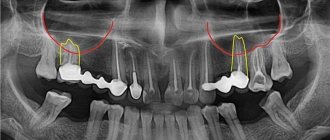
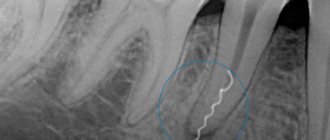
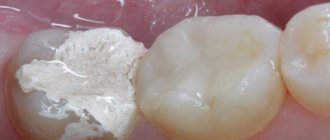
Treatment of the upper chewing teeth is associated with the risk of damage to the maxillary sinuses due to their close anatomical proximity. When treating root canals, filling material may end up in the sinus cavity, which entails the development of serious purulent processes. Our Center has been specializing for many years in providing assistance to patients who have become victims of unsuccessful therapy. Such situations are corrected by experienced maxillofacial surgeons with ENT training using modern gentle surgical techniques
Causes and consequences of filling material in the maxillary sinus
In the maxillary region there are the maxillary sinuses, which occupy most of the internal space. Sometimes they are separated from the upper chewing teeth only by a thin bone septum (bottom of the sinus). During endodontic treatment, especially if the roots of the tooth have grown into the sinus cavity, the dentist may not calculate the effort, damage the apex of the root and the bottom of the sinus, as a result, the filling material falls into the sinus, “taking” purulent masses with it.
It is good if the problem is identified immediately and the patient is referred to a maxillofacial surgeon for immediate removal of the material. Otherwise, inflammation occurs in the sinus and the person comes for help himself, but with consequences.
Long-term presence of filling material in the maxillary sinus is dangerous due to the development of complications:
- chronic odontogenic sinusitis and sinusitis;
- mycetoma (fungal infection of the nasal sinuses);
- inflammatory processes on the roots of adjacent teeth;
- encephalitis and meningitis;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw.
Treatment procedure
Regulations for actions during treatment of a pathological condition:
- The foreign body must be removed; this is the main task of treatment.
- With such a lesion, inflammatory processes regularly develop. They are generated not only by filling material that has found its way into an unusual place, but also by oral microflora that has penetrated into the resulting hole or by swelling from inflammatory processes in the gums. They need to be cleaned.
- The patient needs to undergo treatment of both the maxillary cavities and the oral cavity, eliminating the causes of the disease.
Removal of a foreign body always occurs only through surgery. In this case, the cavity is penetrated through a hole and the object is directly removed. There are two such methods:
- laparoscopic;
- endoscopic.
The first method is more traditional. In this case, an incision is made between the upper lip and gum and the material is removed through the resulting hole. In the second case, the paranasal sinus is punctured in the place where the bone is thinnest and a foreign particle is captured through the resulting hole with a special tool and then brought out.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia and lasts no more than thirty minutes. The second method is most widespread. Laparoscopy is usually used in situations where, for some reason, endoscopy is not recommended.
After this, drug treatment of the inflammatory process is carried out. For this, immunostimulants or antibiotics, as well as other medications, can be used. Additionally, antibacterial solutions or an antiseptic are used to wash the damaged paranasal sinus.
Vitamin complexes are also used in treatment.
Symptoms of complications
A person feels the presence of a foreign body in the sinus 2-3 days after treatment due to the characteristic symptoms of sinusitis. In some cases, it may not manifest itself for months or even years with a strong immune system, but makes itself felt when the body’s defenses are weakened. Also, the rate of development of the pathological process depends on the composition of the filling material that ends up in the sinus, the presence of components in it that can provoke inflammation, and the growth of fungal flora.
Characteristic symptoms:
- chronic nasal congestion;
- aching headaches;
- pain in the upper jaw, worsening with chewing;
- pain when lightly tapping the facial bone under the eye closer to the nose;
- thick purulent nasal discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- increase in body temperature in advanced conditions.
The difference between sinus inflammation due to the presence of filling material in it and sinusitis-sinusitis that accompanies influenza and colds is a one-sided manifestation of symptoms. Signs of odontogenic sinusitis are usually only on the side on which the tooth was treated.
What dangerous consequences does a foreign body lead to?
A foreign object in the maxillary sinuses can lead to the following complications:
- bacterial or fungal sinusitis;
- encapsulation in the form of a cyst or other benign disease;
- granuloma formation.
In more complex cases, suppurative processes in the maxillary sinuses cause the development of the following complications:
- frequent colds and inflammation of the nasal cavity and sinuses;
- meningitis;
- hypertrophy of the mucous membrane;
- damage by coccal flora to other organs and systems (for example, heart muscle).
A particularly dangerous complication is inflammation of the meninges. When meningitis develops, the patient develops the following symptoms:
- significant increase in temperature;
- headache in the forehead;
- frequent vomiting that does not bring relief;
- rash on palms and soles.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor!
And the possible consequences of getting filling materials can only be prevented by timely consultation with a doctor and regular preventive examinations in the mode prescribed by the doctor.
How to warn
Most often, underexamined patients encounter perforation of the maxillary sinus during dental treatment, when the doctor, without a clear understanding of the location of the roots, carries out treatment according to the standard protocol.
Rest assured that in our Center you will not encounter such risks.
The following allows us to prevent the penetration of filling material into the maxillary sinus: CT diagnostics before the start of tooth treatment.
Based on high-precision data, the doctor’s actions are planned and a safe endodontic protocol is selected.
Unfortunately, x-rays, which most clinics resort to due to the lack of expensive equipment, do not provide a complete picture. In our Center, the examination is carried out using a modern CT scanner Sirona Gallileos (Germany) with advanced settings in ENT mode. Such 3D images allow you to study in detail the location of the maxillary sinuses and dental roots, calculate the thickness of the bone septum, and determine the presence of dental cysts. Qualified endodontists
Treatment of teeth bordering the maxillary sinuses should be extremely careful, careful and meticulous. A doctor without experience, sufficient theoretical knowledge and practical skills to work in emergency situations is likely to make mistakes. In our Center, endodontic dental treatment is carried out by specialists with at least 10 years of experience; we do not hire students “off the street” or students immediately after graduation. Minimally invasive techniques for canal treatment under a microscope and 3D filling eliminate the risk of damage to the root canals and sinuses.
CT monitoring after treatment is also required . Before sending the patient home, the doctor must make sure that there is no perforation of the maxillary sinus, no dental material has entered it, and also evaluate the quality of canal filling. If pathological aspects are detected, the patient will have the opportunity to receive immediate help and avoid complications.
In case of unforeseen situations, when the bottom of the maxillary sinus is damaged and filling material gets into it, the patient should be immediately referred to a maxillofacial surgeon to remove the foreign body. Failure to provide timely assistance is fraught with the development of an acute inflammatory process with all the ensuing consequences .
Reasons for appearance
Many patients do not understand how filling material intended for use in dental treatment gets from the gums into the paranasal cavities?
Medicine knows cases of penetration of foreign substances under the following conditions:
- prosthetics;
- installation of seals.
Sometimes the walls between the gums and sinuses are quite thin, so pieces of filling material can easily get into the tissue through their damage. Injuries often occur during the dental treatment process.
The bone at the treatment site can be very thin, and in this case the roots will be located close to the paranasal cavities.
If there is not enough bone tissue at the treatment site, then in some cases the dentist artificially builds up the material. This is necessary for reliable dental treatment. In this situation, damage to the walls and penetration of a piece of dental substance into the sinuses is also often observed.
Filling material, once in the gum layer, often causes pain; a person feels severe pain while chewing food, discomfort after touching the damaged area.
The case when a foreign substance does not cause any reaction in the body is quite rare, but sooner or later they end in edema.
Why is it better to contact the ENT department of dentistry?
If you still find yourself in a difficult situation after unsuccessful dental treatment, you can only eliminate the consequences with a guarantee from an oral and maxillofacial surgeon with ENT training.
Otolaryngologists and ordinary dentists have a fundamentally different approach to the issue of diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the paranasal sinuses of odontogenic (“dental” origin). Each of them solves the problem only in its own part, while it requires an integrated approach.
The complexity of interaction between these two specialists in city clinics, the reluctance of each to delve into the problems of related specialties, and the lack of joint consultations lead to errors in diagnosis and choice of treatment tactics. As a result, the patient goes in a vicious circle from one doctor to another to no avail.
ENT dentistry has a number of undeniable advantages in this regard.:
- an integrated approach to solving the problem;
- accurate diagnosis using CT in ENT mode;
- treatment is carried out by a specialist equally knowledgeable in dentistry and otolaryngology;
- Carrying out gentle dental operations without mandatory hospitalization.
In our Center, operations to eliminate combined dental and ENT pathologies are performed by experienced surgeons with ENT training, candidates of medical sciences.
KolchinSergey Alexandrovich
Maxillofacial surgeon, 7 years of experience
Surgeon with ENT training. He specializes in ENT dentistry, including performing endoscopic operations and carefully removing tumors in the sinuses.
More about the doctor
Odontogenic sinusitis: traditional and endoscopic surgical treatment methods
Errors by a dentist during endodontic treatment of maxillary teeth often lead to the removal of filling material into the maxillary sinus [1, 3, 6]. Mechanical effects, as well as the cytotoxic and sensitizing effect inherent in almost all types of modern pastes for obturation of the root canals of teeth, lead to inflammatory and purulent-necrotic changes in the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus. As a result, an isolated chronic pathological process gradually develops, exerting a pathogenic effect not only on surrounding tissues, but also on the body as a whole [5, 7, 8].
The relevance of research
Current treatment methods for the above category of patients are often associated with surgical trauma to tissues not involved in the pathological process: bone, mucous membrane, soft tissues of the cheek. Some authors propose rather contradictory approaches. Some experts believe that the filling material in the sinus will dissolve over time, others believe that its presence does not have a harmful effect on the sinus mucosa and its functional state. This approach certainly leads to the progression and spread of the inflammatory process from the maxillary sinus to other paranasal sinuses and the orbit.
Some experts believe that the filling material in the sinus will resolve over time, others believe that it does not cause serious harm to the mucous membrane of the sinus and its functional state. A number of authors note that rhinogenic infection often exacerbates the latent odontogenic process, and this combination of sources of infection can lead to to hematogenous dissemination of infection with damage to individual organs and systems of the body [4, 5, 7, 10]. Carrying out only conservative treatment for odontogenic sinusitis caused by the removal of filling material in the maxillary sinus does not ensure complete recovery of the patient; moreover, after physiotherapeutic procedures, most patients experienced increased pain and exacerbation of clinical manifestations [1, 3, 9].
In this regard, complex treatment of patients with this pathology is impossible without surgical removal of the root sealant [1, 3, 11] as soon as possible [2, 3], however, such an intervention is associated with surgical trauma.
A number of studies analyze clinical situations with different localization of filling material in the maxillary sinus - in the cavity, near the lower, medial walls of the sinus, in the lateral corner, in the area of the lower wall of the orbit. The nature of the foreign body, its localization, volume, prevalence, as well as the severity of pathological changes in the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus, of course, require the selection of an adequate surgical technique and tactics for surgical access to the sinus [1, 4, 9].
Purpose of the study
A comparative study of the effectiveness of various methods for removing filling material from the maxillary sinus, including the use of endoscopic techniques, depending on the location of the root sealant in the sinus.
Material and research methods
A total of 72 patients were observed, including 27 men and 45 women, aged from 26 to 54 years, who had filling material in the maxillary sinus from 1 week to 18 months.
46 people (64%) presented with clinical manifestations of exacerbation of chronic maxillary sinusitis; 26 patients (36%) had no complaints during the initial examination, but a foreign body in the maxillary sinus was determined by x-ray. Clinical examination of patients began with a detailed X-ray examination. If necessary, computed tomography (CT) was performed, which made it possible to accurately determine the location and size of the foreign body located in the sinus.
Depending on the surgical technique used to remove filling material from the sinus, patients were divided into 2 groups. In the first group (52 patients), operations were performed using standard surgical instruments and a straight saw. In the second group (20 patients), endoscopic techniques were used.
The surgical intervention using standard surgical instruments was carried out according to a method described in sufficient detail in the literature [1, 3, 4, 9, 11], and is a modification of the Caldwell-Luke operation, the essence of which is as follows: appropriate conduction anesthesia is performed, then an arcuate incision is made in the mucous membrane and periosteum from the canine to the molars (Fig. 1), after partial peeling of the mucoperiosteal flap using a straight saw, a bone window is formed in the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus, over which the mucosa and periosteum are preserved. A window measuring 1.5x1.5 cm is cut out at an angle of 45?. After opening the sinus, the filling material and polyposis-altered mucosa are removed (Fig. 2).
Rice. 1. Detachment of the mucoperiosteal flap, preserving the periosteum and soft tissues (drawing by the authors). Rice. 2. Filling material in the sinus (drawing by the authors).
Then the bone fragment with the periosteum and soft tissues attached to it is returned to its place and fixed with a 5.0 vicryl suture (Fig. 3, 4).
Rice. 3. The bone window is fixed with sutures (drawing by the authors). Rice. 4. The wound is sutured (drawing by the authors).
Depending on the changes in the sinus mucosa, a “gentle” or “radical” maxillary sinusotomy was performed with mandatory complete (under X-ray control) removal of the filling material. 33 and 19 patients were operated on using the “gentle” and “radical” maxillary sinusotomy methods, respectively. Then, over the course of a week, all patients were prescribed 5-7 sessions of physical therapy using the Optodan laser device. By the end of the week, the stitches were removed.
Research results
When performing an X-ray examination, the accumulations of filling material brought into the maxillary sinus had a different appearance: single, clearly defined round intense shadows, many round shadows, clusters of irregularly shaped bodies of various sizes. The localization of these shadows was different, they were detected near the roots of the “causal” teeth and the bottom of the maxillary sinus in 35% of cases, and in 65% of cases they were located in the projection of the roots of neighboring teeth, in the upper medial corner or center of the sinus, and also near the orbital stack.
The main indication for the use of endoscopic technology was the short period of time the foreign body was in the sinus and the absence of pronounced changes in the sinus mucosa. According to the patients, the removal of filling material into the maxillary sinus was initially not accompanied by any symptoms. Painful sensations characteristic of exacerbation of odontogenic sinusitis appeared within 3 months. up to 1 year. It should be noted that in most patients the first clinical signs of the disease were diagnosed after suffering from acute respiratory viral infection. Patients noted a feeling of heaviness, discomfort in the affected sinus area, impaired sense of smell and nasal breathing, unilateral nasal congestion, pain of varying severity, radiating to the teeth and zygomatic area.
In all these patients, the foreign body and altered areas of the mucous membrane, which were mainly hyperplastic in nature, were removed. The length of the process depended on the length of time the filling material was in the sinus. When revising the sinus, the mucous membrane was preserved completely or individual polyps were excised without exposing the bone walls; sinus tamponade was not performed. In the postoperative period, in addition to traditional antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy, vasoconstrictor drugs were prescribed 3 times a day into the nasal passage on the side of the operated sinus, which ensured normal drainage and aeration of the sinus.
In 19 patients, changes in the sinus mucosa were of a diffuse polypous nature, and these patients underwent radical maxillary sinusotomy with the formation of an artificial anastomosis with the nasal cavity. Thus, such pronounced changes in the mucous membrane were observed in patients with a long-term presence of a foreign body in the sinus, even with a small amount of it.
The main indications for the use of endoscopic technology were short periods of presence of a foreign body in the sinus and the absence of pronounced changes in the sinus mucosa. Patients who used this method using endoscopic technology were also divided into two groups, depending on the access.
In the first group of patients, endoscopes were inserted into the sinus through the anterior wall of the sinus (Fig. 5). Eight patients were operated on using this method. In the second group of patients (12 patients), surgical access to the maxillary sinus was carried out through the natural opening in the middle meatus (Fig. 6).
Rice. 5. Maxillary sinusoscopy using endoscopic technology (drawing by the authors). Rice. 6. Endoscopic endonasal maxillary sinusoscopy (drawing by the authors).
This access is more physiological, as it allows to reduce the amount of surgical trauma to a minimum, preserve the “causal” tooth, provide conditions for normalizing the functions of mucociliary clearance into the nasal cavity, and reduce the rehabilitation period of patients by 30% compared to patients of the first group. In the postoperative period, the maxillary sinus was washed daily through the drainage with a Miramistin solution.
During endonasal intervention, correction of intranasal structures and endoscopic monitoring of the condition of the operated area were performed (Fig. 7-8).
Rice. 7. Endoscopic view of the endonasal approach to the maxillary sinus (drawing by the authors). Rice. 8. Correction of intranasal structures and endoscopic monitoring of the condition of the operated area (drawing by the authors).
Complex therapeutic treatment included the use of desensitizing, intranasal vasoconstrictor and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The effectiveness of the methods was assessed according to the following criteria: removal of all filling material from the maxillary sinus, absence of complications and relapses of the disease in the postoperative period at regular intervals.
conclusions
As the research results have shown, all the methods used make it possible to completely remove the filling material from the maxillary sinus. However, it is necessary to clearly differentiate the tactics of surgical intervention, based on the results of radiography and CT scans based on the location of the foreign body in the maxillary sinus and the condition of its mucous membrane, with the involvement of otorhinolaryngologists.
In case of total disruption of pneumatization of the maxillary sinus, signs of blockage of the natural anastomosis with the nasal cavity and disruption of nasal breathing functions, after removal of the filling material, the tactics of endonasal maxillary sinus are indicated with the restoration of natural communication and ventilation of the maxillary sinus through the nose.
The list of references is in the editorial office.
Diagnosis of complications in the maxillary sinus
Diagnostic measures are aimed at determining the size and localization of dental material, the degree and prevalence of inflammation of the mucous and bone tissues of the sinus.
- Visual inspection Performed using a nasal speculum, it allows you to determine the presence of a foreign body in the nasal sinus.
- Computed tomography in a special ENT mode is the most accurate type of diagnosis of combined dental and ENT pathologies today. The advanced settings of our tomograph allow us to evaluate the maxillary sinuses in full. This allows the maxillofacial surgeon not only to determine the presence/absence of a foreign body, but also to assess the condition of the mucous membrane, determine the amount of purulent masses, and the extent of inflammation.
A 3D tomogram gives a complete picture of the condition of the maxillary sinuses, the location of the filling material, and the degree of inflammation
Diagnostics and its features
The most effective way to make a correct diagnosis is computed tomography, but this does not exclude the use of other, more traditional methods:
- conducting a patient interview;
- use of rhinotherapy to study the maxillary sinus;
- X-ray examination;
- MRI;
- puncture of the maxillary sinus.
An experienced doctor can reliably assume the presence of such a disease, but it can be confirmed using computed tomography.
Stages of removing material from the sinuses
Treatment at the Center is comprehensive; we try to combine all procedures in one visit
- Preparation It is important to create sterile conditions to prevent infection of the surgical wound during the intervention. Hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity and treatment of compromised teeth are carried out.
- The operation is performed according to the selected protocol in the operating room of the ENT department. The patient is in a state of drug-induced sleep. After the operation, a CT scan is repeated to assess the quality of the work performed.
- Prosthetics If it is not possible to preserve the causative tooth, digital impressions are immediately taken and a temporary immediate prosthesis is made to hide the aesthetic defect until permanent prosthetics are installed.
To put you to sleep, we use safe ultra-thin sedatives - Propofol or Diprivan. We do not use general anesthesia, since it has a severe effect on the body and is associated with certain risks. Our full-time anesthesiologist monitors the patient’s well-being during the operation. Upon completion of treatment, a person wakes up rested, full of strength and energy, and within half an hour after drinking tea he can return home.
Symptoms of perforation of the maxillary sinuses
Damage to the maxillary sinuses during tooth extraction can be diagnosed if the patient has:
- blood with air bubbles released from the tooth socket;
- the appearance of blood from the nose on the side of removal;
- the appearance of “nasality” in the voice.
If this damage occurred during endodontic treatment or implantation, the doctor can diagnose it based on the following signs:
- failure of an instrument or implant into a tooth socket;
- the appearance of air bubbles in the blood;
- changing the position of the instrument when working in a wound.
Recovery period
Recovery after surgery is the most unpleasant moment for patients. We made sure that this period was as short and painless as possible
No hospitalization
The use of gentle surgical techniques using an ultrasound protocol and microscopic equipment allows us to carry out treatment with the utmost delicacy and minimal trauma. Coming out of sedation is not accompanied by the consequences of general anesthesia; you will not be haunted by nausea, dizziness and clouding of consciousness. Therefore, hospitalization and hospital stay for 3-4 days will not be required ; 30 minutes after the operation you will go home.
For patients with cardiovascular pathologies who require postoperative observation, the Center operates a day hospital department.
A set of procedures for accelerated rehabilitation
For quick recovery after surgery, our Center offers its own method of accelerated rehabilitation. The procedures are aimed at preventing swelling, hematomas, and eliminating pain. The program includes:
Home care
You will receive at home all the medications you need for recovery and instructions for taking them free of charge. In this way, we prevented the purchase of counterfeit products, and you will not need to run to pharmacies on your own after the operation.
The medication kit, selected by a doctor, includes all the necessary medications to improve your well-being and prevent complications.
Please do not violate the frequency of use and follow the recommendations from the leaflet that you will receive along with the medications.
If you have any questions, please contact the phone number listed in the brochure. The postoperative patient support service operates around the clock 24/7.
Treatment of damage to the maxillary sinuses
Treatment is determined by the degree of damage, the presence of foreign bodies in the cavity, as well as the speed of diagnosis and initiation of treatment. The only non-surgical treatment is one that was diagnosed at the time of tooth extraction and does not have signs of infection or the presence of foreign bodies in the sinus. In this case, the doctor does everything to keep the blood clot that closes it in the tooth socket and prevent it from becoming infected. For this purpose, a gauze swab soaked in iodine solution or a special plastic plate is placed in the hole; in rare cases, sutures are required.
These dental procedures are performed in combination with a course of antibiotics, drops with a vasoconstrictor effect and anti-inflammatory drugs. If a foreign object gets inside the maxillary cavity, treatment is carried out surgically through opening and removal of the foreign object and non-viable tissue. The specialists of the Implantmaster clinic not only effectively treat such injuries, but also do everything possible so that their patients know about them only by hearsay.