March 21, 2019
In our age, when dental treatment is completely painless, many people still delay until the last minute and are in no hurry to see dentists, preferring to drown out the discomfort and pain with the help of medications. So, often, due to its fairly good effectiveness and over-the-counter availability from pharmacies, some people prefer to buy Baralgin, which saves them from toothache. And the editors of the UltraSmile.ru portal, as always, stand guard over your health and offer material for reading that will help you take into account all the possible “secrets,” disadvantages and advantages of this drug, as well as a sober approach to its choice.
"Baralgin" and its structural analogues are banned in many countries around the world
"Baralgin" is a non-narcotic drug belonging to the group of pyrazolones. It really helps with toothache and many other types of pain. It also allows you to temporarily get rid of spasmodic pain and reduces fever, because... is an antispasmodic and antipyretic (translated from Latin antipyretic means “against heat”). The desired effect can be achieved through the presence of a component such as metamizole sodium or a more well-known substance in Russia called “analgin” (synonyms: dipirone, ronalgin). Some analogues also contain pitofenone hydrochloride and fenpiverinium bromide, which enhance the positive and negative effects of metamizole. Analgin or dipyrone itself was first discovered back in 1922 by representatives of the German company Hoechst.
Baralgin really helps with toothache
In Russia, Belarus and Tajikistan, “Baralgin” itself, “Baralgin M” and any double drugs or combination drugs that contain analgin are very popular (“Spazgan”, “Spazmalgin” and “Spazmalgon”, “Maxigan”, “ Metamizole sodium", "Tempalgin", "Pentalgin" and others). However, in Europe, America, Japan, Greece, Mexico (more than 44% of such drugs), Saudi Arabia, and the Philippines, drugs of the pyrazolone group are prohibited. Despite the fact that pharmaceutical companies and pharmacies at one time suffered large material losses associated with such a restriction.
What were the reasons for such bans? Researchers have found that drugs of this group, when used uncontrolled and over-the-counter, increase the risk of bone marrow damage by 24 times, contribute to severe failure of the immune system, the appearance of blood diseases (negatively affects leukocytes, destroying white blood cells) and acute allergic reactions, as well as other toxic effects leading to death. In different countries, studies confirming this fact were carried out in different years:
- in 1973, scientists from the United States sounded the alarm: in 1977, drugs based on dipirone (analgin) were withdrawn from the market. In 1978, it was found that more than 7,000 people worldwide suffer from it every year1 (i.e., people experience severe agranulocytosis and, as a result, death),
- In 1986, doctors from Germany conducted their research and found that after taking the drugs, death occurred in 94 cases (of which 39 cases were due to anaphylactic shock2): by 1990, dipyrone drugs completely disappeared from the market.
Studies in many countries have revealed negative consequences of taking the drug.
Further, similar studies were carried out in other countries, and dipirone, and especially combination drugs based on it, were banned in Canada, Italy, Austria, and so on. If you can find them there, then only strictly according to the recipe. However, in Russia, drugs based on it are successfully sold without a prescription and are still used today (according to some data, up to 500 tons of drugs based on analgin are produced per year). "Baralgin" is no exception. In addition, its price seems quite reasonable to many and is approximately 250 rubles for a package of twenty tablets (and the shelf life is good - 4 years).
Analogs and replacement methods
Drugs similar to Baralgin are divided into 2 types:
- Similar in composition (Optalgin, Analgin, Spazdolzin, Sodium Metamizole);
- Having the same therapeutic effect (these drugs are not used to treat toothache).
Spazdolzin analogue of Baralgin for children
Spazdolzin is a drug similar in composition to Baralgin, which is available for children from 2 to 5 years old in the form of rectal suppositories, and for older children and adolescents - in the form of tablets. Although in some cases it is permissible to give tablets to children in a minimal dose.
Suppositories are used in the form of 1 dose according to the following scheme:
- 0-1 years – 100 mg
- 1-3 years – 200 mg
- 3-7 years – 400 mg
- 7-14 years – 600 mg
No more than 4 suppositories are allowed per day. Before inserting the suppository, the child should take a horizontal position.
Tablets are given to the child according to the following instructions:
- 2-3 years – 50-100 mg
- 4-5 years – 150 mg
- 6-7 years – 200 mg
- 8-10 years – 250 mg
- 10-14 years – 300 mg
A child should take no more than 3 tablets per day!
In addition to Spazdolzin, there is an effective children's drug - Kamistal baby gel, which is often used even by adults to relieve toothache.
The gel contains lidocaine, which freezes the inflamed areas, and, thanks to this, the pain subsides. The drug can be used during the period of growth and replacement of teeth in children. Gel analogues: Metrogyl Denta and Dentol.
Baralgin is contraindicated for pregnant women
Pregnant women can risk replacing Baralgin only with the No-shpa tablet, which is relatively harmless. Or rinse your mouth with herbal tinctures. As a rule, every woman should approach pregnancy planning wisely and cure all her teeth before the fetus settles inside, which needs to be cherished and protected.
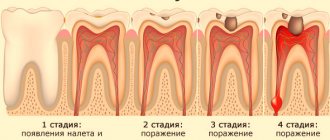
The medicine effectively relieves moderate pain
"Baralgin" is quite effective against toothache, which is of medium and low intensity. For example, it will help cope with the pain of caries, help survive the post-surgical stage of tooth extraction, implantation, osteoplastic surgery or vestibuloplasty.
The drug is quickly absorbed into the blood and helps reduce discomfort after 20 minutes. It is valid for the next four hours. However, you can use it no more than 3-5 days in a row, and certainly not on an ongoing basis. Therefore, if you are worried about toothache, then the most reasonable thing to do would be to take a one-time tablet and make an appointment with a dentist as soon as possible, who will provide symptomatic treatment. You can take a dose not exceeding 6 tablets per day (one tablet contains 500 milligrams of metamizole sodium, i.e. analgin or dipyrone). If there is no effect or you are in no hurry to treat your teeth, then stop taking Baralgin, because it can seriously harm your health.
The drug helps cope with moderate and mild pain
Description of the drug
Baralgin is a strong analgesic and antispasmodic.
It effectively reduces body temperature, stopping the process of inflammation, soothing painful symptoms. Baralgin goes on sale in the form of tablets and ampoules for injection. The pharmaceutical composition of the drug has a complex effect on the body, suppressing the manifestations of the disease and increasing a person’s pain threshold.
The drug formula includes the following ingredients:
- Analgin (metamizole sodium) is a non-steroidal drug, an analgesic from the pyrazolone group
- Pitophenone hydrochloride – containing 3 components with anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, myotropic and analgesic effects
- Phenpiverinium bromide is a combined substance with the same effect as the previous ingredient
Anesthetic components accumulate in the blood and, reaching the required concentration, effectively suppress the sensitivity of receptors, the functions of which are responsible for the conduction of nerve impulses (pain signals) to the brain.
Unlike pure analgin, the analgesic effect of baralgin occurs faster and lasts longer
The effect of analgin is significantly enhanced by the remaining components of the medicinal formula, so the analgesic effect is very pronounced. Within 20-25 minutes the patient has the required concentration of active components in the blood and feels their effect, which lasts up to 4 hours.
Attention! Baralgin cannot relieve acute, debilitating toothache. The instructions contain a list of conditions that can be affected by the drug. All of them involve moderate pain.
Therefore, with aching pain, inflammation of the gums and increased sensitivity of the teeth, Baralgin will be able to provide effective assistance to the patient. But if a person is suffering from deep caries, pulpitis or gumboil, the drug will only alleviate the condition, but will not completely relieve the acute pain.
Tablets can cause stomach pathologies
The instructions for Baralgin say what it helps with. The sphere of its influence is not only toothache, but also pain of various origins, including stomach pain and intestinal colic. However, the drug will cause additional problems if you use it incorrectly. It will cause damage to the gastrointestinal tract, affect the mucous membrane, and lead to peptic ulcers.
So, to eliminate such problems, let's consider a few rules on how to take medicine:
- take the tablets only with meals or immediately after meals,
- take the tablets with plenty of liquid,
- Do not chew the tablets, because They are very bitter and in some people with sensitive mucous membranes, their taste can even cause a gag reflex.
When taking the medicine, the urine may turn red, as stated in the instructions for the drug. You shouldn’t be afraid of this phenomenon, because... it has no clinical significance and disappears without a trace after stopping the pills.
The tablet must be taken with plenty of water.
Temporary pain relief
If you cannot visit a doctor in the near future, and the pain is difficult to endure, you need to turn to painkillers: paracetamol, ibuprofen and others. After their effect ends, you can use antispasmodics, for example, drotaverine. Before taking pharmaceutical drugs, be sure to read the instructions and consult your doctor! Medicines can be supplemented or replaced with traditional methods of pain relief. For example, rinsing with a decoction of herbs (sage, oregano, chamomile) or a soda-salt solution (dilute ⅓ teaspoon of soda and salt in a glass of warm water, rinse your mouth after each meal or attack of pain). Natural propolis also has an analgesic and antiseptic effect if you apply it to the sore area and chew it lightly.
A pulsating tooth is an alarm bell, even if the pain goes away after a while. The problem will not evaporate by itself and will grow like a snowball. We recommend preventing dental problems in advance. To do this, it is enough to visit the dentist only twice a year. The doctor can stop caries in the early stages, prescribe professional hygiene and other strengthening procedures. But if you have a problem with your teeth, don’t try to solve it yourself. You won't treat your own appendicitis, will you? So teeth need a professional approach. Maintain your oral health and maintain a beautiful smile for many years to come.
Do not take the drug with other analgesics
Have you taken Baralgin, but your toothache still won’t go away? In this case, some people try to increase the effect of the medicine and believe that if they take another analgesic, they will be able to avoid complications. However, this opinion is erroneous; the instructions for the drug indicate that with such a combination the toxic effect of the drug, and in particular the toxicity of analgin, can increase significantly. Also take into account the fact that the tablets also enhance the toxic effect of alcohol, which can result in severe liver damage, so exclude the possibility of taking these two components at the same time.
You should take Baralgin with great caution, which helps with toothache in the presence of low blood pressure (sharply lowers blood pressure), with sensitivity and intolerance to analgin (there is a high probability of Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock). The tablets should not be taken by pregnant women, children under 15 years of age, people with glaucoma, or nursing women (if you take the medication, you will be able to return to feeding your baby with breast milk no earlier than 48 hours later).
Baralgin forte No. 100 tablets
Baralgin forte No. 100 tablets
Release form
Tablets containing 500 mg of metamizole sodium as the active substance. 10 (10 x 1 blister), 20 (10 x 2 blisters), 50 (10 x 5 blisters) or 100 tablets (10 x 10 blisters) with instructions for use in a cardboard box.
Compound
Active substance - One tablet contains 500 mg of metamizole sodium. Excipients: magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol 4000.
Description
Round, flat tablets from white to almost white in color with “Baralgin M” engraving on one side and a score line on the other.
Pharmacological properties
Baralgin M refers to non-narcotic drugs, pyrazolone derivatives. It has an analgesic, antipyretic and weak anti-inflammatory effect. The mechanism of action is practically no different from other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Pharmacokinetics
Metamizole is well and quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After oral administration, metamizole is completely metabolized to form active 4-N-methylaminoantipyrine. The connection of the active metabolite with blood plasma proteins is 50-60%. Mainly excreted by the kidneys. After taking 1 g of metamizole, the renal clearance for 4-N-methylaminoantipyrine was 5 ml ± 2 ml/min. The half-life is 2.7 hours. In patients with liver cirrhosis, the half-life of 4-N-methylaminoantipyrine increased threefold and was about 10 hours.
Indications for use
Pain syndrome of various etiologies (acute or chronic): including headache, dental pain, migraine pain, neuralgia, radicular syndrome, muscle pain, and dysmenorrhea. Baralgin M is used for pain of visceral origin (renal, hepatic, intestinal colic) in combination with antispasmodics. Baralgin M can be used to reduce pain after surgical and diagnostic interventions. Increased body temperature during colds and other infectious and inflammatory diseases. The advisability of using the drug is decided in each case depending on the severity, nature and tolerance of the fever.
Contraindications
Baralgin M should not be taken by persons with hypersensitivity to pyraeolons (isopropyl-minophenazole, propyphenazone, phenazone or phenylbutazone), with hepatic porphyria, congenital deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, for the first three months and the last three months of pregnancy, with bronchial asthma and diseases accompanied by bronchospasm, -aspirin asthma-, with severe dysfunction of the liver and kidneys, severe hematopoietic disorders (agranulocytosis, cytoplastic and infectious neutropenia). Baralgin M tablets should not be taken by children under 15 years of age.
Directions for use and doses
A single dose for adults and adolescents over 15 years of age is 500 mg (1 tablet). The maximum single dose can reach 1000 mg (2 tablets). Unless otherwise prescribed, a single dose may be taken up to 2-3 times daily. The maximum daily dose is 3000 mg (6 tablets). The duration of administration is no more than 5 days when prescribed as an analgesic and no more than 3 days when prescribed as an antipyretic. The tablets should be taken with plenty of water. Increasing the daily dose of the drug or the duration of treatment is possible only under the supervision of a physician.
Side effects
Allergic reactions: urticaria, including on the conjunctiva and mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, angioedema, in rare cases, malignant exudative erythema (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome), bronchospastic syndrome, anaphylactic shock. From the hematopoietic organs: leukopenia, rarely agranulocytosis and thrombocytopenia of immune origin. From the urinary system: impaired renal function, oliguria, anuria, proteinuria, very rarely the development of acute interstitial nephritis, red coloring of urine (due to the release of rubazonic acid metabolite). Other: possible decrease in blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbance.
OVERDOSE
In case of overdose, consult a doctor. The following symptoms may occur: nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, oliguria, hypothermia, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, shortness of breath, tinnitus, drowsiness, delirium, impaired consciousness, acute agranulocytosis, hemorrhagic syndrome, acute renal or liver failure, convulsions, paralysis of the respiratory muscles. Treatment: induce vomiting, gastric lavage through a tube; saline laxatives, activated carbon; carrying out forced diuresis, hemodialysis; with the development of convulsive syndrome, intravenous administration of diazepam and fast-acting barbiturates.
INTERACTION WITH OTHER MEDICINES
The simultaneous use of alcohol and metamizole has a reciprocal effect on their effects; when used together with cyclosporine, a decrease in the concentration of cyclosporine in the blood may occur. The simultaneous use of metamizole with other non-narcotic analgesics can lead to mutual enhancement of toxic effects. Tricyclic antidepressants, oral contraceptives, and allopurinol disrupt the metabolism of metamizole in the liver and increase its toxicity. Barbiturates, phenylbutazone and other inducers of microsomal liver enzymes weaken the effect of metamizole. Sedatives and tranquilizers enhance the analgesic effect of the drug. Concomitant use with chlorpromazine or other phenothiazine derivatives can lead to the development of severe hyperthermia. Radiocontrast agents, colloidal blood substitutes and penicillin should not be used during treatment with metamizole. Metamizole, displacing oral hypoglycemic drugs, indirect anticoagulants, glucocorticosteroids and indomethacin from protein binding, increases their activity. Thiamazole and sarcolysin increase the risk of developing leukopenia. The effect is enhanced by codeine, histamine H2 blockers and propranolol.
special instructions
When treating patients receiving cytotoxic drugs, metamizole sodium should only be taken under medical supervision. During pregnancy, especially in the first 3 months and last 3 months, no non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be used. Patients with atonic bronchial asthma and hay fever have an increased risk of developing hypersensitivity reactions. With long-term use, it is necessary to monitor the peripheral blood picture. While taking metamizole sodium, agranulocytosis may develop, and therefore, if an unmotivated rise in temperature, chills, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, stomatitis, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the oral cavity, vaginitis or proctitis is detected, immediate discontinuation of the drug is necessary. It is unacceptable to use the drug to relieve acute abdominal pain (until the cause is determined). Particular caution is required when prescribing to patients with systolic blood pressure below 100 mm Hg. Art. or in cases of circulatory instability (for example, in the case of incipient severe circulatory disorders due to myocardial infarction, multiple trauma, incipient shock), with anamnestic indications of kidney disease (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis) and with a long history of alcoholism. Pregnancy and breastfeeding During the first and last three months of pregnancy, Baralgin M should not be taken. From the fourth to sixth months of pregnancy, Baralgin M should be taken according to strict medical indications. After taking Baralgin M, breastfeeding should be stopped for 48 hours.
Storage conditions At temperatures from +8 °C to +25 °C in a place protected from light. Keep the medicine out of the reach of children!
Best before date
4 years. Do not use after expiration date.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
Without a doctor's prescription.
The medicine is dangerous for children
As we have already found out, tablets are prohibited for children under 15 years of age due to their toxicity, even in single dosages. But narcologists in some areas are sounding the alarm. Thus, in Kyrgyzstan (Kerben), narcologists notice that local youth actively use the painkiller "Baralgin", deliberately causing themselves to be in a cheerful state, because. the medication causes sensations similar to mild intoxication. Of course, for such a condition to occur, you need to eat almost a handful of tablets, but doctors urge parents to be vigilant, because with 10-20 tablets, intoxication of the body is already achieved. And it would be fine if the side effects for children ended only with the appearance of addiction, mental and deviant deviations. But for a child’s body, such a load can end much worse, causing a stroke.
For children with this problem, it is better to choose another drug
It is interesting that regarding contraindications in children, there is quite contradictory information in the advertising of the drug “Baralgin”. For example, tablets cannot be used until the age of 15, but injections (the second form of the drug) can be given after reaching 6 years. However, many experts, in principle, suggest considering the drug as the very last resort not only for children, but also for adults, regardless of the type of pain that occurs.
Finally, we will give you a statement from specialists who are members of the medication commission of the German Medical Association. They argue that analgin-based drugs like Baralgin should be used only in truly severe and life-threatening conditions, for example, after surgery. And the same headache or toothache, intestinal colic are not mortally dangerous if a person seeks to eliminate not only the symptom, but the root cause of their appearance, i.e. undergoing treatment. The editors of the portal UltraSmile.ru agree with this sensible argument, therefore, before taking any medicine, we advise you to think about it and first evaluate the possible benefits and harms. You should also refrain from systematically using any medications without consulting a doctor.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 2 ratings, average: 4.00 out of 5)
toothache
- Dukes, 1987, op cit, p9126
- BUKO Pharma Kampagne, Hoechst, A Cause of Illness? The Pharmabusiness in the Third World, Germany, May 1986, p19.
Pain mistaken for toothache
Diseases and conditions in which pain can be mistaken for dental pain . These are mainly diseases of related areas (paranasal sinuses, organs of vision and hearing, pharynx, cervical vertebrae, brain); The cause may also be diseases of the heart and blood vessels, the musculoskeletal system (spine), the nervous system, as well as mental disorders.
Trigeminal neuralgia. The trigeminal nerve is responsible for sensation in the face and mouth. When it is affected, the pain is very severe and similar to a toothache. Unfortunately, many patients with neuralgia have undergone numerous depulpations and tooth extractions, but continue to experience pain. Despite the patient’s confidence that the cause of the pain is the tooth, the dentist needs to correct the diagnosis and refer the patient to a neurologist. Another option is postherpetic neuralgia, which occurs in people who have had herpes zoster (shingles). Therefore, it is important to inform your dentist if itchy blisters have appeared on the skin and mucous membranes for some time, or this diagnosis has been made.
Cluster headache is a syndrome of unknown origin, characterized by acute, paroxysmal pain. Perhaps this is a form of migraine. Cluster headaches are more common in men aged 30-60 years. Many patients report pain after drinking alcohol.
In classic cases, there is unilateral pain in the upper jaw, maxillary sinus and behind the orbit. Cluster headache is often mistaken for acute pulpitis or periodontitis of the chewing teeth of the upper jaw.
Inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media) is a common disease, especially in children, caused by streptococci. It is well known that with diseases of the chewing teeth, pain can radiate to the ear area. Conversely, with inflammation of the middle ear, the symptoms shift to the back of the upper and lower jaws. After diagnosis, the patient is referred to an otolaryngologist.
Acute maxillary sinusitis (sinusitis). The roots of the teeth of the upper jaw are adjacent to the bottom of the sinus, so inflammation often imitates toothache. Most forms of sinusitis are allergic and are characterized by dull pain in the zygomatic region and alveolar process of the upper jaw.
In acute sinusitis, the pain can be stabbing, pressing, pulsating. Often it radiates to the infraorbital region, to the area of the upper jaw teeth. In this case, the pain is felt not in any one tooth, but in several. It is recommended to contact an ENT specialist.
Diseases of the paranasal sinuses are often chronic and allergic. They tend to be seasonal, because for most people allergens are seeds and pollen of various plants. In countries with a northern climate, the incidence of sinusitis increases in spring and autumn. The patient should be referred to an ENT specialist and an allergist.
Heart diseases. Angina is pain behind the sternum, which can radiate to the left shoulder and along the arm. The pain usually occurs after physical activity. These symptoms are extremely important, since angina pectoris is a harbinger of acute myocardial infarction. Sometimes the pain is felt only in the left shoulder and arm, and even less often in the left corner of the lower jaw.
So, if there are complaints of pain in the posterior part of the lower jaw on the left and there are no objective reasons from the teeth, we can assume the cardiac nature of the pain. In this case, the dentist will refer the patient for a consultation with a cardiologist or therapist.
Salivary stone disease develops in the duct of one of the salivary glands. For a long time, the only symptom was dry mouth. When the stone reaches a critical size, it clogs the salivary duct; toothache appears. Swelling may occur in the submandibular area. To make a diagnosis, several x-rays are taken. The treatment is carried out by a dental surgeon, it consists of making an incision in the duct and removing the stone under local anesthesia.
Pain of musculoskeletal origin can be caused by injury or dysfunction of the muscles of the neck, head, and jaws. Pain can be noted in the area of the teeth, cheek, temple, side of the neck, and back of the head. This group also includes diseases of the temporomandibular joint and the cervical spine. Other joint diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, gout, psoriasis; collagen diseases, or collagenoses) can cause pain in the maxillofacial area.
With internal dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint, complaints of toothache often arise. Joint dysfunction is caused by displacement of the articular disc, the formation of adhesions or due to various forms of arthritis, injuries, yawning, and prolonged opening of the mouth. Manifestations: the mouth does not open completely, when opening the lower jaw moves to the side, clicking or creaking in the joint, as well as pain in front of the tragus of the ear.
The pain is long-lasting, dull, muffled, but can become more acute when opening the mouth wide or chewing. In some cases, the pain radiates to the temple, cheek, and distal parts of the upper and lower jaws. In such cases, the patient may believe that he is experiencing toothache.
Tumors. Pain is rarely a symptom of malignant tumors in the jaw area. In typical cases, there are complaints of tingling or decreased sensitivity (numbness). Most tumors affect not only sensory but also motor nerves.
Atypical pain conditions masquerading as toothache are a group of syndromes that do not correspond to any specific disease. In this case, the patient is usually convinced that the cause of the pain is the teeth” and insists on their treatment or removal. Although the cause is unknown, many experts suggest the nervous system is involved. Atypical pain is usually chronic, aching; patients feel it deep inside the bone and have difficulty localizing it. Sometimes the pain seems to move from one area to another, and there may be complaints of pain throughout the body. The examination should include psychological screening and behavioral tests that assess depressive, anxious, and hostile behavior. It is possible that the primary cause of atypical pain is a psychological disorder. Consultation with a psychologist or psychiatrist is indicated.
Comments
I am terribly afraid of dentists, so for a long time I took Baralgin on a regular basis for toothache, because... helped a lot. I read your article and was really scared of the consequences. How to get rid of your fears and doubts and still decide to go to the doctor?
Alesya (03/23/2019 at 10:03 am) Reply to comment
- Dear Alesya! Realize the fact that today dental treatment is completely painless with the help of the latest and safe anesthetics, and to delay means causing inevitable harm to the entire body as a whole. And to cope with your fears, be sure to read our article on the topic “5 tips on how to stop being afraid of dentists.”
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (03/26/2019 at 09:37) Reply to comment
I read in an article that baralgin causes agranulocytosis. What is this and what are its symptoms?
Valeeva_N (04/03/2019 at 12:56 pm) Reply to comment
- Agranulocytosis is a dangerous pathological disease that suppresses the production of white blood cells (sharply reduces the level of leukocytes in the blood) and affects their function, as a result of which a person’s immune status is impaired, the process of hematopoiesis, and the susceptibility to any infectious or viral disease or bacterial infections increases sharply . In 80% of all cases, the pathology is characterized by death. Main symptoms: shortness of breath, fear of light, rapid heartbeat, sweating, the appearance of ulcers on the body mucosa, fever, general weakness and fatigue.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (03/06/2019 at 09:16) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Contraindications
In what cases should the medicine not be used? The first prohibition is pregnancy: even in later stages, baralgin should be replaced with another painkiller, after consulting with a gynecologist. The medicine is also contraindicated:
- children under fifteen years of age;
- with intestinal obstruction;
- for liver/kidney diseases of a certain etymology;
- for diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- for glaucoma and heart diseases;
- for bronchial asthma and bronchospasms;
- in case of intolerance to the substances of the drug;
- with alcohol intolerance;
- when breastfeeding a baby.
Important! Medicinal substances easily penetrate into body fluids, including breast milk. When feeding an infant, any medications are contraindicated, with some exceptions.
It should be remembered that medicinal substances do not always complement each other harmoniously, therefore, when taking other medications, you need to notify your doctor. Baralgin in combination with some medications can provoke an increase in toxic substances.