Sometimes we experience a special kind of discomfort - it seems that either our head or our eyes hurt. This pain occurs in the sinus area or at the back of the eye. Sometimes it is pulsating, sometimes it is constant. This condition frightens us very much and we want to know what causes this pain? What can be done to alleviate it? Could there be something wrong with my vision?
Let's first answer the last question.
Scientists from the American Academy of Ophthalmology defined "eye pain" as "physical discomfort caused by an eye or other disease." But scientists emphasize that “the location of the pain does not necessarily indicate the cause of the pain.”
In most cases, the cause of a headache felt in the eyes may be hidden in a completely different place. We feel pain in this particular location because of a network of interconnected sensory nerves that penetrate all tissues of the body.
“Almost every pain-sensitive structure in the head transmits the sensation of pain to the eye area,” says Dr. Mark W. Green, MD, professor of neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City. “Just because the eye hurts does not mean that the problem is in the eye itself. In fact, this happens quite rarely."
Green advises to remember one useful rule: if the white part of the eye (sclera) is not red, and there are no complaints about vision - a blurred or distorted picture, it is very unlikely that the headache is associated with the eyes themselves.
Causes
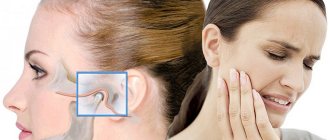
The organs of the skull are interconnected by a network of blood and lymphatic vessels and cranial nerves. These are the channels through which the infection is transmitted from the ears to the eyes, passes to the throat and back. The symptoms are complex. It is difficult to determine the source of inflammation. But there are several main causes of pain in the ears and eyes.
Neuralgia
With inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, pain spreads to the forehead, temple on one side of the face, and ear. The eye muscle on the affected side, the brow ridge, hurts.
The temperature remains normal. The pain comes in attacks, especially severe at night. The site of inflammation is sensitive to touch.
Causes of neuralgia:
- pathologies of the development of skull bones;
- compression due to tumor;
- traumatic brain injury.
The disease is difficult to diagnose. Treatment consists of pain relief. The sensitivity of the trigeminal nerve increases with the changing seasons. Psychosomatic neuralgia manifests itself as an exacerbation of pain during stress.
Otitis
Inflammation of the middle ear occurs due to the spread of coccus bacteria, which causes a runny nose. Otitis externa and otitis media are distinguished. The auricle becomes covered with boils due to the spread of infection from the ear canal.
A fungal infection also spreads in the middle ear. The fungus appears due to the accumulation of moisture.
The eye is affected by the affected ear. The infection occurs when one bottle of drops is used simultaneously to treat the eyes and ears. The result is lacrimation and redness of the conjunctiva.
Labyrinthitis
The inner ear consists of a plexus of passages and resembles a labyrinth. Labyrinthitis is inflammation in the inner part of the hearing aid.
Causes of the disease:
- spread of infection from the middle ear;
- tuberculosis;
- fungus;
- mechanical damage.
Symptoms of labyrinthitis appear 2 weeks after recovery from a respiratory infection. The disease causes dizziness and nystagmus - involuntary movement and tremors of the eyeballs.
Migraine
Hemicrania occurs on one side of the head. Throbbing pain is accompanied by photosensitivity. With migraine with aura, the field of vision is lost. Aching ear pain is accompanied by noise and ringing. In severe conditions, a person experiences auditory hallucinations.
Osteochondrosis
Salt deposits in the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine pinch blood vessels. As a result, brain tissue and cranial organs receive little oxygen. There is sand and a burning sensation in the eyes. There is stuffiness and ringing in the ears.
Intracranial pressure
Increased tone of the vessels of the cranium is a consequence of osteochondrosis. Other causes of pressure:
- thrombosis;
- traumatic brain injury;
- tumor;
- hypertension;
- accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
A drawing, throbbing pain is concentrated on one side of the head, covering the eye and ear.
Flu
An acute respiratory infection affects the mucous membranes of the nose and throat. Abundant mucous masses accumulate in the nasal sinuses. Rhinitis develops into sinusitis, inflammation of the inner, middle ear. Obstruction of the nasal passages deprives the tissues of oxygen.
The eyes feel dry, small capillaries burst due to coughing attacks. This creates a complex of symptoms characteristic of various colds. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Tumor
New growths in the brain create compression on surrounding structures. Pressing pain appears as the tumor grows penetratingly. Compression of blood vessels and nerves causes visual and hearing impairment. Symptoms are characteristic of various diseases, so oncological pathology is difficult to establish.
Primary headache. Major diseases.
The most common forms of primary headache are “tension pain” and migraine, more rarely – cluster headache and other forms.
Tension headache (TTH)
can occur in anyone. This is the most common form of headache and is often characterized as a “normal” or “regular” headache. Attacks can last from 30 minutes to several days. The frequency of attacks varies from person to person, and it can also vary from one person to another during different periods of his life. The pain is described as squeezing, squeezing the head like a hoop or tight hat, usually bilateral, and moderate. In some people it can become chronic (chronic pain is diagnosed if there are more days with a headache than without it). A person experiencing chronic headaches becomes irritable. Weakness, fatigue, decreased appetite, and sleep disturbances may occur. The cause of TTH is physical tension in the muscles and ligaments of the head and neck - the so-called “muscle stress”, which can be a consequence, for example, of working in an uncomfortable position. TTH often occurs in those who work at a computer or whose work involves the need to look at details (jewelers, watchmakers, assemblers of electronic equipment, masters of artistic embroidery, etc.). The emotional factor is also important: emotional tension caused by stress or a state of increased anxiety can also lead to pain.
Migraine
characterized by severe and painful attacks of headache, which are often accompanied by nausea (and in some cases vomiting), as well as intolerance to light and sound. The perception of smells changes, thermal sensations are disrupted. Migraine attacks last from 4 hours to 3 days and can be repeated with a frequency of 1-2 times a year to several times a month. During an attack, so-called “precursors” may be observed - irritability, depression, fatigue, occurring several hours or even days before the onset of pain. In a third of cases, pain is preceded by phenomena called “auras”: 10-30 minutes before the attack there may be visual disturbances (blind spots, flashes, zigzag lines in front of the eyes), tingling and numbness starting from the fingertips and spreading up the body and etc.
Predisposition to migraine is congenital and is associated with disorders in the brain structures responsible for pain and other sensations. Every seventh adult suffers from migraines, with women three times more likely than men. In girls, migraines usually begin during puberty.
Factors that contribute to the development of migraine attacks: chronic fatigue, anxiety or stress, in women - menstruation, pregnancy and menopause.
But a predisposition to seizures does not mean that an attack will definitely happen. There are factors that act as a “trigger” for an attack. An attack can be triggered by: skipping meals, insufficient fluid intake, certain foods, sleep disturbances, physical activity, changes in weather, sudden changes in emotions.
Cluster (or beam) headache
characterized by one-sided sharp (“dagger” or “drilling”) pain. The intensity of the pain rapidly increases within 5-10 minutes, and the attack itself lasts from 15 minutes to 3 hours, during which the patient cannot find a place to rest. The pain is usually localized in the eye area, and the eye may become red and watery. Recurrent attacks form a cluster (that is, they follow each other), the duration of the cluster is from 6 to 12 weeks. This form of pain occurs five times more often in men than in women. However, those who smoke a lot or have smoked in the past are more susceptible to it.
Diagnostics
If pain in the ear and eyes occurs, the following diagnostic procedures are performed:
- if inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is suspected - electroneuromyography;
- to confirm otitis - tympanometry, audiometry, MRI;
- influenza is diagnosed based on the results of a virological examination of a nasal smear;
- increased cranial pressure is determined by MRI and lumbar puncture results.
The degree of damage to the optic nerve is determined using ophthalmoscopy.
In the occipital region of the head
In the back of the head, cephalgia occurs when blood pressure increases, the cause of which is osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondylolisthesis, anomalies in the development of blood vessels in the head or neck.
Severe pain in the back of the head occurs after nervous strain, as a result of spasm of the neck muscles, arteries of the head and neck, and disruption of the outflow of venous blood from the head. It worries patients suffering from occipital neuralgia, vertebrobasilar insufficiency, spinal diseases, and migraines. A sharp headache in the back of the head often occurs with the development of a hypertensive crisis. Sharp, bursting, pulsating headaches in the back of the head are accompanied by pallor of the patient’s face, generalized hyperhidrosis, dry mouth, heart pain and tachycardia.
Chronic arterial hypertension with a slight increase in blood pressure is also characterized by the development of pain mainly in the occipital part of the head. The headache bothers the patient immediately after waking up, intensifies with physical activity, and is often accompanied by swelling of the lower eyelids. Pain is caused by a violation of the outflow of venous blood from the vessels of the head.
Treatment
In accordance with the diagnosis, therapy is prescribed:
- for neuralgia, relieve pain with analgesics, lidocaine-based ointment, and drugs for vasodilation;
- antibacterial drops and ointments are used to treat otitis externa;
- drops against inflammation with an analgesic effect - for internal otitis;
- Ear infections are treated with penicillin and amoxicillin antibiotics - orally, by insertion into the ear through a catheter.
For more serious diagnoses, pain is relieved and the primary cause of symptoms is treated.
Cephalgia in children
Pulsating discomfort in a child that is not accompanied by fever, cough and runny nose should alert parents. In such cases, it is important to consult a doctor. Such manifestations may indicate problems with the child’s health.
The phenomenon can be triggered by:
- disease of the vascular system;
- neuralgia;
- migraine;
- injury;
- emotional condition;
- poor nutrition;
- the presence of provoking external factors.
Prevention
How to prevent the occurrence and spread of infection:
- treat colds promptly;
- do not overcool your head;
- Dry your ears thoroughly after bathing;
- take vitamins to strengthen the immune system;
- use separate bottles of universal drops for treating eyes and ears;
- Carefully clean the ears with cosmetic sticks so as not to damage the eardrum.
Compliance with the rules of prevention and immediate treatment prevents complications. Independent choice of drops, antibiotics, irregular use of drugs only until the first improvement introduces the disease into a chronic state.
The consequence will be the transfer of infection to the lining of the brain - meningitis.
What affects a person's hearing and vision?
Changes in vision can occur due to various factors. Refraction is negatively affected by the presence of congenital or acquired pathologies (myopia, farsightedness, etc.), as well as “dry eye” syndrome, lacrimation, improper work routine, regular exposure to poor-quality lighting, etc. Infectious diseases also play a significant role, to which can lead to:
- Swimming in reservoirs;
- Touching eyes with unwashed hands;
- Decreased general immunity;
- Hypothermia;
- Failure to comply with the wearing regimen and care rules when wearing contact lenses;
- Drafts, etc.
In many ways, the causes of decreased hearing ability are similar to those that affect vision impairment. Hearing can be damaged by even slight moisture getting into the ear canals, pollution, injury, colds, hypothermia, infectious diseases, etc.
In medical practice, doctors are faced with a large number of pathologies associated with the eyes and ears. As a rule, they proceed autonomously from each other. But it happens when these paired organs bother the patient at the same time. In such situations, doctors strongly advise against ignoring disturbing symptoms.
How to quickly relieve an attack of cephalalgia
In cases where a headache does not appear frequently or systematically, and a person definitely does not have diseases that can provoke it, then you can deal with the discomfort on your own. To do this, it is not necessary to use strong medications and call a doctor.
When you feel a severe headache, forget about bad habits, such as smoking and give up alcohol. You should also not apply ice or increase the dose of the analgesic yourself unless your doctor recommends it.
There are a number of actions that need to be taken so that a person with a headache begins to feel better, namely:
- Bring fresh air into the room.
- Free the patient from tight clothing and constricting jewelry, unbutton the shirt collar and raise his legs so that they are higher than head level.
- Reduce indoor lights and sounds to a minimum.
- Give water, it can also be a decoction of soothing and relaxing plants.
- Take a warm foot bath and apply a compress to your head.
- It is necessary to warm a person in cases where the pain intensifies and there is chills.
- Lightly massage the temple area, neck, head, while the person should lie down.
If the above methods do not help within 30 minutes, and only get worse, give the patient an analgesic. If this does not help, then call the ambulance doctors.
Signs and symptoms of presyncope: dizziness, nausea
Symptoms of presyncope are characterized by sudden development, which is usually provoked by certain factors. A stuffy room, tight clothing, stressful situations, excessive physical activity, eating - all this can contribute to the onset of an attack.
The most characteristic symptom of presyncope is dizziness, which may be accompanied by nausea. This indicates disturbances in the functioning of the human autonomic system.
There is a certain risk group of people for whom the presyncope may be permanent. These are people suffering from hypotension (low blood pressure), chronic anemia (low hemoglobin level in the blood, less than 100 units), bradycardia (low heart rate, less than 40 beats).
Any of the described signs is a serious reason to see a doctor. But, since an attack of pre-fainting can occur at any time and in any place, it is necessary to have at least a general understanding of how to provide first aid to the victim or yourself at home.