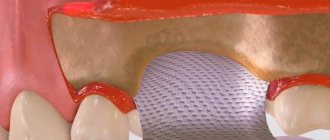
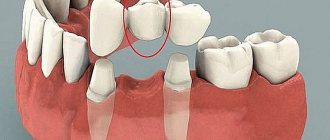
The implant is a titanium pin that is implanted into the bone. Subsequently, a crown is fixed onto it. The intermediate element between the crown and the implant is the abutment.
The abutment is an integral part of the implantation process. The aesthetics, durability and strength, as well as the functional characteristics of the implant, depend on this link. Nowadays, dentistry offers several types of abutments. They differ in size, shape, and are also made from different materials.
Main types of abutments
Standard. It is made according to a template. Abutments are produced in different sizes and shapes. In general, this design can be called universal, because it is suitable in most cases. In addition, the standard abutment has a reasonable price. Disadvantage: when using it, the individual structural features of the dental system are not taken into account and aesthetic defects may occur.
Individual. When making it, the shape of the teeth and gums and the characteristics of the patient’s bite are taken into account. A 3D model of the jaw is used, which eliminates errors and deviations. Such abutments are distinguished by high quality, ideal compatibility, good aesthetic and functional characteristics. Compared to standard abutments, custom abutments are more expensive.
Subtypes of abutments:
Globular. This type is used for mini-implants in case of prolonged absence of a tooth and thinning of the bone tissue.
Temporary. Called the gum former. It is necessary to create a natural gum contour around the implant and is removed immediately after implantation.
Angular. This abutment is used when installing an implant at a certain angle. In cases of structural features of the jaw. The angled abutment ensures an optimal connection between the implant and the crown.
An abutment is a small but very important part that is used to connect an implant located inside the jawbone to the crown, that is, the visible part of a new, artificial tooth.
Abutments are standard and individual.
In this article, we will help you understand their differences and which “adapter” is better.
A standard abutment is a template, factory-made option that is provided by the implant manufacturing company. Often, a dentist makes a choice in favor of one brand or another based on the requirements for prosthetics - after all, the greater the choice of abutments, the higher the likelihood of achieving ideal aesthetics and functionality of the fixed dental crowns.
Standard abutments are considered the most popular, cheaper and mass-produced. They are quite universal, but have a number of disadvantages that are definitely worth mentioning:
- are not able to accurately replicate the shape of the tooth, which sometimes indicates its artificial origin;
- during manufacturing, the manufacturer does not maintain ideal accuracy, minor errors in dimensions are possible;
- do not always exactly fit the shape of the gum, which requires additional surgical intervention to correct it;
- sometimes they put pressure on soft tissue, causing irritation or inflammation after the procedure.
An individual abutment is created for a specific patient. It uses modern material - zirconium dioxide, which is characterized by increased strength and durability. Its advantages are as follows-
- high aesthetics: an individual abutment supports the gum and fits very precisely to it, which allows you to achieve an ideal location of the mucous membrane in the area of the artificial dental crown; the metal is not translucent, which allows you to achieve an ideal appearance even with prosthetics of the front teeth
- repetition of the anatomical shape: an individual abutment is essentially a ground crown slightly smaller in size than the tooth itself. As a result, the artificial crown will have the correct natural shape and reliable fastening due to a tighter fit to the abutment.
- There is no risk of bone loss and implant rejection: when using a factory thin construction, cement can “clog” under the gum and lead to peri-implantitis, which is fraught with bone shrinkage and tissue inflammation.
Thus, the choice is obvious: a custom abutment is indeed much better than a template factory design.
However, the price of the product also plays a role in many respects, because labor costs are higher and the material zirconium dioxide is more expensive than ordinary metal. With all this, in terms of functionality, reliability and aesthetics, such an implant-based design fully justifies its cost.
How not to get confused in all the proposed options and settle on the right one? To do this, you need a consultation with a specialist in his field - an implantologist with experience who will take into account many nuances of the structures themselves and the characteristics of the patient.
What materials are abutments made from?
Functionality, appearance, and aesthetic indicators depend on the materials used.
Basic materials for making abutments:
- Titan. It is considered durable, reliable, biocompatible and affordable. Titanium abutments are used mainly for posterior teeth. If you install such an abutment in the smile area, it will shine through the crown.
- Zirconium. Zirconium abutments are durable and aesthetic. They are quite expensive due to their universal qualities. Ideal for frontal teeth.
- Ceramics. An excellent option for patients with allergies to metals and alloys. Due to the properties of ceramics, such abutments are used for implantation in the smile area.
— Combined abutments. They are an alloy of titanium and zirconium. They are distinguished by high aesthetic and functional indicators. Such abutments are quite expensive and are not offered by many manufacturers.
- Plastic. Plastic abutments are used only as a temporary structure. They have a low cost, and their reliability is also inferior.
“Weak points” of standard abutments
- Factory abutments do not support the gum, which affects aesthetics. After implantation, correction of the gingival margin through plastic surgery may be required.
- Abutments have a standard shape, so they do not follow the shape of the tooth. Their diameter is much smaller than a crown, which also increases the risk of poor installation.
- When fixing a crown, there is a high risk of the cement with which it is attached to flow under the gum. The crown is pressed into the gum to mask the metal of the abutment, which can allow cement to penetrate inside. Over time, this leads to serious complications, including peri-implantitis and implant rejection.
- Poor quality joining of the abutment can subsequently lead to the formation of gaps between the root rod and the crown. This is fraught with inflammation and the ingress of food debris.
- Factory products are made from titanium, and when the gums recede or recede, a dark stripe sometimes becomes noticeable. In addition, the metal can shine through in the light.
How to install an abutment
When one-stage implantation is performed, the implant and abutment are installed simultaneously. Basically, a one-piece structure is used. Afterwards, a temporary crown is immediately fixed. If the classical approach is used, then the implantation process takes place in several stages:
Preparation. This stage is universal for any implantation method. Includes consultation, diagnosis, testing, oral cavity sanitation and some individual indications.
Installation of an implant and gum former. The gum former is a plug that forms the contour of the soft tissue for a more natural appearance of the implant.
Abutment installation. Occurs after the implant has implanted (after 3-6 months). An incision is made in the gum, temporary plugs are removed and the abutment is fixed. The procedure takes place under local anesthesia and takes no more than half an hour. With the express implantation method, instead of making an incision in the gum, a small puncture is made. This avoids swelling and bleeding.
Abutment fixation
After the correct gum contour is formed, the former is removed. Then comes the stage of installing the abutment. There are several ways to attach it to an implant:
Cement fixation. A cement-based material is used. This is a fairly reliable method of fastening. Remaining cement must be carefully removed. If the cement composition gets under the gum, it will be almost impossible to clean it. In such a situation, there is a risk of developing an inflammatory process in the tissues around the implant. Implant failure may occur.
Screw fixation. An abutment is installed through the hole in the crown. Afterwards the hole is closed with a composite material and sanded. This fixation method makes it easy to remove the prosthesis if necessary, but this fastening is less reliable compared to cement.
Manufacturing (modeling) technique in the laboratory
- After the artificial root has healed and the gingival contour has been formed, an impression coping is screwed onto the implant to take an impression .
- The impressions are sent to a dental laboratory to make plaster models .
- The finished model is scanned and transferred to a computer program for modeling.
- An abutment is cut out of a solid block blank using a computerized machine using CAD/CAM technology .
»
Is it possible to replace the abutment?
During the implantation process, several elements are used - implant, abutment, crown. Any of them can fail over time or for certain reasons. The artificial root is made of high-strength titanium, so it has a lifetime service life. The crown and abutment may need to be replaced.
Before implantation, it is recommended to carefully select the manufacturer of the elements. If necessary, it is easier to find a replacement abutment from a trusted and reliable manufacturer. Today, there are many companies offering high-quality implants and components from premium to economy class.
How is it different from standard
An individual abutment, unlike a regular one, is not a round stump, but a full-fledged tooth stump, similar to a natural crown sharpened for a prosthesis. Due to the fact that the standard adapter is much narrower, during fixation, excess cement flows into the space between the implant and the gum. An error can provoke tissue inflammation and rejection of the titanium root in the early or medium term. Such consequences can be easily prevented by installing an individual design.
«
Possible complications
The most serious complication is implant rejection. It is accompanied by inflammation, pain and fever and requires urgent medical attention. In addition, the following complications may be present.
- Premature destruction of sutures, which provokes bleeding. To avoid it, it is important to follow a diet and not load the jaw during the recovery period.
- Severe growth of soft tissue. The problem requires urgent installation of a gum former, so you need to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
- Unreliable fixation of the crown. Most often caused by a violation of the abutment thread, which is a consequence of a manufacturing defect or installation defect.
- Implant loss. Possible due to excessive load or force.
It is important to know! You should not try to straighten or insert the implant yourself. In case of any damage, bleeding or inflammation, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Features, pros and cons of implantation
Today, implantation is one of the most advanced technologies for restoring teeth. Its advantages: high comfort (the patient does not feel the prosthesis as a foreign body in the mouth), physiological load on the jaws and prevention of bone tissue atrophy. The disadvantages include the complexity of medical procedures, as well as the risk of rejection.
The technology is improved every year, new protocols appear, current materials are used, an individual abutment , which improves the solidity of the structure and prevents the formation of inflammatory processes.
Screw type of crown fixation
With the screw type of fixation, the implant consists of two parts: a titanium screw and the crown itself. In this case, the abutment is integrated into the crown and forms one whole with it. And the biggest advantage of this implantation method is the absence of cement connecting material. In this case, the crown can be removed without damage, for example, if professional hygiene is necessary.
A distinctive feature of screw-retained crowns is a small hole in the middle of the chewing surface of the crowns (if we are talking about lateral teeth), and the palatal or lingual surface of the incisors (if these are front teeth), which is tightly sealed with a composite material matching the color of the crown.
To be able to manufacture screw-retained crowns, it is necessary to clearly plan the position of the implant using a surgical template. Otherwise, if the implant is installed at a large angle, you will have to resort to a cement type of fixation.
This is why our doctors pay so much attention to diagnostics and planning in order to determine in advance the position of the implant in the bone tissue relative to the dentition and choose the type of fixation of future crowns. This is important for successful and efficient work.
Painless implantation by our experienced doctors:
- high survival rate of more than 98% , which is higher than the international average of 96%
- the best anesthesia that is suitable for 100% of patients
- implantation in perfectly sterile conditions - no infections
- is possible in 1 day immediately after removal of a damaged tooth
- diagnostics using 23 parameters before implantation for high results
- extended warranty
- high-quality effective treatment at prices in the residential area of Yasenevo
Features of care
types of individual abutments are distinguished by shape : angular, spherical, gum former.
Regardless of the type, the individual device requires special care.
- In the first days after surgery, it is forbidden to use any toothbrush; only rinsing with aseptic solutions and soda is recommended.
- From day 5, the use of brushes with soft bristles is allowed; the paste should not contain abrasive elements that can damage the abutment.
- It is forbidden to eat solid foods, sweets, or drink drinks with dyes until the permanent crown is installed.
- Smoking and drinking alcohol is prohibited.
Stages of installing an abutment on an implant
The process of installing this type of prosthesis should be divided into several stages:
- implantation of the structural base;
- securing the gum former immediately after implantation;
- period of engraftment of the base element (about three months);
- removing the “plug”, securing the connecting element;
- installation of the outer part of the dentures.
There is a scheme according to which, under certain conditions, the connector is mounted immediately after securing the implant, bypassing the stage of gum formation. In this case, the patient must be extremely careful to avoid putting stress on the dentures so that the base does not move.