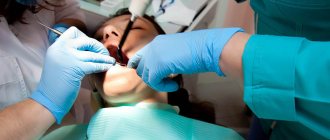
Tooth root caries is a common disease when the neck of the tooth is exposed. It is based on damage to the enamel by microorganisms that feed on food debris and produce acid that can destroy the surface of the teeth. Root caries is often secondary: the infectious process gradually penetrates into deeply located tissues. Inflammation spreads to the nervous tissue of the tooth - the pulp.
With gum recession and other disorders, root caries occurs without visible changes to the enamel. The disease is dangerously asymptomatic for several months or even years. The pathological process occurs inside the tooth and is invisible to the patient.
Make an appointment with a therapist by phone+7(985)532-21-01
Types of caries localizations
Caries (lat. caries rotting) is a slow and hidden pathological process occurring in the hard tissues of the tooth. It is characterized first by focal demineralization of the enamel, then by the destruction of hard tooth tissues with the appearance of a cavity in the dentin. If left untreated, the tooth is lost or complications arise - pulpitis and periodontitis.
Cervical (circular)
The structure of a tooth is divided into a root, a neck and a crown - the latter is located above the gum. The neck and root are located in the gum and are protected by soft mucosal tissue.
When the carious process begins to destroy the tooth in the area of contact of the crown with the mucous membrane, we can talk about the cervical form of caries.
This category is the most difficult to diagnose and treat. It most often affects the incisors. When biting food with incisors, the food is not only “cut off”, but also gets clogged into the gum pockets, moving towards the gums.
Crown caries
Caries has the ability to affect not only healthy, but also already treated teeth - under a filling or crown. If there is a crown, it is difficult to detect, because the tooth does not have a nerve and pain is not felt. There are no external signs for a long time.
The causes of this type of caries are:
- defect of the dental crown with the appearance of access to the tooth tissue underneath it
- poorly treated tooth before prosthetics;
- gum disease;
- poor oral hygiene.
The problem is that the process spreads into the deep layers and spreads to the bone structures, as a result of which the tooth is often completely removed. That is why preventive examinations and an orthopantomogram - a panoramic image of the entire jaw - are so important.
Radical caries
Basal and cervical caries are similar. Both incisors and chewing teeth are affected. Destruction begins with the enamel, gradually moving to the nerve in the root canal. When the process touches bone tissue, it threatens with osteomyelitis.
The main reason for the occurrence is a cariogenic situation in the oral cavity, when plaque accumulates especially quickly. The enamel in the root part of the tooth is much thinner and more easily destroyed. It is most often diagnosed between the ages of 30 and 60 years.
Root caries
Root or subgingival caries occurs hidden. It can be with or without a cavity. Along the flow - active, suspended, secondary. It most often affects molars.
Different types of caries: WHO classification
Caries is a slowly occurring pathological process in hard dental tissues, which develops under the influence of unfavorable external and internal factors. According to statistics, this disease occurs in more than 90% of people in the world.
In this article
- Different types of caries: WHO classification
- How does dental caries develop in the root area?
- Features of the progression of dental caries
- Dental cement caries - main clinical manifestations
- Diagnosis of cement caries: basic and additional methods
- Treatment of cement caries: main stages
- Prevention of root caries
According to the classification of the World Health Organization, there are several types of caries: enamel, dentin, cement, as well as suspended, other, unspecified caries, and odontoplasia. In this article we will talk about dental cement caries, better known as tooth root caries.
What is the danger of this disease?
Caries is dangerous because there are no symptoms for a number of years. It is detected more often in an advanced stage, when tooth extraction becomes the solution.
Visual diagnosis is difficult because all destructive processes occur inside the tooth. Pronounced plaque or tartar hides any stains on the enamel.
The root is hidden under the gum and external irritants do not affect it until a certain time. On the other hand, the root walls are thin, so they are destroyed quickly and with complications.
Diagnosis and symptoms of tooth root caries
Diagnosis of root caries is complicated by the fact that the disease can be asymptomatic for quite a long period of time. A visual examination of the oral cavity only in 11 - 13% of cases helps to identify the presence of the disease. Therefore, additional examination methods are required for diagnosis:
1) probing;
2) X-ray examination (orthopantomogram, radiography, etc.);
3) electrical odontometry (assessment of nerve response);
4) thermometry (checking the reaction to hot and cold).
It is impossible to identify the presence of dental root caries on your own, but basal or cervical caries, which in most cases accompany root damage, is quite possible. This can be done with a toothpick and a mirror. With clean hands, take a toothpick and pass it between the gum and tooth, pressing lightly. If pain occurs or roughness is found on the enamel, there is a possibility of developing caries of the cementum of the tooth root. This means it's time for you to visit the dentist.
Symptoms of root caries, which, as we noted above, may not always appear:
- pain when exposed to high/low temperatures;
- pain when eating sour and sweet foods;
- increased sensitivity of the periodontium;
- discomfort when chewing;
- aesthetic defect at the border with the gum.
Causes of the disease
There are 3 main provoking factors that must act in a complex manner; none of them acts independently:
- Cariesogenic microflora - this includes Mutans streptococci, actinomycetes and certain types of lactobacilli. They should dominate the oral cavity. Bacteria produce organic acids from food carbohydrates, which cause demineralization of cement.
- Consumption of simple carbohydrates is the most cariogenic. Their breakdown produces glucan, which contributes to the appearance of plaque.
- Reduced caries resistance is a deterioration in the resistance of tooth tissue and the body as a whole. This is facilitated by a decrease in calcium content in hard root tissues, bad habits, and lack of saliva.
In addition, the anatomical features of the mouth can also have an effect - a small vestibule, a short frenulum, and bite pathology.
Gum disease, pocket formation
Gum pocket or otherwise periodontitis is a common occurrence in many patients. Many people do not treat it because it does not bother anyone for a long time.
The first manifestation of pathology is bleeding when brushing teeth, although outwardly they may look healthy. Dental pockets or depressions are normal, but their anatomical size should not exceed 3 mm.
Then the pocket is able to self-clean from food debris and epithelial particles. Reservoirs of bacterial accumulations form in deep gaps. This is accompanied by bad breath. Conventional treatment with antibiotics and brushing teeth with toothpaste have no effect.
Causes of periodontitis:
- insufficient hygiene;
- poor quality fillings;
- abnormal position of the dentition, malocclusion;
- hereditary predisposition;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- immunosuppression.
Lifestyle
If you have learned about the risk group for root caries (older age), this does not mean that you can relax. Caries has many causes and can occur at any age if basic precautions are not followed.
Those at risk include smokers, diabetics, pregnant women and even children. The provoking factors in this case are:
- smoking and lack of oral hygiene;
- infrequent brushing of teeth and lack of fluoride;
- poor nutrition with preference for desserts;
- frequent stress;
- alternating hot and cold;
- structural features of the oral cavity;
- alcohol abuse - alcohol breaks down into sugars and acids;
- abuse of coffee and strong tea, which creates an acidic environment in the oral cavity;
- lack of water intake, and therefore lack of saliva;
- gum injuries.
Symptoms of the disease
The process usually occurs without symptoms, but pain may occur when brushing a toothbrush, eating sour, salty, sweet, cold or hot foods.
After eliminating the irritant, everything goes away. The patient can see a doctor if a stain is found on the front surface of the incisors, but often it is hidden under plaque or tartar.
The ongoing carious process gradually reaches the dentin junction, penetrating first into its surface layers and then further. The cavity deepens with bacteria and food debris. There is a smell from the mouth. Irritants cause pain more and more frequently.
With cement caries, teeth become mobile and lose their support, and bleeding gums occur. These are already symptoms of periodontitis. Now, even when chewing food or brushing teeth, severe discomfort occurs.
Digestion begins to suffer. Teeth become hypersensitive to hot or cold.
Next, the process follows the Leus classification:
- Active lesion - the edges of the cavity are undermined. The cavity is filled with softened tissues and tends to grow.
- Suspended caries - no increase in the affected area is observed. The cavity is clean, the bottom is shiny and smooth, the edges are even and dense.
- Secondary caries - occurs under a filling.
When is the best time to remove a tooth?
It is more advisable to cure deep root caries, which develops against the background of severe inflammatory processes, by removing the tooth. There are a number of reasons for this:
- A diseased tooth is a source of infection. If caries was on one root, most likely it will develop in another area.
- A person will constantly be accompanied by bad breath, which is impossible to get rid of.
- Pathology makes teeth mobile, which prevents you from chewing food normally. Problems with the gastrointestinal tract may occur.
- There is a risk of infection entering the circulatory system, resulting in the development of general infections, including sepsis.
In each specific case, the doctor selects an individual treatment program based on medical indications, the patient’s age and financial capabilities.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis is made in stages. Listening to complaints and visual examination make it possible to diagnose caries only in 13% of cases. Classic probing with a sharp probe and inspection with a mirror are informative. This allows you to examine the dentition.
Thermal diagnostics, electroodontometry and x-rays are also performed. If the patient has massive dental plaque, changes in the enamel will not be visible. In this case, professional teeth cleaning is first carried out to remove plaque and stone. All this is possible in a dental clinic.
At the dental clinic
The following types of studies can be performed at the clinic:
- Probing with a thin probe with a curved end - it is inserted under the gum, while the doctor has the opportunity to examine the structure of the tooth, its integrity, the presence of irregularities and chips. With rapidly progressing caries, the edges of the cavity are uneven and sharp. In the remission stage, the surface of the pathological focus is shiny, smooth, hard with smooth edges.
- Electroodontometry - can determine nerve damage and the depth of inflammation. The pulp reacts differently to the current strength.
- Thermal diagnostics - treatment of different areas of the tooth with a stream of water and heated wax. Unpleasant sensations that disappear after removing the irritant indicate caries.
- X-ray - a targeted photograph of one tooth or computed tomography. The presence and localization of obvious or hidden inflammation is determined with millimeter precision.
- Visiography is a special device - a visiograph scans the received data and transfers it to a computer, where the picture is studied from different angles and in detail, revealing the hidden process of inflammation.
Treatment or removal - what determines the outcome
The doctor makes a decision on treatment or tooth extraction after determining the depth of spread and the area of localization of the inflammatory process. It is mandatory to first carry out professional cleaning using an ultrasonic scaler, an AirFlow water-abrasive device and hand tools.
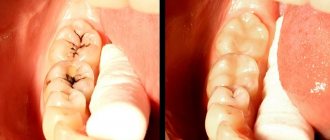
Initial caries is treated with conservative retherapy. For hard tissue defects, preparation and filling are performed. In severe cases, the tooth is removed.
Treatment of the initial stage of root caries
Conservative retherapy includes:
- fluoridation of teeth;
- covering teeth with protective agents
- training in proper oral hygiene
Cleaning in dentistry from stone and plaque
1243900247100
Professional teeth cleaning involves removing the accumulation of all pathogenic microflora around the root.
It involves not only removing plaque, but also stones. This elimination of negative factors protects teeth for a long time.
Antiseptic treatment of affected areas
Treatment of root caries involves drilling out all affected areas with a drill and treating the carious cavity with antiseptics and special preparations. A 2% chlorhexidine solution or a gel based on it is used as an antiseptic for the treatment of carious cavities.
Severe root damage
Modern dental methods make it possible to save a tooth even with extensive damage.
Depending on the specific situation, the doctor may prescribe:
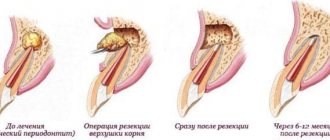
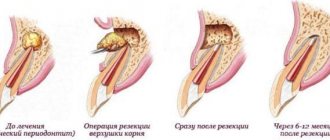
- Resection - removal of the root apex.
- Hemisection - excision of the damaged part along with the crown that is adjacent to it.
- Amputation is the extraction of the affected part of multi-rooted teeth: one of them is removed.
- Separation is the separation of closely spaced teeth if the carious lesion is localized in the area of branching of the root system.
In rare cases, the doctor strengthens and restores the root not with a filling, but by installing a ceramic or metal stump that protects the tooth from fracture and infection. Of course, such treatment methods are expensive and not available to everyone. Most patients have to have their tooth removed.
What to do to protect your gums
If the gum is not treated, inflammation will remain and all treatment will become meaningless. The gums are protected by diathermocoagulation and retraction.
Diathermocoagulation
Diathermocoagulation – excision of excess areas of periodontitis with a coagulation knife. The knife immediately cauterizes the bleeding edges. The procedure is performed when there are severe changes in the gums. In such cases, filling is postponed until the soft tissue is completely regenerated.
Retraction
If the condition of the gums is advanced, treatment of caries becomes impossible - the mucous membrane bleeds and interferes with tooth treatment. This gum is excised or a special device is applied to move the gum back. But more often, retraction is performed - lowering the gingival contour or moving apart the overhanging edges of the gums using special hemostatic threads. A temporary filling is placed until complete healing.
What preventative measures are there?
To keep your teeth healthy for many years, you need to brush your teeth twice a day, use floss and a tongue scraper. After sweets, you should rinse your mouth and chew gum for 5-10 minutes.
Prevention also includes the removal of tartar. A sufficient amount of saliva is also important, so it is necessary to maintain a water regime.
Like any other pathology, caries is better prevented than treated. Therefore, it is important to visit the dentist twice a year for preventive examinations. People at risk should approach this especially responsibly.
Other
Treatment
The stages of treatment of dental caries are generally similar to the stages of treatment of ordinary caries:
- excision of affected tissue;
- treatment with medicinal and antiseptic drugs;
- the root is filled to recreate the shape.
The difference arises in the difficulty of accessing the site of the disease. First you need to clean the pocket and expose the root. As a rule, treatment takes place in two steps - on the first day, carious tissue is removed and the cavity is filled with a temporary glass ionomer filling. At the second appointment, the doctor examines the gums for healing and installs a permanent filling. To treat cement caries, Family Dentistry uses materials that are not affected by saliva, blood and gingival fluid - composites and glass ionomers.
If cement caries is not treated, pulpitis and periodontitis may develop, which will lead to tooth loss. To avoid such consequences, you should visit the dentist once every six months. During the consultation, the doctor will be able to detect signs of caries and, with little effort, get rid of this problem.