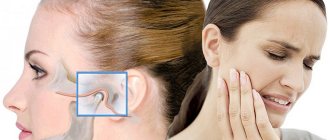
Pain in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) occurs as a result of injury, infection of its structures, or the development of inflammatory or degenerative pathologies. Also, discomfort when chewing food can result from dental problems. In any case, it is necessary to consult a doctor to identify the cause of the pain and carry out treatment. Otherwise, the pathology will soon take a chronic form, difficult to respond to conservative therapy.
There are two main types of TMJ dysfunction:
- Myogenic (source: muscle pain);
- Arthrogenic (associated with TMJ condition).
Myogenic TMJ dysfunction usually occurs due to fatigue or tension in the masseter or accessory muscles. Leads to facial pain, headaches, and sometimes neck pain.
Arthrogenic dysfunction of the TMJ, as a rule, is the result of inflammation, degenerative changes in hard and soft tissues in the joint. It most often occurs due to capsulitis or synoviitis (inflammation), slipped discs, and degenerative arthritis.
Main causes and clinical manifestations
The jaw joint always hurts when its integrity is violated as a result of injury. This kind of damage to bone or cartilage structures is often the result of an impact, a fall from a height, or a traffic accident. Under mechanical influence, the lower and (or) upper jaw is injured. Fractures happen:
- direct or reflected;
- single or multiple;
- open, closed, displaced.
Localization of fractures.
The most severe form is considered to be splintered, requiring complex surgery. The victim finds out that the jaw joint hurts due to a fracture during an X-ray examination at the emergency room. But sometimes, for example, after a fight, the intensity of the discomfort increases gradually. The causes of pain are cracks in the bone, dislocation or subluxation, which disrupt the functioning of the TMJ. The following clinical manifestations indicate injury:
- pain that increases when opening the mouth;
- swelling of the lower jaw;
- stiffness of movement, impaired motor functions.
If the integrity of the skin is damaged during injury, pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate into the joint cavity from the surface of the epidermis. During their life, they release toxic substances that provoke the development of the inflammatory process.
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is an inflammatory pathology of the bone marrow that affects all elements of the bone: periosteum, spongy and compact substance. The pathology is provoked by pathogenic bacteria that penetrate the TMJ with the blood flow from the primary lesions or when the pocket, which is located between the gum and one of the teeth, is damaged. Osteomyelitis can be nonspecific, caused by staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, and pathogenic fungi. A specific disease occurs with tuberculosis of bones and joints, brucellosis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis. When choosing treatment methods, its form is taken into account:
- post-traumatic, most often occurring after open fractures;
- gunshot, the cause of which is a fracture as a result of a bullet wound;
- postoperative, developing due to the installation of wires or the application of compression-distraction devices;
- contact, provoked by the spread of the inflammatory process from soft tissues.
If the jaw joint hurts, then the cause may be endogenous osteomyelitis of the TMJ. Pyogenic bacteria penetrate bone tissue from foci located in other parts of the body. They are carried by blood from phlegmons, infected wounds, soft tissues affected by purulent inflammation.
Acute osteomyelitis is indicated by frequent headaches, elevated body temperature, lack of appetite, insomnia, and fatigue. Chronic pathology is diagnosed quite rarely, usually in young patients. Relapses occur with exacerbation of concomitant diseases, decreased immunity, and hypothermia.
Odontogenic factors
The jaw often hurts when chewing due to the development of an odontogenic inflammatory disease - periodontitis, periostitis. Their complications can also provoke discomfort: abscesses, phlegmons, lymphadenitis, sinusitis. The pathological conditions have one thing in common: the tooth or nearby tissues become the entry gate for pathogenic microorganisms. The infection spreads in various ways, affecting the bone jaw structures, perimaxillary soft tissues, lymph nodes, anatomical formations localized near the TMJ and distant organs.
The cause of pain can be banal caries. If left untreated, the deep parts of the tooth are damaged, including the nerve, pulp, and soft tissue. As a result of demineralization and destruction of hard tooth tissues, a cavity defect is formed, in which the source of infection is located - pathogenic bacteria and fungi.
A patient at a dentist's appointment complains of throbbing, sharp pain, often occurring in the jaw joint at night. Their severity increases when chewing or eating hot or cold food. If the pathology affects the trigeminal nerve, then the lips begin to go numb, the chewing muscle tone decreases, and the pain becomes piercing, radiating to the back of the head, temples, and forehead.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis of the TMJ is a chronic pathology caused by degenerative processes in the tissues of the joint. It is characterized by the gradual destruction of cartilage tissue and the formation of bone growths (osteophytes). As a result of thinning of cartilage and decreased production of synovial fluid, the functional activity of the joint is significantly reduced. While experiencing food or talking, painful sensations arise. When you move your jaw, you hear crunching and clicking sounds. In the morning, the joint swells, but during the day the swelling disappears due to the production of special hormone-like substances in the body. After sleep, some stiffness of movements and joint stiffness are felt.
Under the influence of negative factors, for example, hypothermia or the development of any infection, synovitis can occur - an inflammatory process in the synovium with the accumulation of fluid in the joint cavity. It is often accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication of the body:
- increased body temperature;
- headaches, dizziness;
- dyspeptic disorders.
After about six months, the range of movements of the TMJ is limited, stiffness is observed, and the patient involuntarily shifts the jaw to one side when opening the mouth. The area affected by osteoarthritis may experience numbness and tingling of the skin. Headaches, ear pains, and eye pains occur. Sometimes a person with osteoarthritis turns to an otolaryngologist with complaints of hearing loss. Patients often ask doctors why the jaw joint hurts and why it hurts to open the jaw. Often this indicates the development of ankylosis - complete or partial fusion of the joint space.
Arthritis
The jaw joint often hurts as a result of arthritis. This pathology affects almost all structures of the TMJ - synovial membranes, capsule, cartilaginous and soft tissues, adjacent muscles, ligamentous-tendon apparatus. The disease begins with the development of an inflammatory process in the membrane lining the inner surface of the joint. Gradually it spreads to other structures, which leads to disruption of the functioning of the joint.
| Type of temporomandibular joint arthritis | Causes |
| Specific and nonspecific infectious | The cause of inflammation is the penetration of viruses, pathogenic bacteria or pathogenic fungi into the cavity of the TMJ. These can be Staphylococcus aureus, streptococci, E. coli, pathogens of syphilis, gonorrhea, brucellosis, tuberculosis |
| Reactive | Occurs as a result of infection of the TMJ. But pathology does not develop as a result of the vital activity of microbes and viruses, but due to an inadequate response of the immune system to their penetration |
| Rheumatoid, including juvenile | The development of pathology is provoked by a combination of certain factors. This is a genetic predisposition, infection, a sharp weakening of the body’s defenses |
| Gouty | Occurs when there is a metabolic disorder of uric acid, the salts of which begin to crystallize and deposit in the TMJ |
At first, the clinical manifestations are not pronounced. A person occasionally feels weak and gets tired quickly. Malaise is usually attributed to fatigue after a hard day at work. But the severity of symptoms increases, as does the frequency of their manifestations. Soon the clinical picture is complemented by the leading sign of any form of arthritis - arthralgia, or joint pain. She has a stable wavy character. The intensity of the pain syndrome increases in the second half of the night and in the morning.
Factors that provoke the development of TMJ dysfunction:
Injury
Injury or overstrain of the jaw, or the habit of clenching the jaw tightly can injure the joint. Long-term dental procedures (or those in which the doctor uses force) and some other medical interventions can also lead to injury to the TMJ.
Wrong habits
Clenching teeth, clenching the jaw, grinding teeth (bruxism), biting lips or nails, chewing gum.
Malocclusion
At first, dentists generally considered this pathology as the main cause of TMJ dysfunction. But recent studies have shown that malocclusion, with rare exceptions, does not lead to such a disease.
Psychological factors
Many patients say that symptoms of TMJ dysfunction appeared (or worsened) due to stress, depression, or psychological trauma.
Temporomandibular joint diseases
Some types of arthritis can affect the TMJ (as well as other joints). For example, this sometimes happens with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Many other diseases (Parkinson's disease, myasthenia gravis, strokes, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, etc.) can also lead to uncontrolled movements of the masticatory muscles.
Treatment tactics
When the jaw joint hurts, swells, and range of motion decreases, complex treatment is carried out. After examining the patient and studying the complaints, a series of instrumental and laboratory tests are prescribed to determine the cause of the discomfort. A therapeutic regimen is drawn up, which includes drugs to improve a person’s well-being and prevent the progression of the disease. Further treatment is aimed at eliminating the complications that have arisen. What to do if your jaw joint hurts and you can’t quickly see a doctor:
- immobilize (immobilize) the affected joint. During treatment, wearing orthopedic devices that fix the TMJ is indicated. At home, you can use an elastic bandage for this purpose;
- apply cold to the jaw. The basis of the compress is a bag of ice cubes wrapped in thick cloth. The procedure is carried out every hour for 10 minutes;
- take a tablet of any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) - Nise, Nimesulide, Ketorol, Nurofen, Ibuprofen.
Such activities will allow you to get rid of pain of any intensity. Further therapy depends on the type of pathology diagnosed. For gout, medications are prescribed to accelerate the removal of uric acid salts from the body; for reactive or rheumatoid arthritis, medications are prescribed to correct the immune response. Osteoarthritis is not yet completely treatable, but a course of chondroprotectors can stop its spread. When the jaw joint hurts due to dental problems, treatment is carried out by a dentist.
MRI.
To eliminate mild or moderate discomfort, external agents with anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous, and analgesic effects are used:
- gels Voltaren, Fastum, Nise, Artrosilene;
- ointments Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Ortofen.
After acute inflammation has been relieved, medications for external use with a warming effect are included in treatment regimens. These are Nayatox, Viprosal, Apizartron. They accelerate blood circulation in the TMJ area, stimulating the regeneration of its structures. At home, you can warm up the joint with linen bags filled with hot flaxseeds or sea salt. If the jaw joint near the ear hurts, then an otolaryngologist is involved in the treatment. Usually, Otinum and Otipax drops are used to eliminate pain. Patients are also prescribed a course of vitamins and microelements to strengthen the body’s defenses - Selmevit, Vitrum, Centrum, Complivit, Multitabs.
Timely medical intervention can completely eliminate pain in the jaw joint. But in the case of the development of one of his pathologies, not everything is so simple. Discomfort that occurs while talking or chewing often indicates an existing acute or chronic disease. Some of them cannot yet be completely cured, but contacting a doctor when the first symptoms appear will allow you to stop the pathology and avoid serious consequences.