Bite pathologies are one of the most common reasons for visiting a dentist. People have been engaged in returning teeth “to their place” since ancient times - there is evidence that this issue was of interest in ancient Egypt. However, only in recent decades have doctors come to the conclusion that it is necessary to correct an abnormal bite. Timely orthodontic treatment helps to avoid serious consequences for the entire body in the future. In this article, the leading orthodontist at the ZUUB dental clinic on Lipetskaya in Moscow, Dmitry Anatolyevich Polovkov, talks about the dangers of malocclusion and ways to correct it.
Correct bite - what is it?
Normal, or physiological occlusion, is characterized by the absence of disturbances in the arrangement of the dentition relative to each other with the jaws fully closed. He can be:
- regular, or orthognathic - in this case, the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth by a third of their height and there are no pronounced gaps between the dentition;
- straight - both jaws clearly close;
- biprognathic - both the upper and lower dentition are slightly tilted forward;
- progenic - only the lower jaw is pushed forward a little, but this does not prevent the cutting edges of the teeth from completely closing.
Correct bite is the absence of pronounced gaps between the teeth when the upper teeth are in contact with the lower ones opposite them. Orthodontists determine a bite without pathologies based on the following characteristics.
- The upper front teeth overlap the lower ones by 1/3 of their height.
- The incisors and canines are arranged in an even, arched line without distortions or crevices.
- The upper teeth protrude slightly outward, the lower teeth “look” slightly inward.
- All teeth are clearly below each other.
- The center of the jaws vertically coincides with the midline of the face, there are no protruding parts of the cheekbones or chin.
It is important to remember that in order to form a correct bite, you need to be careful about teething and caring for them.
Removable
The entire period of loss of baby teeth and growth of permanent teeth - from 5-6 years to 11-13 years - the child has a mixed bite. Permanent teeth erupt at certain times and in a certain sequence. If these deadlines are greatly violated in one direction or the other, this can lead to various consequences.
photo: mixed bite in a child
Irregular eruption of permanent teeth
Too early eruption can serve as a symptom of endocrine disorders and even indicate the growth of tumor formations in the jaw.
If, on the contrary, growth is seriously delayed, then such teeth are called impacted - formed, but not grown . This phenomenon can cause not only frequent neurological pain, affect the development and position of neighboring teeth, but also provoke the development of tumors.
Causes of malocclusion
Malocclusion (malocclusion) is due to various reasons: congenital or acquired. An important role is played by genetic factors, as well as insufficient intake of calcium into the mother’s body when carrying a child. Hereditary problems with bite require certain nuances in treatment. Therefore, before carrying out any orthodontic manipulations, the doctor talks with the parents and learns about all the possible factors in the occurrence of pathology.
Acquired malocclusion develops gradually. It appears at different ages due to its own reasons.
In childhood
- Bad habits (finger sucking, pacifiers, chewing on objects).
- Being on artificial feeding.
- Pathological bone formation.
- Teeth grinding (bruxism).
- Lack of sufficient solid food in the child's diet.
- Mouth breathing (formed as a habit or due to respiratory diseases).
- The replacement of baby teeth occurs too sooner or later.
- Pathologies associated with metabolism.
- Calcium and fluoride deficiency.
- Pronounced carious lesion.
- Injuries of the maxillofacial apparatus
In adults
- Installation of unsuitable dentures.
- Diastemas that form as a result of tooth extraction.
- Various types of injuries.
- Lack of space for eights (wisdom teeth).
- Unusual localization of the language.
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Treatment methods
The first thing that needs to be done is preparation from a dentist-therapist in the form of sanitation of the oral cavity. Before installing orthodontic structures, it is important to treat carious and gingival pathological processes and remove tartar using an ultrasonic tip.
Next, surgical preparation may be necessary - extraction of units, removal of excess soft tissue structures, plastic surgery of the labial frenulum. Removal of destroyed or supernumerary units may be required. It happens that further treatment tactics force the extraction of healthy teeth that interfere with the orthodontic process.
What to do if specialists discover an incorrect bite? - be sure to treat. Treatment is divided into 2 periods - active and retention.
Taking into account all the nuances of the clinical situation, at the active stage it is possible to use various correction options:
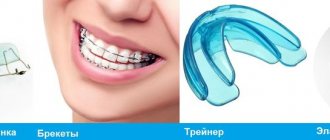
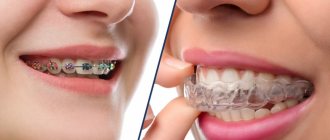
Aligners (transparent aligners).
Transparent soft silicone or polyurethane plates, individually manufactured according to a 3D print. They are worn constantly, removing them only for meals and hygiene. They are not visible in the mouth and do not cause discomfort. It is necessary to meet with an orthodontist once every few months to control the movement of units and receive a new batch of aligners, which are independently changed every 2 weeks. Aligners achieve effective results in cases of crowded units, narrow or wide dentition, or correction of previous treatment with braces.
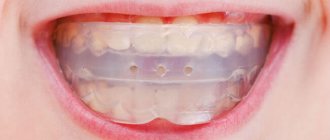
Trainers
Silicone massive mouth guards with sides for wearing at night, and during the day for no more than a few hours. Suitable for treating children under 12 years of age, and at older ages they are used for correction or prevention.
Removable plate-devices.
They are used during the period of primary occlusion to reduce the period of further treatment with braces and improve sound pronunciation. The best results are achieved when interacting with a speech therapist.
Braces
Prescribed for the correction of various bite pathologies. Specialized buttons are attached to the coronal surface of the units with medical glue and connected with an arc. Thanks to the shape memory arch, the alignment of the dental units occurs.
Braces are classified according to:
- Places of attachment - vestibular (external) and lingual (internal).
- The method of attachment to the arch is ligature and self-ligating.
- Materials: plastic, metal, ceramics, titanium, sapphire, silicone.
The cost of a braces system varies depending on its type and the material used. They also need careful home care - special brushes, brushes, pastes, floss.
With age, restrictions on the use of certain systems and materials appear. The older the patient, the longer (more than a year) and more difficult it will be to change the location of the units due to the intractability of the bone tissue. Therefore, you should start correcting your bite as early as possible.
In the final retention period (preservation of the result), the patient has a retainer attached to the inner surface from canine to canine, and it is recommended to wear night guards. This period continues throughout the life of the teeth.
Surgery
Radical orthodontic surgery is considered when there is severe maxillofacial deformity, and all of the above correction methods will not be effective. An incision is made in the gum tissue and the jaw bones are shifted to an anatomical position. It is also possible to use implantation to restore missing units; implants add a fulcrum for the correction of individual areas. To speed up the treatment time, the orthodontist may additionally need mini-implants, which can be unscrewed after their work. They will allow in some cases to avoid surgical intervention and move an entire group of teeth.
Orthopedics
At the end of orthodontic treatment, to achieve the best aesthetic result, it is recommended to perform prosthetic treatment of the frontal group of units with veneers or crowns. This way, the optimal size of the crown parts of the teeth is achieved, suitable for facial characteristics.
Types of malocclusion in adults and children
Dentists usually divide anomalous occlusions into planes.
- Sagittal - characterized by elongated/shortened rows of teeth.
- Transversal - narrowed/expanded dentition is visible.
- Vertical - the presence of shortened/elongated certain areas in the dentition.
In addition, in dental practice it is customary to use the following classification of occlusion.
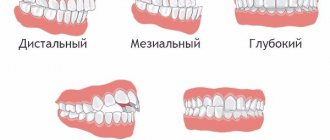
- Distal.
Sagittal occlusion with the upper jaw pushed forward. - Mesial.
Also a sagittal variety, but with the lower jaw moving forward. - Cross.
Transversal pathology with displacement of the jaws, which can only be partially formed, in one direction or another. - Open.
Vertical occlusion occurs with both partial and complete non-occlusion of teeth. - Deep.
The so-called traumatic, contributing to damage to the enamel. Characteristic is almost maximum overlap of the lower rows with the upper ones. - Vertical occlusal anomaly.
In addition to the above listed occlusion disorders, some experts identify 2 more types of anomalies:
- dystopic bite - displacement of one or more teeth;
- reducing - formed due to damaged and (or) lost teeth.
How to correct a child's malocclusion
- Children under 7 years of age
are shown a set of gymnastic exercises and massage that will help solve the problem. - Children under 10 years of age
are already prescribed trainers, with the help of which they can set the desired direction for their teeth. They must be worn for a certain number of hours during the day. But, if the pathologies are more advanced, removable plates and mouthguards are used. Correction of the anomaly takes approximately 2 years. - For children aged 10-12
years, braces are used to correct their bite - special orthodontic structures consisting of a power arch and clasps that set an individual direction for each tooth. They cannot be placed at an earlier age; it is necessary that all milk teeth be replaced by permanent ones. How long to wear braces for malocclusion is determined by the treating orthodontist.
How to correct malocclusion in an adult
A very common treatment method for adults is wearing braces. Transparent aligners (aligners) are also very popular now. They are made of transparent plastic material. Aligners are effective in correcting impaired occlusion, are easy to use and look very aesthetically pleasing. All details about this technique can be found here.
In cases where the patient is not in the mood for long-term bite correction with aligners or braces, there is another solution - microprosthetics. In this case, special overlays are installed on the teeth - veneers, with the help of which you can correct uneven teeth and gaps between them. But if there are serious malocclusions, this technique is not used.
There are bite defects for which only surgical treatment is indicated. Examples include: severe malocclusion, facial asymmetry due to trauma or hereditary causes, and chin dysplasia.
Each method of orthodontic treatment has both indications and contraindications. Only an orthodontist can determine the method of treatment after a thorough examination and full diagnosis.
Pathogenesis
In orthodontics, there are five stages in the formation of the natural anatomical structure of the dentofacial apparatus, and at each of them there is a possibility of the formation of deviations from the norm:
- 0-6 months - manifestation of sucking skill, providing sufficient stimulating load on the tissues.
- From 6 to 36 months. — eruption of milk units that make up the temporary dentition.
- 3-6 years - the preparatory stage, during which the active development of the jaws takes place, necessary for a change in completeness.
- 6-12 years - mixed period, gradual renewal of elements along the entire length of the rows.
- Up to 16 years of age inclusive is the final stage, following which permanent occlusion is formed.
It is worth noting that the formation of anomalies is possible even at the stage of intrauterine stay, being provoked by infectious or chronic diseases, toxic poisoning and other factors affecting the initial characteristics of the rudiments.
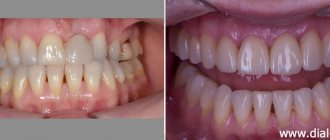
Consequences of malocclusion
It is a mistake to think that a pathological bite concerns only appearance and only leads to an unattractive smile. This is where the problems arise that are more serious. For example, in 90% of people with abnormal occlusion, incorrect posture is also detected. There is a logical explanation for this: with a broken bite, the center of gravity of the head shifts. This in turn affects the compensation mechanisms of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the maxillofacial system. The result of all this is an increase in the pathology of teeth closure.
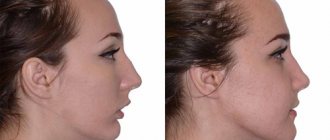
Aesthetically, occlusion abnormalities lead to facial asymmetry. A weak-willed chin becomes pronounced, and lips protrude unattractively.
What is the danger of malocclusion?
In addition to visual problems, more serious dysfunctions often occur, including internal organs.
- Due to increased and uneven load on the teeth, periodontal disease develops and teeth begin to decay.
- Inadequate chewing of food leads to disruption of the digestive system.
- The functioning of the temporomandibular joint is impaired.
- The respiratory system also begins to malfunction.
- Slow metabolism.
- Increased risk of developing caries, especially with cross-closing teeth.
- Problems with pronunciation of sounds.
In addition, with malocclusions, daily dental care becomes much more difficult, which contributes to the constant accumulation of plaque on them.
Make an appointment
right now!
Polovkov Dmitry Anatolievich
Orthodontist
What to do to avoid malocclusion.
The consequences of malocclusion can be avoided by taking measures in time, namely in childhood. Here the responsibility falls largely on parents, who can promptly pay attention to problems and carry out prevention. It is important to take into account the risk of congenital disorders, hereditary predisposition, and also eliminate unfavorable factors:
- prevent the development of rickets and other diseases that impair bone growth;
- bottle feed your baby correctly;
- monitor the position of the child’s body during sleep (posture without tension, head not tilted back, etc.);
- maintain correct posture;
- timely wean your child off the pacifier, thumb sucking habit, toys and other objects;
- treat baby teeth immediately, because their early loss (as well as too late) can negatively affect the bite;
- to prevent nasal breathing disorders, namely to treat diseases of the ENT organs and ARVI.
When anomalies in the development of teeth are identified in childhood, timely assistance from an orthodontist will help solve problems faster than in advanced cases in adults. In children, as a rule, there is no need for surgical intervention yet, and even a complex of therapeutic exercises for the facial muscles can significantly help in correcting the bite.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Prevention
Adults need to regularly take their child to a consultation appointment with a pediatric dentist and orthodontist once every six months. Treatment of pathological foci in mammary units should be carried out in a timely manner. For harmonious sleep, you need to buy your child a suitable pillow.
After 3 years, you need to monitor the grinding of your child’s teeth, which is a natural process. If this does not happen, then grinding is necessary, otherwise the NP will not take its natural anatomical position. Also, in this age interval, interdental spaces appear, which is normal. Jaws grow, and emerging molars need a lot of space. If there are no gaps, then a malocclusion may occur, so you need to contact a specialist to monitor the situation.
Doctors at the branches of family dentistry West Dental in Yanino-1 and Vsevolozhsk offer effective correction of bite pathology using modern treatment techniques, at a reasonable price. An understanding of the prevention and treatment of dental pathology is formed. To make an appointment with our specialists, you can fill out the online form on the website or by calling the administrators.