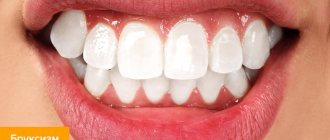
A person who grinds his teeth in his sleep is a serious problem for those around him, and with frequent attacks of grinding, he himself is at risk due to harm to his own health. “Teeth grinding” occurs in both adults and children, and first of all, you should know that it is most often associated with a dental disease.
In medicine, the pathology is known as bruxism, but often a person learns about it only at a dentist’s appointment. Read more about the symptoms of bruxism and ways to overcome the problem later in this article.
Symptoms
You can suspect pathology yourself if you feel pain after waking up:
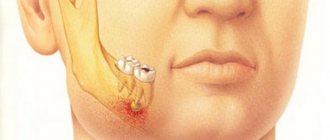
- masticatory muscles
- temporomandibular joints
- sinuses
The possibility of nighttime teeth grinding is also indicated by the following, which do not have an adequate explanation:
- morning headache, dizziness and tingling in the head
- pain in the neck, shoulders, back
- tinnitus
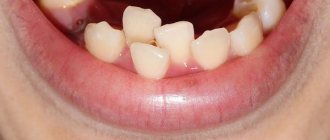
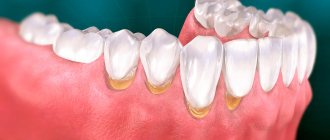
Possible symptoms also include increased daytime sleepiness and the appearance of chips and cracks on the teeth, loose teeth, signs of enamel destruction, and crown fractures.
The described symptoms, neither individually nor in combination, are 100% confirmation of bruxism, but are a serious reason to consult a doctor.
Signs
Odonterism manifests itself:
- grinding,
- clicking
- creaking,
- clanking,
- knocking
- strong clenching of teeth.
It may intensify during stressful situations, physical exertion, at night or during the day. Night-time grinding often irritates loved ones, and daytime grinding often irritates work colleagues. At night, when a person cannot control himself, attacks can last from 15 seconds. up to several minutes at individual intervals.
Half of children under the age of seven are exposed to odonterism, which more often goes away without a trace with age. This symptom cannot be ignored, so as not to cause serious consequences that are dangerous to the body. Adult bruxers, the name given to people who grind their teeth, make up 15%. Most of them have no idea about this.
Teeth grinding is often perceived as a bad habit that can be overcome by willpower. But the fact that teeth grinding occurs in a sleepy state indicates that this problem cannot be solved by willpower.
Most common reasons
Among the main causes of bruxism, experts identify:
- Psychological problems (emotional overstrain, stressful situations, increased nervous stress): in 70% of cases, most researchers see this as the root cause of overexcitation, leading to uncontrolled contractions of the jaw muscles.
- Dental problems (dental anomalies): malocclusion, lack of units of the dentition or its “supercompleteness”, poor-quality treatment or prosthetics, poorly selected braces.
- Otolaryngeal diseases and pathologies (deviated nasal septum, rhinitis, sinusitis, “lower” breathing, adenoids).
- Complications of Huntington's and Parkinson's diseases, traumatic brain injuries.
Modern science has established that bruxism can be inherited.
A bad habit of grinding teeth, similar to a spontaneous desire to bite nails, pencils, etc., cannot be ruled out.
Children
According to statistics, every second child experiences attacks of teeth grinding in their sleep. Experts attribute this to the fragile child’s psyche, which cannot cope with real emotional stress. The main directions of work to correct the situation are timely contact with a neurologist, analysis and improvement of the psychological climate in the children's team and in the family.
Another cause of childhood bruxism is sometimes teething and changing teeth. Experts warn that ignoring the problem can lead to such serious consequences as:
- inflammation of the gums;
- premature tooth loss;
- development of bite pathologies;
- damage to the temporomandibular joint.
Parents often associate children's teeth grinding with the appearance of worms in the child's intestines, but pinworms and other parasites provoke teeth grinding in only 30% of children, so to eliminate risks, it is necessary to show the child to a pediatrician.
In most cases, grinding attacks disappear on their own with age, but contacting a pediatric dentist is necessary if the attacks are prolonged and occur frequently, if there are noticeable signs of gum inflammation or tooth decay, and if bruxism occurs after the age of seven.
Adults
Adults suffering from bruxism account for only 10-15% of the total number of patients. However, this category of patients cannot hope for self-elimination of the problem. In this case, the chronic course of the disease leads to a number of serious problems, including:
- gradual tooth decay;
- erasing crowns and dentures;
- arthritis of the temporomandibular joint.
These problems are formed against the background of a decrease in the quality of life: a person does not get enough sleep, is constantly under stress, feels psychological discomfort, and depression cannot be ruled out in the future.
It has been established that people in professions that require high concentration, precision and accuracy in work (jewelers, watchmakers, surgeons, senior managers) more often suffer from bruxism.
If you have a marked tendency to bruxism, you should: learn to relax, minimize stress factors, limit food intake before bed, include fruits and solid vegetables in your diet, leave only quiet activities for the evening, take warm baths before bed (all of the above is relevant against the background of competent medical treatment) .
How to stop grinding your teeth in your sleep
Odonterism is treated by a dentist, or, if psychosomatic causes are present, by a psychotherapist. Therapy for bruxism depends on the reasons that triggered the appearance of teeth grinding. If symptoms appear due to poor-quality prosthetics, you need to replace the prostheses with better ones. Nervous tension, in which a person begins to chatter his teeth, is relieved by complete relaxation before bed.
The dentist is the first specialist who must differentiate the causes of bruxism
Bruxism therapy methods
In most cases, you can get rid of teeth grinding by using the following methods:
- During sleep, special mouth guards are used to prevent teeth from closing and grinding.
- The patient relaxes, getting rid of tension caused by stress.
- Therapy for increased wear of tooth enamel.
- Orthopedic therapy.
In the chronic form of odonterism, orthopedic dental treatment is used. The chronic course leads to abrasion and loosening, as well as displacement in the dentition. In this case, the teeth are strengthened with special devices that fix them.
The production of mouthguards is carried out according to individual orders, which prevents the teeth from closing and abrading. There is no treatment for symptoms. If the patient’s control of the position of the teeth is negative, a day splint can be used, which should be worn without removing it.
The splint has positive properties: it is not visible to others, does not interfere with the chewing process, and does not create difficulties when talking. A malocclusion can also cause teeth to involuntarily close together. In such cases, repositioning splints are used, which eliminates spasms of the facial and jaw muscles.
Ways to relax before bed
To get rid of teeth grinding, you should learn to relax before going to bed. Helps to relax in the evening:
- Listening to calm music.
- Reading books.
- Walking before bed.
- Relaxing baths.
Will medications help?
If the diagnosis reveals more complex cases, the dentist gives a referral to see a psychotherapist to find out why overstrain develops. For spontaneous grinding of teeth, medications are not used. To relieve tension, sedatives are prescribed, and vitamins are prescribed to maintain the nervous system.
In the most advanced cases, Botox injections are used into the jaw muscles to prevent its spontaneous contraction.
Loading jaws
Treatment for nocturnal bruxism involves loading the jaw with movements. Tired masticatory muscles will not spontaneously contract during daytime wakefulness. Therefore, you should load them with chewing solid food during the day.
In adults, treatment of bruxism is based on the presence of good self-control, which helps achieve long-term results. Doctors recommend relaxing the muscles of the shoulders, neck, and mouth using cold or hot compresses, as well as self-massage and special exercises.
It is recommended to use remineralizing toothpaste and gel to strengthen weakened enamel
You should exclude strong tea, coffee, and hard foods from your diet, and drink enough high-quality water. Procedures to restore dental aesthetics are permitted after complete relief from bruxism.
Treatment of bruxism
In adults, bruxism requires complex treatment, combining dental, psychological and medicinal techniques; The therapy is based on eliminating the causes and relieving spasms in the masticatory muscles.
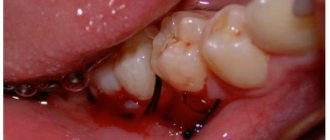
- Dental treatment: performed with the participation of a dentist-therapist, orthodontist and orthopedist, consists of making protective soft mouthguards that are fixed between the teeth, protecting them from injury and abrasion and reducing tension in the jaw (the result of treatment is improved sleep quality and restoration of muscle activity); in case of malocclusion, orthodontic treatment is indicated; in the presence of dentition defects, prosthetics are indicated.
- Psychological treatment: aimed at identifying and eliminating the causes of bruxism attacks and helping with the transfer of psycho-emotional stress; consists of using special relaxing techniques to relax, relieve fatigue, prevent stress in combination with physical therapy and optimization of physical activity. The result of treatment is the relief of nervous tension and increased performance.
- Drug treatment (prescribed by a neurologist): vitamin and mineral complexes, sleeping pills, sedatives.
If there are certain indications, physiotherapy and manual therapy procedures, massage, etc. are also prescribed.
Timely seeking medical help is protection against complications of bruxism, a good night's rest for yourself and comfortable sleep for your loved ones!
Diagnostics
If bruxism is suspected, the attending physician refers the patient for consultation with a sleep disorder specialist (somnologist), neurologist, psychotherapist, dentist, maxillofacial surgeon, ENT doctor, gastroenterologist.
- Examinations by a dentist and a maxillofacial surgeon can identify disorders such as worn enamel, cracks and chips in teeth, their mobility, destruction, damage to the temporofacial joint, changes in bite, etc. If necessary, X-rays and computed tomography are performed.
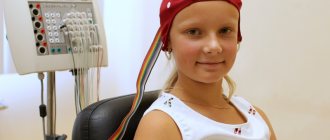
- A somnologist or neurologist may prescribe a comprehensive examination - polysomnography. It is carried out during sleep and includes, among other things, recording of the electromyogram (muscle activity), electroencephalogram (activity of the cerebral cortex), respiratory movements and heart contractions, episodes of snoring, decreased respiratory flow and respiratory arrests. Based on the results of polysomnography, it is possible to identify epileptic activity, OSAS and their connection with pathological spasms of the masticatory muscles.
Polysomnography allows you to diagnose muscle spasms during sleep and identify their connection with apnea and other disorders
- A biochemical analysis is prescribed to determine the level of calcium and magnesium - elements that affect muscle activity.
- An ENT doctor evaluates the condition of the nasal mucosa and nasal septum.
- If GERD is suspected, a gastroenterologist prescribes esophagogastroscopy - scanning the esophagus and stomach using an endoscope.
- A study during sleep using brux checkers - special diagnostic mouthguards - is highly informative and makes it possible to determine the localization of the greatest tension in the masticatory muscles, its connection with changes in the bite and incorrect placement of the dentition.
After receiving a complete picture, an individual treatment plan is drawn up.