A child's body is a developing system that, due to its immaturity, is especially susceptible to infections and viruses. Some diseases especially easily affect children's bodies. Such pathologies include reactive pancreatitis - spasm of the excretory ducts of the pancreas. Today, the concept of “reactive pancreatitis” is not used among gastroenterologists, but it can still be found in pediatric practice1.
Reactive pancreatitis cannot be called a separate disease. Rather, it is a reaction to viral influence, a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, or improperly organized nutrition1.
This form of inflammation of the pancreas in children most often develops as a chronic problem, but in cases of systematic malnutrition, an exacerbation of the disease is possible.
Symptoms of reactive pancreatitis in children
The intensity of the symptoms of reactive pancreatitis largely depends on the age of the child. In children under three years of age, the signs of the disease are usually mild, while in older children they are more pronounced. The main symptom of reactive pancreatitis in children is pain1.
Pain in the reactive form of pancreatitis is concentrated in the navel area (when asked “where does it hurt,” children most often indicate this exact place). But it also happens that the child points to another part of the abdominal cavity. This is due to the immaturity of children's nervous regulation: the baby may feel like it hurts in different parts of the abdomen. That is why only a doctor can accurately link the presence of pain with the manifestation of reactive pancreatitis.
In older children, pain may radiate to the back, forcing young patients to adopt positions that relieve pain - sitting in a chair, leaning forward, or lying on the left side or stomach1.
In addition to pain, concomitant symptoms of reactive pancreatitis in children appear1:
- nausea and uncontrollable vomiting - first with food, and later with gastric juice;
- frequent loose stools (diarrhea may alternate with constipation);
- a slight increase in temperature to 37-38°C;
- lack of appetite, screaming and loud crying in infants and newborns;
- bloating;
- feeling of dry mouth.
Indicators of normal lymph nodes:
- diameter up to approximately 5 mm;
- soft consistency;
- single location, that is, lack of connection with each other or with the skin;
- absence of pain upon palpation (palpation);
- mobility.
Reasons for enlargement and main groups of lymph nodes
| Group of lymph nodes | Typical reasons for the increase |
| Parotid | Pyoderma (inflammation of the scalp accompanied by pus), inflammation of the outer or middle ear, the presence of lice, atopic dermatitis, eczema. |
| Occipital | Various inflammations in the scalp, fungal diseases, rubella, etc. |
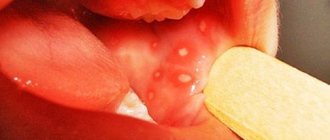
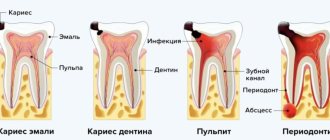
| Submental | Abscess of the jaw, inflammation of the lower lip, damage to the front teeth, stomatitis. |
| Submandibular | Gingivitis, stomatitis, dental damage. |
| Cervical (in the direction of the muscles at the back of the neck) | Sore throat, chronic tonsillitis, tuberculosis of the tonsils, adenoids, infectious form of mononucleosis. |
| Cervical (middle) | Scarlet fever, tonsillitis, “cat scratch disease”, Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin lymphoma ( important - these are malignant oncological processes!), toxoplasmosis. |
| Cervical (lateral) | Tumors, lymph node tuberculosis, nasopharyngeal infections. |
| Elbow | Infections of the forearm or hand. |
| Axillary | Shoulder or arm infections, vaccine reactions, cat scratch disease. |
| Inguinal | Infections of the skin, bones and muscles of the lower extremities, inflammation of the joints, dermatitis, inflammatory processes in the genitals, reaction to a vaccine introduced into the femoral area. |
Causes of reactive pancreatitis in children
Unlike adults, children more often react to infections and inflammations by disrupting the functioning of the pancreas.
The most typical causes of reactive pancreatitis in children are1:
- gross violation of diet;
- regular consumption of fatty and sweet foods, foods high in preservatives and dyes;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- frequent ARVI, flu, colds;
- repeated infection with helminths;
- allergic reaction (to food or medicine);
- congenital pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, contributing to the development of inflammation of the pancreas;
- stress, emotional overload.
Medical practice shows that the key causes of reactive pancreatitis in children are related to nutrition. Namely, with violation of his regime, introduction of harmful foods into the diet, and passion for fast food.
Products that can provoke reactive pancreatitis in children:
- fried foods (both vegetable and butter);
- fatty foods;
- smoked meats;
- spicy seasonings;
- fast food (burgers, chips, French fries, crackers);
- sweets with dyes and artificial additives;
- carbonated drinks;
- packaged juices.
Diagnostics
There is no specific test or examination to confirm the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis; the diagnosis is made clinically. The doctor will examine the rash and ask about the child's symptoms and family history of atopy and allergies. A history of eczema in family members (either as a child or still today) will be an important clue.
Your doctor will rule out other conditions that may cause your skin to become inflamed or itchy. In case of difficulties with diagnosis or severe course of the disease, the pediatrician will refer the child to a pediatric dermatologist or pediatric allergist.
The doctor may ask you to eliminate certain foods (such as eggs, milk, soy, or nuts) from your child's diet for 2 to 3 weeks before reintroducing them and monitoring symptoms. If the diet leads to relief of the rash, and provocation leads to its obvious exacerbation, this will confirm the diagnosis and the need for a diet.
Since there are no accurate laboratory methods for confirming the diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, there are criteria for standardizing the clinical diagnosis (the best known are the Hanifin and Raika criteria).
The criteria are divided into “large” and “small”. To make a diagnosis of atopic dermatitis, it is necessary and sufficient to detect three major and three minor criteria in the patient.
The big ones include:
- itching;
- dermatitis affecting the flexor surfaces in adults, or the face and extensor surfaces in infants;
- chronic or recurrent dermatitis;
- a personal or family history of skin or respiratory allergies.
Small ones include:
- specific facial features: facial pallor, erythema, hypopigmented spots, dark circles under the eyes, cheilitis, infraorbital folds, recurrent conjunctivitis, anterior neck folds;
- typical triggers: emotional factors, environmental factors, food, skin irritants;
- typical complications: susceptibility to skin infections, impaired cellular immunity, predisposition to keratoconus and anterior subcapsular cataracts, immediate skin reactivity;
- other signs: early age of onset, dry skin, ichthyosis, hyperlinearity of the palms, piliary keratosis, dermatitis of the hands and feet, nipple eczema, white dermographism, white pityriasis, perifollicular accentuation.
An explanation of each of these symptoms is beyond the scope of this article; The criteria are given here to help you understand what the doctor is guided by when making a diagnosis of atopic dermatitis.
There are also various scales for assessing the severity of atopic dermatitis used by doctors and scientists, the most famous of which is the SCORAD scale. In this scale, the doctor must note the number, prevalence and severity of symptoms of atopic dermatitis, express them in points, sum up the points and, based on this sum, set the severity of the disease.
Treatment of reactive pancreatitis in children
If symptoms of pancreatitis appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Some forms of pancreatitis require intensive care in a hospital setting!
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out using a blood test (biochemistry) and ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity. If the diagnosis is determined correctly, then the treatment of reactive pancreatitis in children has the same principles as the treatment of the acute form of the disease.
The treatment mechanism for reactive pancreatitis includes diet and complex drug therapy. These could be antibiotics, enzymes, antihistamines - the correct drug treatment regimen should be determined by a doctor.
How to recognize allergic contact dermatitis in a child
The contours of the inflammation often coincide with the outlines of the object that caused the irritation. The rash spreads little beyond the area of skin that came into contact with the causative factor. The skin here becomes red and swollen, very itchy, blisters, wounds and crusts appear.
Fungal and bacterial infections easily attach to wounds and suppuration occurs. Babies may experience an increase in general temperature.
Frequent exacerbation in the same places leads to unpleasant outcomes: areas of increased or decreased pigmentation, scars, thickening and roughening of the skin.
If you notice a rash or red spots on your child’s skin, be sure to see a doctor to get tests done to determine the exact cause and begin treatment.
The disease may worsen. To prevent this from happening, you need to find and eliminate the provoking causes.
Reasons why one cheek is larger than the other
In fact, every person has a difference between one half of the face and the other; they are different, but in some it is less noticeable and in others the defect is very pronounced. Appearance plays a big role in our world. This is how they “meet” a person. In the requirement column for many positions there is a “good appearance” item.
Therefore, every person cares about how he looks. Sometimes, when looking at yourself in the mirror, you may notice that one cheek is larger than the other. What is this, a disease or this body structure? – this is the question asked by those who saw such a flaw.
Today we will dispel all your doubts and conduct a short master class on restoring asymmetry.
Many people complain that one side of their face is different from the other. This becomes noticeable when carefully examining yourself in the mirror or in unsuccessful photographs. Some, noticing that their cheeks are different, begin to “sound the alarm” fearing that they are sick.
Variations in the structure of a person’s face that exceed the natural differences in the right and left halves in significant quantities are considered deformities
In fact, slight asymmetry is present in absolutely every person. This is what makes our face alive, unique and inimitable.
To make sure that each person is not symmetrical, you can take several photos of your friends and cut them into two equal parts along the line of the nose in a photo editor.
Now one of the right halves is “mirrored” and connected to the other, and we do the same with the left parts.
Take such photographs of several people, and you will see that the faces of the right and left halves of the same person are very different.
However, different halves of the face are not always the norm. Let's look at what factors can lead to pathological changes.
Reasons why one side of the face looks very different from the other:
- Improper development of bones and joints, as well as connective or muscle tissue. Such problems can be more or less pronounced, they can only be corrected with proper makeup or plastic surgery.
- Inflammation of the cheek can also lead to its enlargement. After eliminating the problem, the face acquires normal contours.
- Severe strabismus can also develop facial asymmetry. The same applies to torticollis.
- Facial muscles can become severely distorted when nerves become pinched or die. This problem often occurs with strokes and heart attacks.
- An incorrect bite or missing teeth on one side can lead to facial asymmetry. Flux can also cause a similar problem.
- A fracture of the facial bones that did not heal properly.
- The habit of chewing, sleeping or squinting to one side is the most common cause of facial asymmetry.
There are many reasons. Some of them can be avoided by taking timely treatment and controlling your facial expressions.
One side of the face is larger than the other: normal or pathological
If you notice that the sides of your face are different, first of all, you need to determine whether it is pathological or normal. To do this, you need to know the symptoms of the pathology.
If there is facial asymmetry, parchment skin may be present. This symptom is associated with a genetic disease.
Asymmetry, which is considered normal, should not be too obvious. If this is a normal facial structure, then the difference is noticeable only upon careful examination.
Symptoms of abnormal facial asymmetry:
- The affected side is swollen and the tissue may be hard;
- The corners of the mouth and cheek on the affected side are drooping and drooping;
- The affected half of the face loses mobility;
- The folds on the forehead and nose suddenly smooth out sharply;
- The eye on the affected side becomes narrower, or, conversely, larger;
- The eyes, nose and lips on the affected side lose mobility;
- There are speech disorders;
- The affected part is painful.
Even one of these signs suggests that asymmetry is the result of a serious problem. In this case, it needs to be treated.
How to align different halves of the face
If you have identified the fact that the face has significant differences on both sides due to some kind of disease, then to determine the cause, you need to visit a doctor. The specialist will prescribe tests for you, perform an examination and advise the correct treatment.
With good reason we can say that there is not a single person with absolute symmetry of the right and left halves
Asymmetry can occur as a result of drug use. In this case, the face often becomes gray.
To determine the cause of pathological facial asymmetry, you need to visit a doctor. In fact, you may need a number of specialists, but it is best to visit your doctor first.
In this case, you will not waste a lot of time visiting unnecessary medical professionals. The specialist will make a list of doctors you need to visit.
What doctors may be needed for asymmetry:
- Neuropathologist;
- Ophthalmologist;
- Surgeon;
- Orthodontist;
- Dentist.
Once the cause of your illness is discovered, you can undergo treatment and return everything to normal. However, in some cases, additional plastic surgery may be required after treatment.
Gymnastics to restore symmetry or how facial muscles work
Facial muscles are constantly working. However, if this occurs unevenly, asymmetry may occur. This problem also often appears with age. If this is not associated with the presence of serious diseases, then the problem can be eliminated with the help of gymnastics.
Exercises to eliminate facial asymmetry:
- The palms hold the muscles and skin of the forehead, while the eyebrows rise as much as possible up and down;
- We open our eyes as wide as possible and hold this for three counts, relaxing our eyes;
- We inflate our cheeks as much as possible, count to three and retract them, again counting to three;
- We inflate and deflate the cheeks one by one;
- Smile from the top of your mouth without showing your teeth, and then form your lips into a tube;
- We move the jaw forward, left and right.
We perform each exercise ten times. If done regularly, exercise will give the first results within a month.
Jaw displacement and facial asymmetry: how to fix it at home
A normal person's face cannot be completely symmetrical.
The difference between the left and right sides is practically unnoticeable. You can identify small differences if you look closely at a photograph or carefully study a person. But in some cases, asymmetry is pathological in nature and this is the reason for contacting a specialist. In most cases, a clear violation of facial proportions is associated with jaw asymmetry. Let's talk about it in more detail.
Description of facial asymmetry
Normally, imbalances in proportions do not exceed 2-3 millimeters. The left side of the face is characterized by femininity and smoothness of features.
They are slightly elongated in the vertical plane.
The right side is slightly wider, more defined and sharp. But there are also pronounced facial asymmetries associated with profound disorders.
It is not difficult to distinguish physiological deviations from pathologically disturbed proportions. To do this, just look in the mirror. The deformity is expressed in a skewed chin, noticeable displacement of the corners of the mouth, one cheekbone higher than the other.
Jaw displacement is not only a problem of aesthetics, the bite is also disturbed, bruxitis may begin to develop, which as a result is fraught with large inconveniences and expenses during treatment.
Find out what to do if your jaw is jammed on one side.
Symptoms of deformation of the jaw, chin, cheekbones
Facial asymmetry has manifestations. Based on these symptoms, a diagnosis can be made:
- sagging cheeks due to weakness of facial wrinkles;
- the affected part of the face takes on the appearance of a mask, the corner of the lips moves down;
- smoothing natural frontal and nasolabial folds;
- the pained expression of the asymmetrical half;
- obvious violation of facial expressions (difficulty closing an eye, lifting a lip or wrinkling a forehead);
- widening of the palpebral fissure.
In complex cases with damage to the facial nerve, symptoms intensify.
Sometimes the signs are accompanied by pain.
If muscle function deteriorates significantly and affects the side of the neck, the patient develops a pathological tilt of the head. Gradually, one cheek sags, and the sore side of the face smoothes out. Often there are problems with nutrition, and pain manifests itself precisely during chewing food. This material will tell you why teeth go numb.
Causes
There are several factors for the occurrence of facial asymmetry. These may include physiological and pathological disorders. The development of incorrect facial proportions is based on cosmetic, neurological, dermatological and dental problems.
Congenital facial defects leading to asymmetry are quite rare.
Usually, deviations are detected already in the prenatal period, when the fetus is actively developing. Sometimes such disorders are accompanied by various syndromes.
There is also senile facial asymmetry. This is due to age-related changes against the background of developing muscle weakness.
Varieties of curvature
The following changes are observed: a crooked mouth, chin, cheekbones, and a skewed jaw to one side.
Congenital and acquired
Congenital:
- abnormal structure of the cranial bones;
- underdevelopment of the lower jaw;
- developmental disorder of the temporomandibular joint;
- improper formation of the neck muscles;
- damage to connective tissues and the muscular system.
Purchased:
- injuries to the face, jaws, facial bones;
- inflammation or pinching of the facial nerve;
- malocclusion;
- complete secondary and primary adentia (absence of teeth);
- strabismus;
- soft tissue atrophy due to systemic diseases;
- torticollis in children.
Physiological reasons
These factors include bad habits. Incorrect posture with a characteristic tilt of the head to the side for a long time leads to facial asymmetry. The face can change if you constantly chew gum on one side of the jaw or squint your eyes.
If a person sleeps on one side for a long time, this leads to facial distortion.
Pathological:
- neuropathic defects of the facial nerve, Bell's palsy;
- facial contracture after paralysis with increased tone on the healthy side of the face;
- synkinesis (involuntary movements of the muscles of the face or eyes);
- dyskinesia of facial muscles;
- pain syndromes on one side of the face;
- myasthenic syndrome accompanied by asymmetry.
Treatment
In most cases, surgery is used to correct asymmetry. Thanks to facial plastic surgery, it is possible to achieve significant alignment of facial proportions.
Surgical intervention
Before plastic surgery, preparation is required. Usually, to diagnose complex facial asymmetry, an external examination, collection of complaints and consideration of anamnesis are sufficient. A study is required to check for possible inflammation and soft tissue infections.
Until they are eliminated, surgical treatment cannot begin. Facial proportions are measured using special instruments. If the affected side is displaced by more than 5 degrees, the doctor suggests various types of correction.
Find out about the removal of a horizontal, recumbent tooth in this article.
A neurologist will help determine the extent of the facial nerve defect. X-rays are required if the asymmetry is associated with facial trauma. In addition to consulting a surgeon, you will need to undergo an examination by an ophthalmologist, neurosurgeon or dentist.
The final stage of preparation for surgery will be magnetic resonance imaging.
Such a study gives an accurate picture of bones and soft tissues.
Types of operations
- Thread lifting. Polydioxanone threads are injected subcutaneously and dissolve on their own.
Gradually, collagen fibers form in their place. Plastic surgery is suitable for patients with physiological asymmetry caused by age-related changes in the facial contour. The procedure lasts 30-60 minutes, the average duration of the effect is 2 years. - Contour plastic. The cosmetic method involves the use of injections or implants.
Thanks to the operation, you can achieve maximum face lifting and eliminate visible asymmetry. Contour plastic surgery has many contraindications, which are voiced by a specialist. - Blepharoplasty .
Used to correct the skin fold above the eye. With the help of eyelid surgery, pronounced asymmetry of the eyes is eliminated. Additionally, blepharoplasty makes it possible to get rid of swelling under the eyes. If the patient has synkinesis associated with neurological abnormalities, eyelid surgery may not be effective. - Browlift. Browplasty is used to move an asymmetrical eyebrow to a higher position. This method is often used if implants alone are not enough or correction of the forehead is required.
- Rhinoplasty. Used to correct the nose after various injuries. The operation lasts no more than 1.5 hours.
Find out about digital orthopantomography of teeth by clicking on this link.
Massages
If asymmetry is not associated with complex injuries and damage to the facial nerve, you can correct your face with the help of massages.
Unfortunately, this is difficult to do at home.
Only a specialist knows the massage lines and is able to restore the contours of the cheeks and other areas of the face. Finger and palm exposure is effective in case of long-term use. It will take 10 to 20 sessions to achieve the effect.
Possible complications: malocclusion, nervous tics
Uncorrected asymmetry or complete lack of treatment can have consequences. This applies to both the physiological and psychological sides:
- twitching of facial muscles;
- involuntary nervous tic of the eyes and other parts;
- increased risk of soft tissue inflammation;
- chronic headaches;
- high blood pressure;
- stress on the jaws and neck.
Often, against the background of incorrect facial proportions, the patient experiences psychological instability. In the social sphere such a person may feel depressed.
To maintain proportions after surgery, you must adhere to the recommendations of the plastic surgeon.
about how to correct facial misalignment
This video will tell you in detail how to correct facial asymmetry.
Conclusion
- Jaw asymmetry is a complex, but still treatable disease.
- In most cases, the defect is eliminated through surgery.
Depending on the nature of the curvature, rhinoplasty, thread lifting, contour plastic surgery, etc. can be performed. - If the asymmetry is not pathological in nature, then it can be reduced through massages.
- After therapy, it is recommended to do facial exercises and follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Find out about the symptoms of a dislocated lower jaw here.
Source: https://ZubZdorov.online/bolezni/zubov/anomalii/asimmetriya-chelyusti.html
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an allergist-immunologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Allergen-specific immunotherapy (ASIT) - maintenance course (excluding the cost of the drug) | 8100 rub. |
Oncological alertness
Lymph nodes are often enlarged due to lymphogranulomatosis (Hodgkin's lymphoma) or lymphosarcoma (non-Hodgkin's lymphoma). These are malignant processes that are manifested by increased density, painlessness and large diameter of the lymph nodes in the absence of other reasons for their deformation. Lymph nodes enlarge in groups, asymmetrically (for example, on one side of the neck). At the initial stage of the process, their mobility and separate arrangement are maintained. If the oncological process continues without treatment, the lymph nodes may become fused, and moderate pain rarely occurs. Source: N.V. Nagornaya, E.V. Vilchevskaya, A.P. Luachak, E.N. Marchenko, E.V. Bordyugova, A.P. Koval Hodgkin's disease (lymphogranulomatosis) in children // Child's Health, 2013, No. 1 (44), pp. 13-15
Symptoms that require consultation with a doctor are enlarged lymph nodes:
- more than 7 days;
- more than 1 group;
- accompanied by elevated body temperature;
- in a child under one year old;
- progressive over time;
- with changes in local skin.