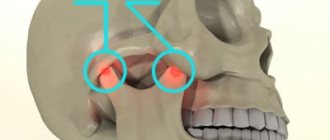
The temporomandibular joint is a complex paired anatomical formation that provides horizontal and vertical movement of the lower jaw relative to the lower jaw. The load on the joint is determined not only by the quality of the food that needs to be chewed, but also by the condition of the dental system. The condition of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) in turn affects our well-being and overall health.
According to data provided in the reports of the World Health Organization for 2021, musculo-articular dysfunction of the TMJ is detected in approximately every second person aged 20 to 50 years. And these are only those cases that are recorded in medical documentation. A fairly large number of people do not associate persistent headaches, clicking in the joints when chewing, difficulty opening the mouth with a painful condition of TMJ and are in no hurry to seek medical help.
Often, the pathology of the temporomandibular joint is detected during an examination performed for another reason, for example, in preparation for prosthetics. At the same time, the variants of joint diseases can be very different from dysfunctional syndrome to habitual joint dislocation.
Structure and functions of the temporomandibular joint
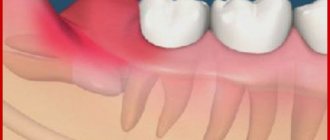
The joint is formed by the head of the horn of the lower jaw and the articular surface (fossa) of the temporal bone. Between these bone formations there is a fibrous intra-articular disc, which is fused on all sides with the joint capsule. Ligaments and muscles help keep the joint in the correct position. They limit the range of motion in the joint. Attempting to exceed this functional limitation causes pain and prevents damage to the TMJ.
The main function of the joint is to ensure movement of the lower jaw in three directions:
- vertical: opening and closing the mouth;
- horizontal: lateral displacements of the lower jaw relative to the upper;
- sagittal: movement of the lower jaw back and forth relative to the upper.
The combination of movements of one jaw relative to the other allows us to chew, speak, and express emotions through facial expressions.
How to act, which doctor to contact
If you undergo preventive examinations in a timely manner, have recently been to the dentist, had teeth treated and removed, have fillings, dentures and braces installed, then it is recommended to wait for a while and observe your condition. Usually the pain subsides a few days after medical procedures. If after 3-5 days they become stronger, then be sure to consult your doctor again.
Haven't you visited the dental clinic for a long time? Then, most likely, pain that spreads not only to damaged teeth, but also throughout the entire jaw, is associated with advanced caries, pulpitis and periodontitis, as well as other dental pathologies. Be sure to make an appointment and get tested. You may need to visit not only a general dentist, but also an orthopedist, orthodontist, and periodontist.
In what situations should you start an examination not with a dentist, but with a therapist or other doctors with a narrow focus (for example, a cardiologist, neurologist, psychologist, oncologist)? This should be done if, in addition to toothache and discomfort in the jaw, you have a stuffy nose, a sore throat, headache, ears, chest pain, a runny nose and cough, you are experiencing overload and severe stress, and you have noticed the appearance of strange growths and tumors.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
toothache
- Meyer G., Bernhardt O., Asselmeyer T. Occlusal disorders of teeth as a decisive factor in the occurrence of headaches // Problems of dentistry, – 2013.
Expert “Obsessive pain in any part of the jaw, gums and teeth is a symptom of pathology. Of course, you can temporarily suppress it with the help of drugs from your home medicine cabinet, reduce it with soda-salt solution and chamomile decoction, but such methods will not get rid of the disease that caused discomfort. Therefore, seeing a doctor is mandatory.” Dental hygienist Victoria Nikolaevna Kashaeva
Consulting specialist
Varlamova Tatyana Vitalievna
Specialization: Dentist-therapist Experience: 5 years
Causes of dysfunction of the masticatory joints
A gnathologist specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of TMJ diseases. In fact, this is a dentist with a narrow specialization. Factors that can lead to temporomandibular joint disease include:
- vascular pathology, which leads to impaired blood supply to the joint;
- increased tone of the muscles of the face and neck (increased tone, spasms);
- violation of occlusion;
- manifestations of psychosomatics.
Occlusion disorders underlie the largest number of cases of TMJ disease. Normally, the antagonist teeth of the upper and lower jaws contact their chewing surfaces in a certain way. The cusps and depressions on the upper surface of the antagonist teeth should contact according to the “pestle and mortar” principle. If the teeth on the jaw are positioned incorrectly and their correct contact is impaired, compensatory mechanisms are activated. In particular, the tone of the chewing muscles changes and the lower jaw shifts in such a way as to achieve full contact of all chewing surfaces of the teeth.
This displacement eliminates the occlusal obstacle, but creates additional stress on the temporomandibular joint. Habitual displacement of the jaw over time leads to damage to the anatomical structures of the joint. Increased tone of the masticatory muscles provokes hemodynamic disturbances in the TMJ area, which does not contribute to rapid regeneration.
If the cause of unpleasant symptoms in the TMJ area is a violation of occlusion, a gnathologist may recommend orthodontic treatment. This is the only way to get rid of the problem, since if the teeth are incorrectly positioned on the jaw, only symptomatic treatment of TMJ problems can be carried out, which will only lead to a temporary improvement in the condition.
Prevention of aching teeth
The best way to prevent an unpleasant symptom is to follow preventive measures. Despite the fact that the enamel itself is very strong, improper lifestyle and exposure to the external environment gradually weaken and destroy it. If you have sensitive enamel, you need to carefully choose hygiene products. In particular, it is recommended to avoid hard toothbrushes and use toothpastes with calcium and fluoride. An equally important point is the right diet. It is necessary to reduce the consumption of spicy, sour and sweet foods to a minimum, and give preference to fermented milk products and foods high in vitamins A and B. Temperature changes are a big stress for sensitive enamel, so the best solution is to drink drinks at room temperature.
Publisher: Expert magazine about dentistry Startsmile.ru
Author of the material: Yaroslav Ikonnikov
Symptoms and prevention of TMJ dysfunction
Pain in the masticatory joint is an extremely rare occurrence. In this regard, patients rarely associate the existing pathological manifestations with the condition of the TMJ. Let's see what symptoms you need to make an appointment with a gnathologist:
- Headache. There are a great many causes of headaches, but the “contribution” of the temporomandibular joint is most often “forgotten” by specialists. Elimination of TMJ pathology often relieves a person of headaches.
- Clicking in the joint. The characteristic sound when opening the mouth is a consequence of dislocation or subluxation of the masticatory joint, which usually resets on its own.
- Limitation of mouth opening. This may be a consequence of swelling of the joint tissue as a result of the development of an inflammatory process or dislocation of the joint.
- Pathological abrasion of tooth enamel.
Measures to prevent the development of TMJ dysfunction include regular visits to the dentist, rational prosthetics, timely treatment and restoration of damaged teeth, and orthodontic treatment as indicated.
Preventive actions
To reduce the risk of dental diseases, you should follow these rules:
- Brush your teeth twice a day.
- Visit the dentist twice a year.
- Preventative professional cleaning of units once a year.
- Avoiding foods that are too hot or cold.
- Carry out enamel whitening only in trusted dental centers.
- Treat your teeth in a timely manner.
- Be more attentive to your health and avoid complications such as otitis media.
- Get rid of bad habits.
- Choose a paste without abrasive particles.
- Additionally, use an antibacterial mouthwash, dental floss and irrigator.
Diagnostics
In order to make a diagnosis, the doctor conducts an examination according to the following scheme:
- Questioning the patient. Of interest to the specialist are complaints, conditions for the appearance of unpleasant symptoms, duration of the disease, previous treatment and its effectiveness.
- External examination and palpation. The gnathologist examines the patient’s face, paying attention to the area where the TMJ is located. By feeling the joints, you can get an idea of its structure and the state of its tissues.
- Dental examination. Anomalies of occlusion and the degree of their severity are identified.
- X-ray examination. The photographs show the bone formations that form the joint. By their relative position one can determine the presence of dislocations and subluxations, and by the thickness of the joint space one can judge the condition of the cartilaginous disc.
Comments
Recently, pain appeared in the lower tooth, which is covered with a crown. Now my lower jaw is also aching, but I’m very afraid to go to the doctor. Will this tooth be removed immediately?
Vika (01/14/2021 at 00:41) Reply to comment
- Dear Vika, seeing a doctor as soon as possible can be the key to saving the tooth that is under the crown. Yes, if an inflammatory process has formed on the root, for example, periodontitis or a cyst, then in order to access the canals, in most cases the artificial crown will have to be removed, and after treatment a new one will have to be installed, but the main thing is that the tooth can be saved.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (01/16/2021 at 09:01) Reply to comment
In the lower jaw, on some teeth, the gums seem to have decreased and in fact they have become bare. How to grow gum back into these places and is it possible? What medicinal and traditional methods of treatment exist?
Julia (02/05/2021 at 08:44) Reply to comment
I know about caries and pulpitis firsthand! You cure one tooth, another begins to crumble ((I would like to know what needs to be done so that they do not collapse one after another!? This is a disaster!
Marina (02/05/2021 at 09:21) Reply to comment
I had a tooth removed and a purulent sac was found in it. More than a year has passed since the tooth was removed, but the pain in that place does not go away. I have never seen redness or swelling on the gums. Tell me, what could be the reason?
Anna (02/05/2021 at 09:46) Reply to comment
When I have a sore throat, I often feel like all my teeth hurt. And my jaw just hurts like crazy, and it radiates into my ear. I can’t live without painkillers. Is it dental problems? Or do you need the help of an ENT specialist here?
Anetochka (03/04/2021 at 10:29) Reply to comment
I have small ulcers on the inside of my cheeks that are bleeding. I thought it was stomatitis and rinsed my mouth with a soda solution, but it had no effect. What could it be? Isn't this cancer?
Stepan Viktorovich (03/04/2021 at 10:34) Reply to comment
it turns out that the problem can be serious, but it would seem to be nothing of the kind; someone might even think that it was just a leak. can this problem be treated as an emergency?
Marina (03/04/2021 at 10:40) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Treatment
A gnathologist can carry out treatment either independently or with the involvement of specialists from other fields. This is especially true when the cause of the development of TMJ pathology has been identified and can be eliminated. The help of an orthodontist is necessary for patients with malocclusion. Wearing a brace system or aligners to correct occlusion has a beneficial effect on the condition of the entire dental system.
Detection of arthrosis or ankylosis of the temporomandibular joint also requires the involvement of specialized specialists. The doctor's specialty will be determined by the cause of the development of degenerative-dystrophic processes in the tissues of the TMJ. Metabolic disorders, injuries, infections will require additional examination and the development of an individual treatment plan.
How to treat aching pain in teeth?
A treatment plan is drawn up after the diagnostic results, when the cause of the pathology is identified and pain is localized. Conventionally, several techniques can be distinguished that are used depending on the factors contributing to the occurrence of pain.
- Therapeutic treatment. It is prescribed when the main cause of aching pain is caries or periodontal disease. In case of caries, filling or endodontic treatment is carried out (if bacteria have penetrated the pulp). In case of periodontal inflammation, special ointments and antiseptics are prescribed, curettage is performed, and in severe cases, teeth are splinted.
- Prosthetics. In the presence of a wedge-shaped defect and serious damage, dental prosthetics are performed with single crowns or bridges. In case of enamel pathologies, the doctor may recommend veneers, which are installed to achieve a certain aesthetics.
- Restoration and strengthening of enamel. What to do if all your teeth ache? If the patient has weakened and thinned enamel, it is necessary to strengthen it. First of all, the doctor treats the enamel surface with special compounds based on calcium and phosphorus, and also prescribes a special diet and means that strengthen the immune system and the health of the body.
To eliminate pain, painkillers (Nurofen, Nimesil and others) can be prescribed. If the aching pain is not associated with dental problems, treatment is carried out by doctors of relevant specializations.
First aid
A joint dislocation or subluxation that occurs for the first time can cause severe pain. Joint dysfunction can also cause pain of the same intensity. Regardless of the cause of the discomfort, you must do the following:
- provide rest to the joint: do not eat, talk as little as possible;
- take a pain reliever;
- Consult a doctor as soon as possible and undergo the necessary examination.
Experts categorically do not recommend heating a sore joint if the cause of the pain is unknown. In case of dysfunction, heat exposure can lead to some relief of the condition, but in case of dislocation, on the contrary, it will cause harm. Under the influence of heat, blood flow to the tissue increases, which contributes to the development of edema and makes reduction difficult. Thus, when trying to help yourself or a loved one, you can unknowingly cause serious harm.
How does the mechanism of tooth pain sensitivity work?
The nerves connected to each tooth and to the gum tissue are part of one of the segments of the peripheral nervous system, namely the facial one. There is one nerve plexus for each jaw, formed by many nerve endings extending from each of the teeth. Greatly simplifying the innervation scheme of the teeth, we can say that they are all ultimately connected to the branches of the facial trigeminal nerve.
And if inflammation occurs anywhere along the innervation, pain signaling this can be felt in all tissues penetrated by nerve endings from this plexus. Therefore, patients who need treatment for caries of several teeth often come to the doctor with a complaint of pain in the entire dentition. The pain spreading throughout all the nerves of the plexus does not allow one to clearly indicate the location of its localization.
about the problem
Pain in the maxillofacial area (myofascial pain syndrome) is a complex interdisciplinary problem in medicine.
Pain in the jaw can occur when teeth, bones, cartilage, muscles, blood vessels and nerves of the maxillofacial area are damaged. The causes of damage can be inflammation, dystrophy, trauma, tumors of the tissues of the maxillofacial area, anomalies in the structure of the skeletal system.
Usually the first specialist people turn to when they experience pain in the jaw area is a dentist. But the cause of pain is not always diseases of the oral cavity and teeth. For some patients, the dentist finds it difficult to diagnose.
Next, patients will undergo examination: by a neurologist to exclude inflammation of the trigeminal and laryngeal nerves, diseases of large vessels of the neck and head; an ophthalmologist to identify diseases of the eye and orbit; an otolaryngologist to examine the nasal passages, sinuses and exclude chronic inflammatory processes.
There is also a group of diseases that do not directly affect the jaw tissue, but the pain they cause can radiate into the jaw. Such pain can occur during myocardial infarction and angina attacks. In this case, pain is simultaneously felt in the left shoulder blade and left arm. Chronic pain in the jaw of an aching nature occurs due to inflammatory processes in the large vessels of the neck and head. To distinguish between these conditions, an in-depth study is required using functional diagnostic methods, MRI, and CT.
If all known diseases are excluded, the question arises, what then causes pain in the maxillofacial area?
The most common cause is a severe spasm of the masticatory muscles, which causes sudden and sharp pain in the jaw when chewing, yawning, opening the mouth wide, etc. Such pain is called myofascial, and the disease is myofascial pain syndrome.
The mechanism of development of myofascial pain and muscle spasm is associated with the formation of painful muscle compactions in the masticatory muscles, which are called “triggers”. The trigger may be located outside the area of pain, and when pressure is applied to it, a painful lumbago occurs in the maxillofacial area.
Pain in the jaw can be aching, intermittent or constant, more acute or dull, accompanied by tingling, numbness and goosebumps. Additional symptoms are possible: twitching of the facial muscles, noise, ringing in the ears, stuffy ears, clicking in the jaw joints, increased sensitivity to cold. In severe cases, the pain spreads to the other half of the face, and it is difficult to open the mouth and chew.
The causes of triggers are: increased excitability of the central nervous system, trauma to the skull and maxillofacial area, cervical osteochondrosis. Therefore, in addition to the jaw area, pain can be observed in the cervico-occipital, as well as in the temporal, frontal and parietal areas of the head.
Thus, pain in the jaw occurs for a wide variety of reasons, and establishing a diagnosis is often very difficult.
Myofascial pain is the most difficult type of facial pain for dentists and specialists to diagnose. Pain and spasms in the jaw muscles are recognized and treated only by a vertebroneurologist.
Causes of osteomyelitis
Penetration of bacteria into bone, which traditionally occurs as follows:
- against the background of tooth damage by caries, that is, by odontogenic means. First, microorganisms penetrate the pulp, after which they enter the hard tissue through the lymph nodes or canals;
- after fur. tooth damage: dislocations, fractures, operations, etc.
- due to the penetration of infection during ENT diseases, skin inflammation, when microorganisms from one source of inflammation pass into the bone.