What does a healthy tongue look like?
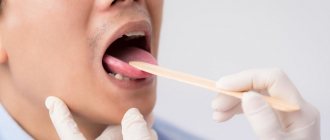
When a person is healthy, his tongue is smooth, soft, and pale pink in color. The movement does not cause discomfort. The papillae on the tongue are not smoothed out: small at the tip, larger closer to the middle. Plaque is white in small quantities and can be easily removed with a toothbrush. The sense of taste is not impaired [1].
In order not to miss the development of unpleasant diseases, regularly conduct an independent examination of your tongue. To do this, follow a few rules:
- Examine your tongue in the morning before brushing your teeth.
- Use natural light.
- Don't strain your tongue.
- Consider what you ate the day before. For example, beets or blueberries color the tongue.
You can comprehensively assess the state of the language by honestly answering a number of questions:
- Tongue color.
- How smooth it is.
- Is there any plaque, what color and density?
- Is the language homogeneous in its structure?
- Are your teeth imprinted on your tongue?
- Cracks in the tongue, ulcers, wounds.
- Is there bad breath?
Diagnostics
An in-person examination by a dentist is enough to detect the problem. Sometimes a doctor can immediately diagnose and prescribe treatment. But if the disease is not of a dental nature, additional examination will be required.
For diagnostic purposes the following is carried out:
- general blood test to identify an infectious process;
- FGDS for detection of peptic ulcer;
- biochemical blood test for glucose content and determination of hormone levels if endocrine disorders are suspected;
- examination by a neurologist and conducting tests to diagnose damage to the nervous system;
- blood test for HIV and hepatitis B, C to find the cause of immunodeficiency;
- examination by an otolaryngologist to detect acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis).
Carrying out all types of diagnostic procedures is not necessary; often the cause is determined at the initial stage. Based on the results of the examination, a treatment regimen is selected.
Reasons for the formation of white spots
Harmless causes of the formation of white spots on the tongue can be dehydration, smoking, poor diet, poor hygiene, and taking certain medications. But this symptom can also hide unpleasant diseases, such as stomatitis, leukoplakia, lichen planus, and gastrointestinal disorders [2].
1. Candidal stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral cavity that is caused by the Candida fungus. White spots are located on the tongue, cheeks, or completely cover the entire mucous membrane down to the pharynx and tonsils. There is also a feeling of dryness and burning. The disease is not dangerous, but requires treatment.
Stomatitis occurs due to long-term use of antibiotics and metabolic disorders. It is also possible to become infected through objects, products or from another person. Predisposing factors include alcohol consumption, smoking, use of dentures, high-carbohydrate diet, and poor oral hygiene [3].
2. Leukoplakia is a white formation in the form of a spot or plaque that cannot be scraped off during examination. Most often they are located on the mucous membrane of the cheeks along the line of closure of the teeth; they can occur on the back or side surfaces of the tongue, on the lips. A common cause of leukoplakia is tobacco. It has a traumatic thermal and chemical effect on the mucous membrane. Sometimes leukoplakia appears due to an allergy to materials used in dental restoration and prosthetics [4].
3. Lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory disease, the target of which is the mucous membranes, skin, and, less often, nails and hair. You can find white spots on the tongue, on the surfaces of the cheeks, and gums. They are usually not painful, but in some cases there may be redness and occasional blistering. Most often, the disease occurs in women aged 40 to 65 years [5]. The cause of oral lichen planus rarely can be determined. The disease may indicate a weakened human immune system. However, it is not infectious and is not inherited.
4. Gastrointestinal diseases. One of the causes of stomach diseases is the microorganism Helicobacter pylori. Its active activity leads to peptic ulcers of the stomach, duodenum, cancers and tumors of the digestive system. The gastrointestinal tract and tongue are closely related. Research shows that spots on the tongue, changes in its color and irregularities in relief, the appearance of plaque and cracks may indicate gastrointestinal diseases.
Diseases as the cause of white plaque
If your tongue is always coated and your mouth smells bad, you should be wary. During an in-person examination, the doctor will examine the condition of the oral cavity and make a preliminary diagnosis. It is possible that the patient will have to undergo blood tests and undergo an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, because the most likely cause of the problem described is diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver. They are always the first to be excluded.
Among the pathologies in which the muscular organ becomes covered with a white coating that is difficult to remove:
- Glossitis. Inflammation of soft tissues, leading to changes in the color and structure of the tongue. Has a viral or bacterial nature. The patient experiences swelling, burning, pain when chewing and swallowing food. His diction is also impaired. In advanced cases, the pathology causes phlegmon of the neck.
- Gastritis. Acute or chronic inflammation of the mucous membranes of the stomach. Manifested by epigastric pain, dyspepsia, nausea, decreased performance. A “telling” symptom of gastritis is plaque on the organ of taste. It is associated with the pathological activity of pathogenic microflora.
- Candidiasis. Mycotic infection of the mouth caused by opportunistic yeast-like fungi Candida albicans. The mucous membranes swell and swell. They bake and crack. The lips begin to peel, and pockets form in their corners. The tongue and throat with thrush are very coated. It gets to the point where the kefir-like slurry can be easily removed with a brush or a teaspoon. But this does not help improve the situation, as soon its volume increases. This happens until medications are taken that destroy candida.
- Chlamydia. The pathology is sexually transmitted and, it would seem, should have nothing to do with oral health. However, in practice everything turns out differently. The violation provokes a sharp decrease in immunity. When the number of chlamydia increases greatly, the oral cavity becomes affected - a sticky white coating appears on its walls.
- Pneumonia. Whitish folds on the sides of the muscular organ most often indicate pathologies of the upper respiratory tract. They can be removed with a brush and paste, but they quickly return as the main provoking factor (pneumonia) continues to act.
- Chronic alcoholism. Alcohol addicts are diagnosed with multiple diseases of internal organs. After binge drinking, they are faced with a white tongue and an unpleasant aftertaste. In this case, the plaque caused by ethanol intoxication never reaches the tip of the tongue and is always localized at its root.
- Lung oncology. Cancer patients with lung damage often have a coated tongue.
The described symptom also occurs among pregnant women. The reason for this is a sharp change in hormonal levels. After childbirth, the situation returns to normal on its own.
When to see a doctor
Visit your dentist if the spots don't go away within a week. White spots, cracks, ulcers and leukoplakia can cause oral cancer. In this case, the sooner a dangerous disease is recognized, the more favorable the outcome awaits the patient [6].
“According to WHO, in the Russian Federation alone in 2015, 589,341 cases of malignant neoplasms were identified (including 270,046 and 319,335 in male and female patients, respectively).
The increase in this indicator compared to 2014 was 4.0%, and these numbers are growing” Mikhalchenko D.V., Associate Professor, Head of the Department of Volgograd State Medical University [6]
Possible diseases
Plaque and soreness of the tongue are not always associated with damage to this particular organ. Sometimes this is a consequence of pathologies of other systems.
Possible diseases:
- glossitis;
- oral candidiasis;
- gastroenteritis, peptic ulcer;
- damage to the nervous system;
- blockage of the salivary ducts;
- acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis);
- endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus);
- autoimmune pathologies;
- infectious diseases (herpes, long-term tuberculosis, etc.);
- leukoplakia (characteristic of severe immunodeficiency).
Often a white coating and pain due to dry tongue accompany dehydration. In this case, the person urgently needs medical help.
Prevention of oral diseases
To avoid the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, follow simple recommendations:
- Pay close attention to your oral hygiene. Use a toothbrush with a special surface to clean your tongue. To get rid of food debris, rinse your mouth with water after eating. Do not neglect brushing your teeth before going to bed, otherwise the bacteria accumulated during the day will actively multiply, causing plaque to appear.
- Eat right. Too spicy and hot food injures the oral cavity and tongue. Eat more vegetables and fruits, and less processed food, to get the most nutrients, vitamins and minerals.
- Give up bad habits. These include not only smoking and alcohol - you should also not bite your nails and pencils, eat poorly washed vegetables, and brush your teeth with inappropriate objects. All this increases the chances of infection.
- Visit your dentist regularly. Preventive examinations will help identify any disease at an early stage and begin treatment in a timely manner.
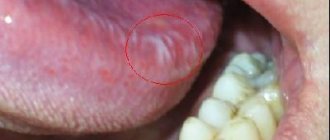
Pimples on tongue
Pimples on the tongue are painful and cause discomfort, but they are easily treated and do not cause complications. A pimple on the tongue can appear for many reasons, most often due to microtrauma of the tongue, stomatitis or herpes. In principle, there cannot be acne on the tongue, since there are no sebaceous glands on it. Those formations that are mistaken for pimples are not actually pimples - they are not filled with purulent exudate. These are small swellings and ulcers on the surface of the tongue. They are white, pink, red, yellow, depending on the complexity of the disease and the cause of formation. Small pimples are very painful, they interfere with eating, talking and even bother the patient at rest.
White pimple on tongue
A white pimple on the tongue most often appears as a result of stomatitis or candidiasis. These two diseases are treated completely differently; you should consult a doctor at the first symptoms in order to correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment. Candidiasis is characterized by white pimples and a coating on the tongue, which in appearance resembles cottage cheese and covers the entire surface of the oral cavity. There are also white pimples on the base, tip and under the tongue.
With stomatitis, small pimples appear on the tongue. There are usually many of them, they can merge with each other. These small white pimples at the tip or root, at the base or underneath are very painful and itchy. The pain intensifies after eating. If such symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Treatment consists of antiseptic treatment of the surface of the oral cavity and lifestyle correction, since the main cause of stomatitis is insufficient oral hygiene.
Red pimple on tongue
Red pimples on the tongue are the main sign of glossitis, an inflammatory disease. Outwardly, they look like inflamed red dots that hurt.
Glossitis can appear for many reasons:
- Allergic reaction;
- alcohol abuse;
- eating too hot and spicy food;
- the presence of the herpes virus.
The appearance of yellow pimples on the tongue is usually not an independent disease. Often with stomatitis or candidiasis, the coating on the surface of the tongue takes on a yellowish rather than white tint. Yellow pimples most often also mean either candidiasis or stomatitis.
Pink pimples on the tongue , like yellow ones, are not an independent disease. Usually they are an early stage of glossitis, when the inflammatory process has not yet reached its peak. If pink acne appears, you should immediately consult a doctor for advice.
The main causes of acne:
Mechanical damage
In the process of chewing or biting food, we bite our tongue, resulting in a slight mechanical injury. The risk of surface damage increases when consuming hard foods with sharp edges (crackers, chips, seeds). A small painful swelling or bump forms at the site of the injury, which after some time turns into a white pimple.
You should exclude spicy and hot foods from your diet, carefully monitor oral hygiene, and after a few days the pimple will disappear on its own.
Allergic reaction
An allergic reaction is possible to food, medicine or toothpaste. This causes small white pimples and sores to form that hurt and irritate when eating or drinking liquids. If your doctor suspects an allergy, it is very important to identify the allergen and eliminate it from your diet.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is a common cause of white or red pimples on the surface of the tongue. The main cause of stomatitis is insufficient oral hygiene, exposure to pathogenic bacteria on the mucous membranes due to dirty hands, unwashed fruits and vegetables. Most often, children suffer from stomatitis, because they tend to put everything in their mouth. At the first suspicion of stomatitis, you should consult a doctor, he will prescribe medications that relieve itching and soreness of the tongue, as well as promote the speedy healing of ulcers and pimples.
Herpes
Herpes can affect all mucous surfaces of the human body, including the oral cavity. In this case, watery pimples may appear on the tongue and inner surface of the cheeks. Without proper treatment, herpes can eventually affect the entire body, including the brain. Therefore, if you have a herpes virus, you should consult a doctor and undergo a course of antiherpetic therapy.
Poor nutrition
If you eat too much spicy and hot food, inflammation of the tongue, or glossitis, may occur. Drinking alcohol in large quantities, as well as smoking, can cause inflammation of the tongue. Therefore, when the first problems appear, you should immediately try to get rid of bad habits.
Pathologies of the patient's internal organs
Pimples on the tongue can be a manifestation of various diseases, including candidiasis or tuberculosis. If a pimple does not go away for a long time, be sure to consult a doctor.
Weakened immunity
If the immune system is weakened as a result of a previous illness or due to a lack of vitamins and microelements, small painful pimples may appear on the surface of the tongue. It is necessary to take immunomodulators, as well as drugs with lactobacilli to normalize intestinal function and correct the activity of the immune system.
You can only get rid of a pimple on your tongue using comprehensive measures. It is necessary to consult a doctor to determine the true cause of its occurrence. The oral cavity should be kept clean, preferably rinsed with a soda solution or a decoction of St. John's wort. It is also necessary to strengthen the immune system and limit the consumption of spicy and too hot foods so as not to irritate the inflamed nodule.
A pimple at the base of the tongue makes it difficult to swallow and even talk; it hurts and causes a lot of trouble. It could be stomatitis, a fungal infection, a sore throat or pharyngitis. Only an experienced doctor can make a correct diagnosis.
A pimple on the tip of the tongue can pop up at the site of a microtrauma as a result of an infection entering the wound.
In any case, it is advisable to consult a doctor and get tested to make an accurate diagnosis.
For any questions, please call: +7 (343) 2000 730; +7 We work daily, without breaks: Mon-Sat 09.00-21.00 Sun 10.00-20.00 We are waiting for you at the address: Ekaterinburg, st. Gottwald 14a, office 6. Dentistry "MK DENT"
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment for stomatitis is comprehensive.
- Anesthesia. To eliminate pain, the dentist may prescribe topical medications containing lidocaine or analgesics.
- Antiviral therapy. If the disease is caused by a herpes virus, the doctor prescribes antiviral drugs of the appropriate group of effects.
- Antibacterial therapy. In case of bacterial stomatitis, local treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions and dental ointments with antibacterial action is mandatory.
- Antifungal therapy. Stomatitis can be the result of fungal activity in the mouth. This form is more common in children, but is not excluded in adults. The specialist prescribes the patient a strict regimen of antifungal drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy. It is carried out in cases of severe inflammation. The dentist recommends taking anti-inflammatory systemic drugs that have a targeted effect depending on the pathogen or cause of tongue stomatitis.
- Diet. Patients with stomatitis are prescribed a diet that excludes foods that can aggravate irritation of the mucous membrane and tongue. So dentists recommend avoiding hot, spicy, sour and salty foods. Smoking and drinking alcohol should be avoided.
Together with the treatment of stomatitis, treatment of diseases of the respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, inflammation of the gums, caries, etc. can be carried out.
Treatment Options
Treatment is closely related to the cause of the condition. Possible treatment regimens:
- antibiotics + antisecretory drugs + histamine receptor blockers + proton pump inhibitors for peptic ulcer disease;
- antifungal agents in the form of capsules, tablets or drops for candidiasis;
- opening the salivary ducts and removing blockages;
- correction of hormonal disorders with hormone replacement drugs;
- anti-inflammatory drugs and local antimicrobial agents for glossitis;
- infusion therapy and oral rehydration solutions for dehydration;
- antibiotic therapy for acute tonsillitis;
- antiretroviral therapy for immunodeficiency due to HIV.
The positive effect of treatment occurs immediately or after 3–5 days. If there is no improvement, a change in therapy or re-examination may be necessary.
There is no need to live with pain in the tongue and endure it, hoping for self-healing. It is better to consult a doctor in a timely manner, discover the cause and remove it, than to wait for serious complications.
Read also: Why does the tongue have a white coating?
Dear patients! Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33
Be healthy and happy!