Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
More than 300 varieties of microorganisms live in the oral cavity (streptococci, lactobacilli, fungi of the genus Candida, staphylococci, etc.), which make up its microflora, or microbiota. Constant humidity, optimal temperature and pH values, the presence of food residues - all this creates favorable conditions for the proliferation of various types of microbes.
The composition of the oral microbiota is individual for each person, so the concept of “normal microflora” is also individual. Many opportunistic microorganisms that make up the normal microflora of the oral cavity play an important role in the etiology and pathogenesis of caries, diseases of the mucous membrane and periodontal tissue. The microbiota of the oral cavity is involved in the primary processes of food digestion and absorption of nutrients, in the synthesis of vitamins, and in maintaining the proper functioning of the immune system.
The qualitative and quantitative composition of microflora usually changes little throughout a person’s life, but under certain factors this is possible. In this case, they speak of an imbalance of microflora, that is, dysbacteriosis, when the proportion of normal microflora decreases, and the growth of pathogenic microorganisms increases.
The ailment itself, designated by the term “dysbacteriosis,” is not a disease and is not included in the official international classifications of diseases. It should be considered as a set of symptoms indicating the presence of pathological processes in various body systems. Occurs in adults and children. Let's talk about oral dysbiosis: how it manifests itself, why it is dangerous, how to treat it.
Stages of development of dysbiosis in the oral cavity
Some researchers identify several stages in the formation of oral dysbiosis:
- Stage 1 - dysbiotic shift (compensated dysbiosis). Characterized by an increase in the number of one type or several types of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity. At this stage there are no manifestations;
- Stage 2 - subcompensated dysbacteriosis. There are fewer lactobacilli, and barely noticeable manifestations appear;
- Stage 3. The lactobacilli needed by the body are replaced by pathogenic microorganisms;
- Stage 4. Yeast-like fungi begin to actively multiply in an unnatural niche for them.
At stages 3 and 4 (decompensated dysbacteriosis), inflammatory elements, ulcers, and excessive keratinization of the oral epithelium may occur.
All this can lead to the development of stomatitis, periodontitis, and periodontal disease. An infection of the nasopharynx may occur.
Symptoms of oral dysbiosis
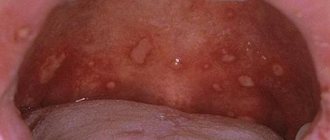
Symptoms designated by the term “oral dysbiosis” occur in many different diseases and syndromes, so the disease is difficult to diagnose. Let's name the signs of an imbalance in the oral microflora:
- bad breath (halitosis);
- metallic taste, burning sensation in the mouth;
- the development of candidiasis, or thrush - a white coating on the tongue and mucous membranes of the cheeks;
- inflammation of the mucous membranes and gums;
- swelling, redness and soreness of the tongue;
- The appearance of so-called jams in the corners of the mouth is characteristic.
The pathology of normal microflora in the mouth is fraught with the danger of endogenous infections.
The listed manifestations are due to the following changes:
- colonization resistance (local immunity) of the mucous membrane is disrupted - yeast-like fungi easily adhere to the surface of the epithelium, where there are optimal conditions for reproduction;
- the bacterial antagonism of normal microflora changes significantly - normally, antagonistic microbes do not allow pathogenic fungi to actively multiply, but with dysbiosis, the former are destroyed, which provokes rapid proliferation of Candida fungi;
- In patients, a significant shift in local protective factors is detected - the weakened defense does not cope with its function, so the volume of pathogenic microflora increases unhindered.
How do probiotics work?
Dysbacteriosis and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity very often cause not only local discomfort, but also discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract and bad breath. Antibiotics, along with pathogenic microorganisms, begin to destroy the beneficial bacteria necessary for humans.
Probiotics are live strains of “friendly” bacteria and bring invaluable benefits to the body:
- help destroy pathogenic microorganisms;
- promote the regeneration of damaged tissues;
- activate the immune system;
- normalize cell metabolism;
- prevent cells from degenerating into malignant formations;
- restore the balance of fluid and beneficial microorganisms;
- prevent allergies;
- removes unpleasant odors from the mouth;
- eliminate toxins produced by pathogenic microorganisms.
Reasons for the formation of oral dysbiosis
The reasons that lead to disturbances in microbiocenosis in the mouth are, for the most part, the same as for dysbacteriosis in other areas of the gastrointestinal tract. These include:
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
- use of antibacterial and antiseptic agents for mouth rinsing. Long-term use of bactericidal rinses, antimicrobial toothpastes, and local antiseptics like chlorhexidine leads to the destruction of not only harmful, but also beneficial bacteria in the oral cavity. At the same time, the resistance of pathogenic flora to antibiotics increases;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases, intoxication and weakening of the macroorganism against their background;
- hypovitaminosis - lack of vitamins.
Often the cause of dysbiosis in the mouth is incorrect or insufficient oral hygiene. A factor that provokes a violation of the microflora of the oral cavity is smoking.
Influence of the state of the oral microflora on other organs and systems
The connection between the general condition of the body and dental health is known. Thus, those patients who have oral diseases are more likely to develop cardiovascular diseases. Clinical studies confirm the presence of oral bacterial microflora in the blood and atherosclerotic plaques. Periodontopathogenic microflora is the main source of local and systemic chronic inflammatory process. Acts as a risk factor for the development of coronary heart disease.
In addition, scientists have discovered a connection between bacteria living in the mouth and the occurrence of migraines.
Another dangerous consequence of disruption of the oral microflora is the aggravation of intestinal and esophageal cancer. One study found that bacteria living in the mouth can trigger the development of colon cancer.
Express methods
There are many answers to the question of how to urgently remove bad breath. Here are the most effective express ways to get rid of bad breath.
- Chewing lemon, lime. This method will not eliminate the stench forever, but it will get rid of it for a few hours. You need to chew a piece of lemon or lime along with the peel. It is also recommended to use citrus zest as an emergency medicine, which you can always carry with you in a fabric bag.
- Coffee. Among coffee lovers, it is rare to find people with bad breath. Caffeine is known to kill unpleasant odors. If you can’t drink a cup of aromatic drink, it is recommended to gnaw 3-4 coffee beans (which you need to put in your pocket or purse in advance). This method will relieve the stench for 7-8 hours. It is not suitable for people suffering from periodic or constant increases in blood pressure. Hypertensive patients are better off chewing a few sprigs of dill or parsley. This method will not only freshen your breath for 8 hours, but also cleanse the oral cavity of bacteria.
- A sprig of cloves helps with terrible odor in the mouth. All you need to do is chew it for a few seconds. Clove essential oil extracted from the plant will not only refresh the oral cavity, but also lift your spirits.
- Juniper will help hide fumes well. It is recommended to chew the berries for several minutes. This method is capable of defeating even the strongest amber after active celebrations with the consumption of large quantities of alcoholic beverages.
- Sour apples can also combat this problem. Fruits will get rid of plaque, bad breath and improve the functioning of the digestive system.
- To get rid of the problem, it is recommended to chew pine nuts or roasted seeds for a few minutes. This will provide fresh breath for 1-2 hours and even get rid of the smell of garlic and onions.
- If you consume half a teaspoon of propolis daily, this will help eliminate stench and accelerate the regeneration of the mucous membrane during the development of inflammatory processes.
- A salt solution will also help get rid of the problem. To do this, you need to rinse your mouth with salty liquid (or sodium chloride 0.9%) for 2-3 minutes. It kills odor and destroys bacteria.
- If you rinse your mouth with any vegetable oil in the morning, it will relieve bad breath for several hours.
It is also recommended to use wormwood for chewing. The plant eliminates bacteria, restores the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and eliminates bad breath. Magnolia has the same properties. All you need to do is chew the plant for 1 minute.
Diagnosis and treatment of oral dysbiosis
Oral cavity dysbiosis syndrome in the initial stages of development is detected during laboratory tests. To diagnose oral dysbiosis, microbiological examination of a smear from the oral mucosa or saliva is used. When diagnosing, the number of opportunistic microorganisms in the test material is determined.
Important: it is necessary to accurately establish the root cause of the disease, which a comprehensive examination of the body will help with, and treat the primary disease.
For pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract that affect the condition of the oral cavity, they are first treated.
If the balance of the oral microflora is disturbed, treatment is mainly used in the form of sanitation and taking medications to normalize the microflora in the mouth. However, all drugs that are used to treat oral dysbiosis are considered drugs with unproven effectiveness. The following is used as therapy for this condition:
- eubiotics - needed to increase the number of beneficial bacteria in the mouth;
- immunomodulators - increase local immunity and prevent the growth of pathogenic microorganisms;
- antimicrobial and antifungal agents.
Oral probiotics (oral probiotics)
Probiotics are live microorganisms that promote the growth of friendly microbiota. Most often, such substances are used to improve intestinal microflora, but not many people know that there are probiotics for the oral cavity.
It is important to understand that probiotics for the oral cavity are represented by one group of substances, and probiotics for the intestines are a completely different one. Scientific research regarding these drugs is very controversial, so dentists recommend using them only as an addition to the prescribed treatment for dysbiosis.
Prevention of dysbiosis in the mouth
Prevention of oral dysbiosis includes the following measures:
- use of antibiotics only as prescribed by a doctor in the recommended course;
- use of alcohol-free and antiseptic rinses for daily oral hygiene, for example, ASEPTA Parodontal Fresh with plant extracts and microelements;
- smoking cessation: it is advisable to eliminate smoking altogether;
- strengthening local immunity: timely sanitation of the oral cavity, maintaining oral hygiene. You also need to strengthen your general immunity.
The main advice for normalizing the microflora of the oral cavity: do not feed the bad microbiota and do not destroy the good one.
Let's summarize: we have given a definition of oral dysbiosis, which is understood as a violation of the ratio between normal and pathogenic microflora in the direction of increasing the latter. They indicated that this condition is not an independent disease, but only a complex of symptoms. The stages of formation of oral dysbiosis, symptoms and causes of disturbances in the microflora of the oral cavity were named. Also from this article you learned how to treat oral dysbiosis and how to prevent its occurrence.
Types of Oral Probiotics
Biologists call the most common types of probiotics:
- Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium (Lactobacillus and bifidobacteria), obtained mainly from dairy products. However, it is important to normalize the population of these bacteria, but not to “overdo it” with them, since their excessive quantity provokes the formation of caries.
- Bacterial strains Bacillus subtilis, L. salivarius WB21, L. casei Shirota, L. brevis, L. reuteri, L. acidophilus may be useful in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
- Candidiasis, the most common cause of oral dysbiosis, can be treated with L. rhamnosus strains (GG and LC705) as well as Propionibacterium freudenreichii ssp. shermanii JS. This type of oral probiotic can be obtained from cheese or other fortified dairy products.
- To treat halitosis (bad breath), probiotics E. coli Nisle 1917 and S. salivarius K12 can be used.
Experts' opinion
Asept products have proven effectiveness. For example, multiple clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on clinical trials to determine/confirm the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: mouth rinse "ASEPTA PARODONTAL" - Solution for irrigator." Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Head. Department of Preventive Dentistry S.B. Ulitovsky, doctor-researcher A.A. Leontiev First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after academician I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry.
- Report on determining/confirming the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: Asepta toothpaste used in combination with Asepta mouthwash and Asepta gum balm Head. Department of PFS Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor S.B. Ulitovsky St. Petersburg State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova. Faculty of Dentistry. Department of Preventive Dentistry.