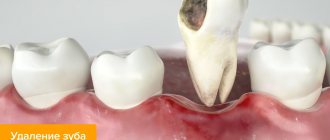
Tooth extraction is a process that traumatizes the gums. After healing a diseased tooth, nerves, ligaments and small blood vessels are torn, which causes bleeding. This is a natural process - the blood does not allow pathogenic organisms to enter the circulatory system, washing them out. And then, curled up, it forms a barrier between unprotected tissues and bacteria. After tooth extraction, white plaque on the gum is not pus, but another stage of protection and restoration of the body.
When removing a tooth, the patient must be prepared:
➢
to moderate bleeding that may last for some time;
➢
the appearance of a dense blood clot in the gum;
➢
unpleasant odor 10-12 hours after surgery;
➢
the formation of a white coating on the blood clot;
➢
pain after surgery;
➢
temperature rise.
The listed symptoms are not a sign of an unsuccessful operation or infection in the body - this is the body’s natural response to tooth extraction.
What is white plaque on the wound after tooth extraction?
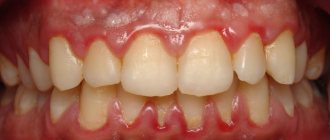
A few hours after the tooth is removed, a dark clot appears in the socket - bluish, black, red or brown. This clot is blood, and it is the primary protection of the socket from bacteria or pieces of food entering it. On the 2nd - 4th day, the patient may see that a coating appears on the clot - yellowish, gray or white. The deposit looks like pus and, together with the resulting bad breath, can alert the patient. However, there is no need to be alarmed - this plaque is not a sign of wound decay and indicates a normal healing process. This special protein compound is fibrin.
A milky plaque (fibrinous) can be very dense, hard or soft. This is no cause for concern. If you come to the dentist with this question for an unscheduled appointment, the specialist will tell you that everything is in order and there is no need to remove the film.
If the film is not removed and the wound is not disturbed, active processes will occur underneath it:
- the blood clot will begin to dissolve;
- the hole will begin to decrease in size;
- young cells, osteoblasts, will begin to move from the edge of the wound to the center;
- The gums will begin to close the wound.
Fibrinous plaque after tooth extraction is a natural stage of gradual recovery of the body, in which it is better not to interfere.
Why you don’t need to remove white plaque after tooth extraction
In some cases, patients intentionally or accidentally remove a blood clot or fibrinous film from the socket. This is not necessary, since removing a clot or film can provoke negative processes.
First of all, an open wound provides access for bacteria to the circulatory system and tissues of the maxillofacial apparatus. Infection can cause serious consequences and require long-term treatment with antibiotics. Also, removing the clot and white plaque increases the pain, since an open wound is more sensitive to any irritants, including drinking drinks and food, during a conversation.
Finally, plaque on the gums after tooth extraction does not need to be cleaned off because this can cause re-bleeding and prolong the wound healing stage.
In any case, there is no need to intentionally remove plaque; this can cause:
- serious complications;
- severe pain;
- improper gum formation;
- long recovery process after tooth extraction.
To avoid accidentally damaging the socket, blood clot or fibrinous film, you must follow the recommendations given by the doctor after the operation.
How not to damage white plaque after wisdom tooth removal
To eliminate the risk of complications and speed up the recovery process, you need to follow the rules of behavior after tooth extraction:
- do not eat or drink for 3 hours after surgery;
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol for a while;
- do not heat the cheek and gums, avoid overheating;
- for the first 24 hours, do not rinse your mouth or brush your teeth;
- Do not go to the bathhouse for a week, do not play sports.
Smoking is contraindicated, as it provokes vasospasm: the bleeding stops too quickly, the blood clot is not formed enough. Hot drinks, warming the cheek, sports training and visiting a bathhouse cause overheating of the body and dilation of blood vessels, which can cause re-bleeding, opening and infection of the wound.
Rinsing and brushing the mouth are acceptable 24 hours after tooth extraction, but they should not be overly vigorous. Hygienic procedures must be moderate so that the blood clot remains in the cavity and the subsequently formed fibrinous protective layer is not damaged. During the recovery period, food should be chewed only on the non-operated side of the jaw.
If you have a fever and severe pain in the first few days after tooth extraction, you can take Paracetamol - this will help reduce discomfort and improve your well-being.
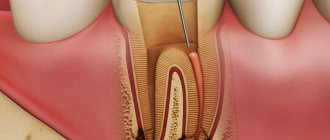
Treatment
Before looking for ways to eliminate white plaque on the tongue, cheeks, and gums, the doctor must determine the cause of its appearance. So, if the problem arose after implantation, traditional teeth cleaning or extraction, you can rinse your mouth with a local antiseptic (the most affordable one is chamomile infusion). The procedure is repeated every 2-3 hours for several days in a row - the plaque should go away.
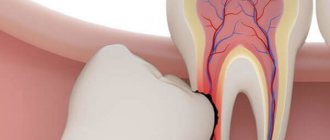
Important! If there are signs of suppuration on the gum (a fistula or cyst has formed), you should not postpone a visit to the dentist - he will open the formation, remove the exudate, and disinfect the resulting cavity.
For dental cysts, patients are advised to undergo surgical intervention. For candidal stomatitis, the patient is prescribed systemic antifungal drugs (Fluconazole, Nystatin, Pimafucin, Clotrimazole), as well as local agents - ointments, gels (for example, Miconazole). Both dentures and the oral mucosa should be treated with antiseptic solutions (Iodinol, Lugol or regular baking soda diluted with water).
Not least important in the successful fight against stomatitis is diet correction. So, from the daily menu for the entire duration of treatment, sweets, flour products, spicy, sour, salty foods and everything that could injure the already “damaged” mucous membrane are excluded. It is noteworthy that not only dentistry, but also gastroenterology, as well as endocrinology, should search for the causes of candidal stomatitis of the oral mucosa.
Leukoplakia in traditional dentistry is considered to be a disease with a high risk of degeneration into gum cancer.
The fight against leukoplakia involves finding and eliminating the factors that caused the development of the disease. Thus, the oral cavity is “freed” from traumatic dentures, sharp tooth edges are ground, and damaged units are restored.
In addition, systemic treatment of leukoplakia includes diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the digestive tract, endocrine disorders, replenishment of vitamin A deficiency in the body, cessation of smoking and alcohol consumption. Areas of the mucous membrane affected by leukoplakia are excised with a laser, removed using the radio wave method, or excised using an electric knife.
Important! In modern dentistry, they have abandoned the treatment of this disease with liquid nitrogen, since after freezing the hardened lesions, scars remain on the mucous membrane.
When white plaque on a wound after tooth extraction requires examination by a doctor
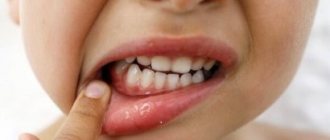
Despite the fact that white plaque after wisdom tooth removal is a natural reaction, the patient needs to conduct a daily self-examination of the oral cavity and consult a doctor for help if alarming symptoms appear.
You should consult a doctor if:
➢
on the 3rd - 4th day the pain does not decrease, it becomes throbbing and intense;
➢
a white, reddish or yellow mass or liquid is released from the wound;
➢
swelling of the gums has intensified or spread to the face;
➢
body temperature rose above 38 degrees.
These signs indicate possible infection or complications. After examining the oral cavity, the dentist, if necessary, may prescribe a course of antibiotics or surgical cleaning of the socket cavity.
Causes
- Weakened immunity. In people with weak immunity, the body's resistance decreases. Candida begins to multiply quickly.
- Hormonal imbalances. Changes in hormonal levels lead to various pathologies, and candidiasis is one of them.
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Diabetes.
- Long-term use of antibiotics. These drugs disrupt the normal microflora. They kill not only pathogenic microorganisms, but also beneficial bacteria.
- Dental diseases. Candidiasis can be provoked by caries and inflammation in the oral cavity.
- Poor oral hygiene. Patients who do not pay proper attention to hygiene are more susceptible to white plaque.
- Dentures. An incorrectly selected denture puts pressure on the mucous membrane, causing it to rub. In these places, the color changes and the tissue structure is disrupted.
- Damage to the mucous membrane. It performs a protective function. Damage provokes various dental pathologies.
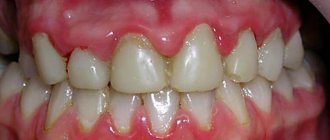
White plaque in the mouth is a sign of more than just candidiasis. It also accompanies other pathological conditions:
- Tooth cyst. This is a protective neoplasm that forms in response to the inflammatory process. When pathological cells die, a cavity with dense walls is formed around the necrosis zone, inside which there is liquid.
- Leukoplakia. This is a dense white growth on the gums and cheeks. Without treatment it leads to keratinization.
- Oncological diseases in the initial stage.
Sometimes a problem arises as a response to external irritation. For example, after brushing or whitening your teeth. In this case, it goes away on its own after some time.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Gum healing
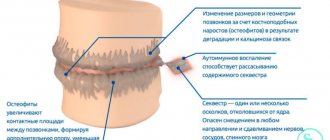
After tooth extraction, you need to be prepared for the fact that pain and swelling may intensify on the second day after surgery. But already on the 3rd - 4th day after the operation, the discomfort will begin to decrease. By this time, the wound healing processes are more active, and by touching the tip of the tongue to the hole, you can feel that a compaction has formed.
During this period, the following are actively developing:
- bone formation in the area of the removed tooth root;
- narrowing of the socket due to the “growth” of the gums;
- formation of the mucous membrane in the socket area.
Fibrinous plaque after tooth extraction persists for a week. It disappears on its own, without mechanical cleaning. Little by little, the mucous membrane begins to turn pink, gradually acquiring a healthy, natural color. Around the 10th day, wound healing is completed: healthy tissue is formed that covers the mouth of the hole. A small depression remains in the area of the removed tooth. The formation of bone tissue at the site of tooth extraction takes much longer - up to 6 months. Changes will be visible on an x-ray.
Natural symptoms after implant placement
- Minor pain syndrome (throbbing pain can appear with any physical activity);
- difficulty swallowing or sore throat;
- elevated body temperature on the first day after implantation;
- bleeding from the wound for 2 days;
- nosebleeds after sinus lift in the upper jaw;
- swelling in the area where the artificial root is implanted;
- numbness of the cheek, part of the tongue, lip or chin;
- whitish coating on the wound;
- increased drowsiness and fatigue;
- unpleasant smell.
You need to rest more so that the body can quickly restore injured tissue. But there are cases when you need to see a dentist.
Dentist's opinion : “Engraftment of the implant system is a complex process that directly depends on the patient’s health condition. When everything is fine, the symptoms that are considered normal after surgery will quickly pass. But if the situation worsens on day 3-4, there may be a risk of developing an inflammatory process or rejection of the structure. It is important not to miss this moment and consult a doctor in time.”