dozen varieties of this disease.
Reasons why lip diseases develop
Human lips are very vulnerable, which often leads to redness, irritation, dryness, and even the formation of wounds and crusts. Most often, cheilitis develops under the influence of external factors.
: low temperature, wind, sun rays. Under their influence, the skin around the mouth dries out, which in itself is unpleasant. If you don't do anything about it, the problem will only get worse.
The second factor that causes lip diseases is various allergens. The culprit of the pathological reaction can be both food and cosmetics. Problems in the functioning of the internal systems of the body can also affect the face.
Most often, the delicate skin around the mouth suffers due to hormonal imbalances, fungal and viral infections. Vitamin deficiency, indigestion and general deterioration of immunity can aggravate the situation.
There are also less common causes of lip disease. They usually lead to certain types of cheilitis.
Types of lip diseases
Cheilitis can be divided into several categories. Here are their names:
- exfoliative;
- glandular;
- meteorological;
- actinic;
- atopic;
- eczematous;
- candida.
In addition, there are other diseases that are not related to cheilitis. Therefore, dryness, peeling, crust formation, and a red border near the lips are causes for serious concern and a reason for examining the entire body.
Atopic cheilitis
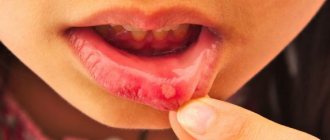
Atopic cheilitis is sometimes called allergic because it is caused by various irritants. The cause of the disease can be food or cosmetics. It turns out that the allergen affects the skin of the lips both from the inside and outside.
The disease manifests itself as inflammation of the red border of the lips. The skin becomes dry and peels. Cracks, itching and burning may occur.
Most often, children and adolescents suffer from lip allergies. Often it is the only symptom of neurodermatitis or atopic dermatitis.
Glandular cheilitis
Glandular cheilitis is an inflammation of the salivary glands, which are located on the surface of the mucous membrane of the lips.
The disease is more common in men over 50 years of age and is characterized by the following symptoms:
- noticeable red dots appear on the lower lip;
- copious secretion of saliva from the inflamed glands, the appearance of “dew drops”;
- dryness, cracks and erosion;
- Bacteria can enter the irritated canals, leading to the formation of pus.
There are primary and secondary forms of glandular cheilitis. The primary disease develops due to genetic predisposition. Secondary lip disease can be caused by lupus, oral leukoplakia, or lichen planus.
Meteorological cheilitis
People have to deal with this disease all the time. Standard chapping, which more often appears in winter, is meteorological cheilitis.
The first sign of the disease is a feeling of skin tightness. In advanced cases, it turns red, dries out, and becomes covered with cracks. This lip inflammation can be treated at home. It is enough to isolate yourself from harmful factors, moisturize and nourish the skin until it is completely restored.
Eczematous cheilitis
Eczematous cheilitis is one of the manifestations of eczema - an inflammatory process of a neuroallergic nature, which most often manifests itself on the face or dry areas of the body. Usually the disease is accompanied by constant dryness and redness. In advanced cases, the skin begins to peel off and become covered with blisters.
The disease often affects the tissue around the lips, so the patient may develop a red border, as in the photo on the right. This area of skin is constantly itchy and itchy.
If the disease is chronic, the symptoms are less pronounced. But in this case, seals appear on the skin.
Actinic cheilitis
Many people believe that lips need to be protected only in winter. Therefore, it is at this time of year that people stock up on moisturizing and nourishing balms to relieve dry and itchy lips. However, delicate skin must be protected not only from frost, but also from the burning sun.
With increased sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation and prolonged exposure to open areas, actinic cheilitis forms. His symptoms are standard:
- dryness, flaking;
- redness and swelling;
- compaction of individual areas.
If you do nothing, your lips become crusty. This is how the body tries to somehow protect the vulnerable part of the face. This symptom appears less frequently than others.
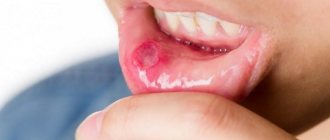
In advanced cases, ulcers, erosions and small compactions occur around the oral cavity. This condition is precancerous.
Exfoliative cheilitis
The exfoliative form of the disease occurs due to stress and disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. Genetic predisposition plays a major role. If your parents had this disease, there is a high risk that you will develop it too.
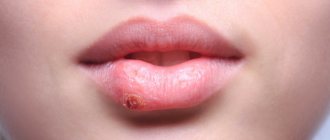
Exfoliative cheilitis on the lips occurs in two forms: exudative and dry. In the first case, you can observe the so-called yellow lips (pictured). A dense crust of this shade forms on the skin.
The yellow crust is easy to tear off; this process does not cause much discomfort. There are no erosions or other damage under the crust.
In the dry form of the disease, a crust also forms on the lips, but not yellow, but a lighter shade. The patient is concerned about dry skin, which explains the name of the disease. There is a desire to lick your teeth, but it is better not to do this: you can cause an infection and provoke more irritation.
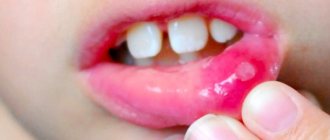
Candidal cheilitis
If the lips are red, inflamed and crusted with a cheesy coating of white or yellowish color, it means that the cause of these symptoms is candidiasis. If you clean off the plaque, inflamed areas of skin will be exposed. How such a lip disease manifests itself is shown in the photo.
The disease occurs due to the excessive development of the Candida fungus. The pathogen lives on the human mucous membranes constantly, but the active development of the fungus begins only under favorable conditions, which include:
- decreased immunity due to past illnesses or lack of nutrients;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- a sharp change in climate to a hotter and more humid one.
Fungal inflammation of the lips begins externally, but can spread to the internal tissues of the oral cavity, thus leading to candidal stomatitis.
Lip cancer
Many of these diseases, if not given proper attention to their treatment, lead to cancer. Perhaps this is the most terrible disease that can affect the lips and oral cavity.
At first, the symptoms of cancer are unremarkable. The lips will turn red and there will be slight inflammation. The skin may become dry and cracked. If the patient moisturizes and nourishes the affected tissues, but the lips remain sore for several weeks, he should sound the alarm and consult a specialist. Later, ulcers and lumps may appear.
Usually, if treatment is started correctly and on time, the cancer recedes completely. Only in rare cases are relapses possible.
There is another disease that is compared to cancer - Manganotti syndrome. The disease manifests itself in the form of a noticeable ulcer on the lip, which is precancerous. However, due to the fact that in most cases the syndrome still develops into a tumor, it is more often classified as oncological diseases.
Diagnostics
The cause of the symptom is determined by a dentist or maxillofacial surgeon. If the pain is neuropathic, a consultation with a neurologist is required; if malignant neoplasia is suspected, an examination by an oncologist is required. For cheilitis, herpes simplex and traumatic injuries, the basis of diagnosis is complaints and examination data; additional studies are not prescribed or are carried out to a minimum extent. Neuralgia is confirmed based on the clinical picture and the results of palpation of trigger points. Taking into account the nature of the disease, the examination plan includes:
- Cytological or histological examination.
It is a basic way to verify the diagnosis of lip cancer and lichen planus. For patients with cheilitis, according to indications, it is performed for differentiation from other pathologies. For herpes simplex, it is carried out if it is necessary to identify the virus. - Other laboratory tests.
Patients with cheilitis are prescribed a biochemical blood test to identify metabolic disorders and possible precipitating diseases. For herpes, PCR, RIF, and ELISA are performed. In patients with lichen planus, accumulation of immunoglobulin M is detected by direct immunofluorescence. - Visualization techniques
. The presence of lichen is indicated by a yellowish-orange glow when examining fingerprint smears under a Wood's lamp. Patients with cancer are shown an ultrasound of the lip and radiography of the lower jaw. If there are signs of metastasis, an extensive examination is carried out, including ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, chest X-rays.
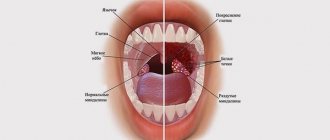
Visual inspection of lips
Features of cheilitis in children
Lips suffer due to minimal protection. In children it is even weaker, so cheilitis worries them somewhat more often. In addition to children, the risk group includes the elderly and pregnant women.
The main causes of cheilitis in childhood:
- allergic reaction to food;
- use of products for the care of the skin of the lips and around them, not intended for children;
- genetic predisposition;
- infectious and fungal infections;
- weather.
Typically, infantile cheilitis does not develop until critical stages. When children's lips turn red, parents immediately begin to treat them. After all, people pay more attention to the health of the younger generation than to their own. If cheilitis in children still requires treatment, therapy should not be delayed longer than a few weeks. The main thing is to remove all allergens from the children's diet and balance the diet.
Prevention
As you know, prevention is cheaper than treatment. In addition, preventing a disease is much easier than curing it, although this will require regularly following some rules.
Pay more attention to oral hygiene. To prevent the formation of cracks, it is necessary to protect the skin and mucous membranes of the mouth from adverse effects: unlearn the habit of licking the lips and corners of the mouth, use medicinal cosmetics for dry skin (lipstick, balm, cream). To avoid infection of the skin of the lips from the oral cavity, it is necessary to regularly brush your teeth, see a dentist, and promptly treat caries and inflammatory gum diseases.
Follow the rules of nutrition. If cracks appear in the corners of the mouth, exclude from the diet spicy, sour and salty foods that irritate the mucous membrane and skin. Include less acidic fruits and vegetables in your daily diet, as well as foods containing iron and riboflavin (beef, liver, dairy products, cabbage, potatoes, peanuts, almonds and others).
Give up bad habits. Smoking is a provoking factor in the development of this disease.
How to treat lips with cheilitis
The most important thing in treating cheilitis is to identify its cause, which is difficult to do without professional help. You'll have to contact a specialist. First, it is better to go to a therapist, and he will then refer you to a specialist doctor.
Typically, treatment for diseases of the lips and skin around the mouth is based on eliminating not the symptoms, but the root cause. It includes lifestyle changes, proper nutrition, and medication.
If the cause of inflammation is an infectious or fungal infection, local drugs are included in the therapy. Typically, patients are prescribed various medicinal ointments for external use, which must be applied to damaged skin several times a day:
- anti-inflammatory – Tetracycline, Erythromycin;
- antifungal – Clotrimazole;
- hormonal – Prednisolone.
To cure lips, you need to influence them not only from the outside, but also from the inside. The skin around the mouth often suffers from a lack of B vitamins, so they are often prescribed in the treatment of lips.
Treatment
Conservative therapy
The list of therapeutic measures is determined taking into account the characteristics of the pathology that causes pain in the lip:
- Cheilitis
. Provoking factors (dental pathologies, meteorological influences, contact with cosmetics) are excluded or minimized, and neurotic disorders are treated. Anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, antiallergic ointments (including hormonal ones), protective creams, immunocorrectors, and general antiviral agents are used. - Herpes
. The tendency to relapse necessitates complex therapy aimed at restoring immunity. Antiviral drugs are used in the first 5-7 days of illness, subsequently immunomodulators and recombinant alpha-interferons are prescribed. After 1-2 months it is recommended to vaccinate. - Lichen planus
. To eliminate inflammation and pain in ulcerative defects, topical corticosteroids, pain relief with local anesthetics, and medications to stimulate regeneration are indicated. To prevent fungal infections during treatment with steroids, antifungal agents are prescribed orally. For neurotic disorders, sedative therapy is required, for allergic predisposition - hyposensitizing therapy, for immunodeficiencies - immunomodulatory therapy. - Injuries
. Patients with chronic damage require treatment of carious teeth to eliminate the traumatic factor. In other cases, in the absence of wounds requiring surgical treatment, a gentle diet, cold to reduce swelling, then dry heat to accelerate resorption are advised. - Trigeminal neuralgia
. Therapy is carried out using anticonvulsants, antispasmodics, and antihistamines. Therapeutic blockades with glucocorticoids and physiotherapeutic procedures are effective: ultraphonophoresis with hydrocortisone, galvanization with novocaine. - Lip cancer
. In stage 1, in some cases, radiotherapy is used as the main treatment method. For patients with advanced stages, radiotherapy and chemotherapy are prescribed in the pre- and postoperative period or carried out as part of palliative treatment.
Surgery
Surgical techniques for pain in the lip are rarely used. Exceptions are open injuries and cancer. For fresh wounds, PSO of the wound of the maxillofacial area is necessary. Neoplasms are excised, and according to indications, a Vanach operation, a Kreill operation, and other interventions involving the removal of regional lymph nodes are performed. For patients with damage to the branches of the trigeminal nerve and persistent neuralgia, methods of stereotactic radiosurgery and percutaneous radiofrequency destruction may be recommended.
How to get rid of unpleasant symptoms at home
It is not worth treating at home without seeing a doctor. However, there are ways that you can resort to to reduce discomfort:
- If your lips become inflamed due to the sun or cold, it is advisable that they are always covered with a protective layer of balm.
- For severe itching and burning, which occur in almost all forms of cheilitis, cold compresses will help. Before applying them, the skin is covered with a layer of balm so that the lips are treated simultaneously with the reduction of pain.
- If your lips are red and covered with cracks, sores or any other open wounds, you need to make sure that bacteria do not get into them. The surrounding skin and teeth should be treated with a cotton pad soaked in hydrogen peroxide or Miramistin. Special antiseptic ointments will have the best effect.
- If pain and itching are unbearable, painkillers can be used. Ointments with a cooling effect will have the same effect.
All methods of folk treatment for cheilitis will be useless if you resort to them thoughtlessly - without consulting a doctor. In most cases, inflammation, redness and itching of the lips are harmless. Such symptoms can go away even without therapy, but sometimes they indicate dangerous diseases, so medical help should not be neglected.