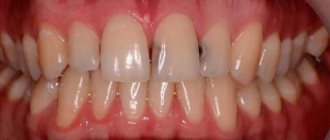
Complications of bruxism
How the disease can be complicated if symptoms are ignored and intervention is delayed:
- hypertrophic changes in facial muscles;
- difficulties in mobility of the lower jaw;
- gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis;
- fibrosis of soft tissues;
- lichen planus on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity;
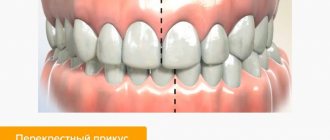
- malocclusion;
- carious lesions;
- grinding down teeth to the base;
- joint dysfunction;
- tooth loss;
- violation of facial aesthetics;
- depression, sleep problems.
Causes of Bruxism
Parents often wonder why their child grinds his teeth in his sleep. Unfortunately, no doctor knows the exact causes of bruxism in children. Experts correlate the occurrence of the disease with factors such as:
- teething pain;
- psychological factors: stress, anxiety, abnormal emotional development;
- neurological factors: epilepsy, enuresis, etc.;
- dental factors: malocclusion and dentition (extra teeth, adentia), improper orthodontic treatment (incorrectly selected braces, etc.);
- dehydration of the body;
- allergy;
- helminthiasis (worms);
- intoxication due to various diseases;
- endocrine disorders, etc.
Bruxomania - teeth grinding while awake
Young children under 3 years of age may grind their teeth during the day if they are teething. So, by squeezing and unclenching their jaws, they try to get rid of the unpleasant sensation in the gums.
Involuntary grinding can also occur due to the fact that the lower row of teeth protrudes more forward or the upper row of teeth hangs excessively over the lower one. If, when closing the jaw, gaps are visible between the teeth, the baby is grinding due to an incorrectly formed bite.
Correct bite is not the norm, but rather the exception. 10% of the adult population can boast of a beautiful smile, while for everyone else, problems with the dental system develop in childhood.
Children over 3 years of age who do not have bite problems suffer from bruxomania if they have an extremely excitable nervous system or a stressful environment.
Dangerous symptoms: when should you see a doctor?
The question of when to start treatment for bruxism in children worries many parents.
As a rule, the disease goes away on its own, without any consequences, by the age of 12–13 years. This is due to the fact that by this period the formation of molars is completed. No treatment is required for this form of bruxism. However, there are times when the picture is not so rosy. You should contact your doctor immediately if your child exhibits the following symptoms:
- headache and/or toothache in the morning;
- rapid wear of teeth;
- long and intense attacks at night (more than 10 seconds).
Complicated bruxism in children leads to quite unpleasant consequences, including gum disease and significant tooth wear.
Tips for parents
To have a restful sleep, instead of watching cartoons, outdoor activities and computer games, take a walk down the street in the evening. Before going to bed, a child can take a relaxing bath and listen to a good fairy tale that does not contain scary characters.
Contact your dentist even if there are no problems with your teeth, but bruxism is present. He will select a special mouth guard for night wear. It does not eliminate grinding, but protects teeth from abrasion.
Half of children grind their teeth, so there is no need to panic at a single grinding sound. You should be concerned about frequent squeaks.
To prevent a child from grinding his teeth, the cause must be found and eradicated. Make sure he avoids stressful situations, eats right and doesn't overwork himself.
Psychological help
The psyche of children and teenagers is unstable. Therefore, psychological factors, including anxiety, often lead to the development of bruxism.
In an anxious state, other symptoms may be observed: the habit of pulling and twisting hair, biting nails, etc.
The trigger for bruxism can be changes in a child’s life: moving, changing schools, parents’ divorce, various conflicts, etc. In such cases, a psychologist will help.
What should the mother do and how to help the child?
You can help your child cope with teeth grinding at home. The task of parents is to relax the child, especially in the evening. Suitable for relieving tension:
- massage;
- exercise therapy;
- correct daily routine;
- walks in the open air;
- drinking enough water;
- exclusion from the diet of foods that excite the nervous system: chocolate, coffee, tea, Coca-Cola, Pepsi, etc.;
- last meal – an hour before bedtime;
- hot bath before bed;
- refusal of active games, quiet activities in the evening: drawing, listening to lullabies, etc.
In addition, heart-to-heart conversations with your child can help. If the child does not speak out, he will go to bed with anxious thoughts. This will trigger an attack.
The following techniques will help reduce facial muscle tension:
- heat compresses (including for pain in the morning);
- chewing solid food;
- giving up chewing gum.
Children
According to statistics, every second child experiences attacks of teeth grinding in their sleep. Experts attribute this to the fragile child’s psyche, which cannot cope with real emotional stress. The main directions of work to correct the situation are timely contact with a neurologist, analysis and improvement of the psychological climate in the children's team and in the family.
Another cause of childhood bruxism is sometimes teething and changing teeth. Experts warn that ignoring the problem can lead to such serious consequences as:
- inflammation of the gums;
- premature tooth loss;
- development of bite pathologies;
- damage to the temporomandibular joint.
Parents often associate children's teeth grinding with the appearance of worms in the child's intestines, but pinworms and other parasites provoke teeth grinding in only 30% of children, so to eliminate risks, it is necessary to show the child to a pediatrician.
In most cases, grinding attacks disappear on their own with age, but contacting a pediatric dentist is necessary if the attacks are prolonged and occur frequently, if there are noticeable signs of gum inflammation or tooth decay, and if bruxism occurs after the age of seven.
Bruxism in adults: causes
Bruxism also occurs in adults, and the disease appears in both sexes with equal frequency.
The question of why teeth grind in their sleep remains open: the exact reasons have not been established. Various factors can lead to the disease:
- psychological: fatigue, stress, depression, anxiety neurosis, complexes, a special type of personality (vulnerable or hyperactive nature);
- neurological: epilepsy, cervical osteochondrosis, lesions of the trigeminal nerve, apnea, somnambulism (sleepwalking), nightmares;
- dental: malocclusion, jaw defects (over-row teeth, their absence or incorrect location), joint pathology, uncomfortable braces or dentures, incorrectly installed fillings, etc.;
- hereditary factor;
- other factors (not recognized by all doctors): acid reflux into the esophagus, helminths, snoring, impaired nasal breathing (enlarged adenoids, frequent rhinitis or deviated septum in the nose), lack of vitamins.
In 70% of cases, teeth grinding is the result of psychological problems.
Symptoms
You can suspect pathology yourself if you feel pain after waking up:
- masticatory muscles
- temporomandibular joints
- sinuses
The possibility of nighttime teeth grinding is also indicated by the following, which do not have an adequate explanation:
- morning headache, dizziness and tingling in the head
- pain in the neck, shoulders, back
- tinnitus
Possible symptoms also include increased daytime sleepiness and the appearance of chips and cracks on the teeth, loose teeth, signs of enamel destruction, and crown fractures.
The described symptoms, neither individually nor in combination, are 100% confirmation of bruxism, but are a serious reason to consult a doctor.
People suffering from bruxism complain of:
- pain of various origins: headache, ear, tooth, face, jaw and neck;
- increased sensitivity and mobility of teeth;
- erasing enamel;
- damage to teeth, crowns, etc.;
- inflammatory processes of the gums;
- insomnia, irritability, etc.
Symptoms worsen under stress. Most of these symptoms are short-term and correctable. However, if left untreated, there can be more serious consequences: facial asymmetry, hearing loss, severe wear and tear and broken teeth. In some cases, teeth are worn down almost to the roots.
With regular grinding at night, the mental health of the patient and those around him suffers. People don't get enough sleep and experience fatigue, anxiety and depression.
You can identify the symptoms of bruxism yourself by external examination in the mirror. Upon inspection you will find:
- worn teeth, cracks and chips on them;
- teeth marks on the cheeks and tongue;
- change in bite;
- damage to prostheses;
- thickening of the jaw bones.
There may also be a crunching/clicking sound when moving the jaws. Sometimes patients have difficulty opening/closing their mouth.
Important! At rest, the teeth of the upper and lower jaws should not touch each other.
Treatment
Bruxism in adults does not go away on its own. A dentist can help determine whether the problem is serious and requires treatment.
The main goal of treating nocturnal bruxism is to relax the masticatory muscles. Moreover, the treatment method directly depends on the severity and cause of the disease. Accordingly, you may need the help of the following specialists:
- dentist, orthodontist;
- neurologist;
- psychologist, psychotherapist.
The most effective dental treatment methods are:
- plastic splints and individual night guards - linings that protect the dentition from abrasion;
- Mandibular thrusters: also used for snoring;
- teeth grinding: the method eliminates jaw defects;
- prosthetics: the method is used for severe abrasion.
Medications may also be part of complex therapy:
- muscle relaxants: administered before bed to relax facial muscles;
- Botox: Injected in extreme cases to reduce the force of muscle contraction.
Since psychological factors most often lead to teeth grinding, you may need the help of a psychologist and psychotherapist. The psychotherapist will prescribe medications to normalize sleep and relieve anxiety, antidepressants.
Psychological treatment of bruxism in adults requires an individual approach. A psychologist will help identify and understand the conflict, and also stabilize the emotional state. Ultimately, the patient will learn to relax his jaws and get rid of the habit of clenching his teeth under stress.
The main task of the patient is relaxation. Methods such as:
- massage, including face and neck;
- light exercise, sports;
- yoga, meditation;
- evening walks;
- listening to pleasant music or reading before bed;
- baths with aromatic oils or herbs (chamomile, lemon balm, special mixtures, etc.);
- soothing teas and mixtures;
- exclusion from the evening diet of foods rich in caffeine (coffee, tea) and carbohydrates: this excites the nervous system;
- giving up bad habits: smoking, alcohol;
- full sleep.
To relieve muscle hypertonicity, you need to:
- take medications with magnesium, potassium and B vitamins;
- make warm compresses, herbal lotions, apply a heating pad (including at night);
- chew solid food (apples, carrots, crackers);
- give up chewing gum, do not chew a pencil/pen, or nails.
Try to relax your face and keep your jaws open while at rest. If you find it difficult to do this, use the following practice: purse your lips and hold the tip of your tongue between your teeth. Remember! Self-medication will not help with advanced or severe forms of bruxism.
Be sure to consult a dentist: the doctor will determine the causes of bruxism and prescribe adequate treatment. If medical recommendations are followed, the prognosis is favorable.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of bruxism involves studying the patient’s complaints, as well as assessing indirect signs based on the results of a routine visual examination. The leading method of objective diagnosis is the use of Brux Checkers - special mouthguards that are made on the basis of a plaster cast of the patient’s jaw. These aligners allow the detection of occlusal obstructions. The doctor issues brux checkers to wear overnight, after which the patient submits them to the clinic for analysis. Using diagnostic aligners, a specialist determines which teeth bear the greatest load.
Electromyography and polysomnography methods make it possible to register the pathological activity of the masticatory muscles and confirm the diagnosis of bruxism.
But, as a rule, it is possible to understand the reasons only with the help of comprehensive diagnostics. So, in the case of bruxism in adults, psychosomatics may occur, so consultation with a psychologist or psychotherapist will be required.